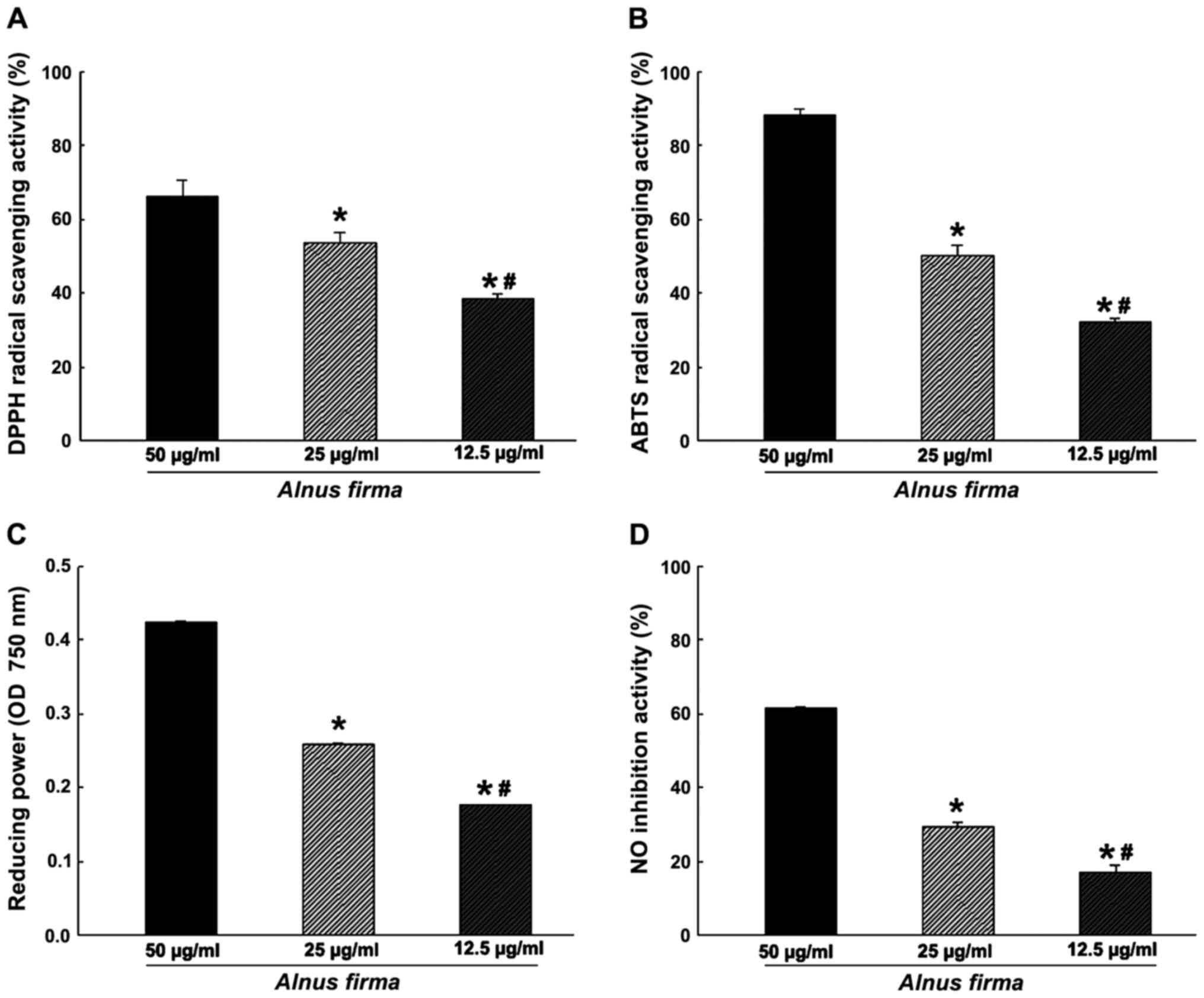
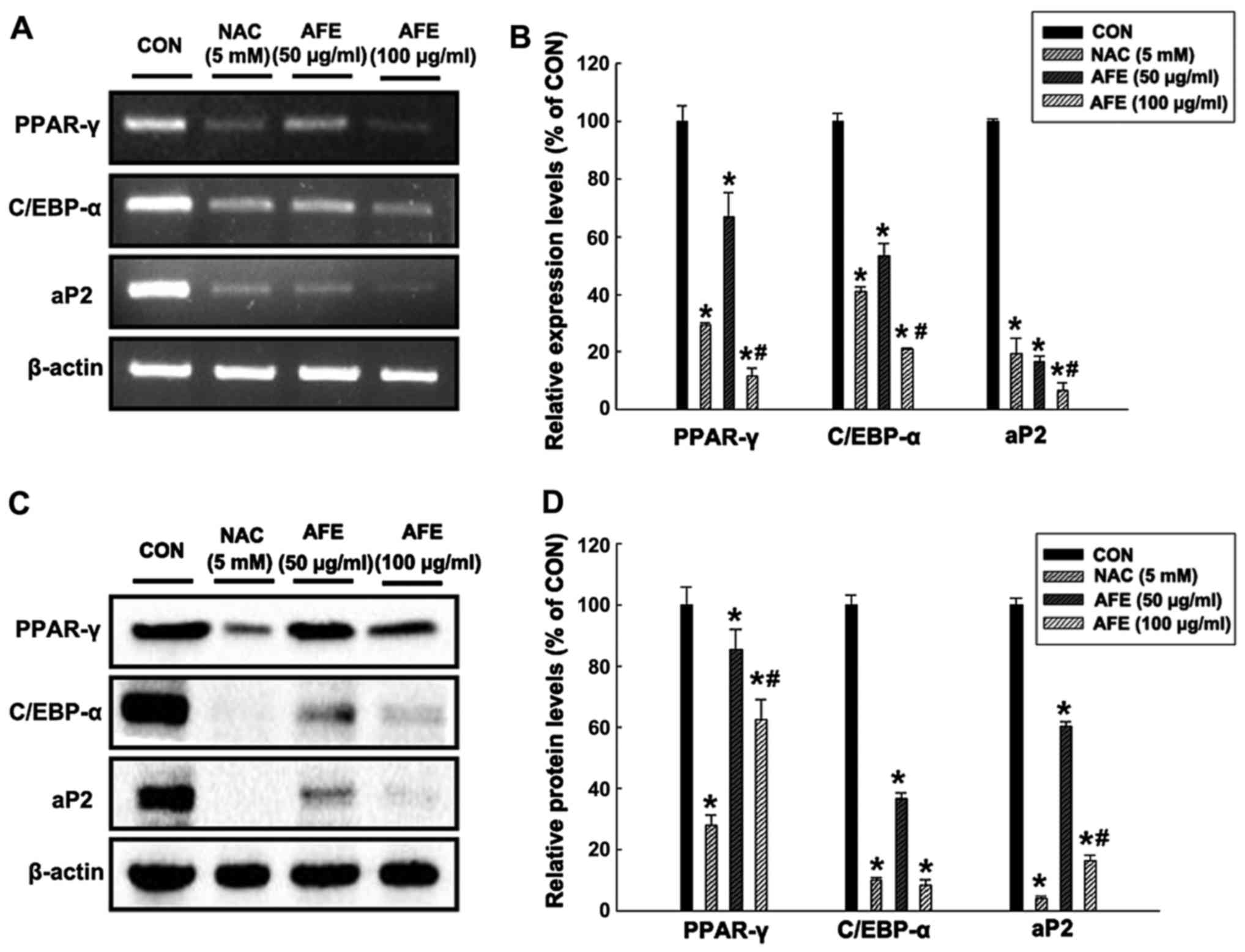
|
1
|
Dröge W and Dröge W: Free radicals in the
physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev. 82:47–95.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Halliwell B, Aeschbach R, Löliger J and
Aruoma OI: The characterization of antioxidants. Food Chem Toxicol.
33:601–617. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT,
Mazur M and Telser J: Free radicals and antioxidants in normal
physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:44–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yamashina K, Miller BE and Heppner GH:
Macrophage-mediated induction of drug-resistant variants in a mouse
mammary tumor cell line. Cancer Res. 46:2396–2401. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fridovich I: Superoxide dismutases. An
adaptation to a paramagnetic gas. J Biol Chem. 264:7761–7764.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Spiegelman BM and Flier JS: Obesity and
the regulation of energy balance. Cell. 104:531–543. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marcelin G and Chua S Jr: Contributions of
adipocyte lipid metabolism to body fat content and implications for
the treatment of obesity. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 10:588–593. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Holst D and Grimaldi PA: New factors in
the regulation of adipose differentiation and metabolism. Curr Opin
Lipidol. 13:241–245. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Ferranti S and Mozaffarian D: The
perfect storm: Obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic
consequences. Clin Chem. 54:945–955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee OH, Kwon YI, Hong HD, Park CS, Lee BY
and Kim YC: Production of reactive oxygen species and changes in
antioxidant enzyme activites during differentiation of 3T3-L1
adipocyte. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 52:70–75. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sureda A, Tauler P, Aguiló A, Cases N,
Fuentespina E, Córdova A, Tur JA and Pons A: Relation between
oxidative stress markers and antioxidant endogenous defences during
exhaustive exercise. Free Radic Res. 39:1317–1324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim HK, Kwon YJ, Kim YE and Nahmgang B:
Changes of total polyphenol content and antioxidant activity of
aster scaber thunb extracts with different microwave assisted
extraction conditions. Korean J Food Preserv. 11:88–95. 2004.
|
|
13
|
Larson RA: The antioxidants of higher
plants. Phytochemistry. 27:969–978. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Schöner S and Heinrich Krause G:
Protective systems against active oxygen species in spinach:
Response to cold acclimation in excess light. Planta. 180:383–389.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gutfinger T: Polyphenols in olive oils. J
Am Oil Chem Soc. 58:966–968. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Moreno MI, Isla MI, Sampietro AR and
Vattuone MA: Comparison of the free radical-scavenging activity of
propolis from several regions of Argentina. J Ethnopharmacol.
71:109–114. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mitsunaga T, Doi T, Kondo Y and Abe I:
Color development of proanthocyanidins in vanillin-hydrochloric
acid reaction. J Wood Sci. 44:125–130. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chu YH, Chang CL and Hsu HF: Flavonoid
content of several vegetables and their antioxidant activity. J Sci
Food Agric. 80:561–566. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala
A, Yang M and Rice-Evans C: Antioxidant activity applying an
improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol
Med. 26:1231–1237. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oyaizu M: Antioxidative activities of
browning products of glucosamine fractionated by organic solvent
and thin-layer chromatography. J Jpn Soc Food Sci. 35:771–775.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kato H, Lee IE, Chuyen V, Kim SB and
Hayase F: Inhibition of nitrosamine formation by nondialyzable
melanoidins. Agric Biol Chem. 51:1333–1388. 1987.
|
|
22
|
Ou B, Hampsch-Woodill M and Prior RL:
Development and validation of an improved oxygen radical absorbance
capacity assay using fluorescein as the fluorescent probe. J Agric
Food Chem. 49:4619–4626. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee OH, Kwon YI, Apostolidis E, Shetty K
and Kim YC: Rhodiola-induced inhibition of adipogenesis involves
antioxidant enzyme response associated with pentose phosphate
pathway. Phytother Res. 25:106–115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki
M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M and
Shimomura I: Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact
on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 114:1752–1761. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blumberg JM, Tzameli I, Astapova I, Lam
FS, Flier JS and Hollenberg AN: Complex role of the vitamin D
receptor and its ligand in adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol
Chem. 281:11205–11213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaur C and Kapoor HC: Antioxidant activity
and total phenolic content of some Asian vegetables. Int J Food Sci
Technol. 37:153–161. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Machowetz A, Poulsen HE, Gruendel S,
Weimann A, Fitó M, Marrugat J, de la Torre R, Salonen JT, Nyyssönen
K, Mursu J, et al: Effect of olive oils on biomarkers of oxidative
DNA stress in Northern and Southern Europeans. FASEB J. 21:45–52.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Heim KE, Tagliaferro AR and Bobilya DJ:
Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and
structure-activity relationships. J Nutr Biochem. 13:572–584. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Fine AM: Oligomeric proanthocyanidin
complexes: History, structure, and phytopharmaceutical
applications. Altern Med Rev. 5:144–151. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stević T, Savikin K, Zdunić G, Stanojković
T, Juranić Z, Janković T and Menković N: Antioxidant, cytotoxic,
and antimicrobial activity of Alnus incana (L.) ssp. incana Moench
and A. viridis (Chaix) DC ssp. viridis extracts. J Med Food.
13:700–704. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Acero N and Muñoz-Mingarro D: Effect on
tumor necrosis factor-α production and antioxidant ability of black
alder, as factors related to its anti-inflammatory properties. J
Med Food. 15:542–548. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H, Choi YM, Lee JS, Park JS, Yeon KS
and Han CS: Drying and antioxidant characteristics of the shiitake
(Lentinus edodes) mushroom in a conveyer type far-infrared dryer. J
Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 36:250–254. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim MB, Hyun SH, Park JS, Kang M, Ko YH
and Lim SB: Integral antioxidative capacity of extracts by
pressurized organic solvent from natural plants in Jeju. J Korean
Soc Food Sci Nutr. 37:1491–1496. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sati SC, Sati N and Sati OP: Bioactive
constituents and medicinal importance of genus Alnus. Pharmacogn
Rev. 5:174–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee M, Song JY, Chin YW and Sung SH:
Anti-adipogenic diarylheptanoids from Alnus hirsuta f. sibirica on
3T3-L1 cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 23:2069–2073. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hanasaki Y, Ogawa S and Fukui S: The
correlation between active oxygens scavenging and antioxidative
effects of flavonoids. Free Radic Biol Med. 16:845–850. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rice-Evans CA, Miller NJ and Paganga G:
Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and
phenolic acids. Free Radic Biol Med. 20:933–956. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cao G, Sofic E and Prior RL: Antioxidant
and prooxidant behavior of flavonoids: Structure-activity
relationships. Free Radic Biol Med. 22:749–760. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
MacDonald-Wicks LK, Wood LG and Garg ML:
Methodology for the determination of biological antioxidant
capacity in vitro: A review. J Sci Food Agric. 86:2046–2056. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Que F, Mao L, Zhu C and Xie G: Antioxidant
properties of Chinese yellow wine, its concentrate and volatiles.
LWT Food Sic Technol. 39:111–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Tachakittirungrod S, Okonogi S and
Chowwanapoonpohn S: Study on antioxidant activity of certain plants
in Thailand: Mechanism of antioxidant action of guava leaf extract.
Food Chem. 103:381–388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Duh PD: Antioxidant activity of burdock
(Arctium lappa Linné): Its scavenging effect on free-radical and
active oxygen. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 75:455–461. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Calzadilla P, Sapochnik D, Cosentino S,
Diz V, Dicelio L, Calvo JC and Guerra LN: N-acetylcysteine reduces
markers of differentiation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int J Mol Sci.
12:6936–6951. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Baehner RL, Boxer LA and Davis J: The
biochemical basis of nitroblue tetrazolium reduction in normal
human and chronic granulomatous disease polymorphonuclear
leukocytes. Blood. 48:309–313. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Eruslanov E and Kusmartsev S:
Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry.
Methods Mol Biol. 594:57–72. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Morrison RF and Farmer SR: Insights into
the transcriptional control of adipocyte differentiation. J Cell
Biochem. 33(Suppl 32): 59–67. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Graves RA, Budavari AI
and Spiegelman BM: mPPAR gamma 2: Tissue-specific regulator of an
adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev. 8:1224–1234. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hilger-Eversheim K, Moser M, Schorle H and
Buettner R: Regulatory roles of AP-2 transcription factors in
vertebrate development, apoptosis and cell-cycle control. Gene.
260:1–12. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Makowski L and Hotamisligil GS: Fatty acid
binding proteins - the evolutionary crossroads of inflammatory and
metabolic responses. J Nutr. 134:2464S–2468S. 2004.
|