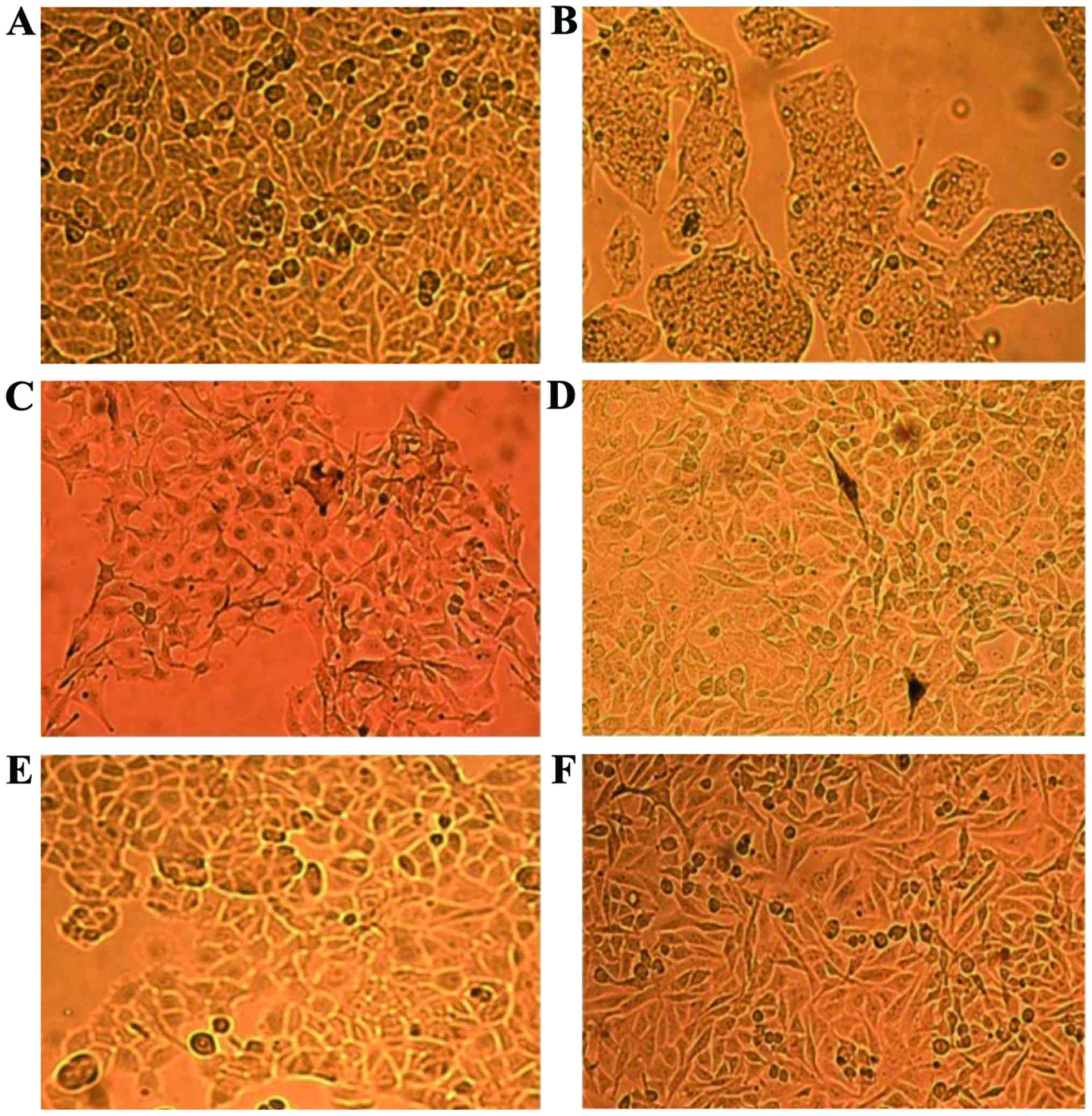
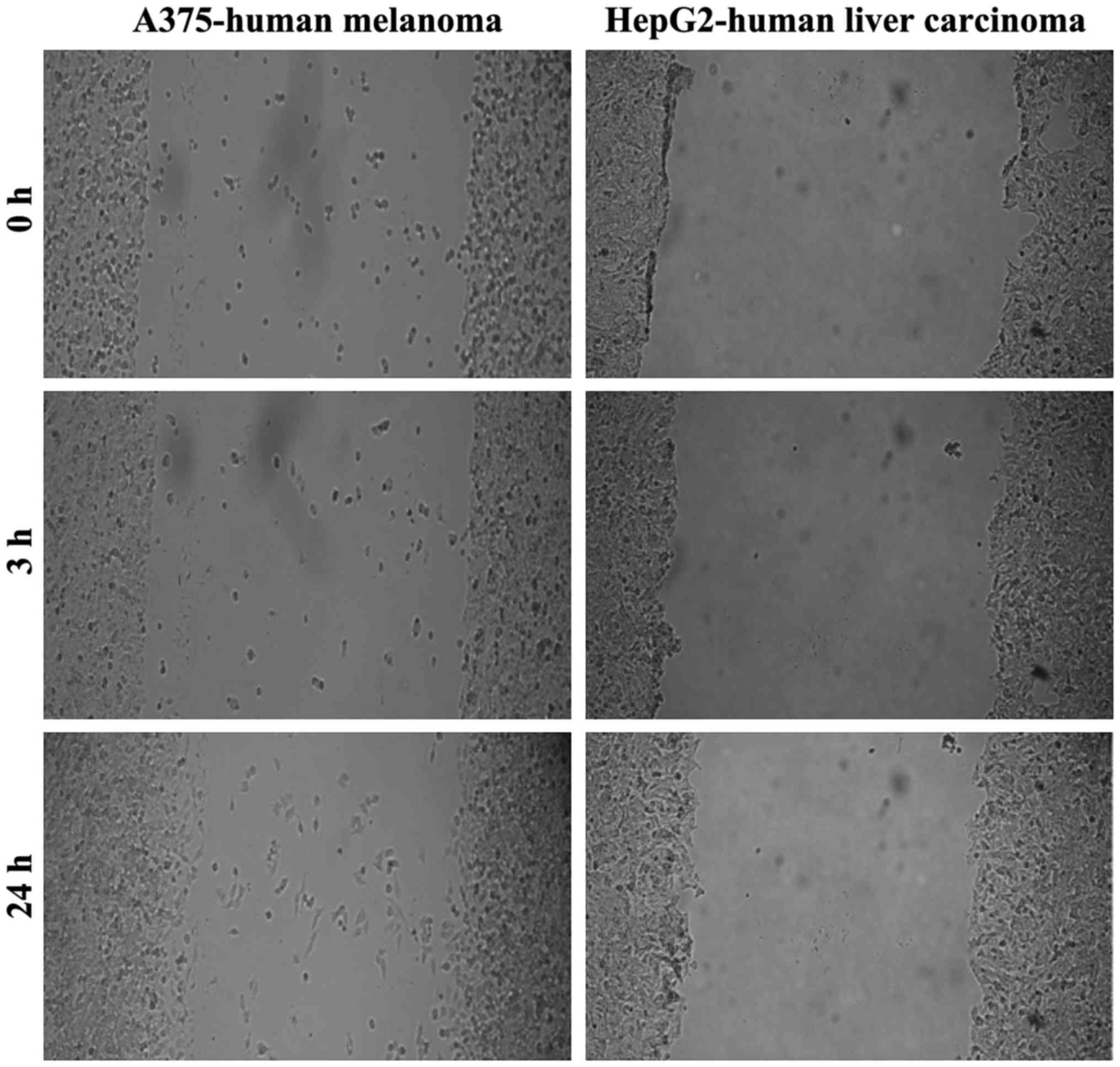
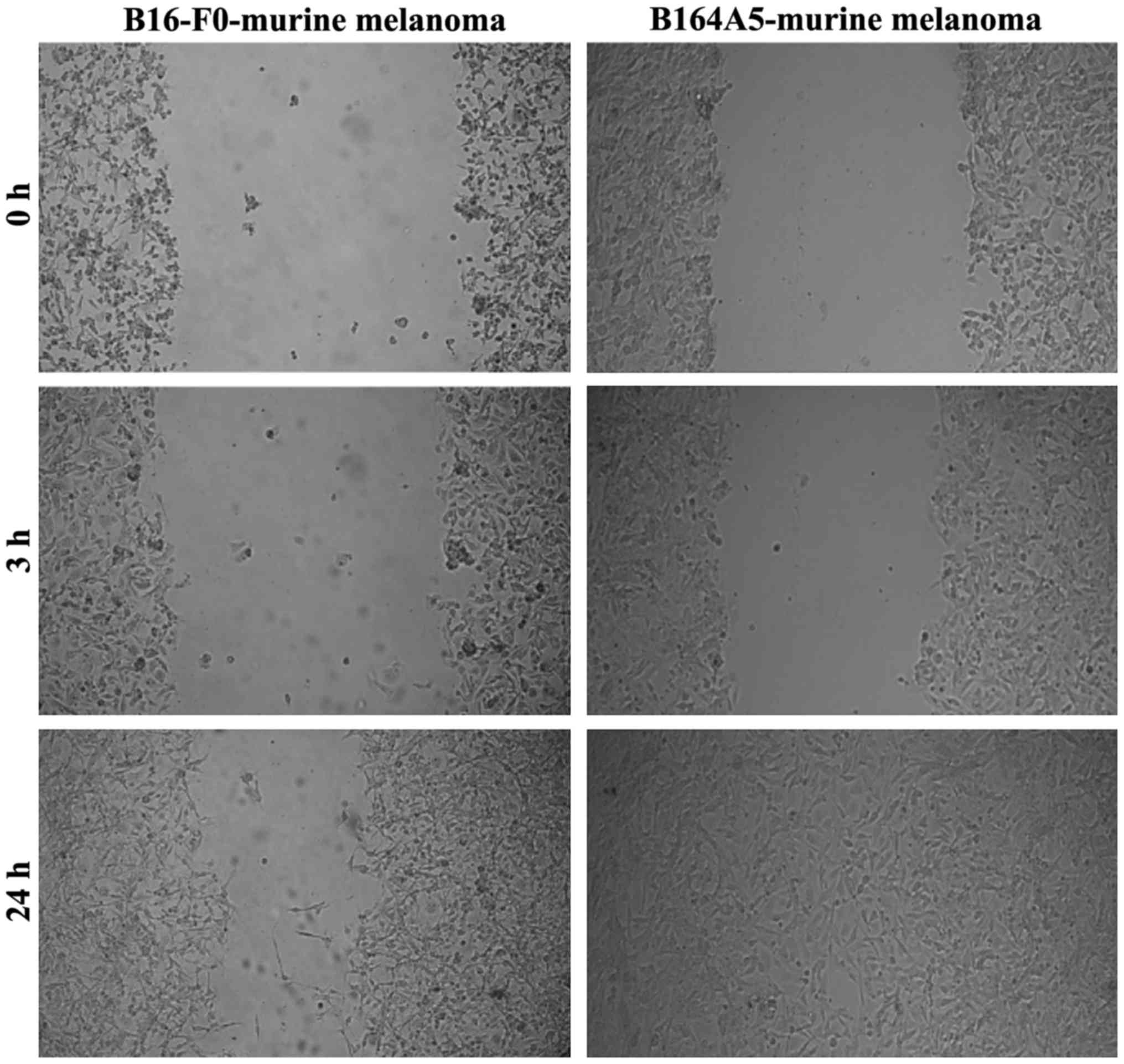
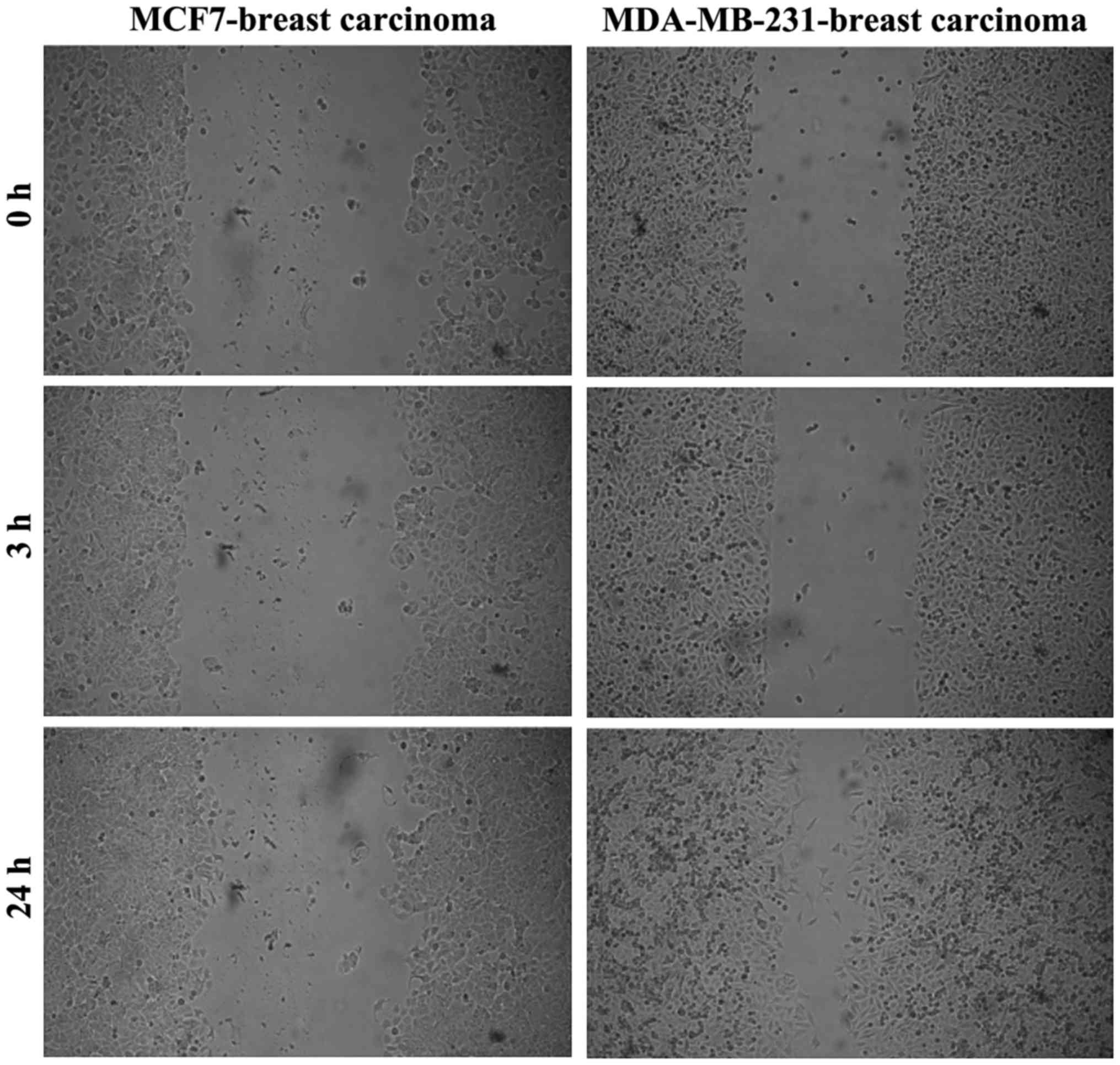
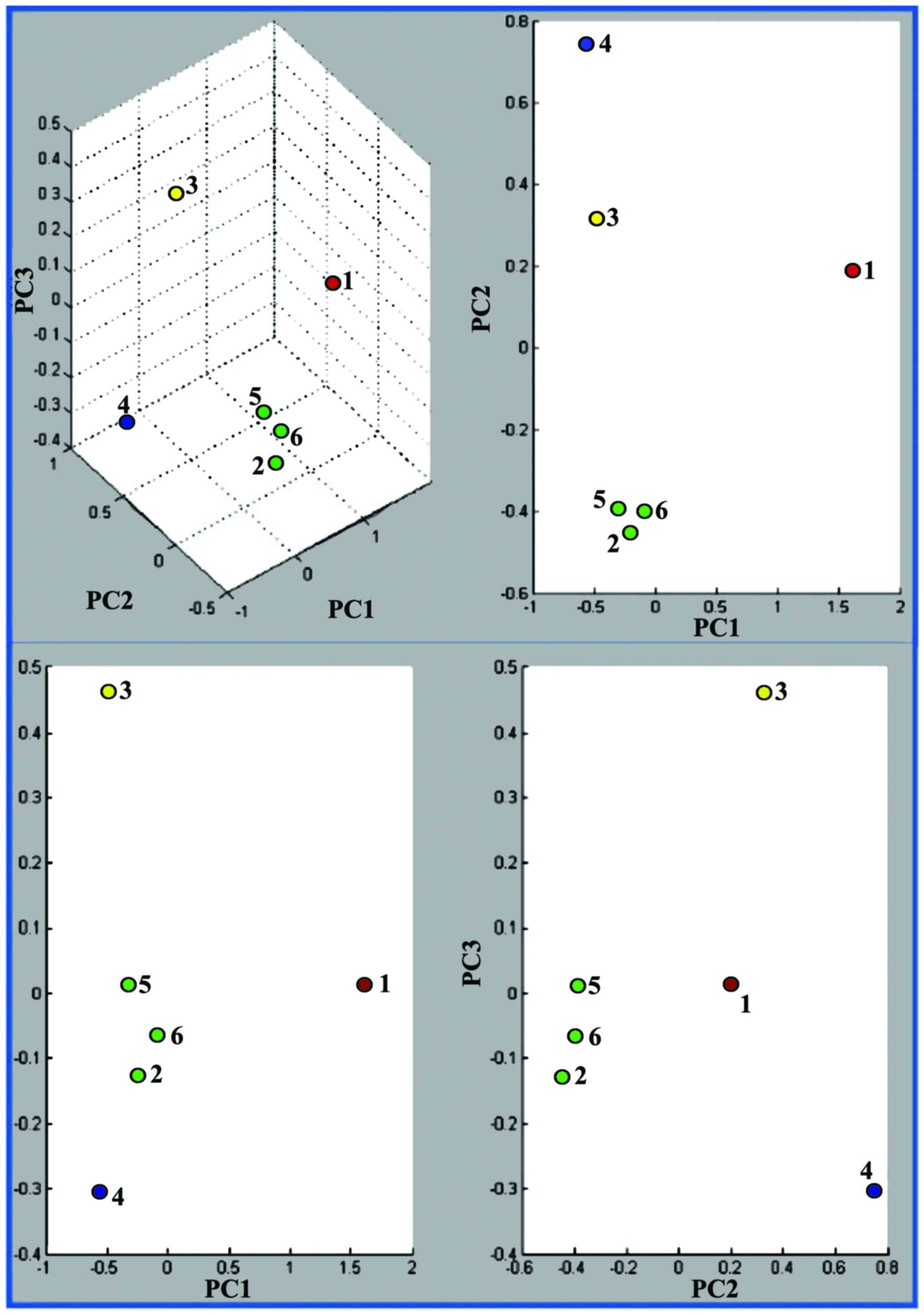
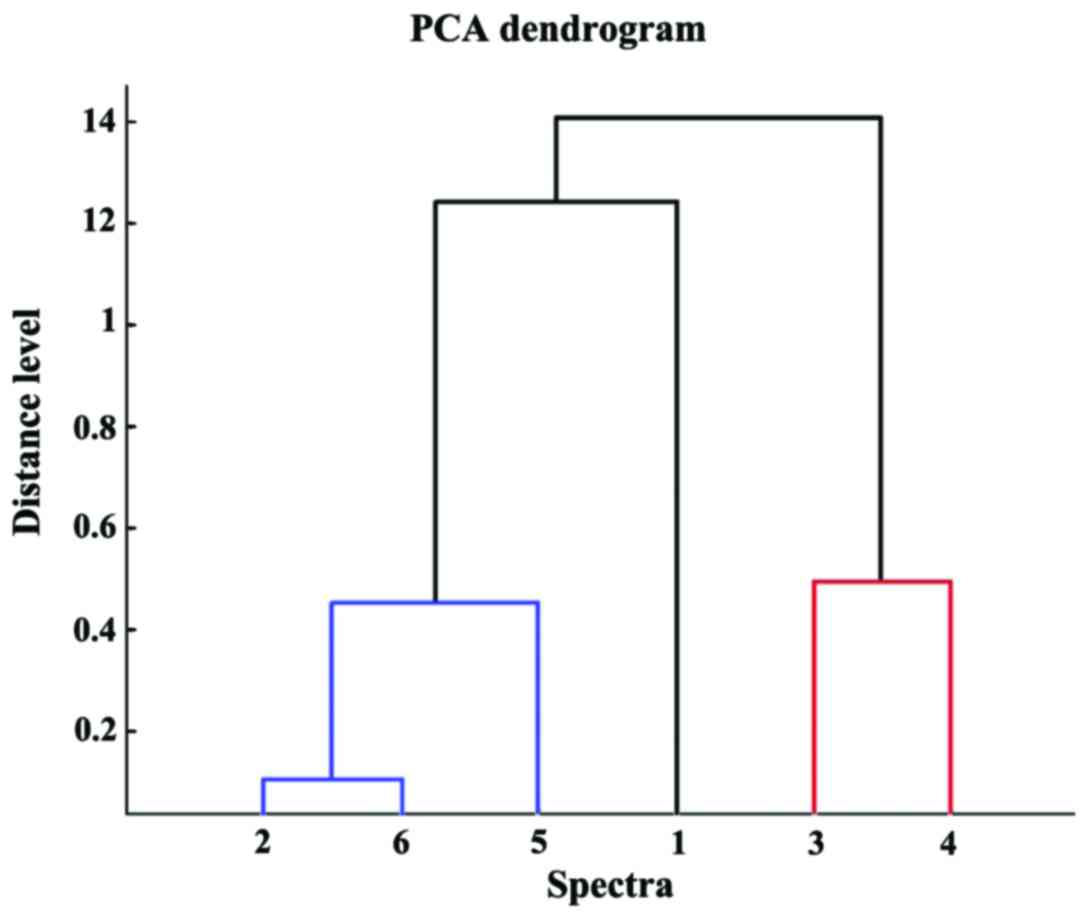
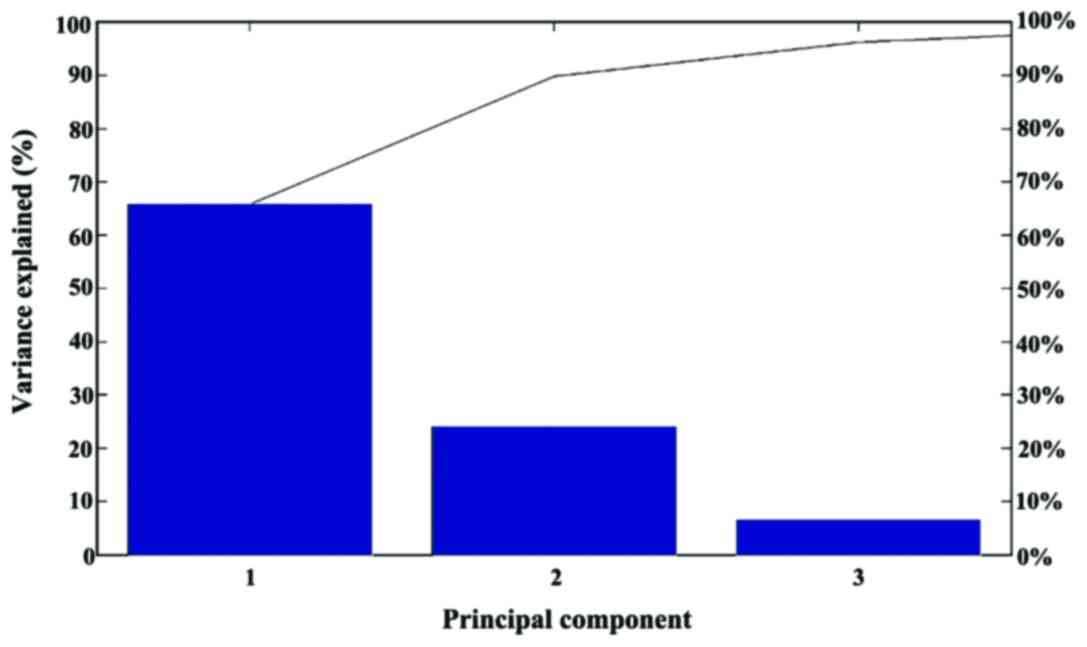
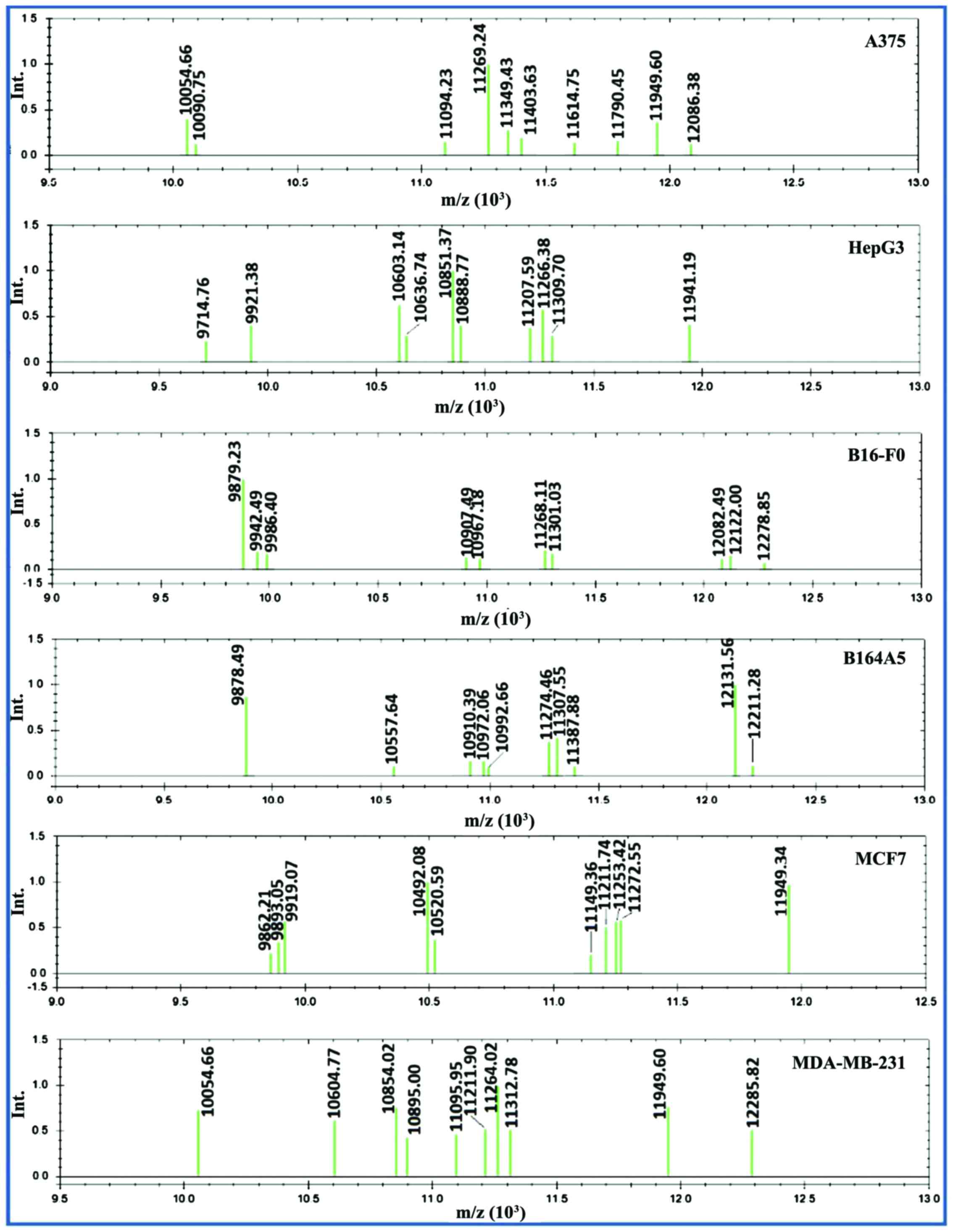
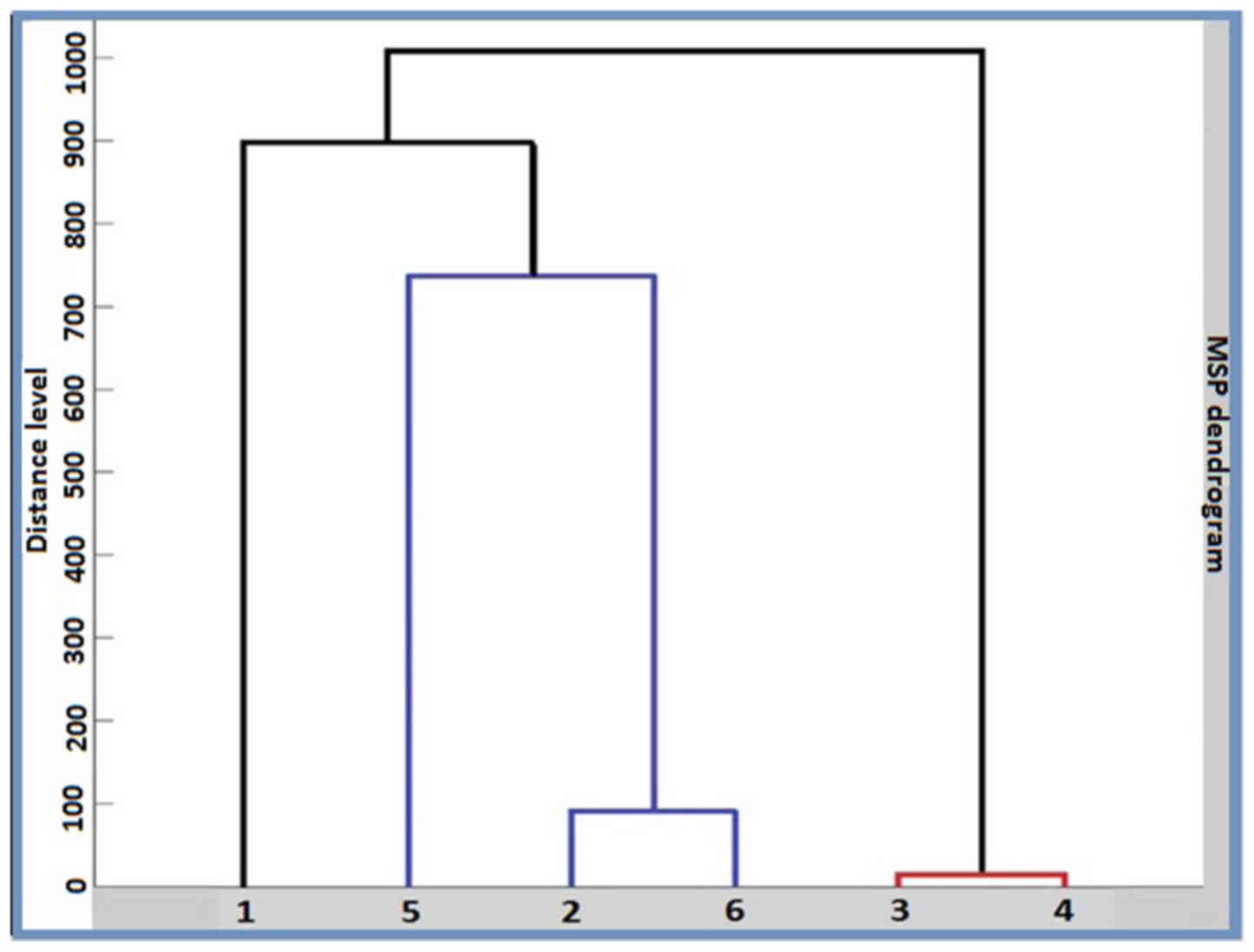
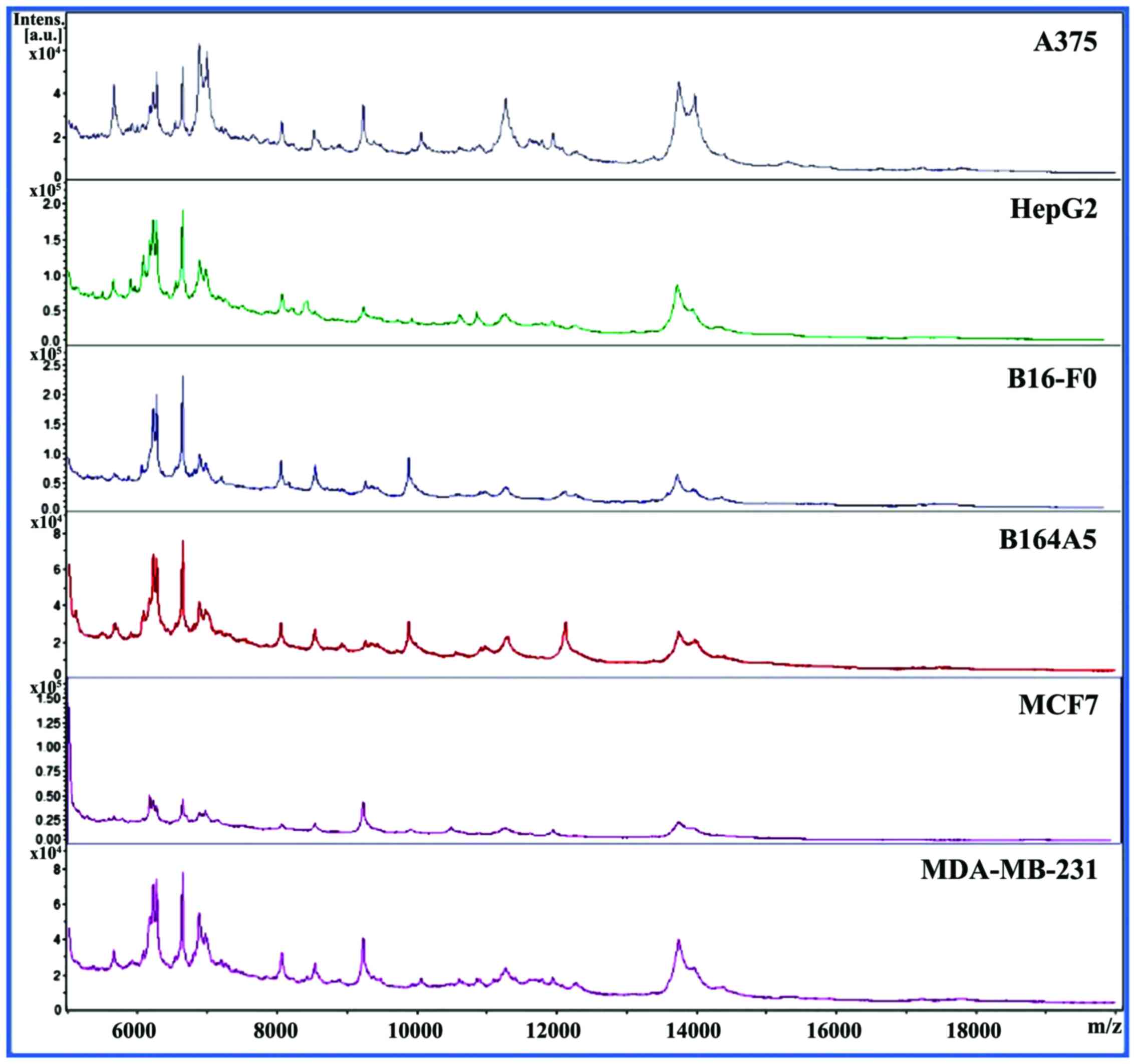
|
1
|
Kallow W, Erhard M, Shah HN, Raptakis E
and Welker M: MALDI-TOF MS for Microbial Identification: Years of
Experimental Development to an Established Protocol. Mass
Spectrometry for Microbial Proteomics. Shah HN and Gharbia SE: John
Wiley & Sons, Ltd; Chichester: pp. 255–276. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shah HN and Gharbia SE: Mass Spectrometry
for Microbial Proteomics. John Wiley and Sons Ltd; Chichester, UK:
2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yang C, He Z and Yu W: Comparison of
public peak detection algorithms for MALDI mass spectrometry data
analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 10:42009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jarman KH, Daly DS, Anderson KK and Wahl
KL: A new approach to automated peak detection. Chemom Intell Lab
Syst. 69:61–76. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Singhal N, Kumar M, Kanaujia PK and Virdi
JS: MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: An emerging technology for
microbial identification and diagnosis. Front Microbiol. 6:7912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karger A, Bettin B, Lenk M and
Mettenleiter TC: Rapid characterisation of cell cultures by
matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometric
typing. J Virol Methods. 164:116–121. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Scalf M, Berggren TW, Westphall
MS and Smith LM: Identification of mammalian cell lines using
MALDI-TOF and LC-ESI-MS/MS mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass
Spectrom. 17:490–499. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Povey JF, O'Malley CJ, Root T, Martin EB,
Montague GA, Feary M, Trim C, Lang DA, Alldread R, Racher AJ, et
al: Rapid high-throughput characterisation, classification and
selection of recombinant mammalian cell line phenotypes using
intact cell MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry fingerprinting and PLS-DA
modelling. J Biotechnol. 184:84–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang P, Gao Q, Suo Z, Munthe E, Solberg S,
Ma L, Wang M, Westerdaal NA, Kvalheim G and Gaudernack G:
Identification and characterization of cells with cancer stem cell
properties in human primary lung cancer cell lines. PLoS One.
8:e570202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dirks WG and Drexler HG: Authentication of
Cancer Cell Lines by DNA Fingerprinting. Cancer Cell Culture:
methods and Protocols. 1st edition. Langdon SP: Humana Press;
Totowa, NJ: pp. 33–42. 2004
|
|
11
|
Greve B, Kelsch R, Spaniol K, Eich HT and
Götte M: Flow cytometry in cancer stem cell analysis and
separation. Cytometry A. 81:284–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duraiyan J, Govindarajan R, Kaliyappan K
and Palanisamy M: Applications of immunohistochemistry. J Pharm
Bioallied Sci. 4(Suppl 2): S307–S309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Coricovac DE, Moacă EA, Pinzaru I, Cîtu C,
Soica C, Mihali CV, Păcurariu C, Tutelyan VA, Tsatsakis A and
Dehelean CA: Biocompatible Colloidal Suspensions Based on Magnetic
Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and
Toxicological Profile. Front Pharmacol. 8:1542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hillenkamp F and Karas M: Mass
spectrometry of peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted
ultraviolet laser desorption/ionization. Methods Enzymol.
193:280–295. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Flatley B, Malone P and Cramer R: MALDI
mass spectrometry in prostate cancer biomarker discovery. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1844:940–949. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cho YT, Chiang YY, Shiea J and Hou MF:
Combining MALDI-TOF and molecular imaging with principal component
analysis for biomarker discovery and clinical diagnosis of cancer.
Genomic Medicine, Biomarkers and Health Sciences. 4:3–6. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rodrigo MA, Zitka O, Krizkova S, Moulick
A, Adam V and Kizek R: MALDI-TOF MS as evolving cancer diagnostic
tool: A review. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 95:245–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nawarak J, Huang-Liu R, Kao SH, Liao HH,
Sinchaikul S, Chen ST and Cheng SL: Proteomics analysis of A375
human malignant melanoma cells in response to arbutin treatment.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1794:159–167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Heger Z, Rodrigo MA, Krizkova S, Zitka O,
Beklova M, Kizek R and Adam V: Identification of estrogen receptor
proteins in breast cancer cells using matrix-assisted laser
desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (Review).
Oncol Lett. 7:1341–1344. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Corona G, De Lorenzo E, Elia C, Simula MP,
Avellini C, Baccarani U, Lupo F, Tiribelli C, Colombatti A and
Toffoli G: Differential proteomic analysis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 36:93–99. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Kriegsmann J, Kriegsmann M and Casadonte
R: MALDI TOF imaging mass spectrometry in clinical pathology: A
valuable tool for cancer diagnostics (Review). Int J Oncol.
46:893–906. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Delorme A, Sejnowski T and Makeig S:
Enhanced detection of artifacts in EEG data using higher-order
statistics and independent component analysis. Neuroimage.
34:1443–1449. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bodanese B, Silveira FL, Zângaro RA,
Pacheco MTT, Pasqualucci CA and Silveira L Jr: Discrimination of
basal cell carcinoma and melanoma from normal skin biopsies in
vitro through Raman spectroscopy and principal component analysis.
Photomed Laser Surg. 30:381–387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alexandrov T: MALDI imaging mass
spectrometry: Statistical data analysis and current computational
challenges. BMC Bioinformatics. 13(Suppl 16): S112012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Norris JL and Caprioli RM: Imaging mass
spectrometry: A new tool for pathology in a molecular age.
Proteomics Clin Appl. 7:733–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bumbrah GS and Sharma RM: Raman
spectroscopy - Basic principle, instrumentation and selected
applications for the characterization of drugs of abuse. Egypt J
Forensic Sci. 6:209–215. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ghebremedhin M, Heitkamp R, Yesupriya S,
Clay B and Crane NJ: Accurate and rapid differentiation of
Acinetobacter baumannii strains by Raman spectroscopy: a
comparative study. J Clin Microbiol. 55:2480–2490. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Geiger T, Wehner A, Schaab C, Cox J and
Mann M: Comparative proteomic analysis of eleven common cell lines
reveals ubiquitous but varying expression of most proteins. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 11:M111.0140502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pan C, Kumar C, Bohl S, Klingmueller U and
Mann M: Comparative proteomic phenotyping of cell lines and primary
cells to assess preservation of cell type-specific functions. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 8:443–450. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Mladkova J, Sanda M, Matouskova E and
Selicharova I: Phenotyping breast cancer cell lines EM-G3, HCC1937,
MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 using 2-D electrophoresis and affinity
chromatography for glutathione-binding proteins. BMC Cancer.
10:4492010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nagaraja GM, Othman M, Fox BP, Alsaber R,
Pellegrino CM, Zeng Y, Khanna R, Tamburini P, Swaroop A and Kandpal
RP: Gene expression signatures and biomarkers of noninvasive and
invasive breast cancer cells: Comprehensive profiles by
representational difference analysis, microarrays and proteomics.
Oncogene. 25:2328–2338. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Danciu C, Falamas A, Dehelean C, Soica C,
Radeke H, Barbu-Tudoran L, Bojin F, Pînzaru SC and Munteanu MF: A
characterization of four B16 murine melanoma cell sublines
molecular fingerprint and proliferation behavior. Cancer Cell Int.
13:752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Avram S, Coricovac DE, Pavel IZ, Pinzaru
I, Ghiulai R, Baderca F, Soica C, Muntean D, Branisteanu DE,
Spandidos DA, et al: Standardization of A375 human melanoma models
on chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane and Balb/c nude mice.
Oncol Rep. 38:89–99. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|