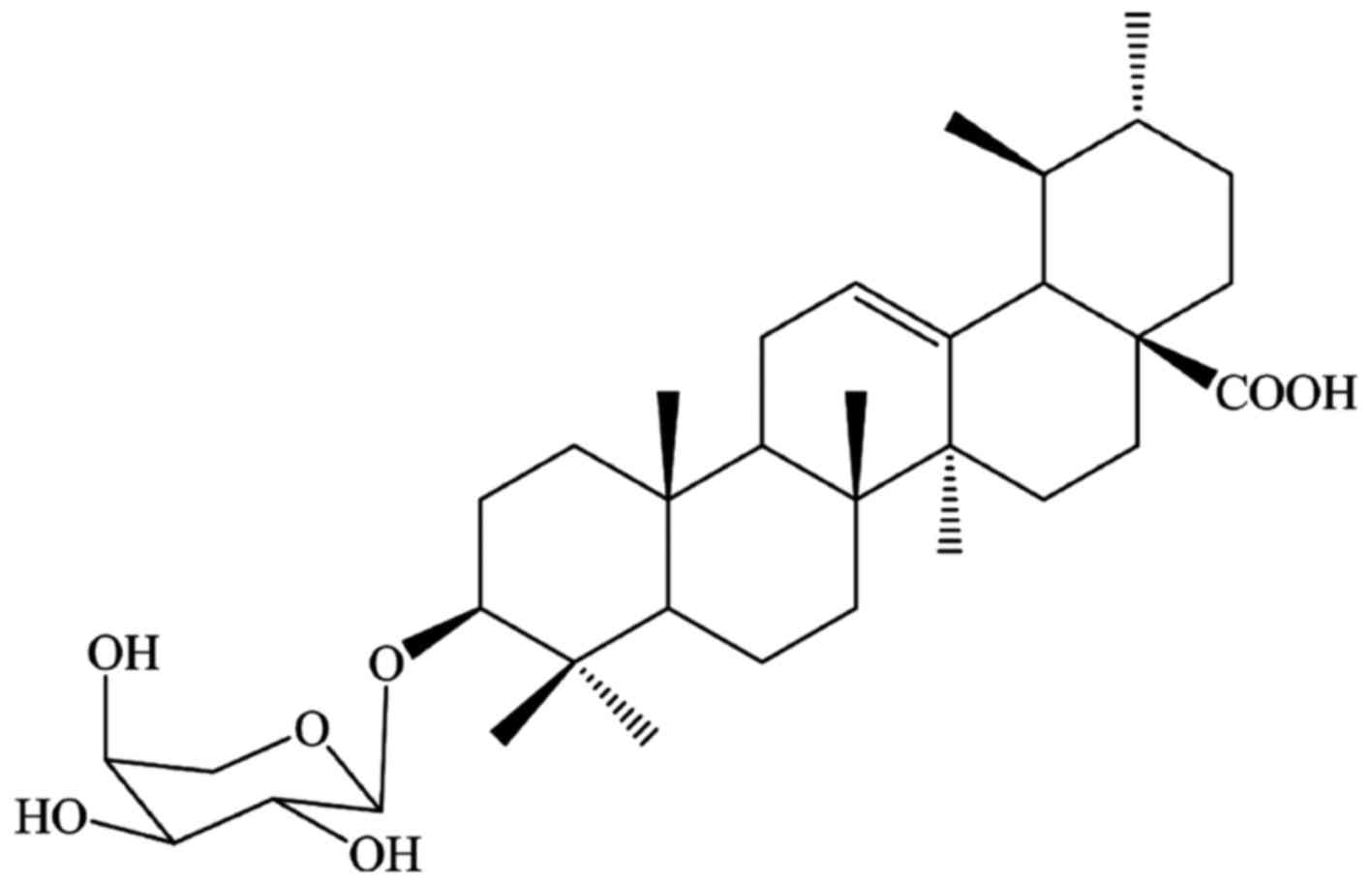
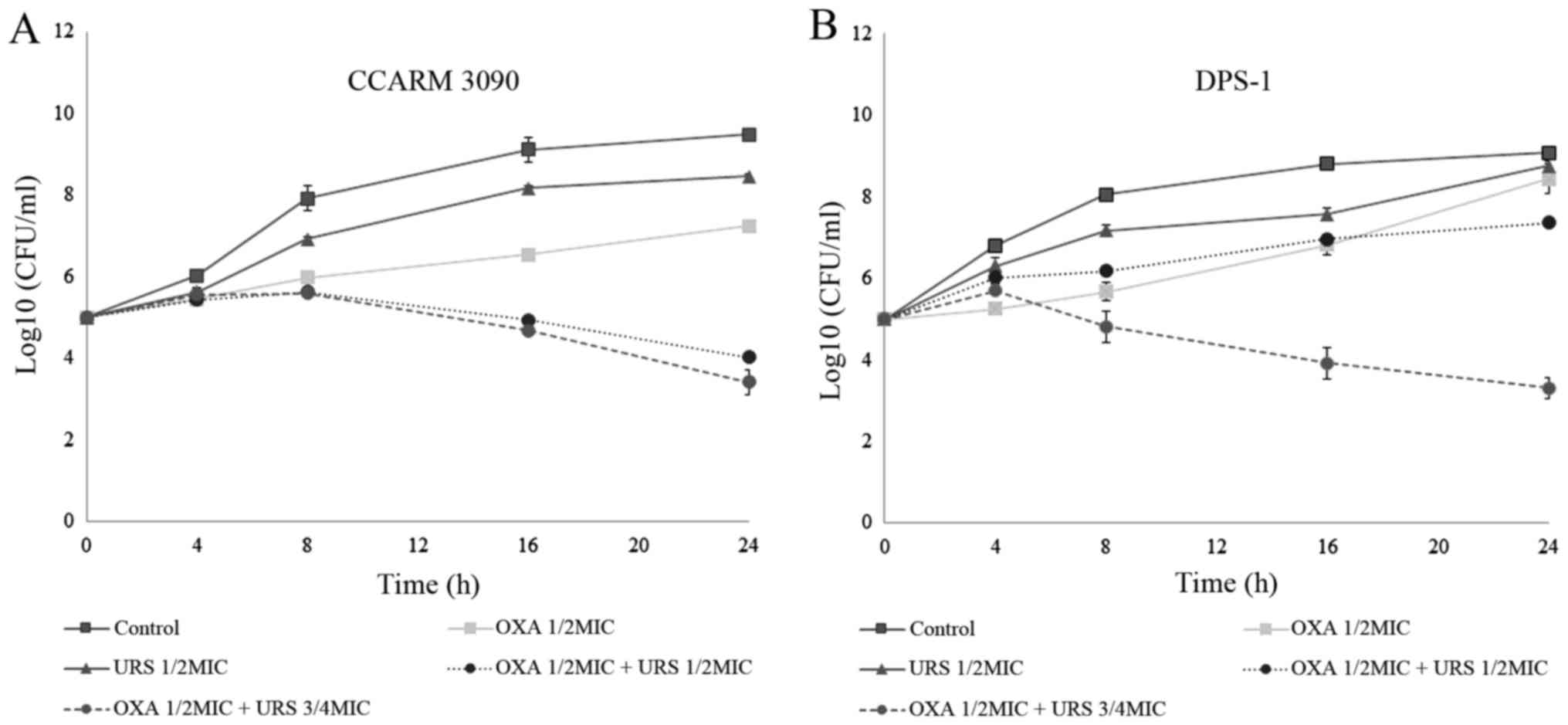
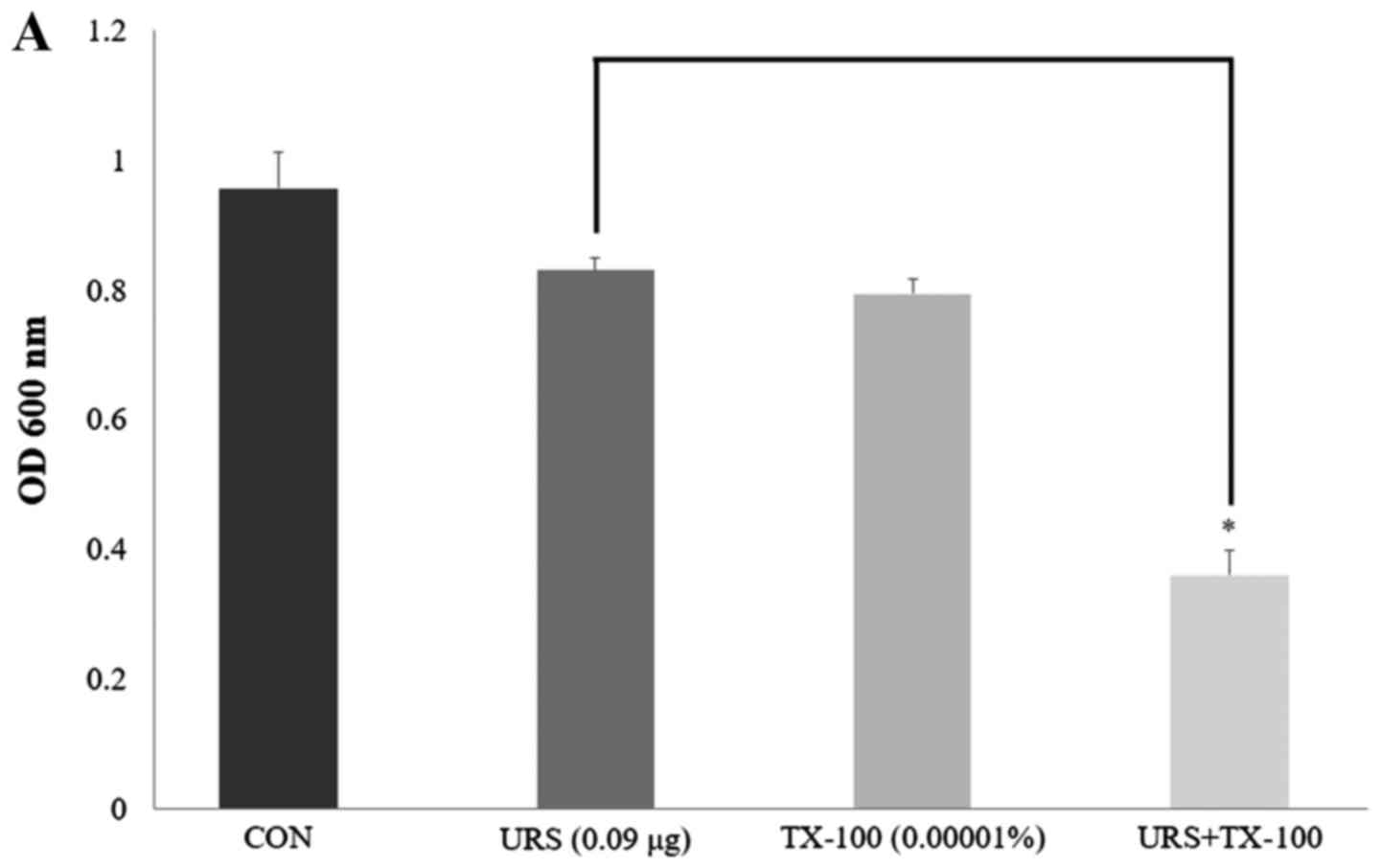
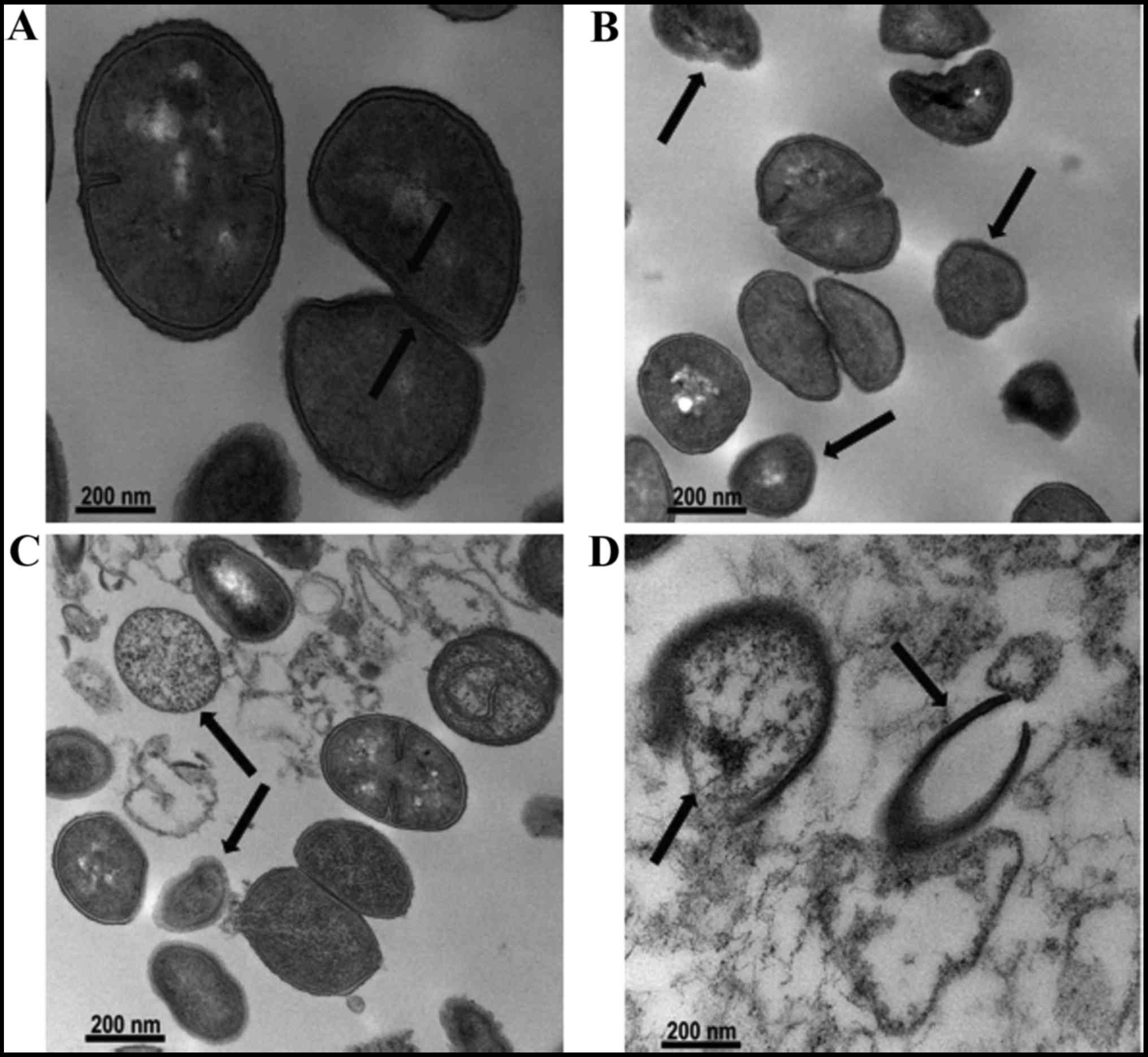
|
1
|
Jiang JH and Peleg AY:
Daptomycin-nonsusceptible Staphylococcus aureus: The role of
combination therapy with daptomycin and gentamicin. Genes (Basel).
6:1256–1267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mahdiyoun SM, Kazemian H, Ahanjan M, Houri
H and Goudarzi M: Frequency of aminoglycoside-resistance genes in
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates from
hospitalized patients. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 9:e350522016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Hu Y, Liu A, Vaudrey J, Vaiciunaite B,
Moigboi C, McTavish SM, Kearns A and Coates A: Combinations of
β-lactam or amino-glycoside antibiotics with plectasin are
synergistic against methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One. 10:e01176642015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ekambaram SP, Perumal SS, Balakrishnan A,
Marappan N, Gajendran SS and Viswanathan V: Antibacterial synergy
between rosmarinic acid and antibiotics against
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Intercult
Ethnopharmacol. 5:358–363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Poulsen MØ, Jacobsen K, Thorsing M,
Kristensen NR, Clasen J, Lillebæk EM, Skov MN, Kallipolitis BH,
Kolmos HJ and Klitgaard JK: Thioridazine potentiates the effect of
a beta-lactam antibiotic against Staphylococcus aureus
independently of mecA expression. Res Microbiol. 164:181–188. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
McConeghy KW, Bleasdale SC and Rodvold KA:
The empirical combination of vancomycin and a β-lactam for
Staphylococcal bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis. 57:1760–1765. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee YS, Lee DY, Kim YB, Lee SW, Cha SW,
Park HW, Kim GS, Kwon DY, Lee MH and Han SH: The mechanism
underlying the antibacterial activity of Shikonin against
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2015:5205782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lowy FD: Antimicrobial resistance: The
example of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest. 111:1265–1273.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tenover FC: Mechanisms of antimicrobial
resistance in bacteria. Am J Med. 119(Suppl 1): S3–S70. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ike B, Ugwu MC, Ikegbunam MN, Nwobodo D,
Ejikeugwu C, Gugu T and Esimone CO: Prevalence, antibiogram and
molecular characterization of comunity-acquired
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in AWKA, Anambra
Nigeria. Open Microbiol J. 10:211–221. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Santiago C, Pang EL, Lim KH, Loh HS and
Ting KN: Reversal of ampicillin resistance in MRSA via inhibition
of penicillin-binding protein 2a by Acalypha wilkesiana. BioMed Res
Int. 2014:9653482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park SY, Yook CS, Nohara T, Mizutani T and
Tanaka T: Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of genetic
relationships among Acanthopanax species. Arch Pharm Res.
27:1270–1274. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Park SY: Studies on RAPD analysis and
triterpenoidal constituents of Acanthopanax species. Kumamoto
University Press. 3:1–3. 2002.
|
|
14
|
Zhang XD, Liu XQ, Kim YH and Whang WK:
Chemical constituents and their acetyl cholinesterase inhibitory
and antioxidant activities from leaves of Acanthopanax henryi:
Potential complementary source against Alzheimer's disease. Arch
Pharm Res. 37:606–616. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim JH, Liu XQ, Dai L, Yook CS and Lee KT:
Cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory effects of root bark extracts of
Acanthopanax henryi. Chin J Nat Med. 12:121–125. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grace G, Paulo SE and Seligmann O: A new
saponin from mate, Ilex paraguariensis. J Nat Prod. 52:1367–1370.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li Z: Simultaneous determination of
fifteen triterpenoid saponins in different medicinal parts of
Acanthopanax henryi by HPLC CAD ESI MS. Study on chemical
constituents of Acanthopanax henryi (Oliv.) Harms. Hunan University
of Traditional Chinese Medicine; pp. 45–66. 2015
|
|
18
|
Joung DK, Kang OH, Seo YS, Zhou T, Lee YS,
Han SH, Mun SH, Kong R, Song HJ, Shin DW, et al: Luteolin
potentiates the effects of aminoglycoside and β-lactam antibiotics
against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. Exp
Ther Med. 11:2597–2601. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Joung DK, Mun SH, Choi SH, Kang OH, Kim
SB, Lee YS, Zhou T, Kong R, Choi JG, Shin DW, et al: Antibacterial
activity of oxyresveratrol against methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus and its mechanism. Exp Ther Med.
12:1579–1584. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi YJ, Chen J and Xu M: A new method for
antimicrobial susceptibility testing of in vitro-cultured bacteria
by means of resonance light scattering technique. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 18:118–123. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Timurkaynak F, Can F, Azap ÖK, Demirbilek
M, Arslan H and Karaman SÖ: In vitro activities of non-traditional
antimicrobials alone or in combination against multidrug-resistant
strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii
isolated from intensive care units. Int J Antimicrob Agents.
27:224–228. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mun SH, Kang OH, Joung DK, Kim SB, Seo YS,
Choi JG, Lee YS, Cha SW, Ahn YS, Han SH, et al: Combination therapy
of Sophoraflavanone B against MRSA: In vitro synergy testing. Evid
Based Complement Altern Med. 2013:8237942013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Choi JG, Kang OH, Brice OO, Lee YS, Chae
HS, Oh YC, Sohn DH, Park H, Choi HG, Kim SG, et al: Antibacterial
activity of Ecklonia cava against methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella spp. Foodborne Pathog Dis.
7:435–441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Farooqui A, Khan A, Borghetto I, Kazmi SU,
Rubino S and Paglietti B: Synergistic antimicrobial activity of
Camellia sinensis and Juglans regia against multidrug-resistant
bacteria. PLoS One. 10:e01184312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cordwell SJ, Larsen MR, Cole RT and Walsh
BJ: Comparative proteomics of Staphylococcus aureus and the
response of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive strains
to Triton X-100. Microbiology. 148:2765–2781. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shibata H, Saito H, Yomota C, Kawanishi T
and Okuda H: Alterations in the detergent-induced membrane
permeability and solubilization of saturated
phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol liposomes: Effects of poly(ethylene
glycol)-conjugated lipid. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 60:1105–1111.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Linnett PE and Beechey RB: Inhibitors of
the ATP synthethase system. Methods Enzymol. 55:472–518. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mun SH, Kim SB, Kong R, Choi JG, Kim YC,
Shin DW, Kang OH and Kwon DY: Curcumin reverse methicillin
resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules. 19:18283–18295.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hartmann M, Berditsch M, Hawecker J,
Ardakani MF, Gerthsen D and Ulrich AS: Damage of the bacterial cell
envelope by antimicrobial peptides gramicidin S and PGLa as
revealed by transmission and scanning electron microscopy.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 54:3132–3142. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sambrook J and Russell DW: Molecular
Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press; New York, NY: 1989
|
|
31
|
Eom SH, Kang SK, Lee DS, Myeong JI, Lee J,
Kim HW, Kim KH, Je JY, Jung WK and Kim YM: Synergistic
antibacterial effect and antibacterial action mode of
chitosan-ferulic acid conjugate against methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 26:784–789. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Klitgaard JK, Skov MN, Kallipolitis BH and
Kolmos HJ: Reversal of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus
aureus by thioridazine. J Antimicrob Chemother. 62:1215–1221. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eom SH, Lee DS, Jung YJ, Park JH, Choi JI,
Yim MJ, Jeon JM, Kim HW, Son KT, Je JY, et al: The mechanism of
antibacterial activity of phlorofucofuroeckol-A against
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 98:9795–9804. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Irvin RT, MacAlister TJ and Costerton JW:
Tris(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane buffer modification of Escherichia
coli outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 145:1397–1403.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Joung DK, Joung H, Yang DW, Kwon DY, Choi
JG, Woo S, Shin DY, Kweon OH, Kweon KT and Shin DW: Synergistic
effect of rhein in combination with ampicillin or oxacillin against
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Exp Ther Med.
3:608–612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ba X, Harrison EM, Lovering AL, Gleadall
N, Zadoks R, Parkhill J, Peacock SJ, Holden MT, Paterson GK and
Holmes MA: Old drugs to treat resistant bugs: Methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus isolates with mecC are susceptible to a
combination of penicillin and clavulanic acid. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 59:7396–7404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Choi JG, Choi JY, Mun SH, Kang OH, Bharaj
P, Shin DW, Chong MS and Kwon DY: Antimicrobial activity and
synergism of Sami-Hyanglyun-Hwan with ciprofloxacin against
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Asian Pac J Trop Med.
8:538–542. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mot YY, Othman I and Sharifah SH:
Synergistic antibacterial effect of co-administering
adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and Ophiophagus hannah
L-amino acid oxidase in a mouse model of methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus-infected wounds. Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:52017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rolfe MD, Rice CJ, Lucchini S, Pin C,
Thompson A, Cameron AD, Alston M, Stringer MF, Betts RP, Baranyi J,
et al: Lag phase is a distinct growth phase that prepares bacteria
for exponential growth and involves transient metal accumulation. J
Bacteriol. 194:686–701. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Alharbi NS, Khaled JM, Alzaharni KE,
Mothana RA, Alsaid MS, Alhoshan M, Dass LA, Kadaikunnan S and
Alobaidi AS: Effects of Piper cubeba L. essential oil on
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An AFM and TEM study.
J Mol Recognit. 30:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Joung DK, Mun SH, Lee KS, Kang OH, Choi
JG, Kim SB, Gong R, Chong MS, Kim YC, Lee DS, et al: The
antibacterial assay of tectorigenin with detergents or ATPase
inhibitors against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:7165092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Carvalho JF, Azevedo ÍM, Rocha KB,
Medeiros AC and Carriço AD: Oxacillin magnetically targeted for the
treatment of methicillin-resistant S. aureus infection in rats.
Acta Cir Bras. 32:46–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hong SB, Rhee MH, Yun BS, Lim YH, Song HG
and Shin KS: Synergistic anti-bacterial effects of Phellinus baumii
ethyl acetate extracts and β-lactam antimicrobial agents against
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Lab Med.
36:111–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Dong J, Qiu J, Wang J, Li H, Dai X, Zhang
Y, Wang X, Tan W, Niu X, Deng X, et al: Apigenin alleviates the
symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia by inhibiting the
production of alpha-hemolysin. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 338:124–131.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Mun SH, Kong R, Seo YS, Zhou T, Kang OH,
Shin DW and Kwon DY: Subinhibitory concentrations of punicalagin
reduces expression of virulence-related exoproteins by
Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 363:1–6. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|