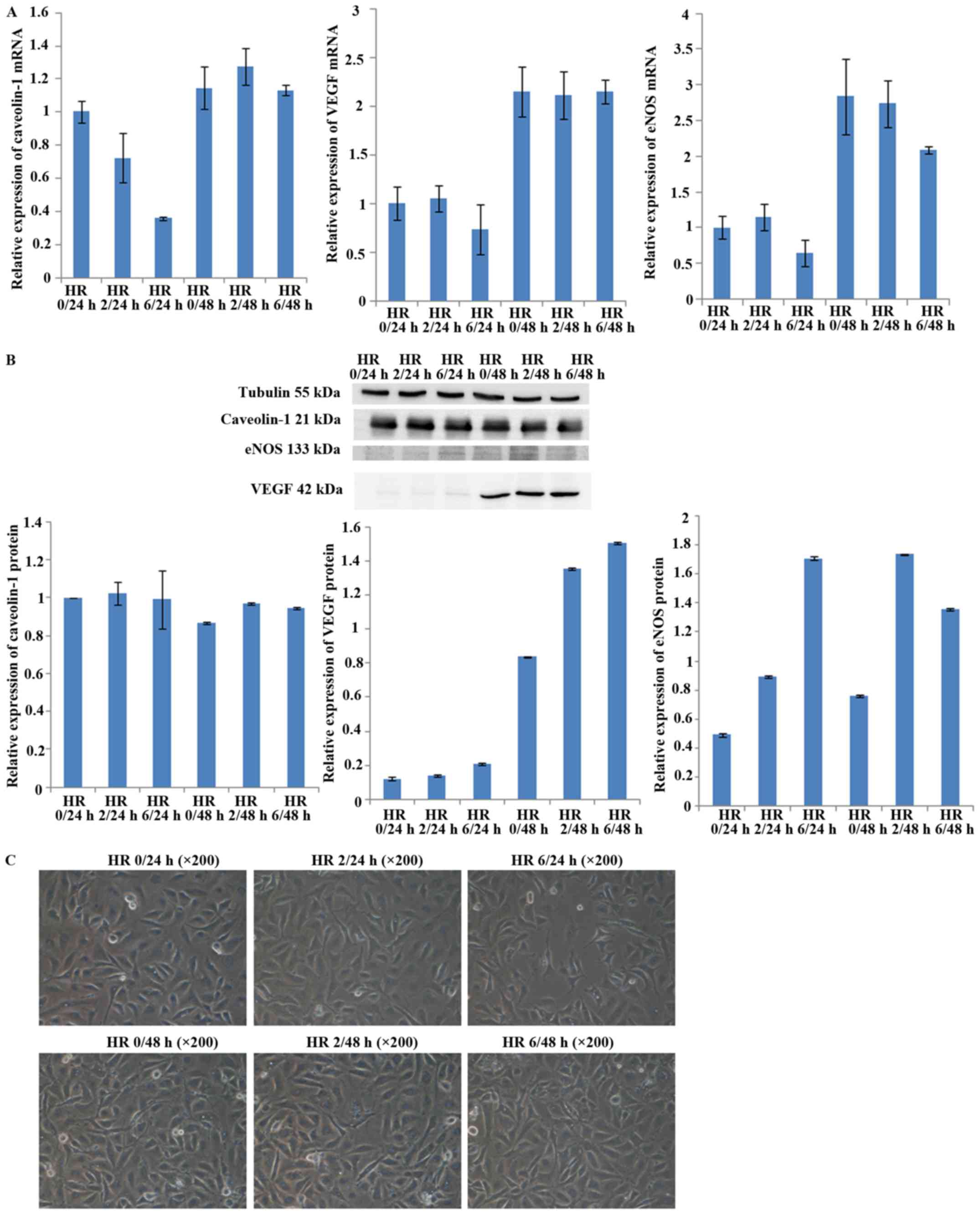
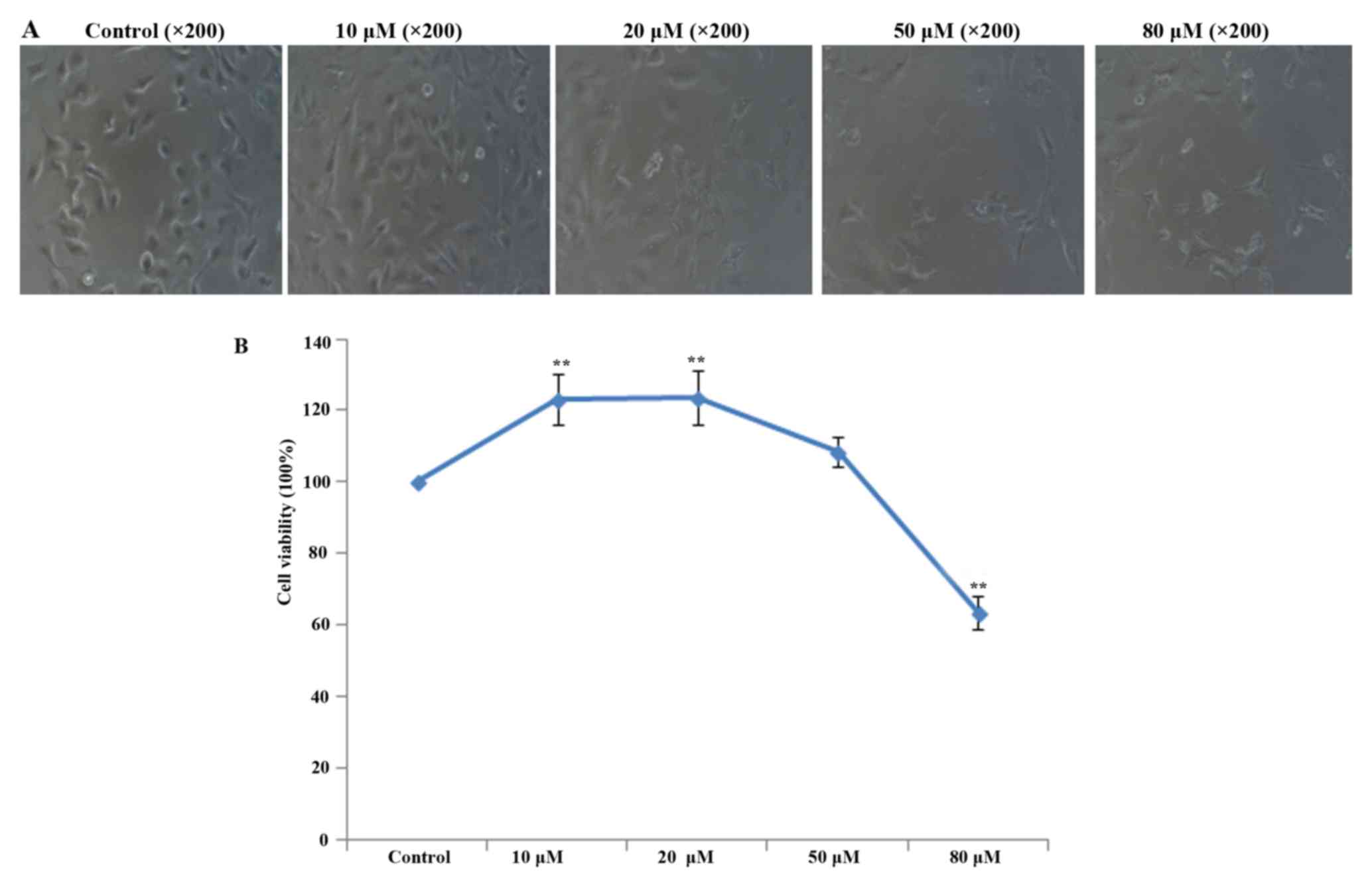
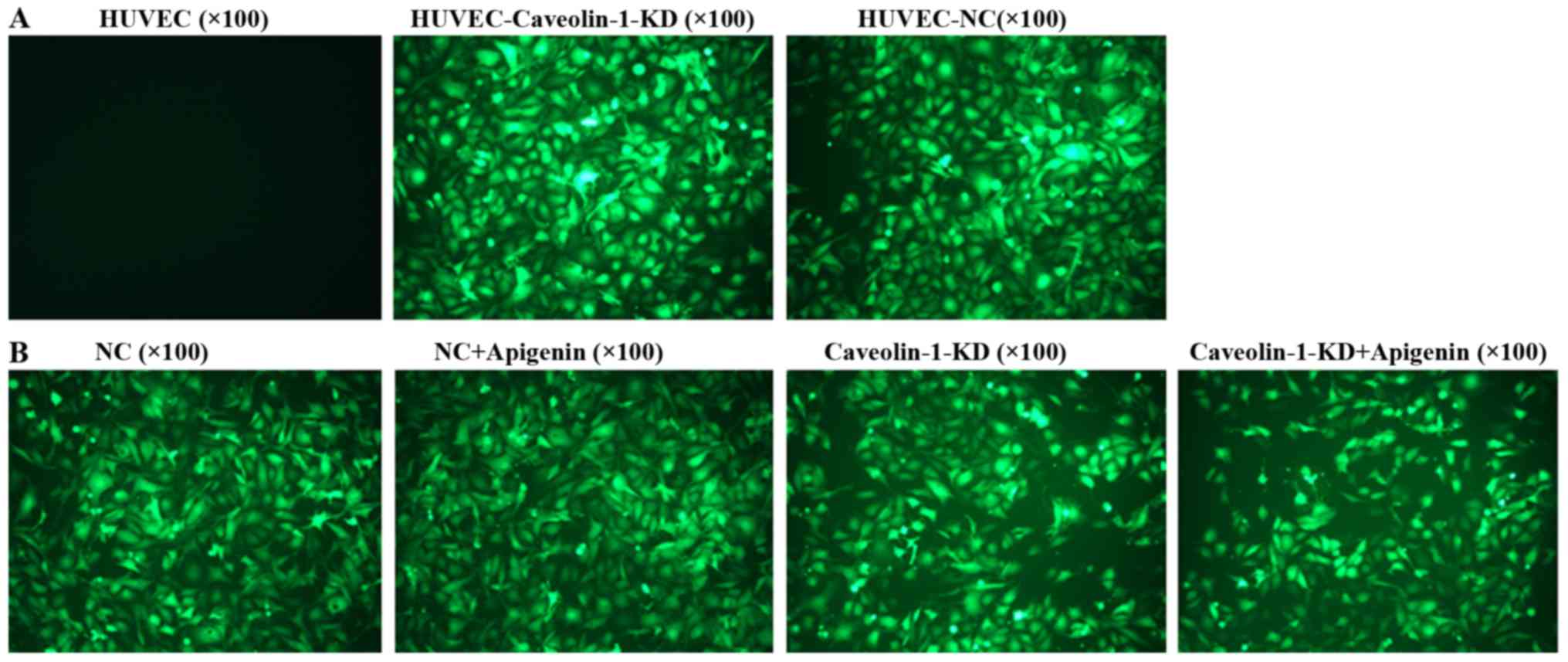
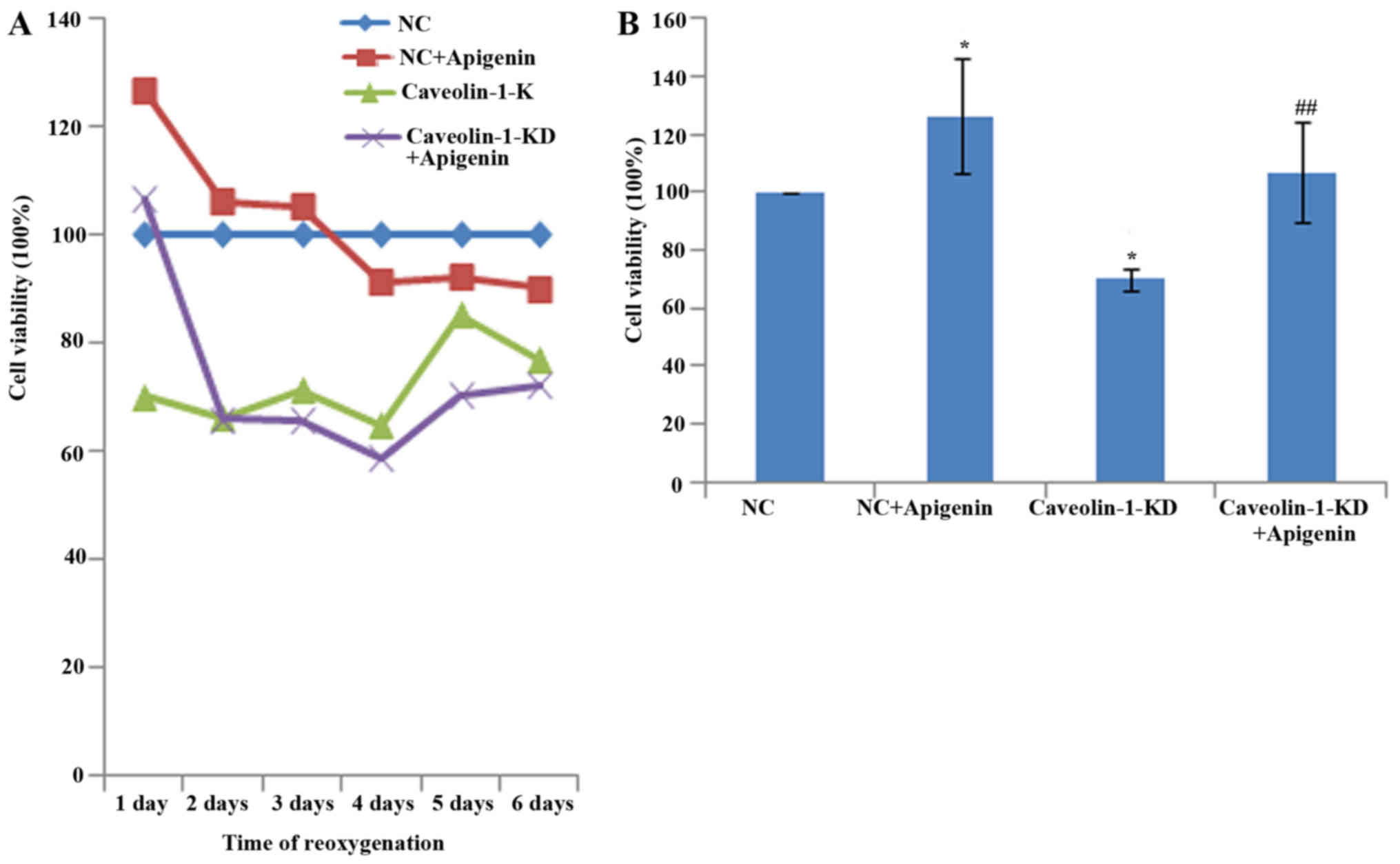
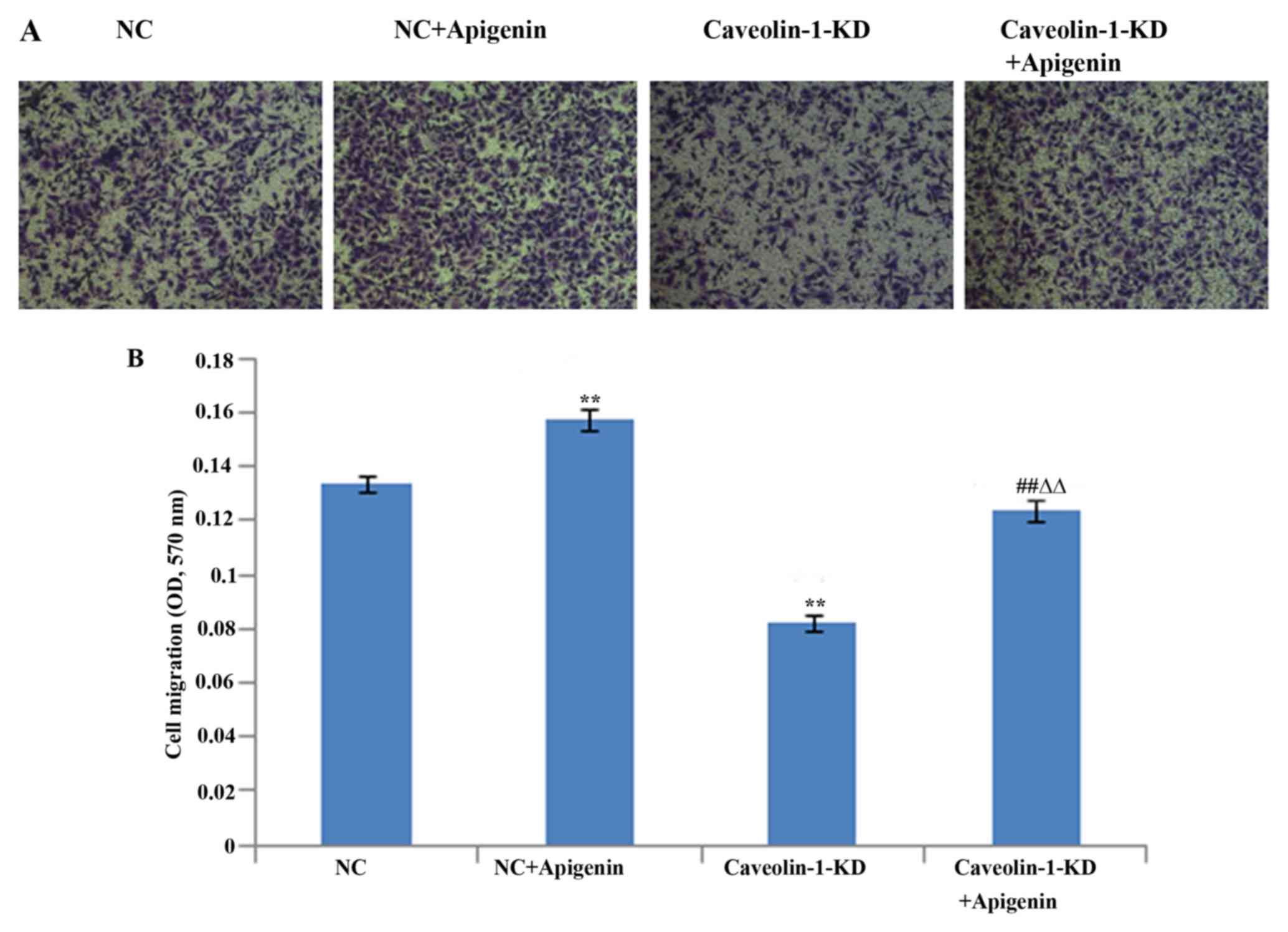
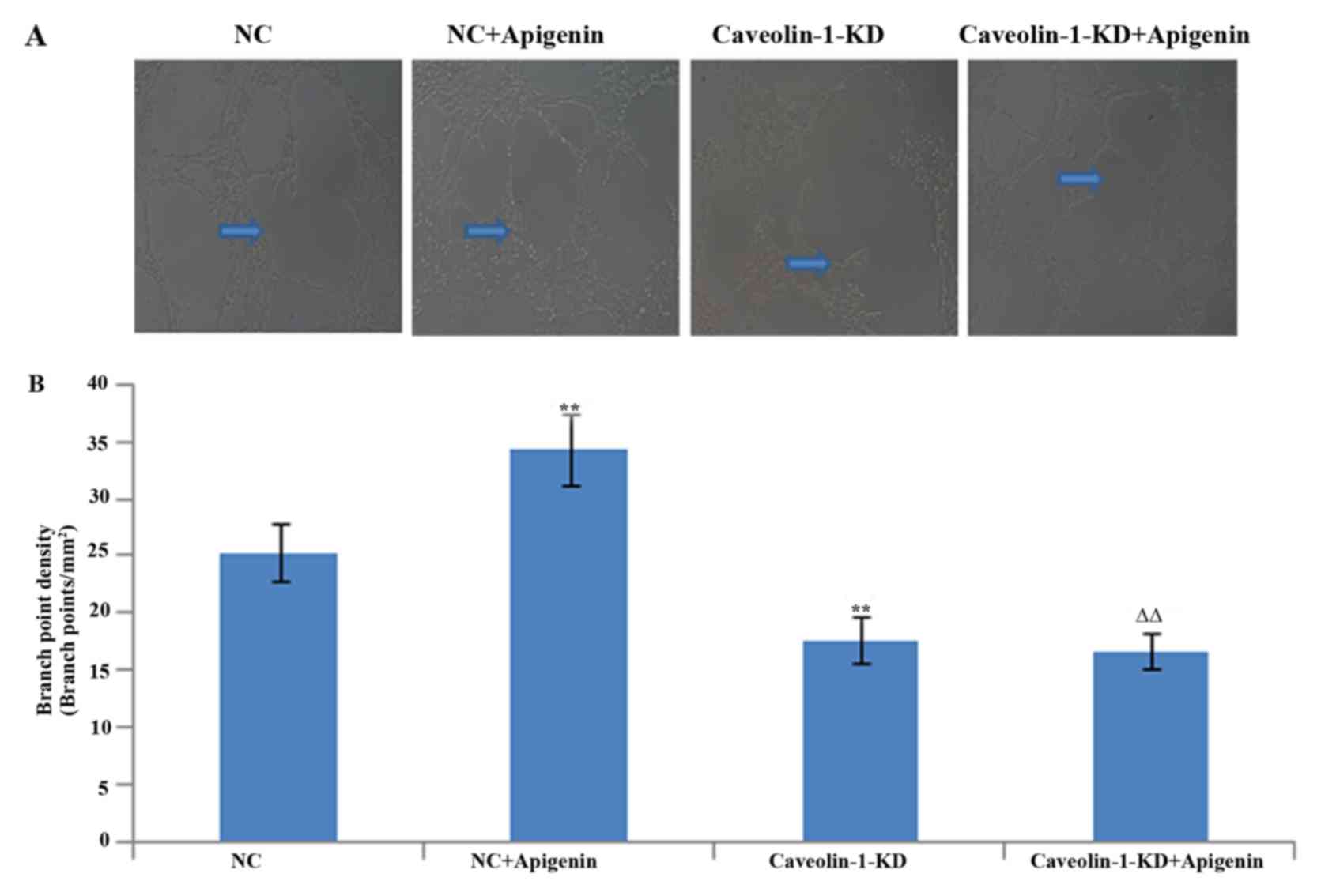
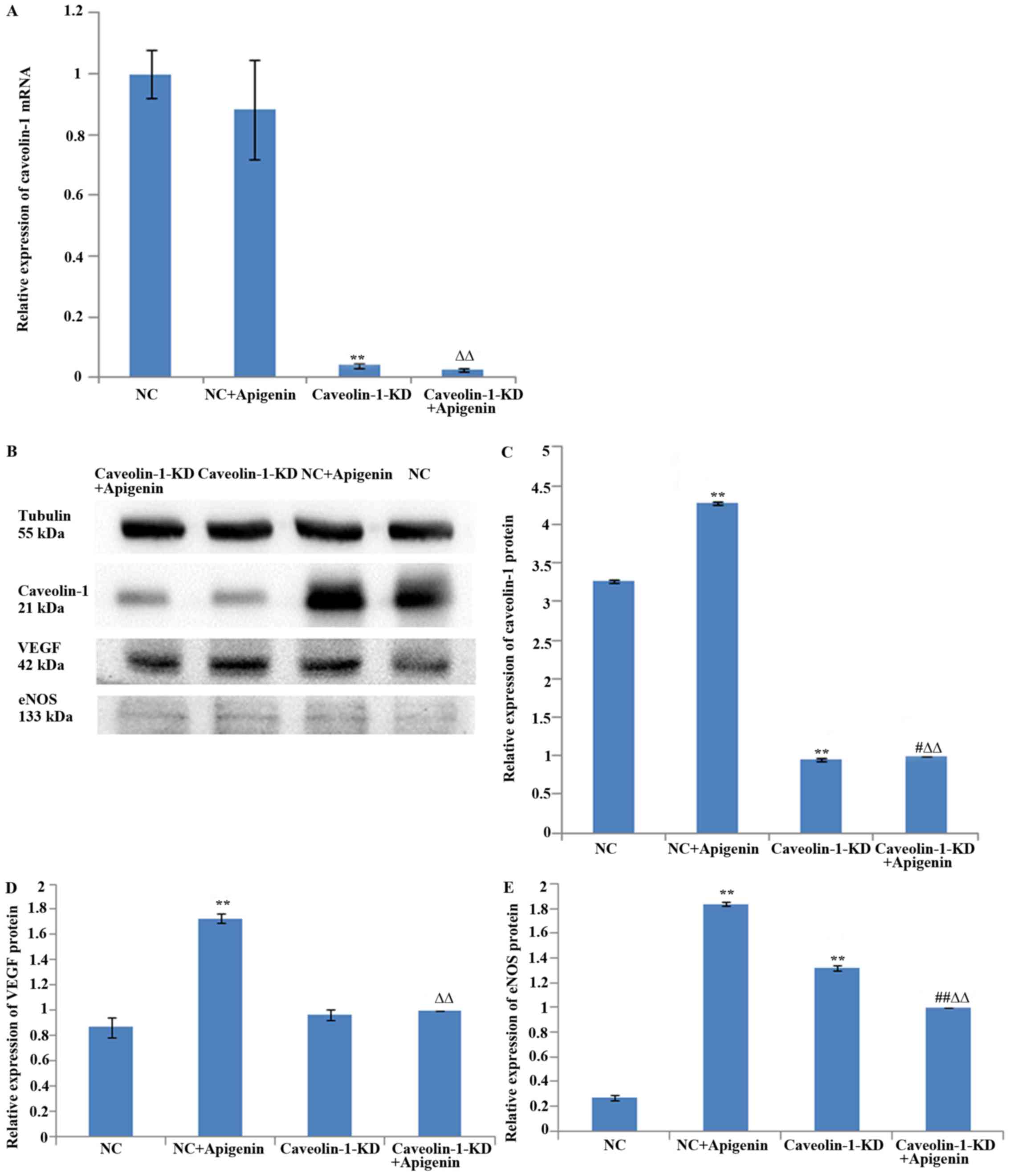
|
1
|
Semenza GL: Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis,
and arteriogenesis: Mechanisms of blood vessel formation and
remodeling. J Cell Biochem. 102:840–847. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kofler S, Nickel T and Weis M: Role of
cytokines in cardiovascular diseases: A focus on endothelial
responses to inflammation. Clin Sci (Lond). 108:205–213. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Papetti M and Herman IM: Mechanisms of
normal and tumor-derived angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
282:C947–C970. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shergill U, Das A, Langer D, Adluri R,
Maulik N and Shah VH: Inhibition of VEGF- and NO-dependent
angiogenesis does not impair liver regeneration. Am J Physiol Regul
Integr Comp Physiol. 298:R1279–R1287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yoshida D, Akahoshi T, Kawanaka H,
Yamaguchi S, Kinjo N, Taketomi A, Tomikawa M, Shirabe K, Maehara Y
and Hashizume M: Roles of vascular endothelial growth factor and
endothelial nitric oxide synthase during revascularization and
regeneration after partial hepatectomy in a rat model. Surg Today.
41:1622–1629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan TP, Yeh JC, Leung KW, Yue PY and Wong
RN: Angiogenesis: From plants to blood vessels. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 27:297–309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rahman A and Swärd K: The role of
caveolin-1 in cardiovascular regulation. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
195:231–245. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sowa G: Caveolae, caveolins, cavins, and
endothelial cell function: New insights. Front Physiol. 2:1202012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mundy DI, Machleidt T, Ying YS, Anderson
RG and Bloom GS: Dual control of caveolar membrane traffic by
microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci. 115:4327–4339.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Navarro A, Anand-Apte B and Parat MO: A
role for caveolae in cell migration. FASEB J. 18:1801–1811. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao Y, Zhao Y, Pan J, Yang L, Huang T,
Feng X, Li C, Liang S, Zhou D, Liu C, et al: Treadmill exercise
promotes angiogenesis in the ischemic penumbra of rat brains
through caveolin-1/VEGF signaling pathways. Brain Res. 1585:83–90.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu J, Wang XB, Park DS and Lisanti MP:
Caveolin-1 expression enhances endothelial capillary tubule
formation. J Biol Chem. 277:10661–10668. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Frank PG, Woodman SE, Park DS and Lisanti
MP: Caveolin, caveolae, and endothelial cell function. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1161–1168. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gratton JP, Bernatchez P and Sessa WC:
Caveolae and caveolins in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res.
94:1408–1417. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fleming I and Busse R: Molecular
mechanisms involved in the regulation of the endothelial nitric
oxide synthase. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 284:R1–R12.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ju H, Zou R, Venema VJ and Venema RC:
Direct interaction of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase and
caveolin-1 inhibits synthase activity. J Biol Chem.
272:18522–18525. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang QQ, Cheng N, Yi WB, Peng SM and Zou
XQ: Synthesis, nitric oxide release, and α-glucosidase inhibition
of nitric oxide donating apigenin and chrysin derivatives. Bioorg
Med Chem. 22:1515–1521. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Woodman OL and Chan EC: Vascular and
anti-oxidant actions of flavonols and flavones. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 31:786–790. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Olszanecki R, Gebska A, Kozlovski VI and
Gryglewski RJ: Flavonoids and nitric oxide synthase. J Physiol
Pharmacol. 53:571–584. 2002.
|
|
21
|
Guerrero JA, Lozano ML, Castillo J,
Benavente-García O, Vicente V and Rivera J: Flavonoids inhibit
platelet function through binding to the thromboxane A2 receptor. J
Thromb Haemost. 3:369–376. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu LZ, Fang J, Zhou Q, Hu X, Shi X and
Jiang BH: Apigenin inhibits expression of vascular endothelial
growth factor and angiogenesis in human lung cancer cells:
Implication of chemo-prevention of lung cancer. Mol Pharmacol.
68:635–643. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ansó E, Zuazo A, Irigoyen M, Urdaci MC,
Rouzaut A and Martínez-Irujo JJ: Flavonoids inhibit hypoxia-induced
vascular endothelial growth factor expression by a HIF-1
independent mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol. 79:1600–1609. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li XM, Niu WZ and Chen X: Effect of
apigenin on expression of VEGF in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion
rats. Chin J Pathophysiol. 26:2473–2477. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Niu WZ, Li XM, Wang G, Han X and Chen X:
Effects of apigenin on caveolin -1 expression of focal cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Chin Tradit Herbal Drugs.
41:1658–1662. 2010.
|
|
26
|
Li Q, Wu J, Wei P, Xu Y, Zhuo C, Wang Y,
Li D and Cai S: Overexpression of forkhead Box C2 promotes tumor
metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in colon cancer via
regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Cancer Res.
5:2022–2034. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Taylor AC, Seltz LM, Yates PA and Peirce
SM: Chronic whole-body hypoxia induces intussusceptive angiogenesis
and microvascular remodeling in the mouse retina. Microvasc Res.
79:93–101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lopez-Jornet P, Camacho-Alonso F,
Gómez-Garcia F, Molina Miñano F, Cañas X, Serafín A, Castillo J and
Vicente-Ortega V: Effects of potassium apigenin and verbena extract
on the wound healing process of SKH-1 mouse skin. Int Wound J.
11:489–495. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu P, Rudick M and Anderson RG: Multiple
functions of caveolin-1. J Biol Chem. 277:41295–41298. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chidlow JH Jr and Sessa WC: Caveolae,
caveolins, and cavins: Complex control of cellular signalling and
inflammation. Cardiovasc Res. 86:219–225. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shen J, Ma S, Chan P, Lee W, Fung PC,
Cheung RT, Tong Y and Liu KJ: Nitric oxide down-regulates
caveolin-1 expression in rat brains during focal cerebral ischemia
and reperfusion injury. J Neurochem. 96:1078–1089. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Luo J, Lau WM, Zheng G, Fu S, Wang
TT, Zeng HP, So KF, Chung SK, Tong Y, et al: Caveolin-1 plays a
crucial role in inhibiting neuronal differentiation of neural
stem/progenitor cells via VEGF signaling-dependent pathway. PLoS
One. 6:e229012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tahir SA, Park S and Thompson TC:
Caveolin-1 regulates VEGF-stimulated angiogenic activities in
prostate cancer and endothelial cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
8:2286–2296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roy S and Sen CK: miRNA in wound
inflammation and angiogenesis. Microcirculation. 19:224–232. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Peng W, Yu Y, Li T, Zhu Y and Chen H: The
effects of small interfering RNA-targeting tissue factor on an in
vitro model of neovascularization. Mol Vis. 19:1296–1303.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fukumura D, Gohongi T, Kadambi A, Izumi Y,
Ang J, Yun CO, Buerk DG, Huang PL and Jain RK: Predominant role of
endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial growth
factor-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:2604–2609. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qing M, Görlach A, Schumacher K, Wöltje M,
Vazquez-Jimenez JF, Hess J and Seghaye MC: The hypoxia-inducible
factor HIF-1 promotes intramyocardial expression of VEGF in infants
with congenital cardiac defects. Basic Res Cardiol. 102:224–232.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Drab M, Verkade P, Elger M, Kasper M, Lohn
M, Lauterbach B, Menne J, Lindschau C, Mende F, Luft FC, et al:
Loss of caveolae, vascular dysfunction, and pulmonary defects in
caveolin-1 gene-disrupted mice. Science. 293:2449–2452. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Razani B, Engelman JA, Wang XB, Schubert
W, Zhang XL, Marks CB, Macaluso F, Russell RG, Li M, Pestell RG, et
al: Caveolin-1 null mice are viable but show evidence of
hyper-proliferative and vascular abnormalities. J Biol Chem.
276:38121–38138. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao YY, Liu Y, Stan RV, Fan L, Gu Y,
Dalton N, Chu PH, Peterson K, Ross J Jr and Chien KR: Defects in
caveolin-1 cause dilated cardiomyopathy and pulmonary hypertension
in knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:11375–11380. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Maniatis NA, Shinin V, Schraufnagel DE,
Okada S, Vogel SM, Malik AB and Minshall RD: Increased pulmonary
vascular resistance and defective pulmonary artery filling in
caveolin-1−/−mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
294:L865–L873. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mehta D and Malik AB: Signaling mechanisms
regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev. 86:279–367. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Siddiqui MR, Komarova YA, Vogel SM, Gao X,
Bonini MG, Rajasingh J, Zhao YY, Brovkovych V and Malik AB:
Caveolin-1-eNOS signaling promotes p190RhoGAP-A nitration and
endothelial permeability. J Cell Biol. 193:841–850. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen Z, Bakhshi FR, Shajahan AN, Sharma T,
Mao M, Trane A, Bernatchez P, van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Bonini MG,
Skidgel RA, et al: Nitric oxide-dependent Src activation and
resultant caveolin-1 phosphorylation promote eNOS/caveolin-1
binding and eNOS inhibition. Mol Biol Cell. 23:1388–1398. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tong X and Pelling JC: Targeting the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis by apigenin for cancer prevention. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 13:971–978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fang J, Zhou Q, Liu LZ, Xia C, Hu X, Shi X
and Jiang BH: Apigenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis through
decreasing HIF-1alpha and VEGF expression. Carcinogenesis.
28:858–864. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Tong X, Mirzoeva S, Veliceasa D, Bridgeman
BB, Fitchev P, Cornwell ML, Crawford SE, Pelling JC and Volpert OV:
Chemopreventive apigenin controls UVB-induced cutaneous
proliferation and angiogenesis through HuR and thrombospondin-1.
Oncotarget. 5:11413–11427. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|