|
1
|
American Diabetes Association: Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 28(Suppl
1): S37–S42. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Flier JS, Underhill LH, Polonsky KS,
Sturis J and Bell GI: Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus-A
genetically programmed failure of the beta cell to compensate for
insulin resistance. N Engl J Med. 334:777–783. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C and Shaw
J: IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of the prevalence of
diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 94:311–321.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ling C and Groop L: Epigenetics: A
molecular link between environmental factors and type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes. 58:2718–2725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mahajan A, Go MJ, Zhang W, Below JE,
Gaulton KJ, Ferreira T, Horikoshi M, Johnson AD, Ng MC, Prokopenko
I, et al DIAbetes Genetics Replication And Meta-analysis (DIAGRAM)
Consortium; Asian Genetic Epidemiology Network Type 2 Diabetes
(AGEN-T2D) Consortium; South Asian Type 2 Diabetes (SAT2D)
Consortium; Mexican American Type 2 Diabetes (MAT2D) Consortium;
Type 2 Diabetes Genetic Exploration by Nex-generation sequencing in
muylti-Ethnic Samples (T2D-GENES) Consortium: Genome-wide
trans-ancestry meta-analysis provides insight into the genetic
architecture of type 2 diabetes susceptibility. Nat Genet.
46:234–244. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Voight BF, Scott LJ, Steinthorsdottir V,
Morris AP, Dina C, Welch RP, Zeggini E, Huth C, Aulchenko YS,
Thorleifsson G, et al MAGIC investigators; GIANT Consortium: Twelve
type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale
association analysis. Nat Genet. 42:579–589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferrannini E, Nannipieri M, Williams K,
Gonzales C, Haffner SM and Stern MP: Mode of onset of type 2
diabetes from normal or impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes.
53:160–165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhou K, Donnelly LA, Morris AD, Franks PW,
Jennison C, Palmer CN and Pearson ER: Clinical and genetic
determinants of progression of type 2 diabetes: A DIRECT study.
Diabetes Care. 37:718–724. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Mamas M, Dunn WB, Neyses L and Goodacre R:
The role of metabolites and metabolomics in clinically applicable
biomarkers of disease. Arch Toxicol. 85:5–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kaddurah-Daouk R, Kristal BS and
Weinshilboum RM: Metabolomics: A global biochemical approach to
drug response and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 48:653–683.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wilson ID, Nicholson JK, Castro-Perez J,
Granger JH, Johnson KA, Smith BW and Plumb RS: High resolution
'ultra performance' liquid chromatography coupled to oa-TOF mass
spectrometry as a tool for differential metabolic pathway profiling
in functional genomic studies. J Proteome Res. 4:591–598. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo K, Bamforth F and Li L: Qualitative
metabolome analysis of human cerebrospinal fluid by
13C-/12C-isotope dansylation labeling combined with liquid
chromatography Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass
spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 22:339–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nicholson JK and Lindon JC: Systems
biology: Metabonomics. Nature. 455:1054–1056. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee Y, Khan A, Hong S, Jee SH and Park YH:
A metabolomic study on high-risk stroke patients determines low
levels of serum lysine metabolites: A retrospective cohort study.
Mol Biosyst. 13:1109–1120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Suhre K: Metabolic profiling in diabetes.
J Endocrinol. 221:R75–R85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ,
Stevens RD, Lien LF, Haqq AM, Shah SH, Arlotto M, Slentz CA, et al:
A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that
differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin
resistance. Cell Metab. 9:311–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang TJ, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Cheng S,
Rhee EP, McCabe E, Lewis GD, Fox CS, Jacques PF, Fernandez C, et
al: Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat
Med. 17:448–453. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang-Sattler R, Yu Z, Herder C, Messias
AC, Floegel A, He Y, Heim K, Campillos M, Holzapfel C, Thorand B,
et al: Novel biomarkers for pre-diabetes identified by
metabolomics. Mol Syst Biol. 8:6152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng S, Rhee EP, Larson MG, Lewis GD,
McCabe EL, Shen D, Palma MJ, Roberts LD, Dejam A, Souza AL, et al:
Metabolite profiling identifies pathways associated with metabolic
risk in humans. Circulation. 125:2222–2231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Drogan D, Dunn WB, Lin W, Buijsse B,
Schulze MB, Langenberg C, Brown M, Floegel A, Dietrich S,
Rolandsson O, et al: Untargeted metabolic profiling identifies
altered serum metabolites of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a
prospective, nested case control study. Clin Chem. 61:487–497.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Anjana RM, Shanthi Rani CS, Deepa M,
Pradeepa R, Sudha V, Divya Nair H, Lakshmipriya N, Subhashini S,
Binu VS, Unnikrishnan R, et al: Incidence of diabetes and
prediabetes and predictors of progression among Asian Indians:
10-Year follow-up of the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study
(CURES). Diabetes Care. 38:1441–1448. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jee SH, Batty GD, Jang Y, Oh DJ, Oh BH,
Lee SH, Park SW, Seung KB, Kimm H, Kim SY, et al: The Korean Heart
Study: Rationale, objectives, protocol, and preliminary results for
a new prospective cohort study of 430,920 men and women. Eur J Prev
Cardiol. 21:1484–1492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Want EJ, O'Maille G, Smith CA, Brandon TR,
Uritboonthai W, Qin C, Trauger SA and Siuzdak G: Solvent-dependent
metabolite distribution, clustering, and protein extraction for
serum profiling with mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 78:743–752.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu T, Park Y, Johnson JM and Jones DP:
apLCMS - adaptive processing of high-resolution LC/MS data.
Bioinformatics. 25:1930–1936. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. JR Stat Soc B. B57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
27
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Smith CA, O'Maille G, Want EJ, Qin C,
Trauger SA, Brandon TR, Custodio DE, Abagyan R and Siuzdak G:
METLIN: A metabolite mass spectral database. Ther Drug Monit.
27:747–751. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
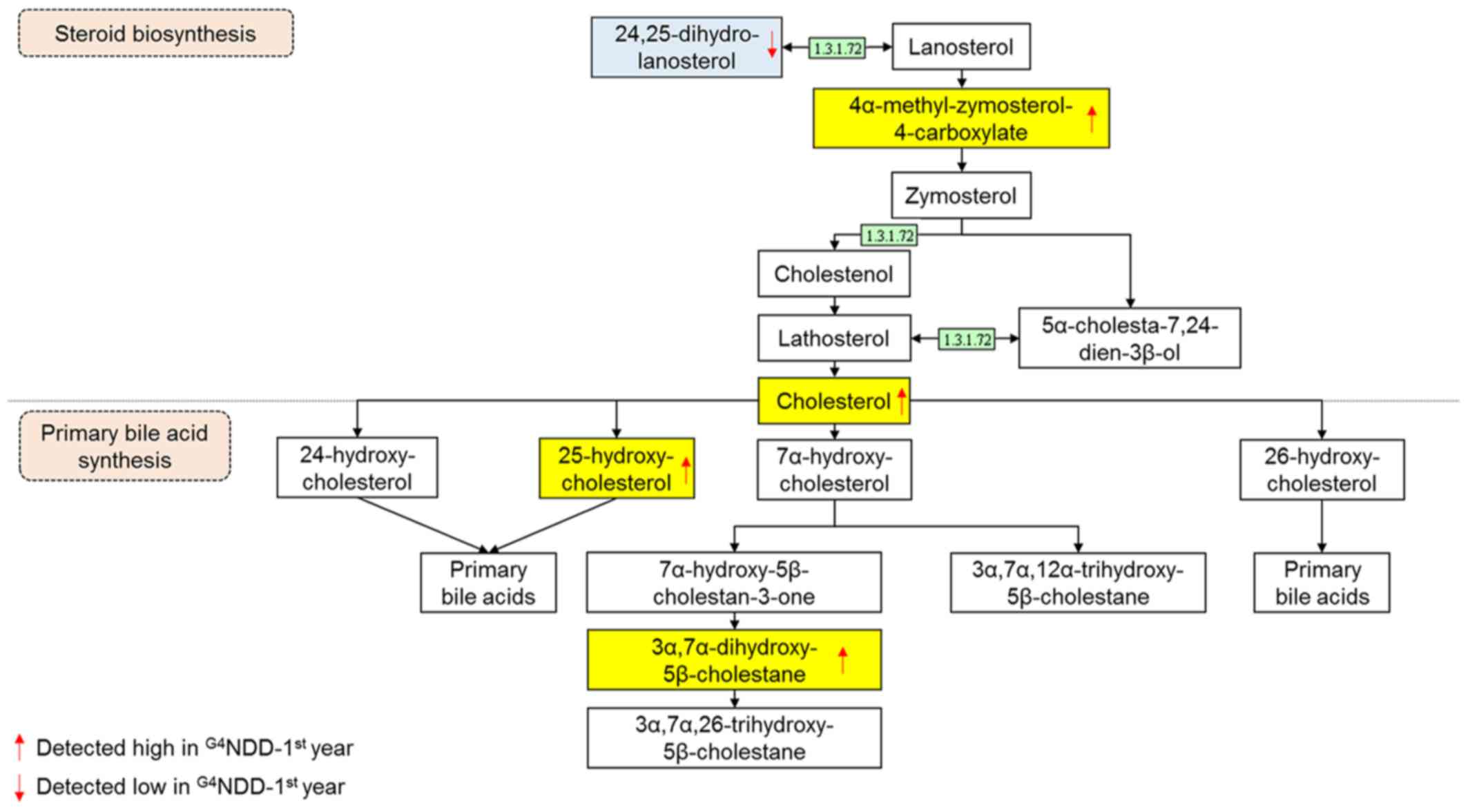
Prawitt J, Caron S and Staels B: Bile acid
metabolism and the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep.
11:160–166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li T, Francl JM, Boehme S, Ochoa A, Zhang
Y, Klaassen CD, Erickson SK and Chiang JY: Glucose and insulin
induction of bile acid synthesis: Mechanisms and implication in
diabetes and obesity. J Biol Chem. 287:1861–1873. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Tomkin GH and Owens D: Obesity diabetes
and the role of bile acids in metabolism. J Transl Int Med.
4:73–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Russell DW: Cholesterol biosynthesis and
metabolism. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 6:103–110. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Simons K and Ikonen E: How cells handle
cholesterol. Science. 290:1721–1726. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fernández C, Suárez Y, Ferruelo AJ,
Gómez-Coronado D and Lasunción MA: Inhibition of cholesterol
biosynthesis by Delta22-unsaturated phytosterols via competitive
inhibition of sterol Delta24-reductase in mammalian cells. Biochem
J. 366:109–119. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luu W, Zerenturk EJ, Kristiana I, Bucknall
MP, Sharpe LJ and Brown AJ: Signaling regulates activity of DHCR24,
the final enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. J Lipid Res. 55:410–420.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Berisha SZ, Serre D, Schauer P, Kashyap SR
and Smith JD: Changes in whole blood gene expression in obese
subjects with type 2 diabetes following bariatric surgery: A pilot
study. PLoS One. 6:e167292011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dai M, Zhu XL, Liu F, Xu QY, Ge QL, Jiang
SH, Yang XM, Li J, Wang YH, Wu QK, et al: Cholesterol synthetase
DHCR24 induced by insulin aggravates cancer invasion and
progesterone resistance in endometrial carcinoma. Sci Rep.
7:414042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moh A, Zhang W, Yu S, Wang J, Xu X, Li J
and Fu XY: STAT3 sensitizes insulin signaling by negatively
regulating glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta. Diabetes. 57:1227–1235.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weyer C, Bogardus C, Mott DM and Pratley
RE: The natural history of insulin secretory dysfunction and
insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
J Clin Invest. 104:787–794. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K,
Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE and Tataranni PA: Hypoadiponectinemia in
obesity and type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin
resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
86:1930–1935. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schiller J, Zschörnig O, Petković M,
Müller M, Arnhold J and Arnold K: Lipid analysis of human HDL and
LDL by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and (31)P-NMR. J Lipid Res.
42:1501–1508. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|