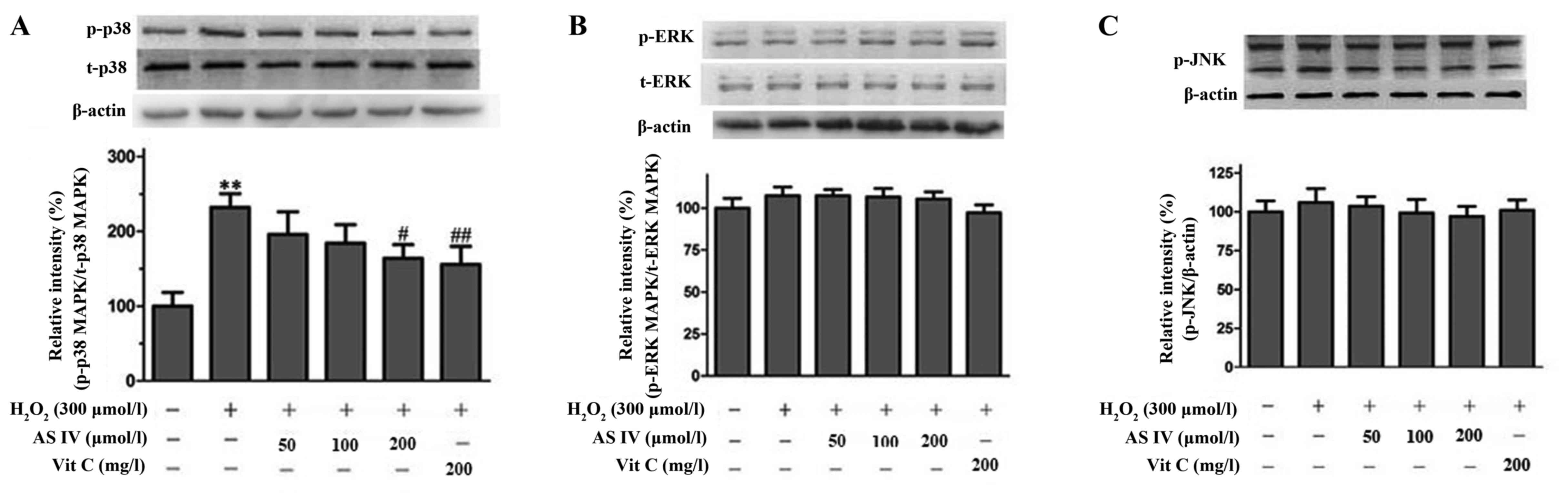
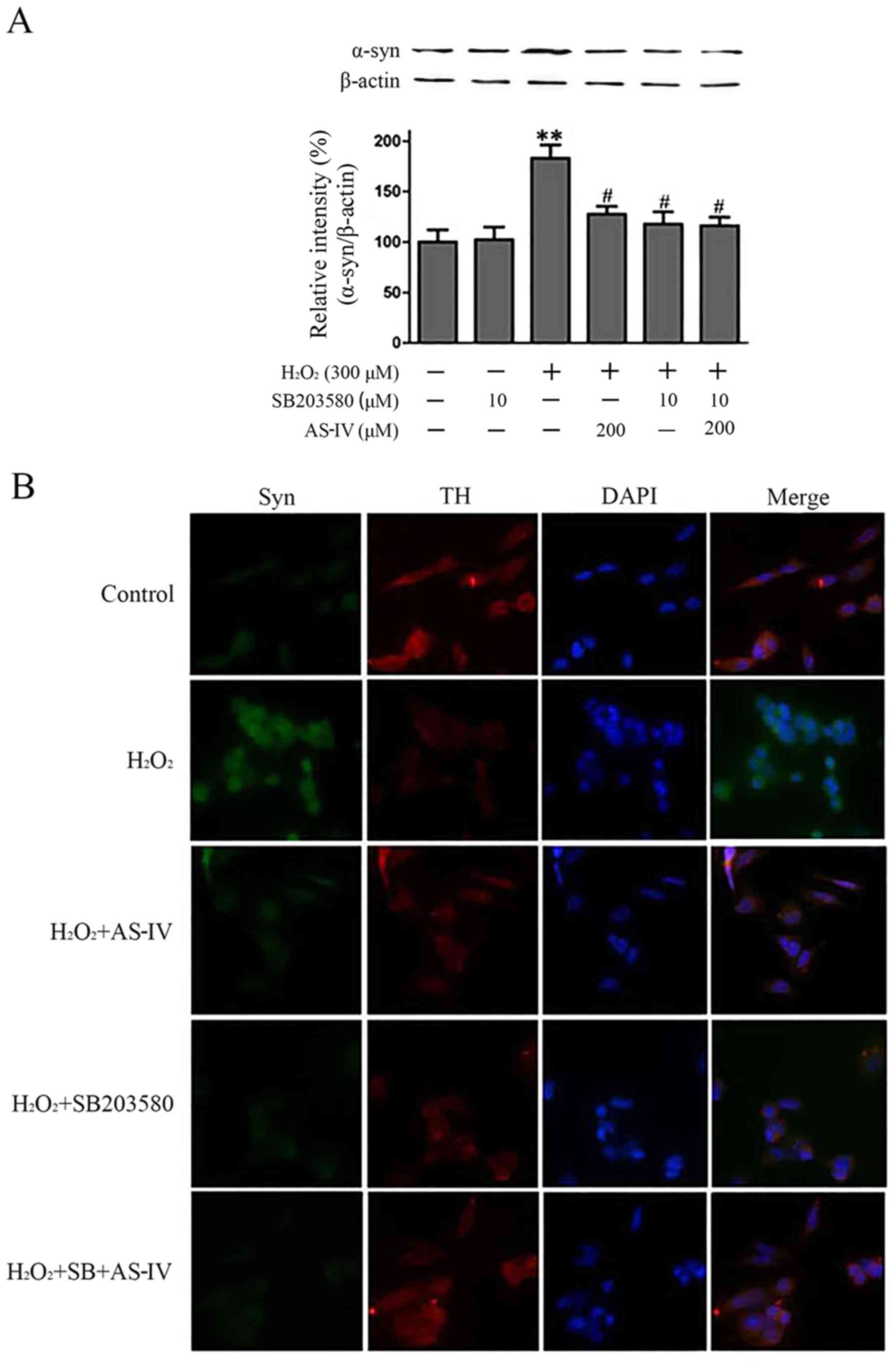
|
1
|
Lesage S and Brice A: Parkinson's disease:
from monogenic forms to genetic susceptibility factors. Hum Mol
Genet. 18(R1): R48–R59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Braak H, Rüb U, Gai WP and Del Tredici K:
Idiopathic Parkinson's disease: possible routes by which vulnerable
neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown
pathogen. J Neural Transm Vienna. 110:517–536. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schapira AH: Mitochondrial dysfunction in
neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem Res. 33:2502–2509. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jenner P and Olanow CW: Oxidative stress
and the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 47(Suppl
3): S161–S170. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Owen AD, Schapira AH, Jenner P and Marsden
CD: Oxidative stress and Parkinson's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
786:217–223. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orth M and Schapira AH: Mitochondrial
involvement in Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Int. 40:533–541.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brown JM and Yamamoto BK: Effects of
amphetamines on mitochondrial function: role of free radicals and
oxidative stress. Pharmacol Ther. 99:45–53. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gandhi S and Wood NW: Molecular
pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 14:2749–2755.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Satoh T, Sakai N, Enokido Y, Uchiyama Y
and Hatanaka H: Free radical-independent protection by nerve growth
factor and Bcl-2 of PC12 cells from hydrogen peroxide-triggered
apoptosis. J Biochem. 120:540–546. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wada T and Penninger JM: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene. 23:2838–2849.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nakano H, Nakajima A, Sakon-Komazawa S,
Piao JH, Xue X and Okumura K: Reactive oxygen species mediate
crosstalk between NF-kappaB and JNK. Cell Death Differ. 13:730–737.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhu X, Lee HG, Raina AK, Perry G and Smith
MA: The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in
Alzheimer's disease. Neurosignals. 11:270–281. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu G, Zhang C, Yin J, Li X, Cheng F, Li
Y, Yang H, Uéda K, Chan P and Yu S: α-Synuclein is differentially
expressed in mitochondria from different rat brain regions and
dose-dependently down-regulates complex I activity. Neurosci Lett.
454:187–192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rao F, Zhang L, Wessel J, Zhang K, Wen G,
Kennedy BP, Rana BK, Das M, Rodriguez-Flores JL, Smith DW, et al:
Tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in catecholamine
biosynthesis: discovery of common human genetic variants governing
transcription, autonomic activity, and blood pressure in vivo.
Circulation. 116:993–1006. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Javoy-Agid F, Hirsch EC, Dumas S,
Duyckaerts C, Mallet J and Agid Y: Decreased tyrosine hydroxylase
messenger RNA in the surviving dopamine neurons of the substantia
nigra in Parkinson's disease: an in situ hybridization study.
Neuroscience. 38:245–253. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Houghton PJ and Howes MJ: Natural products
and derivatives affecting neurotransmission relevant to Alzheimer's
and Parkinson's disease. Neurosignals. 14:6–22. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen LW, Wang YQ, Wei LC, Shi M and Chan
YS: Chinese herbs and herbal extracts for neuroprotection of
dopaminergic neurons and potential therapeutic treatment of
Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 6:273–281.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ren S, Zhang H, Mu Y, Sun M and Liu P:
Pharmacological effects of Astragaloside IV: a literature review. J
Tradit Chin Med. 33:413–416. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang WD, Zhang C, Liu RH, Li HL, Zhang
JT, Mao C, Moran S and Chen CL: Preclinical pharmacokinetics and
tissue distribution of a natural cardioprotective agent
astragaloside IV in rats and dogs. Life Sci. 79:808–815. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li ZP and Cao Q: Effects of astragaloside
IV on myocardial calcium transport and cardiac function in ischemic
rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 23:898–904. 2002.
|
|
23
|
Zhang WJ, Hufnagl P, Binder BR and Wojta
J: Antiinflammatory activity of astragaloside IV is mediated by
inhibition of NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule
expression. Thromb Haemost. 90:904–914. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luo Y, Qin Z, Hong Z, Zhang X, Ding D, Fu
JH, Zhang WD and Chen J: Astragaloside IV protects against ischemic
brain injury in a murine model of transient focal ischemia.
Neurosci Lett. 363:218–223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM,
Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R and Goedert M: Alpha-synuclein in Lewy
bodies. Nature. 388:839–840. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J,
Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra
A, Nussbaum R, et al: alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes
Parkinson's disease. Science. 302:8412003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakashima A, Hayashi N, Kaneko YS, Mori K,
Sabban EL, Nagatsu T and Ota A: Role of N-terminus of tyrosine
hydroxylase in the biosynthesis of catecholamines. J Neural Transm
(Vienna). 116:1355–1362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fahn S and Cohen G: The oxidant stress
hypothesis in Parkinson's disease: evidence supporting it. Ann
Neurol. 32:804–812. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Smith MA, Perry G, Richey PL, Sayre LM,
Anderson VE, Beal MF and Kowall N: Oxidative damage in Alzheimer's.
Nature. 382:120–121. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Markesbery WR: Oxidative stress hypothesis
in Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 23:134–147. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Emerit J, Edeas M and Bricaire F:
Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomed
Pharmacother. 58:39–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Halliwell B: Oxidative stress and
neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem. 97:1634–1658.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu XJ, Zheng YJ, Cui YY, Zhu L, Lu Y and
Chen HZ: Propofol attenuates oxidative stress-induced PC12 cell
injury via p38 MAP kinase dependent pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
28:1123–1128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Heo SR, Han AM, Kwon YK and Joung I: 62
protects SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells against
H2O2-induced injury through the PDK1/Akt
pathway. Neurosci Lett. 450:45–50. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xiong Y, Ding H, Xu M and Gao J:
Protective effects of asiatic acid on rotenone- or
H2O2-induced injury in SH-SY5Y cells.
Neurochem Res. 34:746–754. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yuan H, Zheng JC, Liu P, Zhang SF, Xu JY
and Bai LM: Pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease: oxidative stress,
environmental impact factors and inflammatory processes. Neurosci
Bull. 23:125–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chan WS, Durairajan SS, Lu JH, Wang Y, Xie
LX, Kum WF, Koo I, Yung KK and Li M: Neuroprotective effects of
astragaloside IV in 6-hydroxydopamine-treated primary nigral cell
culture. Neurochem Int. 55:414–422. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tian X, Guo LP, Hu XL, Huang J, Fan YH,
Ren TS and Zhao QC: Protective effects of Arctium lappa L. roots
against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell injury and potential
mechanisms in SH-SY5Y cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:335–344. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jia Z, Zhu H, Misra HP and Li Y: Potent
induction of total cellular GSH and NQO1 as well as mitochondrial
GSH by 3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and
primary human neurons: protection against neurocytotoxicity
elicited by dopamine, 6-hydroxydopamine, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, or
hydrogen peroxide. Brain Res. 1197:159–169. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hu XL, Niu YX, Zhang Q, Tian X, Gao LY,
Guo LP, Meng WH and Zhao QC: Neuroprotective effects of kukoamine B
against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and potential
mechanisms in SH-SY5Y cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 40:230–240.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Totterdell S, Hanger D and Meredith GE:
The ultrastructural distribution of alpha-synuclein-like protein in
normal mouse brain. Brain Res. 1004:61–72. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Uversky VN: Alpha-synuclein misfolding and
neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 9:507–540. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu S, Uéda K and Chan P: Alpha-synuclein
and dopamine metabolism. Mol Neurobiol. 31:243–254. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Eguchi M, Monden K and Miwa N: Role of
MAPK phosphorylation in cytoprotection by pro-vitamin C against
oxidative stress-induced injuries in cultured cardiomyoblasts and
perfused rat heart. J Cell Biochem. 90:219–226. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ruffels J, Griffin M and Dickenson JM:
Activation of ERK1/2, JNK and PKB by hydrogen peroxide in human
SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: role of ERK1/2 in
H2O2-induced cell death. Eur J Pharmacol.
483:163–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kwon SH, Kim JA, Hong SI, Jung YH, Kim HC,
Lee SY and Jang CG: Loganin protects against hydrogen
peroxide-induced apoptosis by inhibiting phosphorylation of JNK,
p38 and ERK 1/2 MAPKs in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Int. 58:533–541.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|