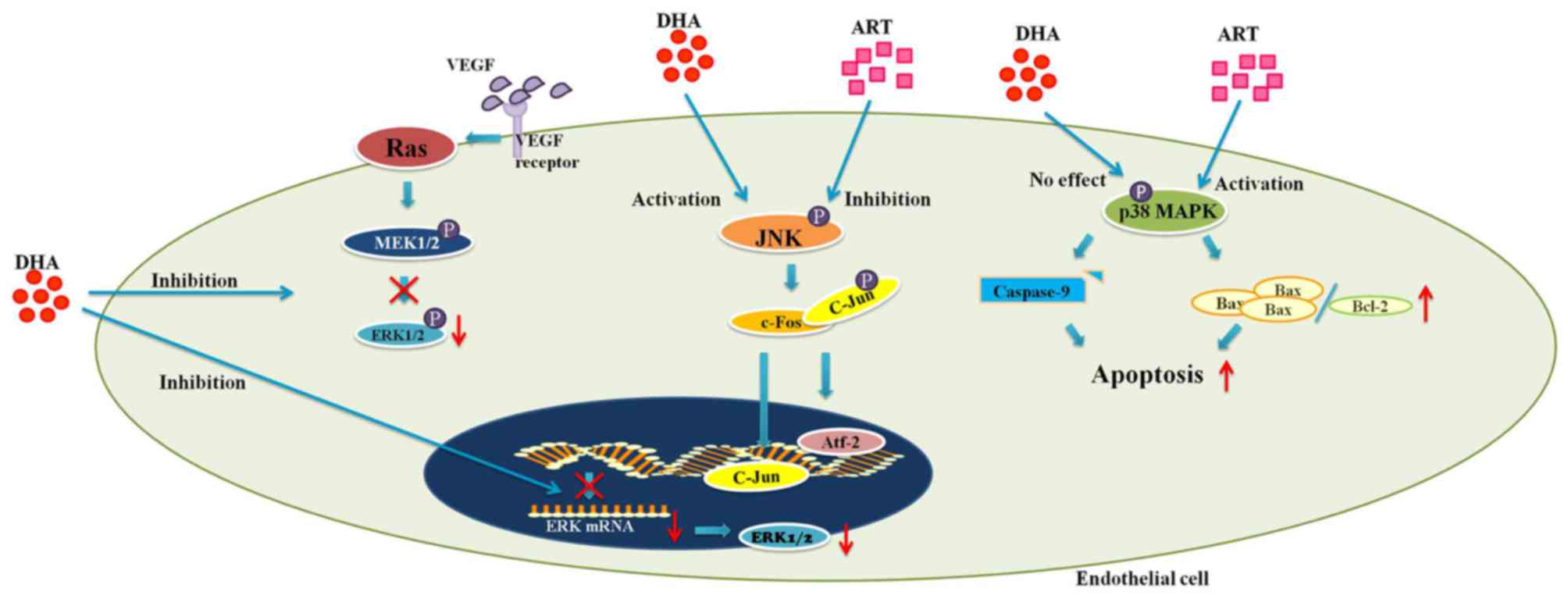
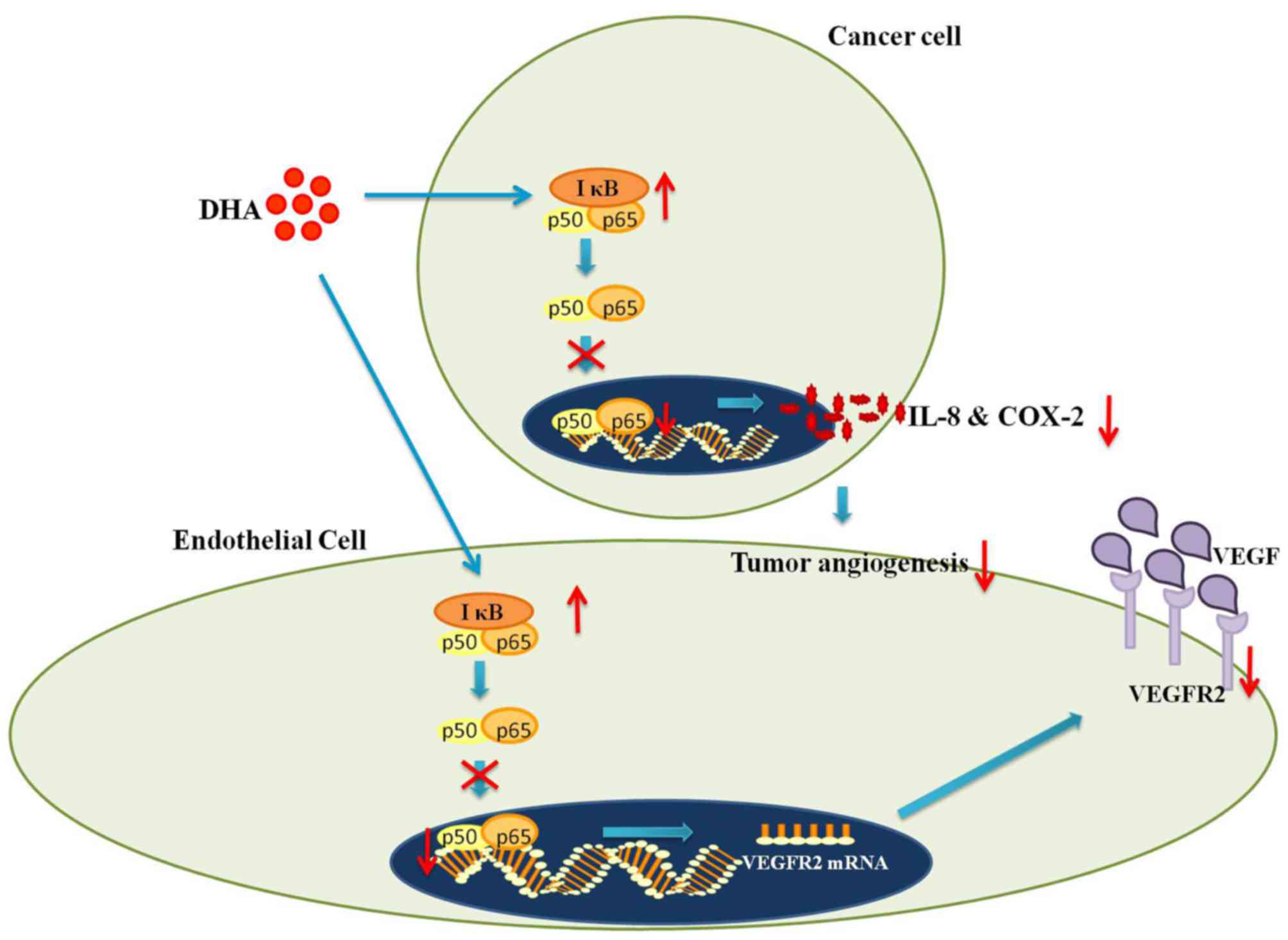
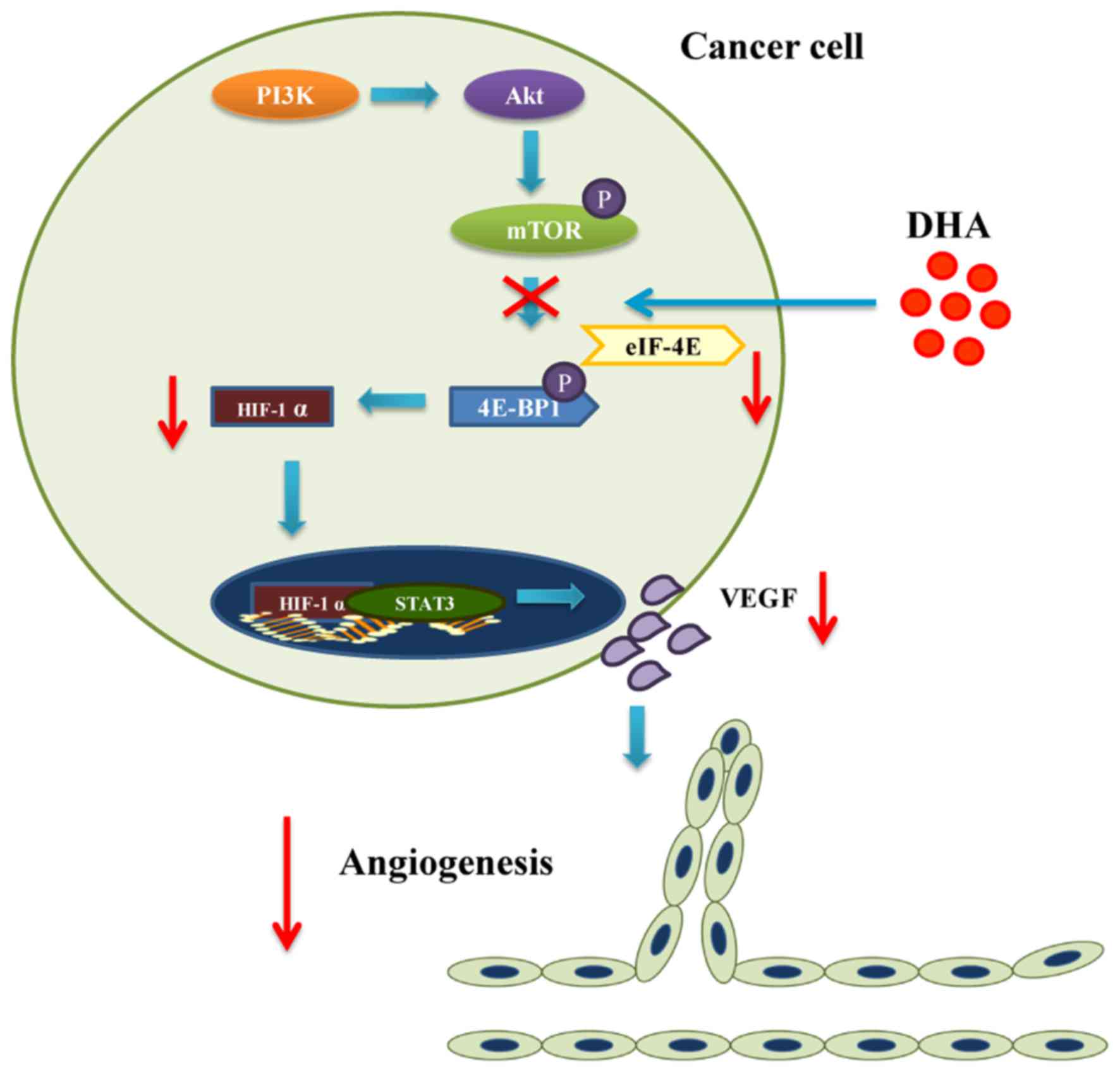
|
1
|
Dong F, Tian H, Yan S, Li L, Dong X, Wang
F, Li J, Li C, Cao Z, Liu X, et al: Dihydroartemisinin inhibits
endothelial cell proliferation through the suppression of the ERK
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 35:1381–1387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dong F, Zhou X, Li C, Yan S, Deng X, Cao
Z, Li L, Tang B, Allen TD and Liu J: Dihydroartemisinin targets
VEGFR2 via the NF-κB pathway in endothelial cells to inhibit
angiogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:1479–1488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Guo L, Dong F, Hou Y, Cai W, Zhou X, Huang
AL, Yang M, Allen TD and Liu J: Dihydroartemisinin inhibits
vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell
migration by a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent
pathway. Exp Ther Med. 8:1707–1712. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oh S, Jeong IH, Shin WS and Lee S: Growth
inhibition activity of thioacetal artemisinin derivatives against
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
13:3665–3668. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oh S, Jeong IH, Ahn CM, Shin WS and Lee S:
Synthesis and antiangiogenic activity of thioacetal artemisinin
derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem. 12:3783–3790. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oh S, Jeong IH, Shin WS and Lee S:
Synthesis and antiangiogenic activity of exo-olefinated
deoxoartemisinin derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 14:3683–3686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ricci J, Park J, Chung WY, Park KK and
Jung M: Concise synthesis and antiangiogenic activity of
artemisinin-glycolipid hybrids on chorioallantoic membranes. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 20:6858–6860. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ho WE, Peh HY, Chan TK and Wong WS:
Artemisinins: Pharmacological actions beyond anti-malarial.
Pharmacol Ther. 142:126–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng R, Li C, Li C, Wei L, Li L, Zhang Y,
Yao Y, Gu X, Cai W, Yang Z, et al: The artemisinin derivative
artesunate inhibits corneal neovascularization by inducing
ROS-dependent apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:3400–3409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nagy JA, Dvorak AM and Dvorak HF: VEGF-A
and the induction of pathological angiogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol.
2:251–275. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ferrara N: VEGF and the quest for tumour
angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:795–803. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ferrara N: VEGF-A: A critical regulator of
blood vessel growth. Eur Cytokine Netw. 20:158–163. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Crespo-Ortiz MP and Wei MQ: Antitumor
activity of artemisinin and its derivatives: From a well-known
antimalarial agent to a potential anticancer drug. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2012:2475972012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Arden GB, Wolf JE and Tsang Y: Does dark
adaptation exacerbate diabetic retinopathy? Evidence and a linking
hypothesis. Vision Res. 38:1723–1729. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crawford TN, Alfaro DV III, Kerrison JB
and Jablon EP: Diabetic retinopathy and angiogenesis. Curr Diabetes
Rev. 5:8–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He Y, Fan J, Lin H, Yang X, Ye Y, Liang L,
Zhan Z, Dong X, Sun L and Xu H: The anti-malaria agent artesunate
inhibits expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human rheumatoid arthritis
fibroblast-like synoviocyte. Rheumatol Int. 31:53–60. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer,
vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1:27–31. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Polverini PJ: Angiogenesis in health and
disease: Insights into basic mechanisms and therapeutic
opportunities. J Dent Educ. 66:962–975. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang SJ, Sun B, Cheng ZX, Zhou HX, Gao Y,
Kong R, Chen H, Jiang HC, Pan SH, Xue DB, et al: Dihydroartemisinin
inhibits angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer by targeting the NF-κB
pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 68:1421–1430. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jeong E, Song HJ, Lim S, Lee SJ, Lim JE,
Nam DH, Joo KM, Jeong BC, Jeon SS, Choi HY, et al: Repurposing the
anti-malarial drug artesunate as a novel therapeutic agent for
metastatic renal cell carcinoma due to its attenuation of tumor
growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 6:33046–33064.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu XX, Yang L, Li YJ, Zhang D, Chen Y,
Kostecká P, Kmoníčková E and Zídek Z: Effects of sesquiterpene,
flavonoid and coumarin types of compounds from Artemisia annua L.
on production of mediators of angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rep.
65:410–420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Odaka Y, Xu B, Luo Y, Shen T, Shang C, Wu
Y, Zhou H and Huang S: Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the mammalian
target of rapamycin-mediated signaling pathways in tumor cells.
Carcinogenesis. 35:192–200. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Corsello MA and Garg NK: Synthetic
chemistry fuels interdisciplinary approaches to the production of
artemisinin. Nat Prod Rep. 32:359–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mott BT, He R, Chen X, Fox JM, Civin CI,
Arav-Boger R and Posner GH: Artemisinin-derived dimer phosphate
esters as potent anti-cytomegalovirus (anti-CMV) and anticancer
agents: A structure-activity study. Bioorg Med Chem. 21:3702–3707.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee S: Artemisinin, promising lead natural
product for various drug developments. Mini Rev Med Chem.
7:411–422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh NP and Panwar VK: Case report of a
pituitary macroadenoma treated with artemether. Integr Cancer Ther.
5:391–394. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen H, Shi L, Yang X, Li S, Guo X and Pan
L: Artesunate inhibiting angiogenesis induced by human myeloma
RPMI-8226 cells. Int J Hematol. 92:587–597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nagelschmitz J, Voith B, Wensing G, Roemer
A, Fugmann B, Haynes RK, Kotecka BM, Rieckmann KH and Edstein MD:
First assessment in humans of the safety, tolerability,
pharmacokinetics, and ex vivo pharmacodynamic antimalarial activity
of the new artemisinin derivative artemisone. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 52:3085–3091. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ansari MT, Saify ZS, Sultana N, Ahmad I,
Saeed-Ul-Hassan S, Tariq I and Khanum M: Malaria and artemisinin
derivatives: An updated review. Mini Rev Med Chem. 13:1879–1902.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Haynes RK, Fugmann B, Stetter J, Rieckmann
K, Heilmann HD, Chan HW, Cheung MK, Lam WL, Wong HN, Croft SL, et
al: Artemisone - a highly active antimalarial drug of the
artemisinin class. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 45:2082–2088. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jung M, Tak J, Chung WY and Park KK:
Antiangiogenic activity of deoxoartemisinin derivatives on
chorioallantoic membrane. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 16:1227–1230. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shen K, Ji L, Lu B and Wang Z: c-Jun
N-terminal kinase mediated VEGFR2 sustained phosphorylation is
critical for VEGFA-induced angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 64:17–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miura S, Matsuo Y and Saku K: Jun
N-terminal kinase inhibitor blocks angiogenesis by blocking VEGF
secretion and an MMP pathway. J Atheroscler Thromb. 15:69–74. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Grossi V, Peserico A, Tezil T and Simone
C: p38α MAPK pathway: A key factor in colorectal cancer therapy and
chemoresistance. World J Gastroenterol. 20:9744–9758. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Z, Meng D, Li G, Xu J, Tian K and Li Y:
Celecoxib combined with diacerein effectively alleviates
osteoarthritis in rats via regulating JNK and p38MAPK signaling
pathways. Inflammation. 38:1563–1572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma X, Liu Y, Wang Q, Chen Y, Liu M, Li X,
Xiang R, Wei Y, Duan Y and Han J: Tamoxifen induces the development
of hernia in mice by activating MMP-2 and MMP-13 expression.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1038–1048. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sato Y, Kanno S, Oda N, Abe M, Ito M,
Shitara K and Shibuya M: Properties of two VEGF receptors, Flt-1
and KDR, in signal transduction. Ann NY Acad Sci. 902:201–207.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Szade A, Grochot-Przeczek A, Florczyk U,
Jozkowicz A and Dulak J: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of
inflammation-induced angiogenesis. IUBMB Life. 67:145–159. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gupta K, Kshirsagar S, Li W, Gui L,
Ramakrishnan S, Gupta P, Law PY and Hebbel RP: VEGF prevents
apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells via opposing
effects on MAPK/ERK and SAPK/JNK signaling. Exp Cell Res.
247:495–504. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Weston CR and Davis RJ: The JNK signal
transduction pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 19:142–149. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dong F, Han J, Jing G, Chen X, Yan S, Yue
L, Cao Z, Liu X, Ma G and Liu J: Dihydroartemisinin transiently
activates the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway in endothelial cells.
Oncol Lett. 12:4699–4704. 2016.
|
|
45
|
Firestone GL and Sundar S: Anticancer
activities of artemisinin and its bioactive derivatives. Expert Rev
Mol Med. 11:e322009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Devasagayam TP, Tilak JC, Boloor KK, Sane
KS, Ghaskadbi SS and Lele RD: Free radicals and antioxidants in
human health: Current status and future prospects. J Assoc
Physicians India. 52:794–804. 2004.
|
|
47
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Shared principles
in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 132:344–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Oliver KM, Taylor CT and Cummins EP:
Hypoxia. Regulation of NFkappaB signalling during inflammation: The
role of hydroxylases. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:2152009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hsiao KY, Chang N, Lin SC, Li YH and Wu
MH: Inhibition of dual specificity phosphatase-2 by hypoxia
promotes interleukin-8-mediated angiogenesis in endometriosis. Hum
Reprod. 29:2747–2755. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Suffee N, Richard B, Hlawaty H, Oudar O,
Charnaux N and Sutton A: Angiogenic properties of the chemokine
RANTES/CCL5. Biochem Soc Trans. 39:1649–1653. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mateo J, García-Lecea M, Cadenas S,
Hernández C and Moncada S: Regulation of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha by nitric oxide through mitochondria-dependent and
-independent pathways. Biochem J. 376:537–544. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu H, He Y, Yang X, Liang L, Zhan Z, Ye Y,
Yang X, Lian F and Sun L: Anti-malarial agent artesunate inhibits
TNF-alpha-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines via
inhibition of NF-kappaB and PI3 kinase/Akt signal pathway in human
rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 46:920–926. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Karar J and Maity A: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
in angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci. 4:512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao YG, Wang Y, Guo Z, Gu AD, Dan HC,
Baldwin AS, Hao W and Wan YY: Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates
inflammatory disease by its reciprocal effects on Th and regulatory
T cell function via modulating the mammalian target of rapamycin
pathway. J Immunol. 189:4417–4425. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen Q, Chen L, Wu X, Zhang F, Jin H, Lu
C, Shao J, Kong D, Wu L and Zheng S: Dihydroartemisinin prevents
liver fibrosis in bile duct ligated rats by inducing hepatic
stellate cell apoptosis through modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway.
IUBMB Life. 68:220–231. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Feng X, Li L, Jiang H, Jiang K, Jin Y and
Zheng J: Dihydroartemisinin potentiates the anticancer effect of
cisplatin via mTOR inhibition in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer
cells: Involvement of apoptosis and autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 444:376–381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liao K, Li J and Wang Z:
Dihydroartemisinin inhibits cell proliferation via
AKT/GSK3β/cyclinD1 pathway and induces apoptosis in A549 lung
cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:8684–8691. 2014.
|
|
59
|
Tan SS, Ong B, Cheng C, Ho WE, Tam JK,
Stewart AG, Harris T, Wong WS and Tran T: The antimalarial drug
artesunate inhibits primary human cultured airway smooth muscle
cell proliferation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:451–458.
2014.
|