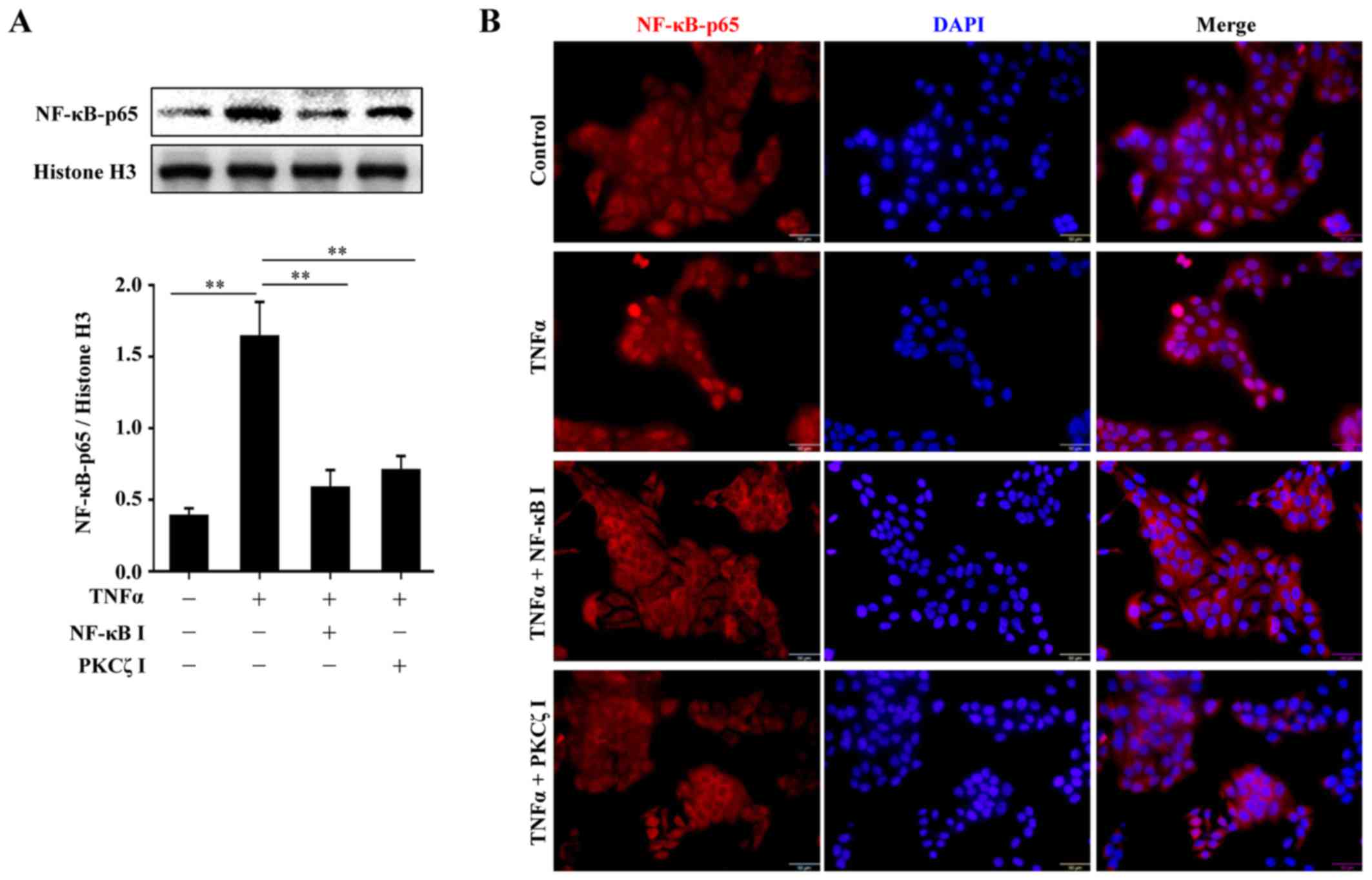
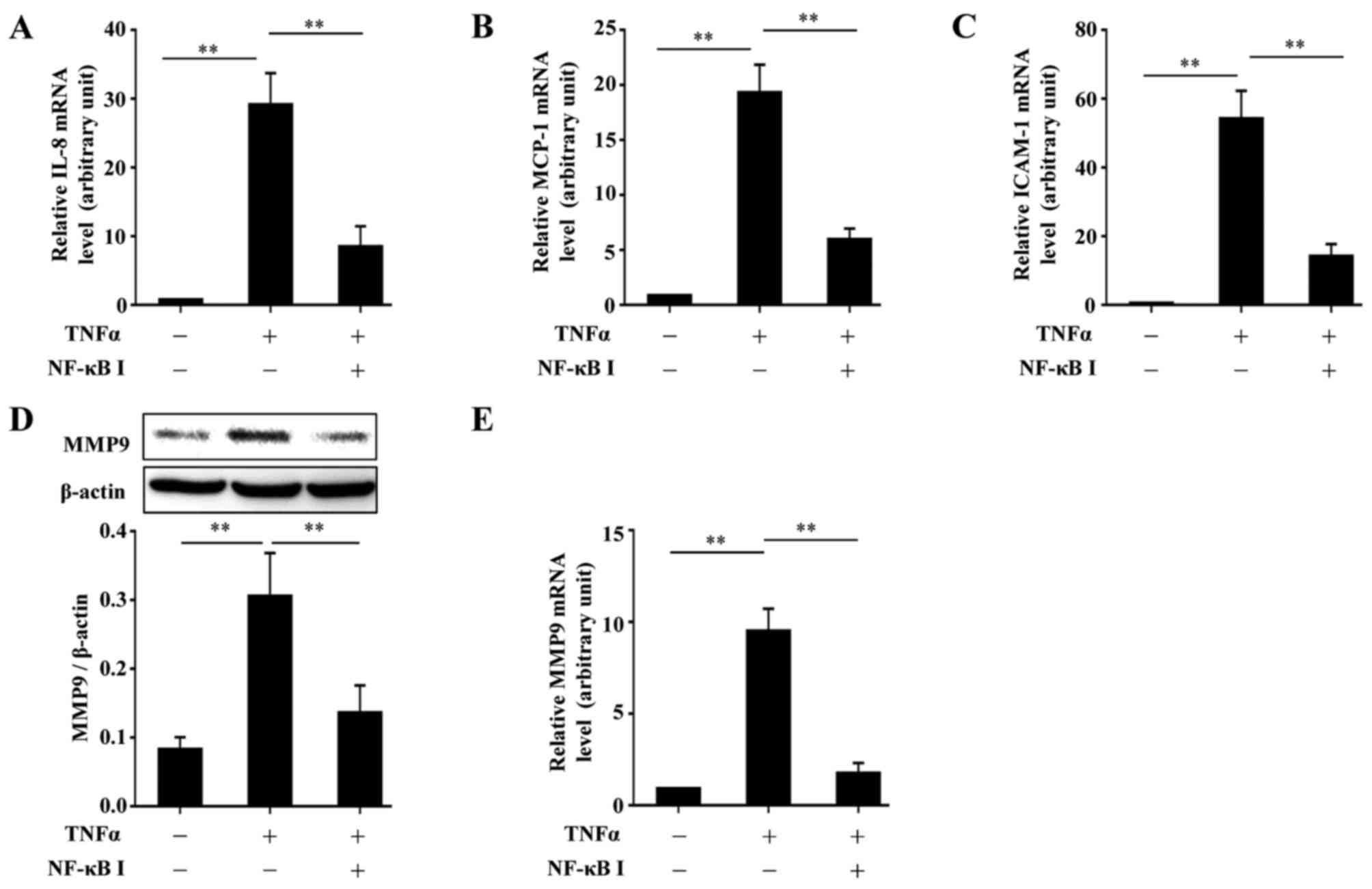
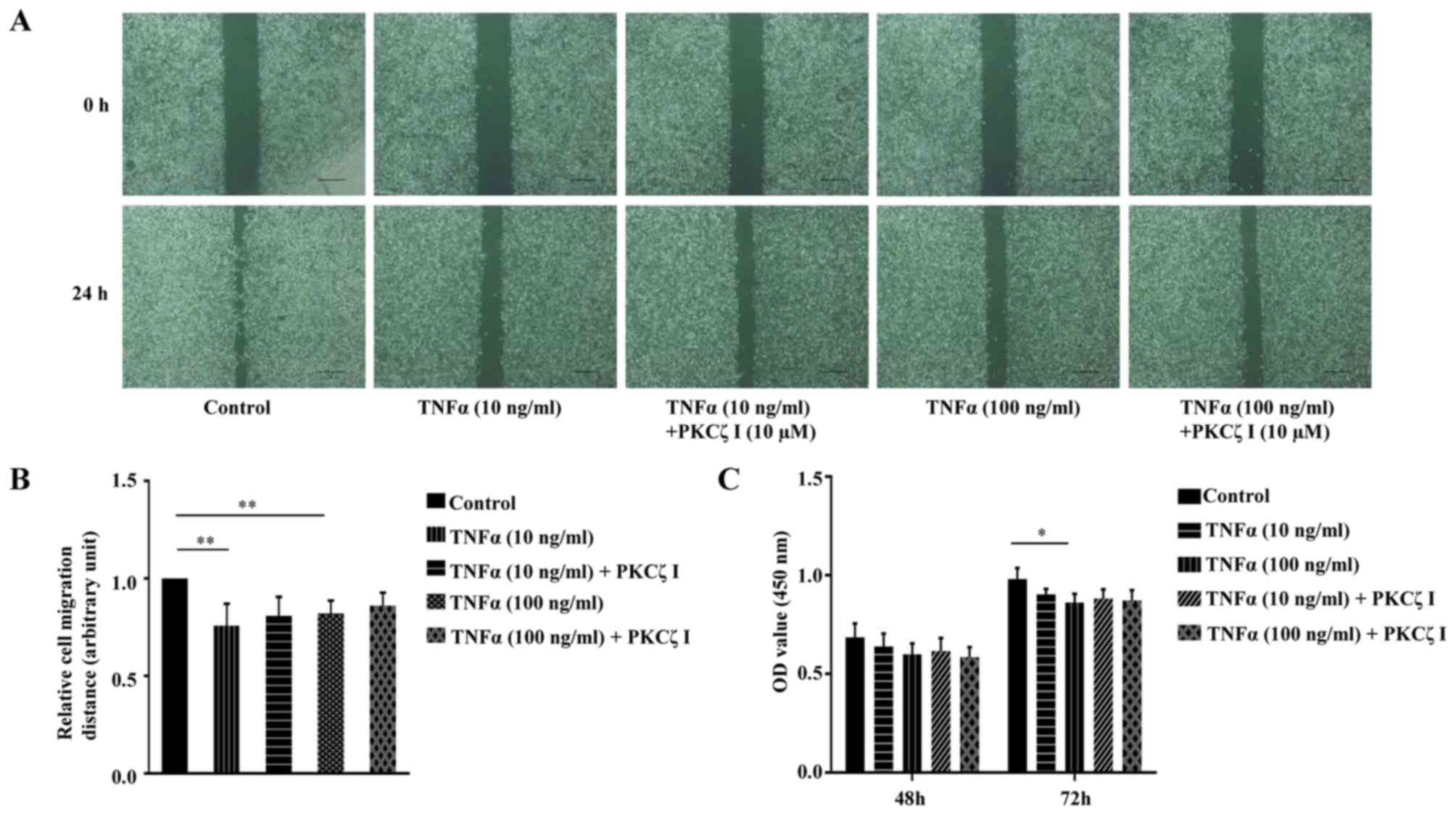
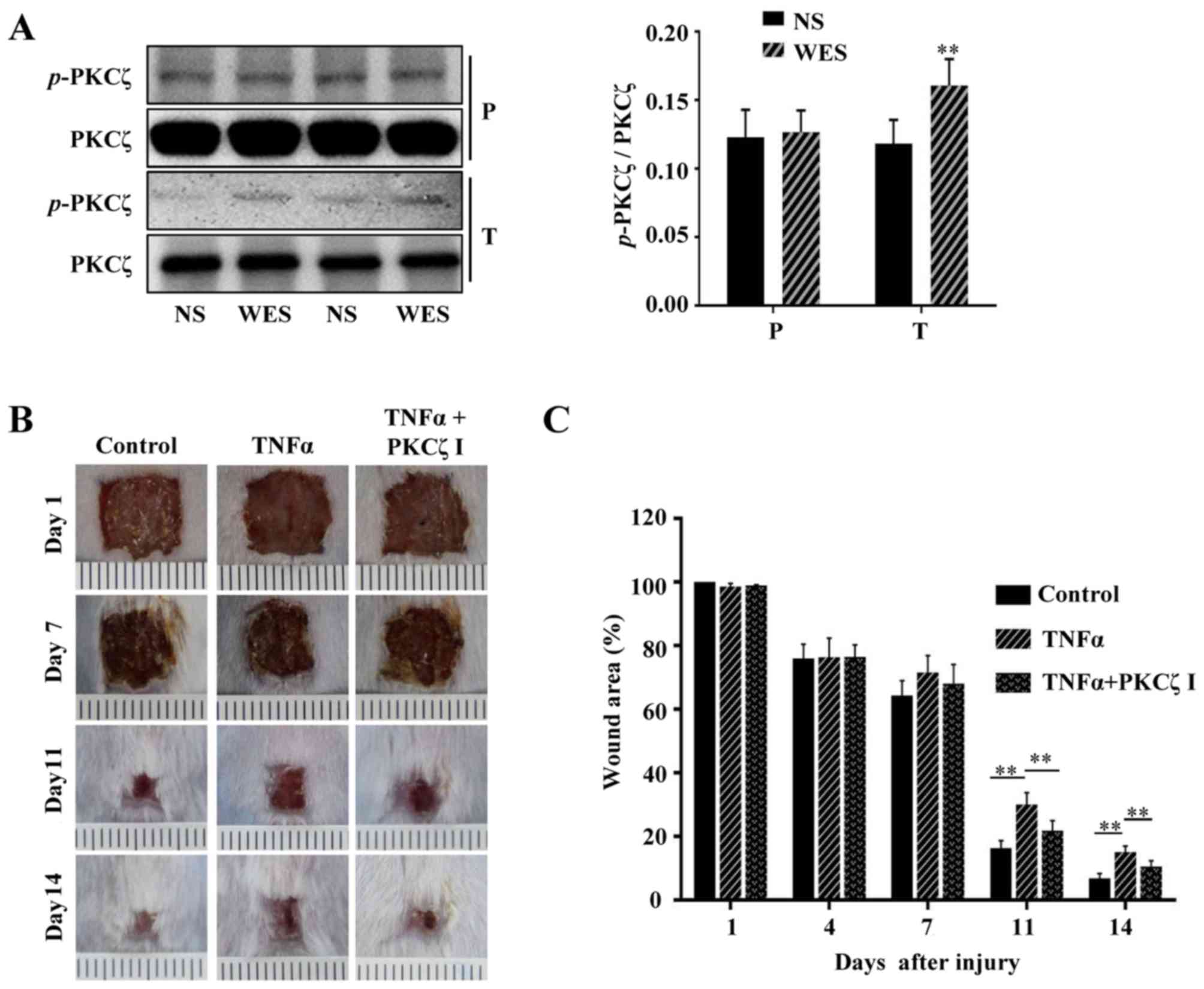
|
1
|
Martin P and Nunan R: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing.
Br J Dermatol. 173:370–378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Streit M, Beleznay Z and Braathen LR:
Topical application of the tumour necrosis factor-alpha antibody
infliximab improves healing of chronic wounds. Int Wound J.
3:171–179. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu F, Zhang C and Graves DT: Abnormal cell
responses and role of TNF-α in impaired diabetic wound healing.
BioMed Res Int. 2013:7548022013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Barker JN, Mitra RS, Griffiths CE, Dixit
VM and Nickoloff BJ: Keratinocytes as initiators of inflammation.
Lancet. 337:211–214. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wetzler C, Kämpfer H, Stallmeyer B,
Pfeilschifter J and Frank S: Large and sustained induction of
chemokines during impaired wound healing in the genetically
diabetic mouse: Prolonged persistence of neutrophils and
macrophages during the late phase of repair. J Invest Dermatol.
115:245–253. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lan CC, Wu CS, Huang SM, Wu IH and Chen
GS: High-glucose environment enhanced oxidative stress and
increased interleukin-8 secretion from keratinocytes: New insights
into impaired diabetic wound healing. Diabetes. 62:2530–2538. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trengove NJ, Stacey MC, MacAuley S,
Bennett N, Gibson J, Burslem F, Murphy G and Schultz G: Analysis of
the acute and chronic wound environments: The role of proteases and
their inhibitors. Wound Repair Regen. 7:442–452. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rayment EA, Upton Z and Shooter GK:
Increased matrix metal-loproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity observed in
chronic wound fluid is related to the clinical severity of the
ulcer. Br J Dermatol. 158:951–961. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lan CC, Liu IH, Fang AH, Wen CH and Wu CS:
Hyperglycaemic conditions decrease cultured keratinocyte mobility:
Implications for impaired wound healing in patients with diabetes.
Br J Dermatol. 159:1103–1115. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang C, Ponugoti B, Tian C, Xu F,
Tarapore R, Batres A, Alsadun S, Lim J, Dong G and Graves DT: FOXO1
differentially regulates both normal and diabetic wound healing. J
Cell Biol. 209:289–303. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Galkowska H, Olszewsk WL, Wojewodzka U,
Mijal J and Filipiuk E: Expression of apoptosis- and cell
cycle-related proteins in epidermis of venous leg and diabetic foot
ulcers. Surgery. 134:213–220. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Spravchikov N, Sizyakov G, Gartsbein M,
Accili D, Tennenbaum T and Wertheimer E: Glucose effects on skin
keratinocytes: Implications for diabetes skin complications.
Diabetes. 50:1627–1635. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosse C, Linch M, Kermorgant S, Cameron
AJ, Boeckeler K and Parker PJ: PKC and the control of localized
signal dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:103–112. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ohno S: Intercellular junctions and
cellular polarity: The PAR-aPKC complex, a conserved core cassette
playing fundamental roles in cell polarity. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
13:641–648. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yin J, Liu Z, Li H, Sun J, Chang X, Liu J,
He S and Li B: Association of PKCζ expression with
clinicopathological characteristics of breast cancer. PLoS One.
9:e908112014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Butler AM, Scotti Buzhardt ML, Li S, Smith
KE, Fields AP and Murray NR: Protein kinase C zeta regulates human
pancreatic cancer cell transformed growth and invasion through a
STAT3-dependent mechanism. PLoS One. 8:e720612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun R, Gao P, Chen L, Ma D, Wang J,
Oppenheim JJ and Zhang N: Protein kinase C zeta is required for
epidermal growth factor-induced chemotaxis of human breast cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 65:1433–1441. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang S, Ouyang N, Lin L, Chen L, Wu W, Su
F, Yao Y and Yao H: HGF-induced PKCζ activation increases
functional CXCR4 expression in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
7:e291242012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen R, Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Zhang X,
Zhang F, Shieh CH, Yang D and Zhang N: Quantitative study of the
interactome of PKCζ involved in the EGF-induced tumor cell
chemotaxis. J Proteome Res. 12:1478–1486. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao H, Hwang JW, Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT,
Leitges M, Kishore N, Li X and Rahman I: Protein kinase C zeta
mediates cigarette smoke/aldehyde- and lipopolysaccharide-induced
lung inflammation and histone modifications. J Biol Chem.
285:5405–5416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Leverence JT, Medhora M, Konduri GG and
Sampath V: Lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine expression in
alveolar epithelial cells: Role of PKCζ-mediated p47 phox
phosphorylation. Chem Biol Interact. 189:72–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang X, Chen LY, Doerner AM, Pan WW,
Smith L, Huang S, Papadimos TJ and Pan ZK: An atypical protein
kinase C (PKC zeta) plays a critical role in
lipopolysaccharide-activated NF-kappa B in human peripheral blood
monocytes and macrophages. J Immunol. 182:5810–5815. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aveleira CA, Lin CM, Abcouwer SF, Ambrósio
AF and Antonetti DA: TNF-α signals through PKCζ/NF-κB to alter the
tight junction complex and increase retinal endothelial cell
permeability. Diabetes. 59:2872–2882. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goren I, Müller E, Schiefelbein D,
Christen U, Pfeilschifter J, Mühl H and Frank S: Systemic
anti-TNFalpha treatment restores diabetes-impaired skin repair in
ob/ob mice by inactivation of macrophages. J Invest Dermatol.
127:2259–2267. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakayama T, Fujisawa R, Yamada H, Horikawa
T, Kawasaki H, Hieshima K, Izawa D, Fujiie S, Tezuka T and Yoshie
O: Inducible expression of a CC chemokine liver- and
activation-regulated chemokine (LARC)/macrophage inflammatory
protein (MIP)-3 alpha/CCL20 by epidermal keratinocytes and its role
in atopic dermatitis. Int Immunol. 13:95–103. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sanz MJ, Hartnell A, Chisholm P, Williams
C, Davies D, Weg VB, Feldmann M, Bolanowski MA, Lobb RR and
Nourshargh S: Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced eosinophil
accumulation in rat skin is dependent on alpha4 integrin/vascular
cell adhesion molecule-1 adhesion pathways. Blood. 90:4144–4152.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tremblay C, Paradis M and Doré M:
Expression of E- and P-selectin in tumor necrosis factor-induced
dermatitis in dogs. Vet Pathol. 38:261–268. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Speiser W, Kapiotis S, Kopp CW, Simonitsch
I, Jilma B, Jansen B, Exner M and Chott A: Effect of intradermal
tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced inflammation on coagulation
factors in dermal vessel endothelium. An in vivo study of human
skin biopsies. Thromb Haemost. 85:362–367. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Movat HZ, Burrowes CE, Cybulsky MI and
Dinarello CA: Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction
induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic
action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and
microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 129:463–476. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sharpe RJ, Margolis RJ, Askari M, Amento
EP and Granstein RD: Induction of dermal and subcutaneous
inflammation by recombinant cachectin/tumor necrosis factor (TNF
alpha) in the mouse. J Invest Dermatol. 91:353–357. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT and Wooten MW: Of
the atypical PKCs, Par-4 and p62: Recent understandings of the
biology and pathology of a PB1-dominated complex. Cell Death
Differ. 16:1426–1437. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Diaz-Meco MT and Moscat J: The atypical
PKCs in inflammation: NF-κB and beyond. Immunol Rev. 246:154–167.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maldonado RF, Sá-Correia I and Valvano MA:
Lipopolysaccharide modification in Gram-negative bacteria during
chronic infection. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 40:480–493. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Harada Y, Edamatsu H and Kataoka T: PLCε
cooperates with the NF-κB pathway to augment TNFα-stimulated
CCL2/MCP1 expression in human keratinocyte. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 414:106–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raingeaud J and Pierre J: Interleukin-4
downregulates TNFalpha-induced IL-8 production in keratinocytes.
FEBS Lett. 579:3953–3959. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Youn GS, Kwon DJ, Ju SM, Choi SY and Park
J: Curcumin ameliorates TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 expression and
subsequent THP-1 adhesiveness via the induction of heme oxygenase-1
in the HaCaT cells. BMB Rep. 46:410–415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nigro P, Abe J, Woo CH, Satoh K, McClain
C, O' Dell MR, Lee H, Lim JH, Li JD, Heo KS, et al: PKCzeta
decreases eNOS protein stability via inhibitory phosphorylation of
ERK5. Blood. 116:1971–1979. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liang H, Baudouin C, Behar-Cohen F,
Crisanti P and Omri B: Protein kinase C-zeta mediates retinal
degeneration in response to TNF. J Neuroimmunol. 183:104–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao Y, Fishelevich R, Petrali JP, Zheng
L, Anatolievna MA, Deng A, Eckert RL and Gaspari AA: Activation of
keratinocyte protein kinase C zeta in psoriasis plaques. J Invest
Dermatol. 128:2190–2197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vaalamo M, Weckroth M, Puolakkainen P,
Kere J, Saarinen P, Lauharanta J and Saarialho-Kere UK: Patterns of
matrix metal-loproteinase and TIMP-1 expression in chronic and
normally healing human cutaneous wounds. Br J Dermatol. 135:52–59.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wong VW, Garg RK, Sorkin M, Rustad KC,
Akaishi S, Levi K, Nelson ER, Tran M, Rennert R, Liu W, et al: Loss
of keratinocyte focal adhesion kinase stimulates dermal proteolysis
through upregulation of MMP9 in wound healing. Ann Surg.
260:1138–1146. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Reiss MJ, Han YP, Garcia E, Goldberg M, Yu
H and Garner WL: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 delays wound healing in
a murine wound model. Surgery. 147:295–302. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Van den Steen PE, Proost P, Wuyts A, Van
Damme J and Opdenakker G: Neutrophil gelatinase B potentiates
interleukin-8 tenfold by aminoterminal processing, whereas it
degrades CTAP-III, PF-4, and GRO-alpha and leaves RANTES and MCP-2
intact. Blood. 96:2673–2681. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Opdenakker G, Van den Steen PE, Dubois B,
Nelissen I, Van Coillie E, Masure S, Proost P and Van Damme J:
Gelatinase B functions as regulator and effector in leukocyte
biology. J Leukoc Biol. 69:851–859. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hussain S, Assender JW, Bond M, Wong LF,
Murphy D and Newby AC: Activation of protein kinase Czeta is
essential for cytokine-induced metalloproteinase-1, -3, and -9
secretion from rabbit smooth muscle cells and inhibits
proliferation. J Biol Chem. 277:27345–27352. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Basso FG, Pansani TN, Turrioni AP, Soares
DG, de Souza Costa CA and Hebling J: Tumor necrosis factor-α and
interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 impair in vitro migration and
induce apoptosis of gingival fibroblasts and epithelial cells,
delaying wound healing. J Periodontol. 87:990–996. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lei M, Bai X, Yang T, Lai X, Qiu W, Yang L
and Lian X: Gsdma3 is a new factor needed for TNF-α-mediated
apoptosis signal pathway in mouse skin keratinocytes. Histochem
Cell Biol. 138:385–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sun J, Han J, Zhao Y, Zhu Q and Hu J:
Curcumin induces apoptosis in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-treated
HaCaT cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 13:170–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|