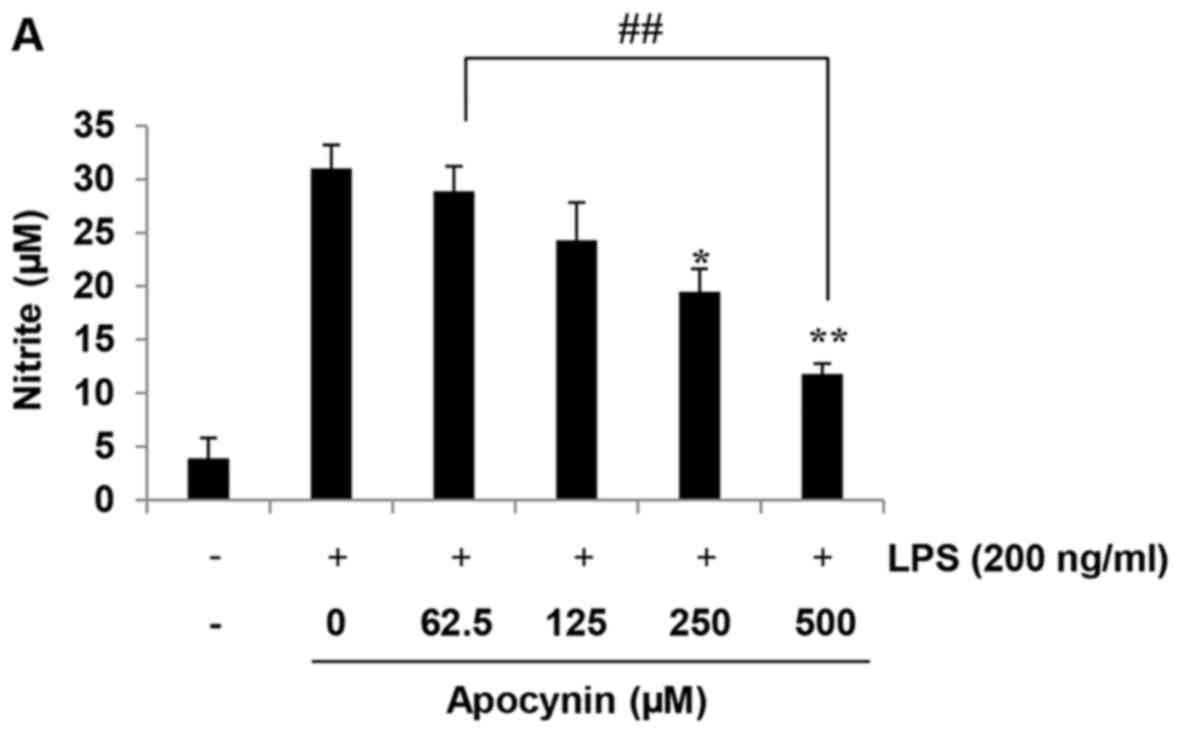
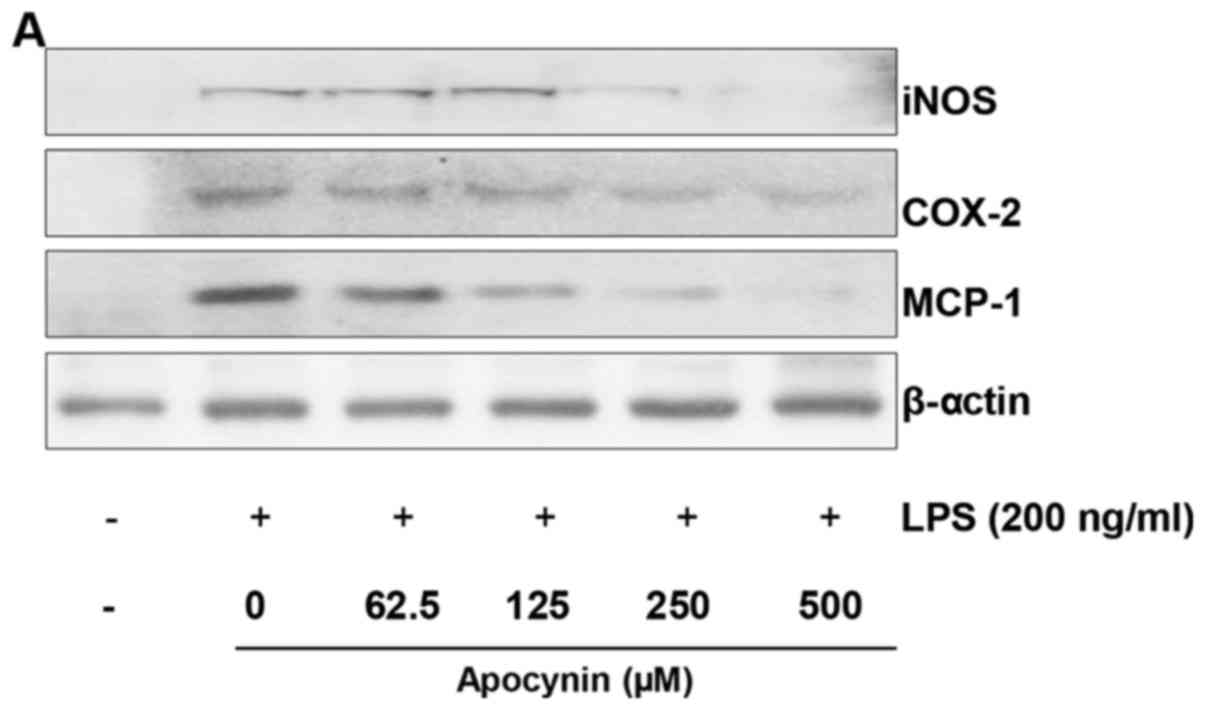
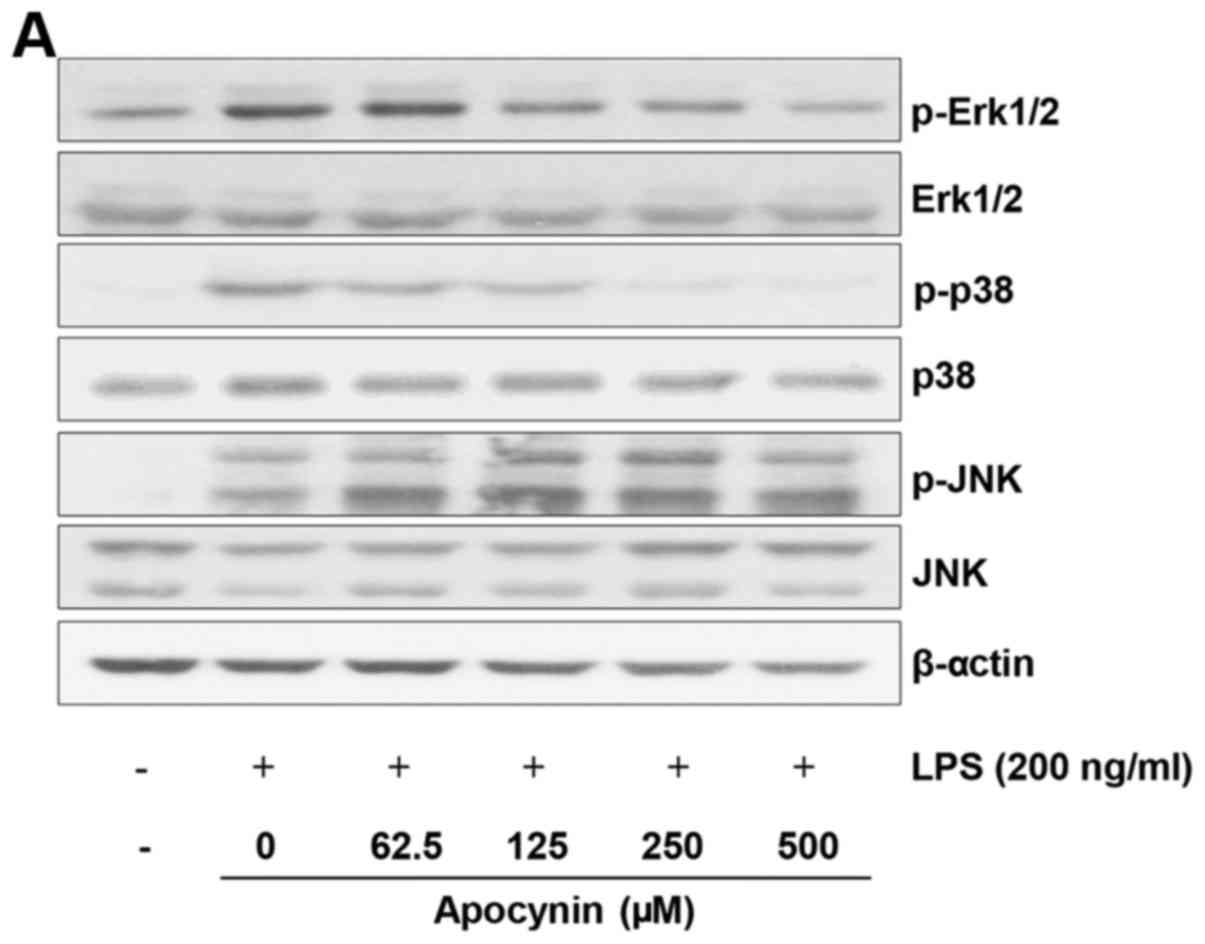
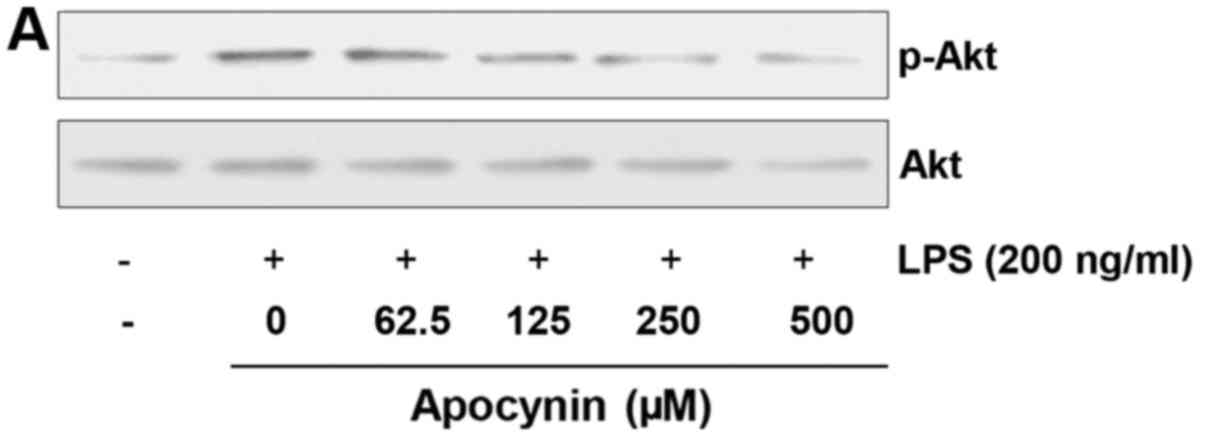
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Radeke HH and Resch K: The inflammatory
function of renal glomerular mesangial cells and their interaction
with the cellular immune system. Clin Investig. 70:825–842. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Almeida WS, Maciel TT, Di Marco GS,
Casarini DE, Campos AH and Schor N: Escherichia coli
lipopolysaccharide inhibits renin activity in human mesangial
cells. Kidney Int. 69:974–980. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hsing CH, Chou W, Wang JJ, Chen HW and Yeh
CH: Propofol increases bone morphogenetic protein-7 and decreases
oxidative stress in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 26:1162–1172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S and Sawaya
BE: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 29:313–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Poukkanen M, Vaara ST, Pettilä V, Kaukonen
KM, Korhonen AM, Hovilehto S, Inkinen O, Laru-Sompa R, Kaminski T,
Reinikainen M, et al FINNAKI study group: Acute kidney injury in
patients with severe sepsis in Finnish Intensive Care Units. Acta
Anaesthesiol Scand. 57:863–872. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen YC, Chen CH, Ko WS, Cheng CY, Sue YM
and Chen TH: Dipyridamole inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced
cyclooxygenase-2 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 via heme
oxygenase-1-mediated reactive oxygen species reduction in rat
mesangial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 650:445–450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nagai T, Urushihara M, Kinoshita Y, Jamba
A, Kondo S and Kagami S: Differential regulation of angiotensin
II-induced extracellular signal regulated kinase-1/2 and -5 in
progressive glomerulonephritis. Nephrology (Carlton). 21:950–958.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee JW, Kwon JH, Lim MS, Lee HJ, Kim SS,
Lim SY and Chun W: 3,4,5-Trihydroxycinnamic acid increases
heme-oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and decreases macrophage infiltration in
LPS-induced septic kidney. Mol Cell Biochem. 397:109–116. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee JW, Bae CJ, Choi Y-J, Kim SI, Kim NH,
Lee HJ, Kim SS, Kwon YS and Chun W: 3, 4, 5-Trihydroxycinnamic acid
inhibits LPS-induced iNOS expression by suppressing NF-κB
activation in BV2 microglial cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
16:107–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vo VA, Lee JW, Park JH, Kwon JH, Lee HJ,
Kim SS, Kwon YS and Chun W: N-(p-Coumaryol)-tryptamine suppresses
the activation of JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway in LPS-challenged
RAW264. 7 cells Biomol Ther (Seoul). 22:200–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ha YM, Ham SA, Kim YM, Lee YS, Kim HJ, Seo
HG, Lee JH, Park MK and Chang KC: β1-adrenergic receptor-mediated
HO-1 induction, via PI3K and p38 MAPK, by isoproterenol in RAW
264.7 cells leads to inhibition of HMGB1 release in LPS-activated
RAW 264.7 cells and increases in survival rate of CLP-induced
septic mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:769–777. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fidan H, Sahin O, Yavuz Y, Kilbas A,
Cetinkaya Z, Ela Y, Ozen OA and Altuntas I: Caffeic acid phenethyl
ester reduces mortality and sepsis-induced lung injury in rats.
Crit Care Med. 35:2822–2829. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Park SY, Seetharaman R, Ko MJ, Kim DY, Kim
TH, Yoon MK, Kwak JH, Lee SJ, Bae YS and Choi YW: Ethyl linoleate
from garlic attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory
cytokine production by inducing heme oxygenase-1 in RAW264.7 cells.
Int Immunopharmacol. 19:253–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsoyi K, Lee TY, Lee YS, Kim HJ, Seo HG,
Lee JH and Chang KC: Heme-oxygenase-1 induction and carbon
monoxide-releasing molecule inhibit lipopolysaccharide
(LPS)-induced high-mobility group box 1 release in vitro and
improve survival of mice in LPS- and cecal ligation and
puncture-induced sepsis model in vivo. Mol Pharmacol. 76:173–182.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park EJ, Lim JH, Nam SI, Park JW and Kwon
TK: Rottlerin induces heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) up-regulation through
reactive oxygen species (ROS) dependent and PKC delta-independent
pathway in human colon cancer HT29 cells. Biochimie. 92:110–115.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Paracatu LC, Zeraik ML, Bertozo LC,
Bartolomeu AA, Filho LC, Fonseca LM and Ximenes VF: Synthesis,
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of an apocynin-derived
dihydrocoumarin. Med Chem. 13:93–100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nam YJ, Kim A, Sohn DS and Lee CS:
Apocynin inhibits Toll-like receptor-4-mediated activation of NF-κB
by suppressing the Akt and mTOR pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 389:1267–1277. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hwang YJ, Lee SJ, Park JY, Chun W, Nam SJ,
Park JM, Park SC, Choi DH and Kang CD: Apocynin suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through the
inhibition of MAP kinase signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells. Drug
Dev Res. 77:271–277. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sharma M, Kaur T and Singla SK: Role of
mitochondria and NADPH oxidase derived reactive oxygen species in
hyperoxaluria induced nephrolithiasis: Therapeutic intervention
with combinatorial therapy of N-acetyl cysteine and Apocynin.
Mitochondrion. 27:15–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abdelmageed ME, El-Awady MS and Suddek GM:
Apocynin ameliorates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats.
Int Immunopharmacol. 30:163–170. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lafeber FP, Beukelman CJ, van den Worm E,
van Roy JL, Vianen ME, van Roon JA, van Dijk H and Bijlsma JW:
Apocynin, a plant-derived, cartilage-saving drug, might be useful
in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford).
38:1088–1093. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Radeke HH, Meier B, Topley N, Flöge J,
Habermehl GG and Resch K: Interleukin 1-α and tumor necrosis
factor-α induce oxygen radical production in mesangial cells.
Kidney Int. 37:767–775. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Migliorini A, Ebid R, Scherbaum CR and
Anders HJ: The danger control concept in kidney disease: Mesangial
cells. J Nephrol. 26:437–449. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu F, Zhang W, Li L, Zheng F, Shao X, Zhou
J and Li H: Inhibitory effects of honokiol on
lipopolysaccharide-induced cellular responses and signaling events
in human renal mesangial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 654:117–121. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Brown Z, Strieter RM, Neild GH, Thompson
RC, Kunkel SL and Westwick J: IL-1 receptor antagonist inhibits
monocyte chemotactic peptide 1 generation by human mesangial cells.
Kidney Int. 42:95–101. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Namiki M, Kawashima S, Yamashita T, Ozaki
M, Hirase T, Ishida T, Inoue N, Hirata K, Matsukawa A, Morishita R,
et al: Local overexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
at vessel wall induces infiltration of macrophages and formation of
atherosclerotic lesion: Synergism with hypercholesterolemia.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:115–120. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Spoettl T, Hausmann M, Herlyn M, Gunckel
M, Dirmeier A, Falk W, Herfarth H, Schoelmerich J and Rogler G:
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) inhibits the
intestinal-like differentiation of monocytes. Clin Exp Immunol.
145:190–199. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, Boman K, Tarkowski A
and Hallmans G: Up regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
expression in anti-citrulline antibody and immunoglobulin M
rheumatoid factor positive subjects precedes onset of inflammatory
response and development of overt rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum
Dis. 66:121–123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Izikson L, Klein RS, Charo IF, Weiner HL
and Luster AD: Resistance to experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis in mice lacking the CC chemokine receptor (CCR)2.
J Exp Med. 192:1075–1080. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heumüller S1, Wind S, Barbosa-Sicard E,
Schmidt HH, Busse R, Schröder K and Brandes RP: Apocynin is not an
inhibitor of vascular NADPH oxidases but an antioxidant.
Hypertension. 51:211–217. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Vo VA, Lee JW, Chang JE, Kim JY, Kim NH,
Lee HJ, Kim SS, Chun W and Kwon YS: Avicularin inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by suppressing ERK
phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
20:532–537. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee I-S, Lim J, Gal J, Kang JC, Kim HJ,
Kang BY and Choi HJ: Anti-inflammatory activity of xanthohumol
involves heme oxygenase-1 induction via NRF2-ARE signaling in
microglial BV2 cells. Neurochem Int. 58:153–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Surh YJ, Kundu JK and Na HK: Nrf2 as a
master redox switch in turning on the cellular signaling involved
in the induction of cytoprotective genes by some chemopreventive
phytochemicals. Planta Med. 74:1526–1539. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin W, Wu RT, Wu T, Khor TO, Wang H and
Kong AN: Sulforaphane suppressed LPS-induced inflammation in mouse
peritoneal macrophages through Nrf2 dependent pathway. Biochem
Pharmacol. 76:967–973. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yates MS, Tran QT, Dolan PM, Osburn WO,
Shin S, McCulloch CC, Silkworth JB, Taguchi K, Yamamoto M, Williams
CR, et al: Genetic versus chemoprotective activation of Nrf2
signaling: Overlapping yet distinct gene expression profiles
between Keap1 knockout and triterpenoid-treated mice.
Carcinogenesis. 30:1024–1031. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kawakami T, Takahashi T, Shimizu H,
Nakahira K, Takeuchi M, Katayama H, Yokoyama M, Morita K, Akagi R
and Sassa S: Highly liver-specific heme oxygenase-1 induction by
interleukin-11 prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced
hepatotoxicity. Int J Mol Med. 18:537–546. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee JW, Bae CJ, Choi YJ, Kim SI, Kwon YS,
Lee HJ, Kim SS and Chun W: 3,4,5-trihydroxycinnamic acid inhibits
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation by Nrf2 activation in
vitro and improves survival of mice in LPS-induced endotoxemia
model in vivo. Mol Cell Biochem. 390:143–153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Boonloh K, Lee ES, Kim HM, Kwon MH, Kim
YM, Pannangpetch P, Kongyingyoes B, Kukongviriyapan U,
Thawornchinsombut S, Lee EY, et al: Rice bran protein hydrolysates
attenuate diabetic nephropathy in diabetic animal model. Eur J
Nutr. Dec 21–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim SE, Lee EO, Yang JH, Kang JHL, Suh YH
and Chong YH: 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin
J2 inhibits human immunodeficiency virus-1 tat-induced
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/CCL2 production by blocking the
extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 signaling pathway
independently of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ and
heme oxygenase-1 in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurosci Res.
90:1732–1742. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mouzaoui S, Djerdjouri B, Makhezer N,
Kroviarski Y, El-Benna J and Dang PM: Tumor necrosis
factor-α-induced colitis increases NADPH oxidase 1 expression,
oxidative stress, and neutrophil recruitment in the colon:
Preventive effect of apocynin. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:3124842014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Maldonado PD, Molina-Jijón E,
Villeda-Hernández J, Galván-Arzate S, Santamaría A and
Pedraza-Chaverrí J: NAD(P)H oxidase contributes to neurotoxicity in
an excitotoxic/prooxidant model of Huntington's disease in rats:
Protective role of apocynin. J Neurosci Res. 88:620–629. 2010.
|
|
43
|
Hamilton CA, Brosnan MJ, Al-Benna S, Berg
G and Dominiczak AF: NAD(P)H oxidase inhibition improves
endothelial function in rat and human blood vessels. Hypertension.
40:755–762. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Park YM, Park MY, Suh Y-L and Park JB:
NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitor prevents blood pressure elevation and
cardiovascular hypertrophy in aldosterone-infused rats. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 313:812–817. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Adler S and Huang H: Oxidant stress in
kidneys of spontaneously hypertensive rats involves both oxidase
overexpression and loss of extracellular superoxide dismutase. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 287:F907–F913. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cruz-Álvarez S, Santana-Martínez R,
Avila-Chávez E, Barrera-Oviedo D, Hernández-Pando R,
Pedraza-Chaverri J and Maldonado PD: Apocynin protects against
neurological damage induced by quinolinic acid by an increase in
glutathione synthesis and Nrf2 levels. Neuroscience. 350:65–74.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qiu J, Zhao J, Li J, Liang X, Yang Y,
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Fu H, Korantzopoulos P, Tse G, et al: Apocynin
attenuates left ventricular remodeling in diabetic rabbits.
Oncotarget. 8:38482–38490. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|