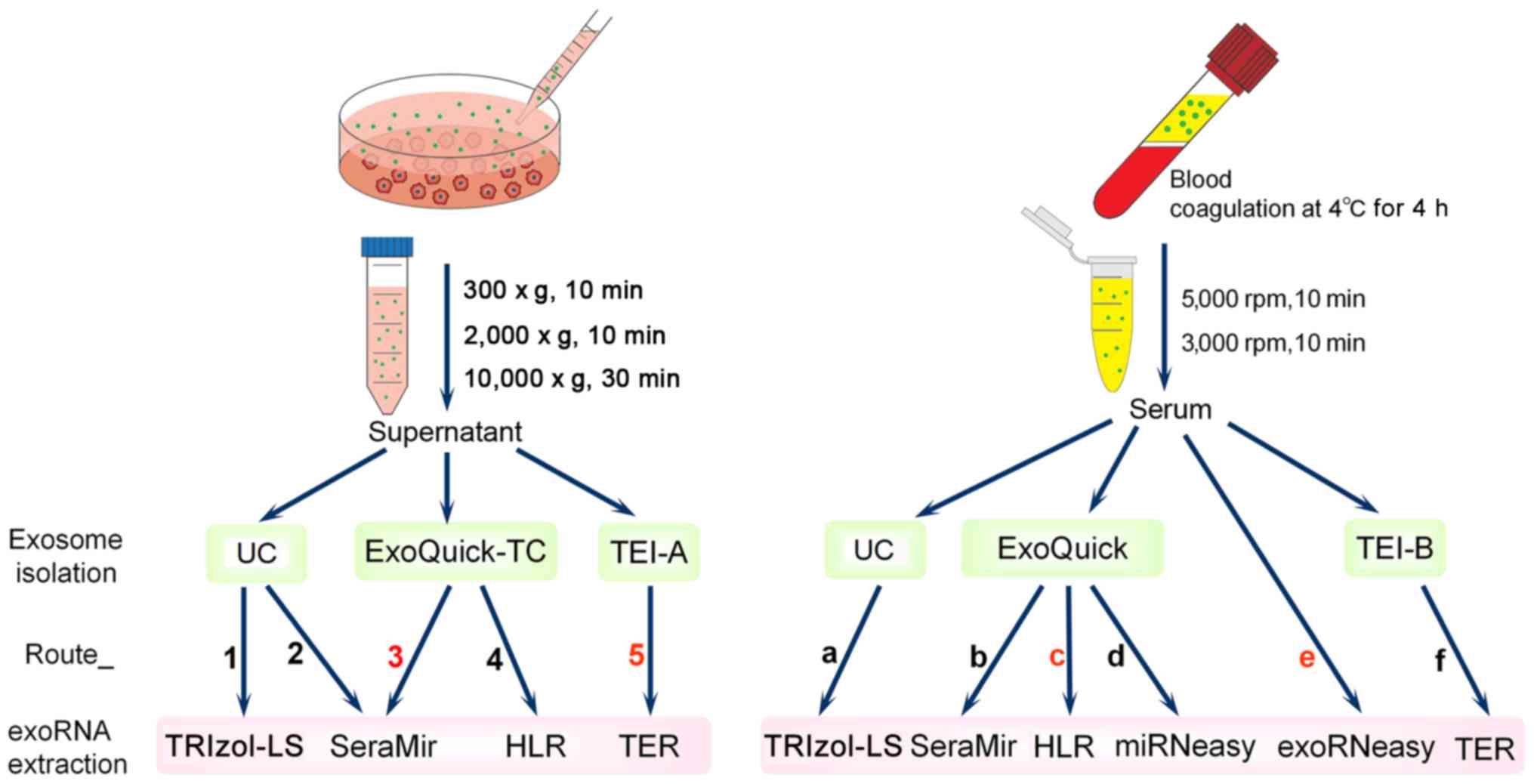
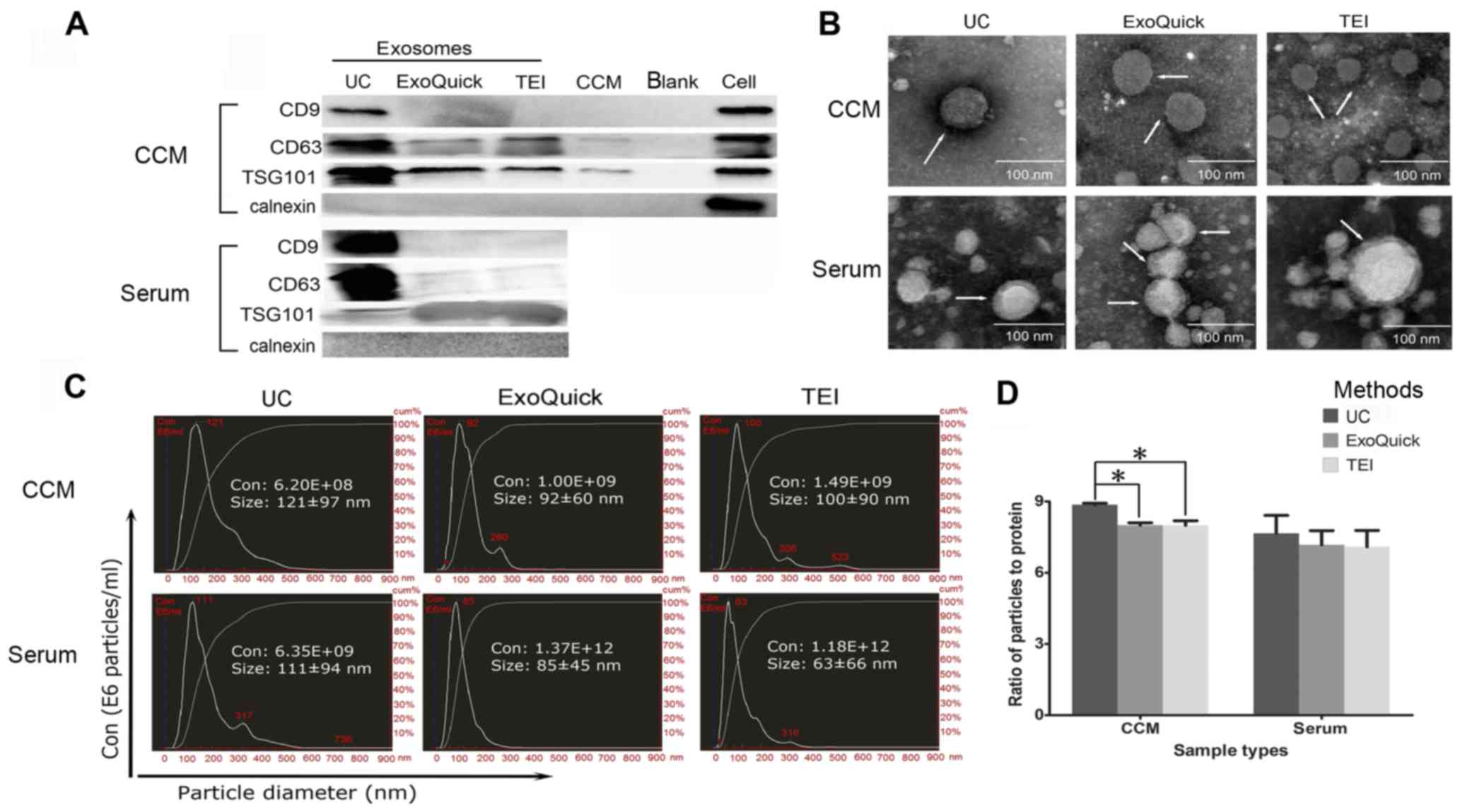
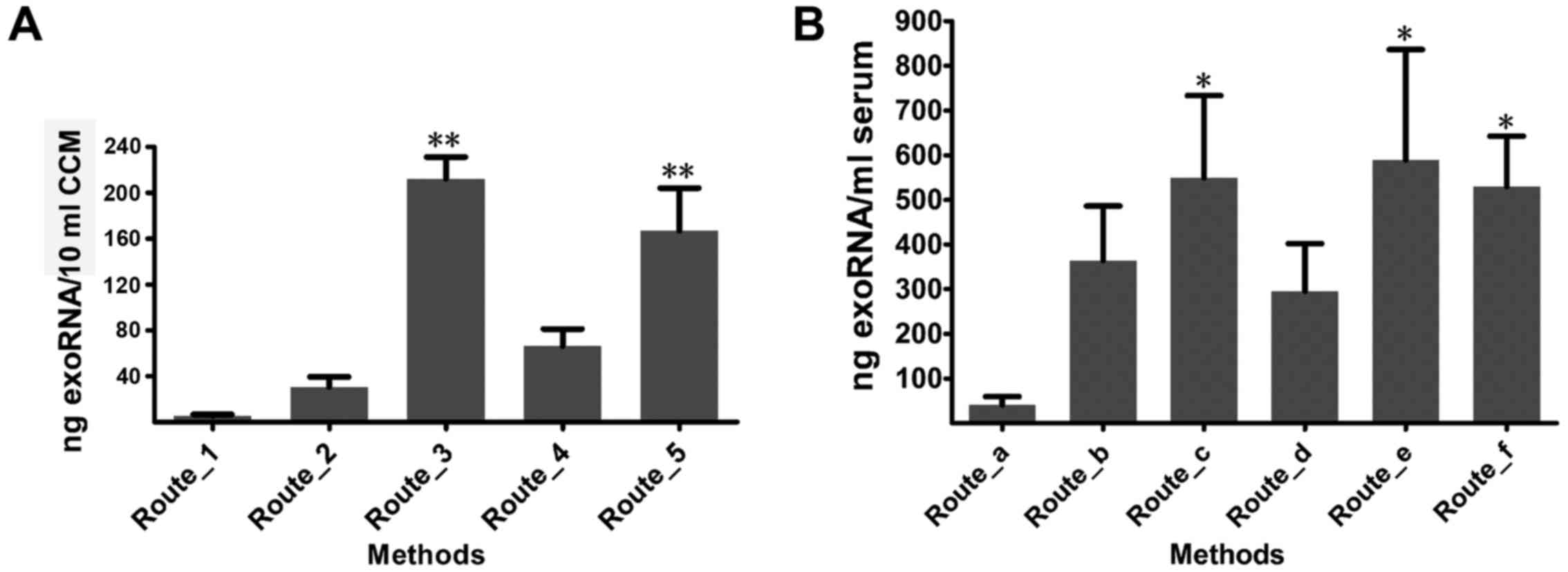
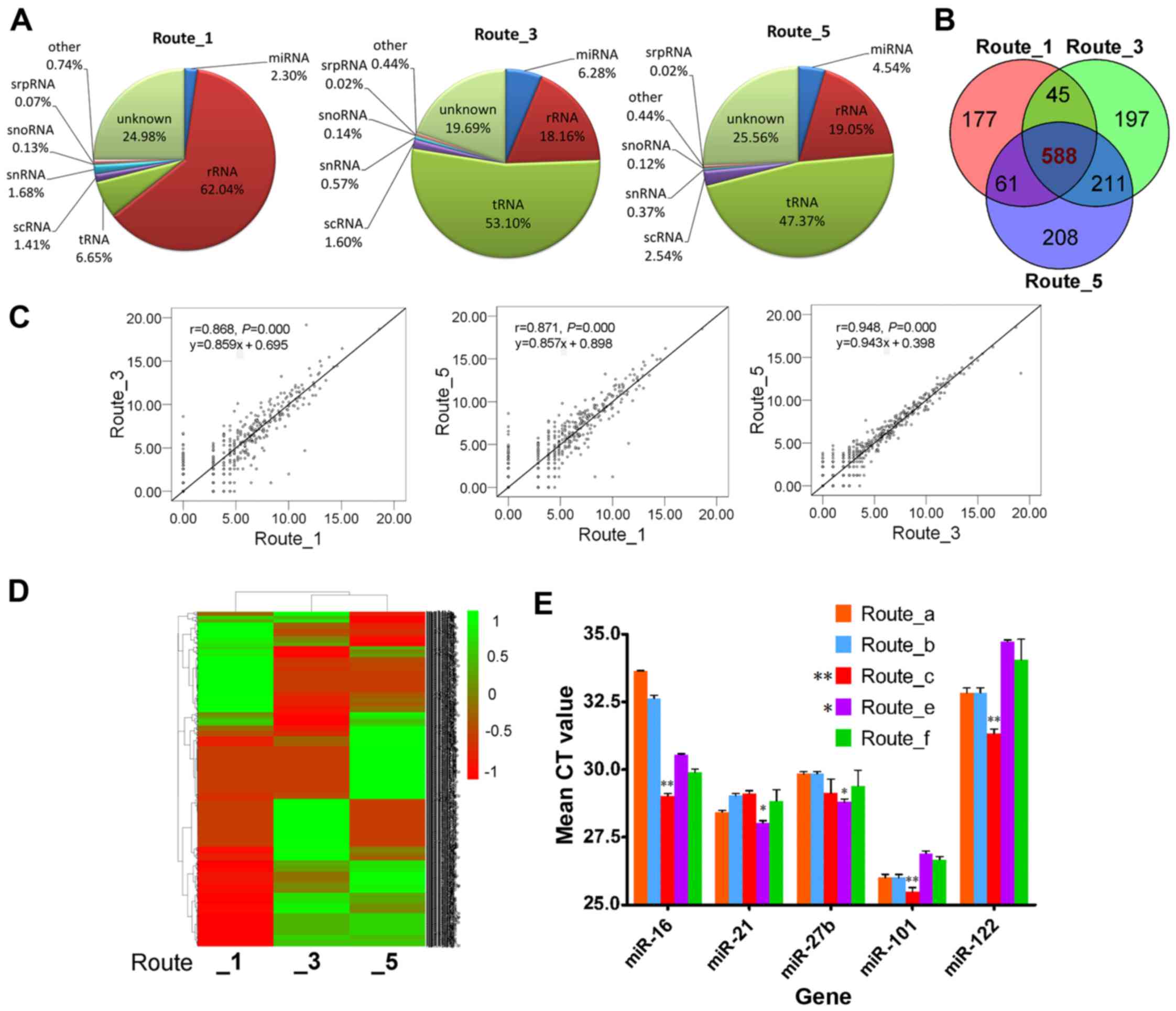
|
1
|
van der Pol E, Böing AN, Harrison P, Sturk
A and Nieuwland R: Classification, functions, and clinical
relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 64:676–705.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
An T, Qin S, Xu Y, Tang Y, Huang Y, Situ
B, Inal JM and Zheng L: Exosomes serve as tumour markers for
personalized diagnostics owing to their important role in cancer
metastasis. J Extracell Vesicles. 4:275222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, Fernandez
AF, Gammon ST, Kaye J, LeBleu VS, Mittendorf EA, Weitz J, Rahbari
N, et al: Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early
pancreatic cancer. Nature. 523:177–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cocucci E, Racchetti G and Meldolesi J:
Shedding microvesicles: Artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol.
19:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G and Clayton
A: Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture
supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. Chapter
3: Unit 3.22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Musante L, Tataruch D, Gu D, Benito-Martin
A, Calzaferri G, Aherne S and Holthofer H: A simplified method to
recover urinary vesicles for clinical applications, and sample
banking. Sci Rep. 4:75322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, Sze NS, Choo A,
Chen TS, Salto-Tellez M, Timmers L, Lee CN, El Oakley RM, et al:
Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Stem Cell Res (Amst). 4:214–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shao H, Chung J, Lee K, Balaj L, Min C,
Carter BS, Hochberg FH, Breakefield XO, Lee H and Weissleder R:
Chip-based analysis of exosomal mRNA mediating drug resistance in
glioblastoma. Nat Commun. 6:69992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, Ji H,
Mathivanan S, Scott AM and Simpson RJ: Comparison of
ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and
immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer
cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods. 56:293–304. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu L, Qu XH, Sun YL, Qian YM and Zhao XH:
Novel method for extracting exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. World J Gastroenterol. 20:6651–6657. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schageman J, Zeringer E, Li M, Barta T,
Lea K, Gu J, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R and Vlassov AV: The
complete exosome workflow solution: From isolation to
characterization of RNA cargo. BioMed Res Int. 2013:2539572013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lobb RJ, Becker M, Wen SW, Wong CS,
Wiegmans AP, Leimgruber A and Möller A: Optimized exosome isolation
protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell
Vesicles. 4:270312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eldh M, Lötvall J, Malmhäll C and Ekström
K: Importance of RNA isolation methods for analysis of exosomal
RNA: Evaluation of different methods. Mol Immunol. 50:278–286.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Enderle D, Spiel A, Coticchia CM, Berghoff
E, Mueller R, Schlumpberger M, Sprenger-Haussels M, Shaffer JM,
Lader E, Skog J, et al: Characterization of RNA from exosomes and
other extracellular vesicles isolated by a novel spin column-based
method. PLoS One. 10:e01361332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rekker K, Saare M, Roost AM, Kubo AL,
Zarovni N, Chiesi A, Salumets A and Peters M: Comparison of serum
exosome isolation methods for microRNA profiling. Clin Biochem.
47:135–138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Van Deun J, Mestdagh P, Sormunen R,
Cocquyt V, Vermaelen K, Vandesompele J, Bracke M, De Wever O and
Hendrix A: The impact of disparate isolation methods for
extracellular vesicles on downstream RNA profiling. J Extracell
Vesicles. 3:32014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
El-Khoury V, Pierson S, Kaoma T, Bernardin
F and Berchem G: Assessing cellular and circulating miRNA recovery:
The impact of the RNA isolation method and the quantity of input
material. Sci Rep. 6:195292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li M, Rai AJ, DeCastro GJ, Zeringer E,
Barta T, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R and Vlassov AV: An optimized
procedure for exosome isolation and analysis using serum samples:
Application to cancer biomarker discovery. Methods. 87:26–30. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Quackenbush JF, Cassidy PB, Pfeffer LM,
Boucher KM, Hawkes JE, Pfeffer SR, Kopelovich L and Leachman SA:
Isolation of circulating microRNAs from microvesicles found in
human plasma. Methods Mol Biol. 1102:641–653. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Josson S, Gururajan M, Sung SY, Hu P, Shao
C, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lichterman J, Duan P, Li Q, et al: Stromal
fibroblast-derived miR-409 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and prostate tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 34:2690–2699.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lötvall J, Hill AF, Hochberg F, Buzás EI,
Di Vizio D, Gardiner C, Gho YS, Kurochkin IV, Mathivanan S,
Quesenberry P, et al: Minimal experimental requirements for
definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A
position statement from the International Society for Extracellular
Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 3:269132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cvjetkovic A, Lötvall J and Lässer C: The
influence of rotor type and centrifugation time on the yield and
purity of extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. Mar
25–2014.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gercel-Taylor C, Atay S, Tullis RH,
Kesimer M and Taylor DD: Nanoparticle analysis of circulating
cell-derived vesicles in ovarian cancer patients. Anal Biochem.
428:44–53. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caradec J, Kharmate G, Hosseini-Beheshti
E, Adomat H, Gleave M and Guns E: Reproducibility and efficiency of
serum-derived exosome extraction methods. Clin Biochem.
47:1286–1292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Webber J and Clayton A: How pure are your
vesicles? J Extracell Vesicles. Jan 10–2013.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lamparski HG, Metha-Damani A, Yao JY,
Patel S, Hsu DH, Ruegg C and Le Pecq JB: Production and
characterization of clinical grade exosomes derived from dendritic
cells. J Immunol Methods. 270:211–226. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moret I, Sánchez-Izquierdo D, Iborra M,
Tortosa L, Navarro-Puche A, Nos P, Cervera J and Beltrán B:
Assessing an improved protocol for plasma microRNA extraction. PLoS
One. 8:e827532013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|