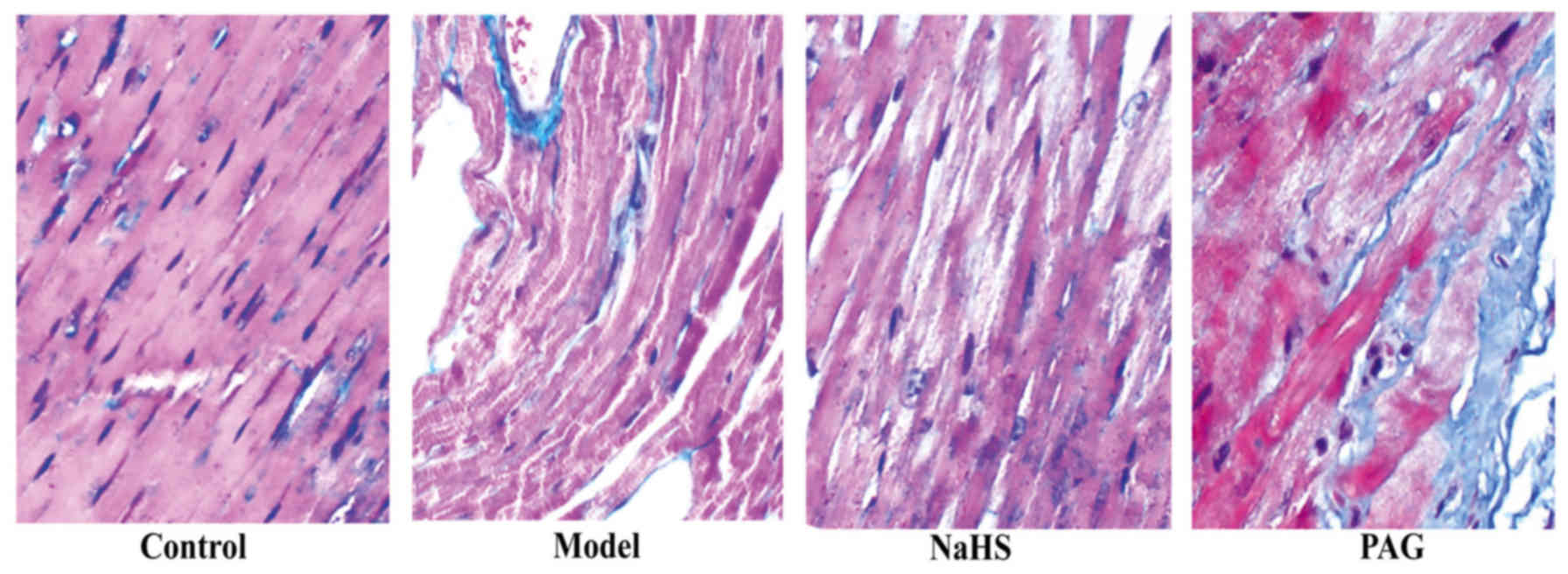
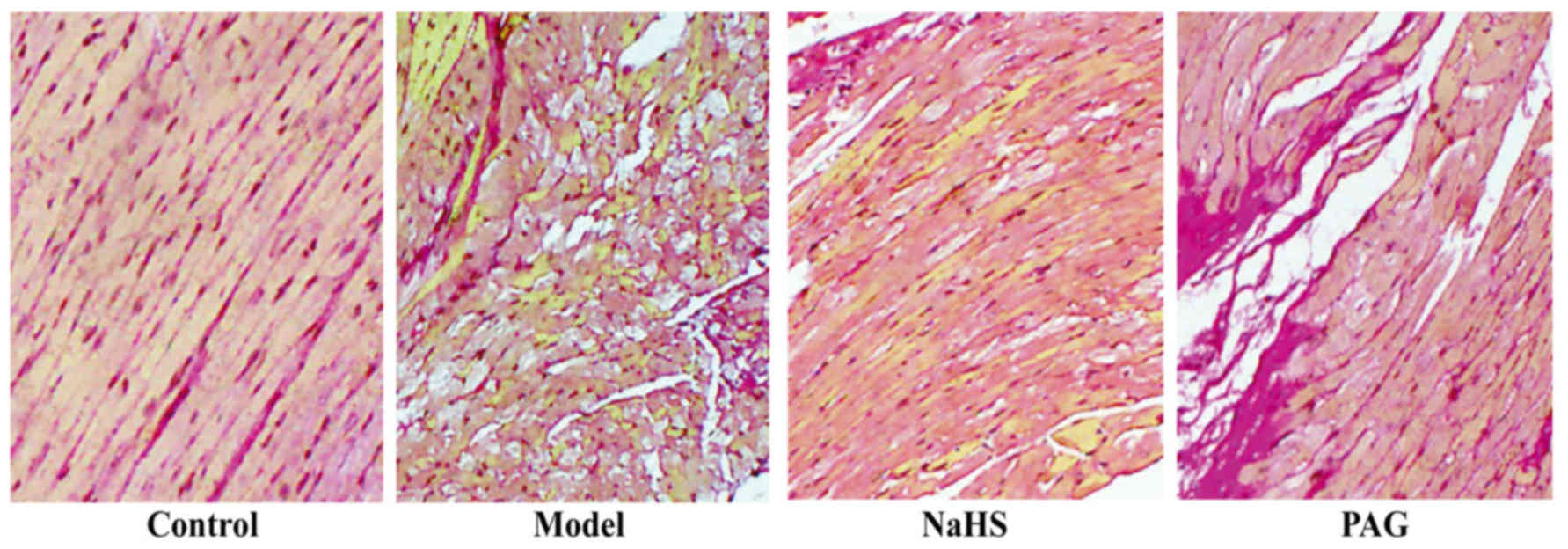
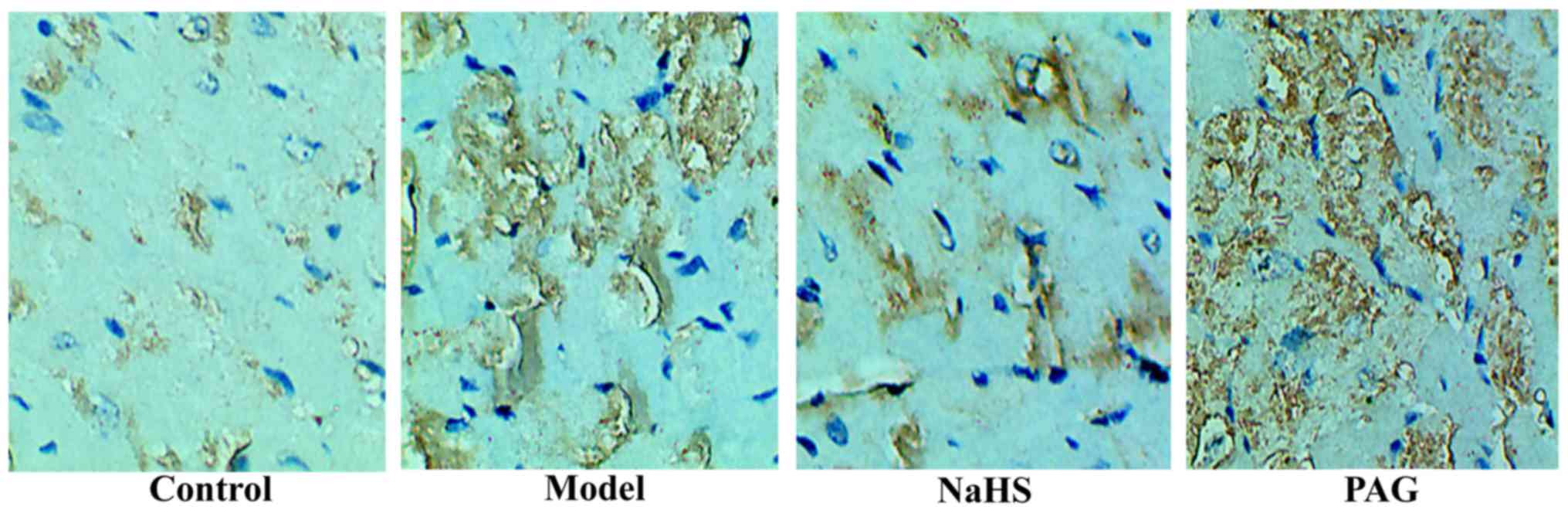
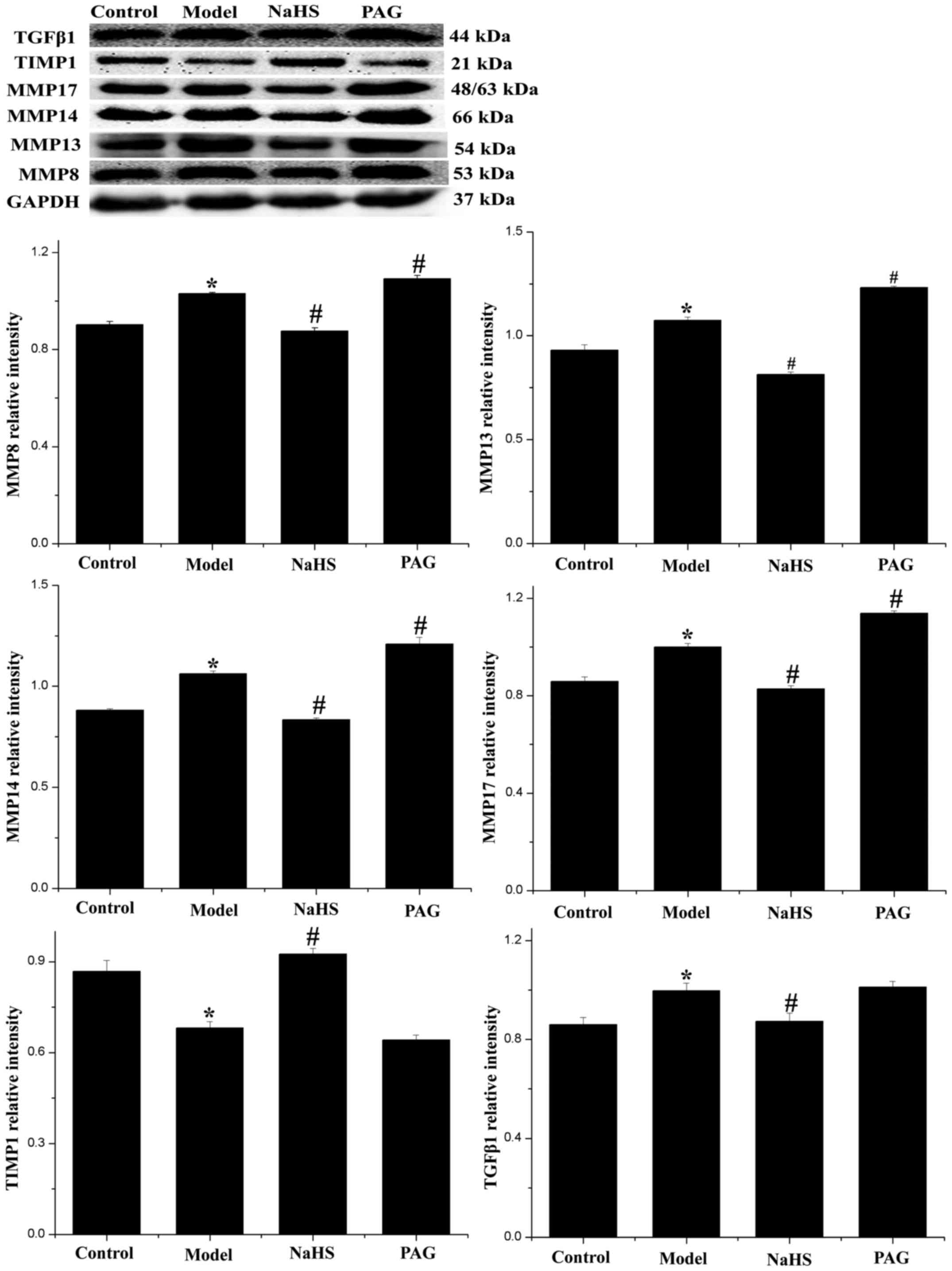
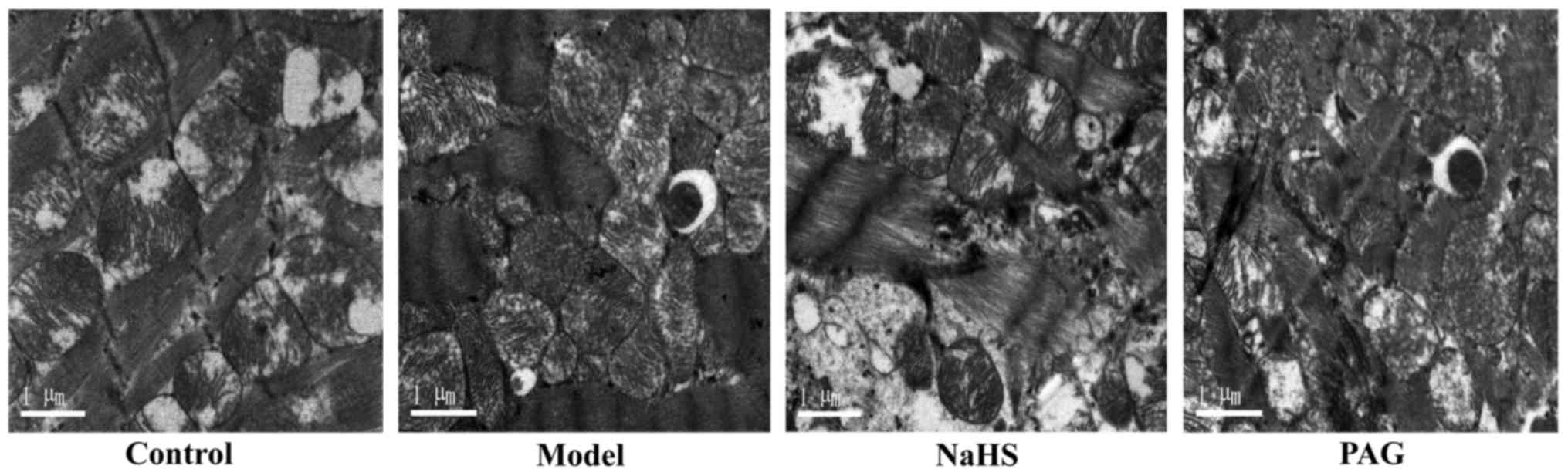
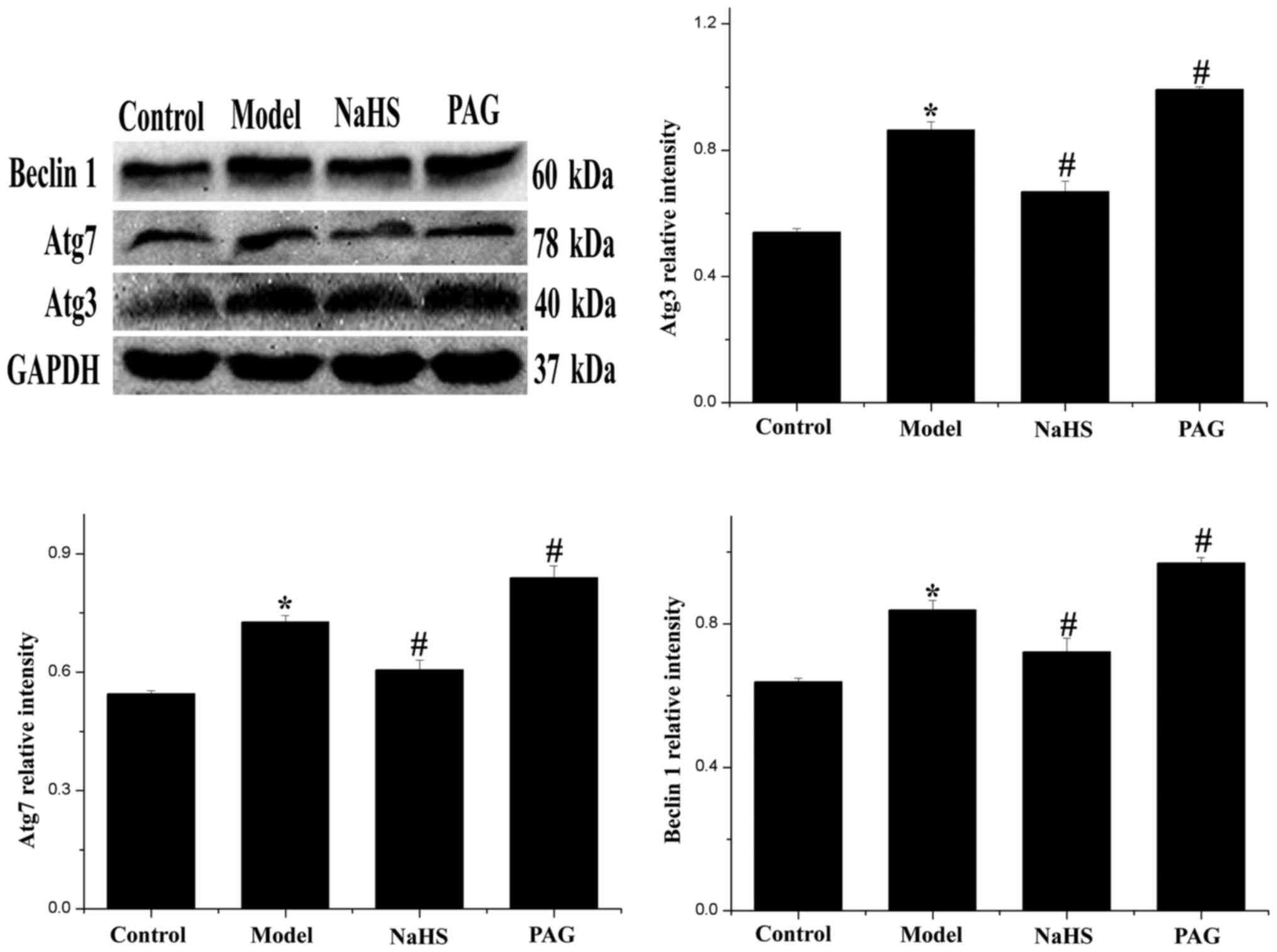
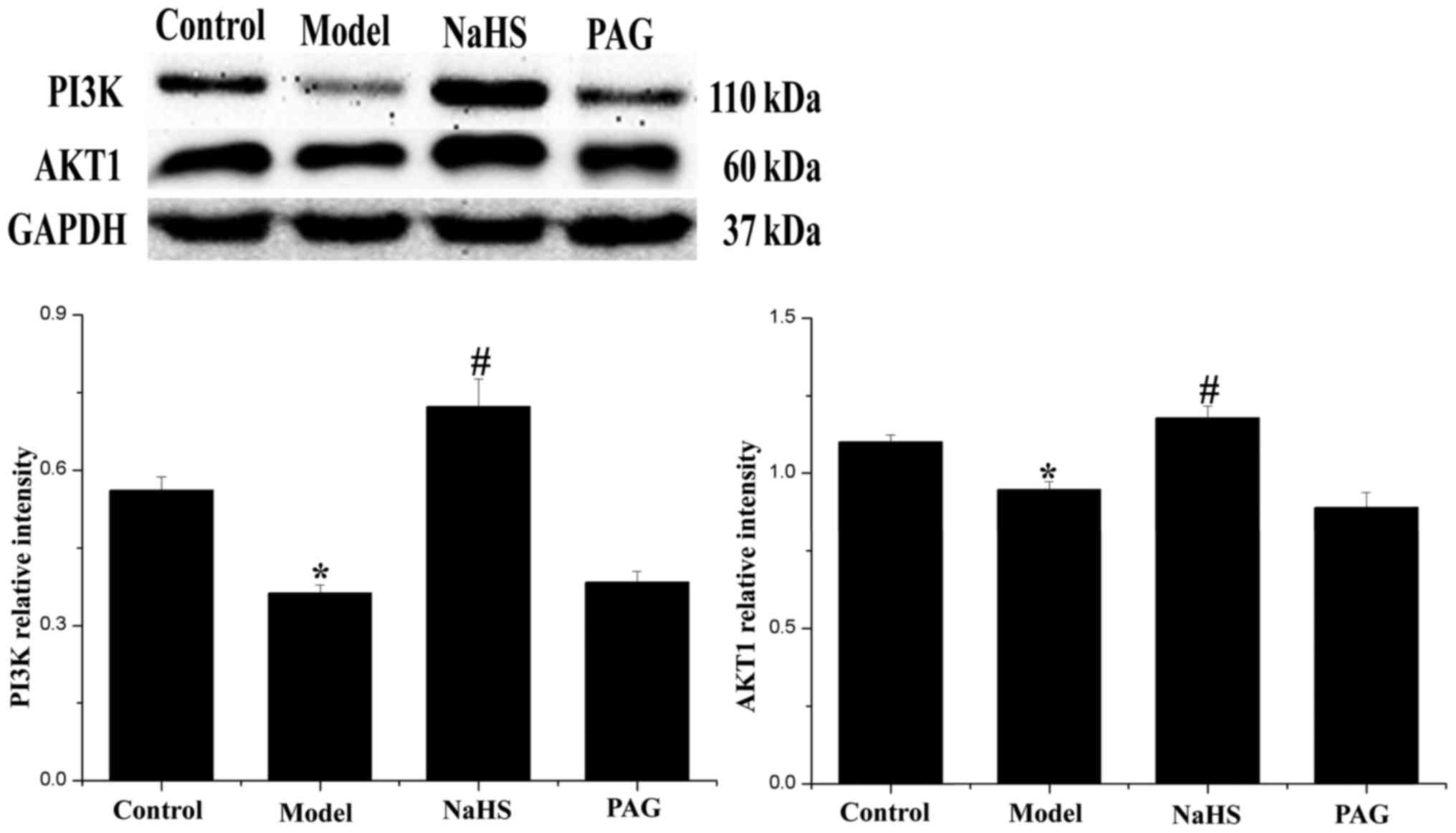
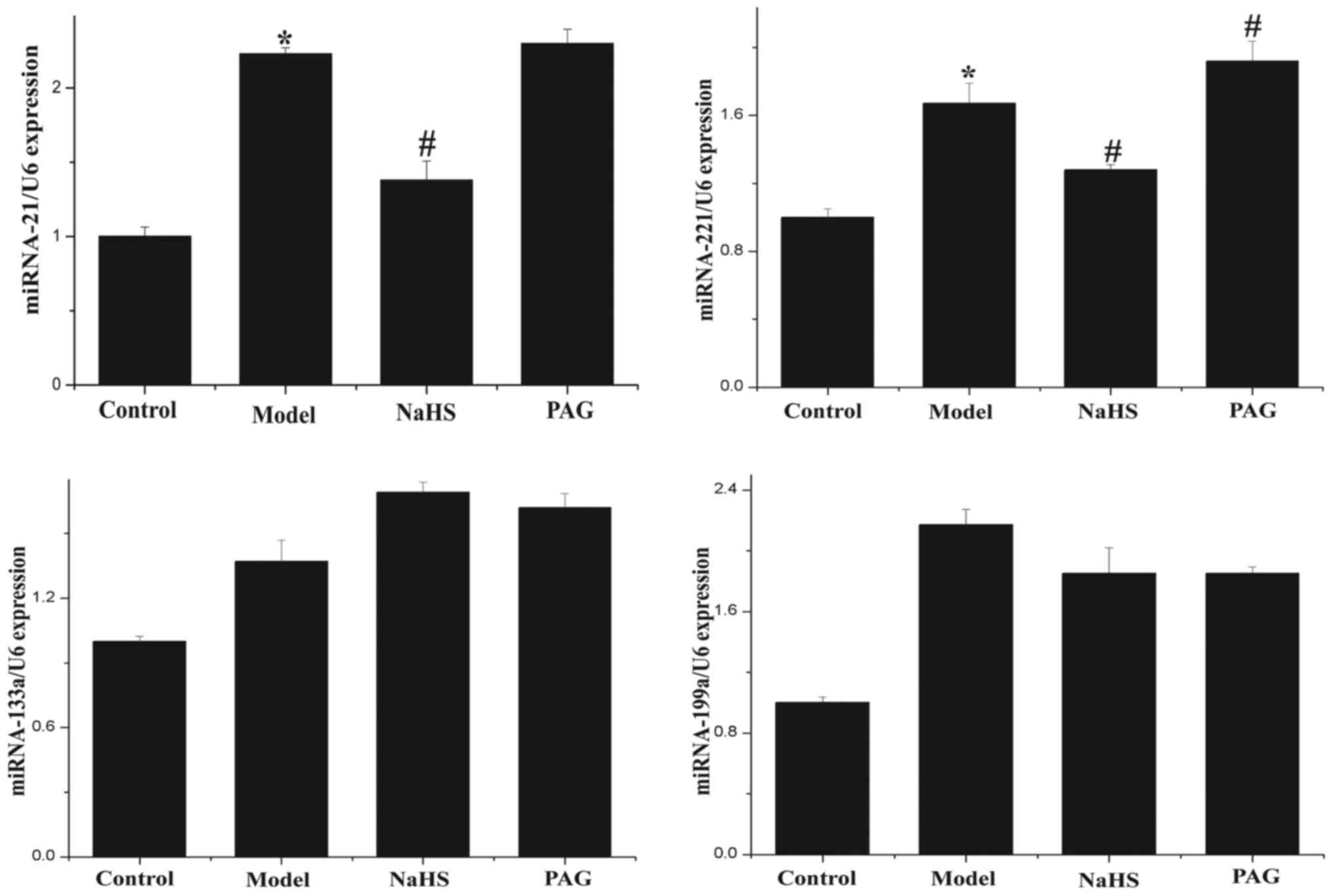
|
1
|
Piano MR and Phillips SA: Alcoholic
cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiologic insights. Cardiovasc Toxicol.
14:291–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Piano MR: Alcoholic cardiomyopathy:
Incidence, clinical characteristics, and pathophysiology. Chest.
121:1638–1650. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Basu S, Rajakaruna S, Reyes B, Van
Bockstaele E and Menko AS: Suppression of MAPK/JNK-MTORC1 signaling
leads to premature loss of organelles and nuclei by autophagy
during terminal differentiation of lens fiber cells. Autophagy.
10:1193–1211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gottlieb RA and Mentzer RM Jr: Autophagy:
An affair of the heart. Heart Fail Rev. 18:575–584. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Jian J, Xuan F, Qin F and Huang R:
Bauhinia championii flavone inhibits apoptosis and autophagy via
the PI3K/Akt pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rats. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:5933–5945. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Younce CW, Wang K and Kolattukudy PE:
Hyperglycaemia-induced cardiomyocyte death is mediated via MCP-1
production and induction of a novel zinc-finger protein MCPIP.
Cardiovasc Res. 87:665–674. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu H, Rothermel BA and Hill JA: Autophagy
in load-induced heart disease. Methods Enzymol. 453:343–363. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma S, Wang Y, Chen Y and Cao F: The role
of the autophagy in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1852:271–276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jie X, Qin X, Cai X, Yang L, Xing Y, Li J,
Zhang L, Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang X, et al: Mitochondrial JNK
activation triggers autophagy and apoptosis and aggravates
myocardial injury following ischemia/reperfusion. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1852:262–270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang L, Ding WY, Wang ZH, Tang MX, Wang
F, Li Y, Zhong M, Zhang Y and Zhang W: Early administration of
trimetazidine attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats by
alleviating fibrosis, reducing apoptosis and enhancing autophagy. J
Transl Med. 14:109–112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo R, Hu N, Kandadi MR and Ren J:
Facilitated ethanol metabolism promotes cardiomyocyte contractile
dysfunction through autophagy in murine hearts. Autophagy.
8:593–608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Liu N,
Williams AH, McAnally J, Gerard RD, Richardson JA and Olson EN: A
signature pattern of stress-responsive microRNAs that can evoke
cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
103:18255–18260. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jing L, Jin C, Lu Y, Huo P, Zhou L, Wang Y
and Tian Y: Investigation of microRNA expression profiles
associated with human alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Cardiology.
130:223–233. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Calvert JW, Coetzee WA and Lefer DJ: Novel
insights into hydrogen sulfide - mediated cytoprotection. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:1203–1217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Zhou X, An G and Chen J: Hydrogen sulfide
improves left ventricular function in smoking rats via regulation
of apoptosis and autophagy. Apoptosis. 19:998–1005. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang M, Shan H, Chang P, Wang T, Dong W,
Chen X and Tao L: Hydrogen sulfide offers neuroprotection on
traumatic brain injury in parallel with reduced apoptosis and
autophagy in mice. PLoS One. 9:e872412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Toldo S, Das A, Mezzaroma E, Chau VQ,
Marchetti C, Durrant D, Samidurai A, Van Tassell BW, Yin C, Ockaili
RA, et al: Induction of microRNA-21 with exogenous hydrogen sulfide
attenuates myocardial ischemic and inflammatory injury in mice.
Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 7:311–320. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ge W and Ren J: mTOR-STAT3-notch
signalling contributes to ALDH2-induced protection against cardiac
contractile dysfunction and autophagy under alcoholism. J Cell Mol
Med. 16:616–626. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Guo H, Sa Y, Huang J, Wang Z, Wang L, Xie
M and Lv X: Urethral reconstruction with small intestinal submucosa
seeded with oral keratinocytes and TIMP-1 siRNA transfected
fibroblasts in a rabbit model. Urol Int. 96:223–230. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Johnson KM and Crocker SJ: TIMP-1 couples
RhoK activation to IL-1β-induced astrocyte responses. Neurosci
Lett. 609:165–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schoppet M and Maisch B: Alcohol and the
heart. Herz. 26:345–352. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Laurent D and Edwards JG: Alcoholic
cardiomyopathy: Multigenic changes underlie cardiovascular
dysfunction. J Cardiol Clin Res. 2:10222014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Law BA, Levick SP and Carver WE:
Alterations in cardiac structure and function in a murine model of
chronic alcohol consumption. Microsc Microanal. 18:453–461. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dancy M and Maxwell JD: Alcohol and
dilated cardiomyopathy. Alcohol Alcohol. 21:185–198.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Wu Y, Chen J, Zhao S and Li H:
Pirfenidone attenuates cardiac fibrosis in a mouse model of
TAC-induced left ventricular remodeling by suppressing NLRP3
inflammasome formation. Cardiology. 126:1–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
An Z, Yang G, He YQ, Dong N, Ge LL, Li SM
and Zhang WQ: Atorvastatin reduces myocardial fibrosis in a rat
model with post-myocardial infarction heart failure by increasing
the matrix metalloproteinase-2/tissue matrix metalloproteinase
inhibitor-2 ratio. Chin Med J (Engl). 126:2149–2156. 2013.
|
|
27
|
Dixon IM, Ju H, Reid NL, Scammell-La Fleur
T, Werner JP and Jasmin G: Cardiac collagen remodeling in the
cardiomyopathic Syrian hamster and the effect of losartan. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 29:1837–1850. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cowan KN, Jones PL and Rabinovitch M:
Regression of hypertrophied rat pulmonary arteries in organ culture
is associated with suppression of proteolytic activity, inhibition
of tenascin-C, and smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Circ Res.
84:1223–1233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Polyakova V, Loeffler I, Hein S, Miyagawa
S, Piotrowska I, Dammer S, Risteli J, Schaper J and Kostin S:
Fibrosis in endstage human heart failure: Severe changes in
collagen metabolism and MMP/TIMP profiles. Int J Cardiol.
151:18–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Elrod JW, Calvert JW, Morrison J, Doeller
JE, Kraus DW, Tao L, Jiao X, Scalia R, Kiss L, Szabo C, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
by preservation of mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S
A. 104:15560–15565. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
King AL and Lefer DJ: Cytoprotective
actions of hydrogen sulfide in ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Exp
Physiol. 96:840–846. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qian H and Liu L: Protective effect of
hydrogen sulfide on mice with experimental viral myocarditis and
its mechanism. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 30:708–712.
2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou X, An G and Lu X: Hydrogen sulfide
attenuates the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Clin Sci
(Lond). 128:325–335. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhou X, Lu X, Xu W and Chen J: Protective
effects of hydrogen sulfide against chronic alcohol intake-induced
left ventricular remodeling in rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.
27:221–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Awata S, Nakayama K, Suzuki I and Kodama
H: Effect of cysteine on the inactivation of cystathionine
gamma-lyase by D, L-propargylglycine. Acta Med Okayama. 43:329–335.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ashford TP and Porter KR: Cytoplasmic
components in hepatic cell lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 12:198–202.
1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zeglinski MR, Davies JJ, Ghavami S, Rattan
SG, Halayko AJ and Dixon IM: Chronic expression of Ski induces
apoptosis and represses autophagy in cardiac myofibroblasts.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863(6 Pt A): 1261–1268. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M,
Sakoda H, Asano T, Levine B and Sadoshima J: Distinct roles of
autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: Roles of
AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy.
Circ Res. 100:914–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baehrecke EH: Autophagy: Dual roles in
life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:505–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu H, Tannous P, Johnstone JL, Kong Y,
Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Le V, Levine B, Rothermel BA and Hill
JA: Cardiac autophagy is a maladaptive response to hemodynamic
stress. J Clin Invest. 117:1782–1793. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miyata S, Takemura G, Kawase Y, Li Y,
Okada H, Maruyama R, Ushikoshi H, Esaki M, Kanamori H, Li L, et al:
Autophagic cardiomyocyte death in cardiomyopathic hamsters and its
prevention by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Am J Pathol.
168:386–397. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiao T, Luo J, Wu Z, Li F, Zeng O and Yang
J: Effects of hydrogen sulfide on myocardial fibrosis and
PI3K/AKT1-regulated autophagy in diabetic rats. Mol Med Rep.
13:1765–1773. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Shui M, Liu X, Zhu Y and Wang Y: Exogenous
hydrogen sulfide attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by
inhibiting autophagy in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 22:1–6.
2016.
|
|
44
|
Sun L, Jin H, Sun L, Chen S, Huang Y, Liu
J, Li Z, Zhao M, Sun Y, Tang C, et al: Hydrogen sulfide alleviates
myocardial collagen remodeling in association with inhibition of
TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Mol Med. 20:503–515. 2015.
|
|
45
|
Lin L, Liu X, Xu J, Weng L, Ren J, Ge J
and Zou Y: High-density lipoprotein inhibits mechanical
stress-induced cardiomyocyte autophagy and cardiac hypertrophy
through angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. J
Cell Mol Med. 19:1929–1938. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang ZG, Wang Y, Huang Y, Lu Q, Zheng L,
Hu D, Feng WK, Liu YL, Ji KT, Zhang HY, et al: bFGF regulates
autophagy and ubiquitinated protein accumulation induced by
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion via the activation of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Sci Rep. 5:92872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dany M, Rimmani HH, Matar SA and Hajj
Hussein I: mTORC2-Akt signaling axis is implicated in myocardial
compensation and fibrosis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 29:745–753.
2015.
|
|
48
|
Usunier B, Benderitter M, Tamarat R and
Chapel A: Management of fibrosis: The mesenchymal stromal cells
breakthrough. Stem Cells Int. 2014:3402572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Wang H, Cui L, Zhang Y, Liu Y,
Chu X, Liu Z, Zhang J and Chu L: Continuing treatment with Salvia
miltiorrhiza injection attenuates myocardial fibrosis in chronic
iron-overloaded mice. PLoS One. 10:e01240612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Raaf L, Noll C, Cherifi Mel H, Samuel JL,
Delcayre C, Delabar JM, Benazzoug Y and Janel N: Myocardial
fibrosis and TGFB expression in hyperhomocysteinemic rats. Mol Cell
Biochem. 347:63–70. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Araki S, Izumiya Y, Rokutanda T, Ianni A,
Hanatani S, Kimura Y, Onoue Y, Senokuchi T, Yoshizawa T, Yasuda O,
et al: Sirt7 contributes to myocardial tissue repair by maintaining
transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway. Circulation.
132:1081–1093. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Condorelli G, Latronico MV and Dorn GW II:
MicroRNAs in heart disease: Putative novel therapeutic targets? Eur
Heart J. 31:649–658. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang M, Wang Y, Zang W, Wang H, Chu H, Li
P, Li M, Zhang G and Zhao G: Downregulation of microRNA-182
inhibits cell growth and invasion by targeting programmed cell
death 4 in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 35:39–46.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chen C, Jia KY, Zhang HL and Fu J: miR-195
enhances cardio-myocyte apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation
injury via downregulating c-myb. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:3410–3416. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yu J, Wu SW and Wu WP: A tumor-suppressive
microRNA, miRNA-485-5p inhibits glioma cell proliferation and
invasion by down-regulating TPD52L2. Am J Transl Res. 9:3336–3344.
2017.
|
|
56
|
Nouraee N and Mowla SJ: miRNA therapeutics
in cardiovascular diseases: Promises and problems. Front Genet.
6:2322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Iacopo F, Lorenzo C, Calogero E, Matteo P,
Riccardo PN, Veronica S, Valentina B, Riccardo L, Cristian S, Maria
MC, et al: Review in translational cardiology: MicroRNAs and
myocardial fibrosis in aortic valve stenosis, a deep insight on
left ventricular remodeling. J Cardiovasc Echogr. 26:109–114. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Chen S, Puthanveetil P, Feng B, Matkovich
SJ, Dorn GW II and Chakrabarti S: Cardiac miR-133a overexpression
prevents early cardiac fibrosis in diabetes. J Cell Mol Med.
18:415–421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Thum T, Gross C, Fiedler J, Fischer T,
Kissler S, Bussen M, Galuppo P, Just S, Rottbauer W, Frantz S, et
al: MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating
MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature. 456:980–984. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liang H, Zhang C, Ban T, Liu Y, Mei L,
Piao X, Zhao D, Lu Y, Chu W and Yang B: A novel reciprocal loop
between micro- RNA-21 and TGFβRIII is involved in cardiac fibrosis.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2152–2160. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang C, Wang S, Zhao P, Wang X, Wang J,
Wang Y, Song L, Zou Y and Hui R: miR-221 promotes cardiac
hypertrophy in vitro through the modulation of p27 expression. J
Cell Biochem. 113:2040–2046. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Garofalo M, Di Leva G, Romano G, Nuovo G,
Suh SS, Ngankeu A, Taccioli C, Pichiorri F, Alder H, Secchiero P,
et al: miR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance
tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell.
16:498–509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cheng M, Wu G, Song Y, Wang L, Tu L, Zhang
L and Zhang C: Celastrol-induced suppression of the miR-21/ERK
signalling pathway attenuates cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:1928–1938. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yu X, Li R, Shi W, Jiang T, Wang Y, Li C
and Qu X: Silencing of microRNA-21 confers the sensitivity to
tamoxifen and fulvestrant by enhancing autophagic cell death
through inhibition of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway in breast cancer
cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 77:37–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen Q, Zhou Y, Richards AM and Wang P:
Up-regulation of miRNA-221 inhibits hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced
autophagy through the DDIT4/mTORC1 and Tp53inp1/p62 pathways.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:168–174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|