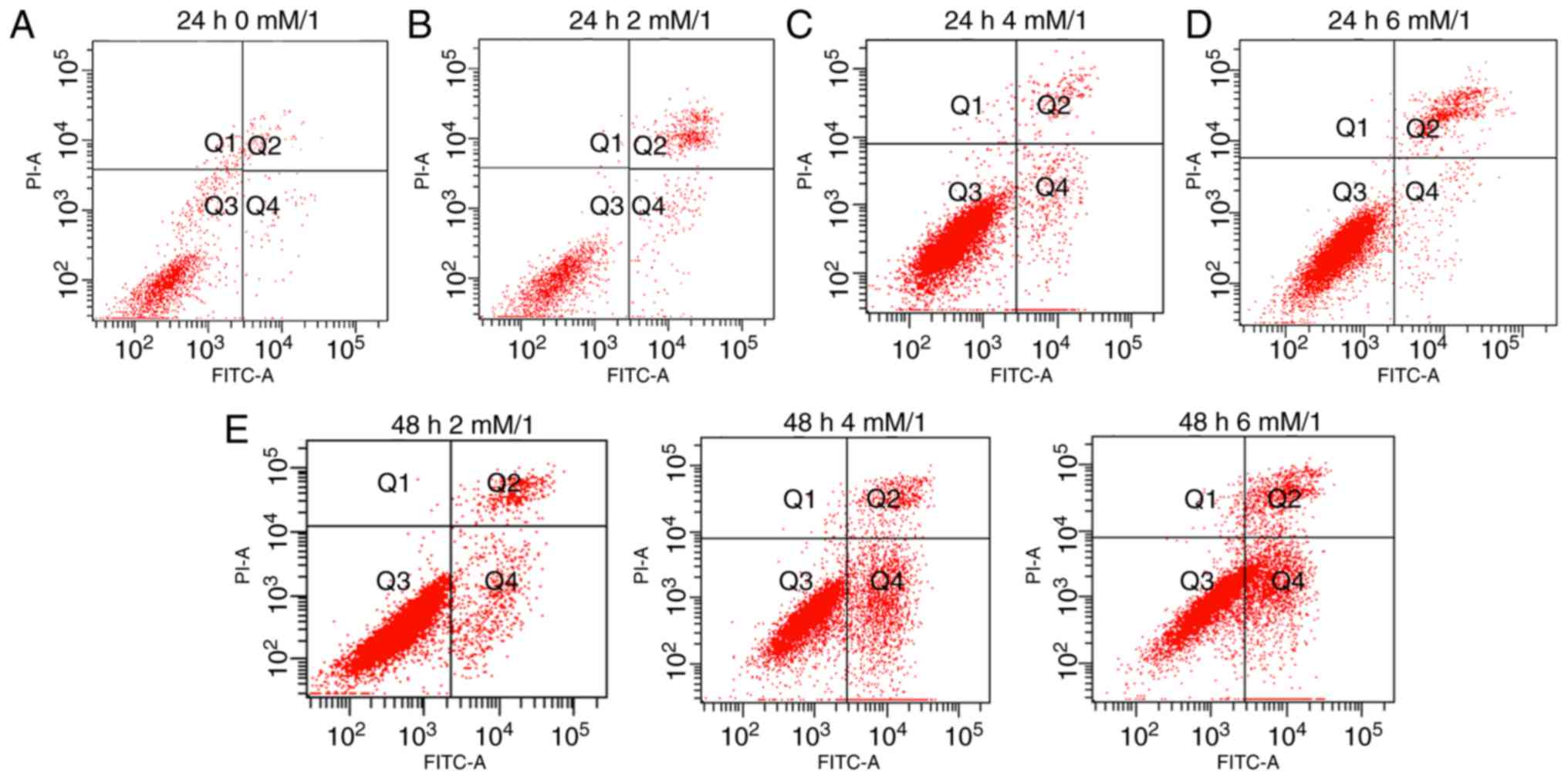
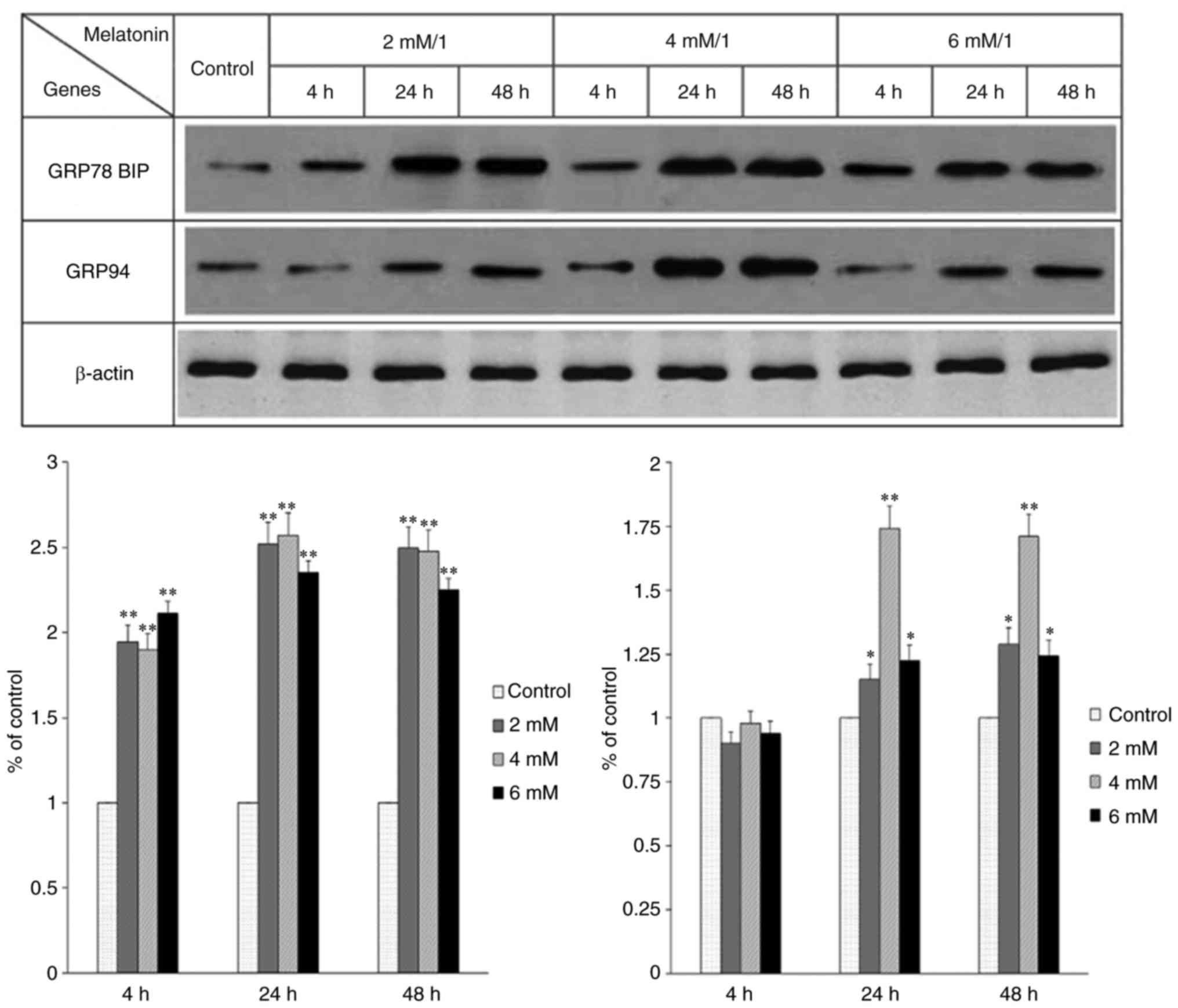
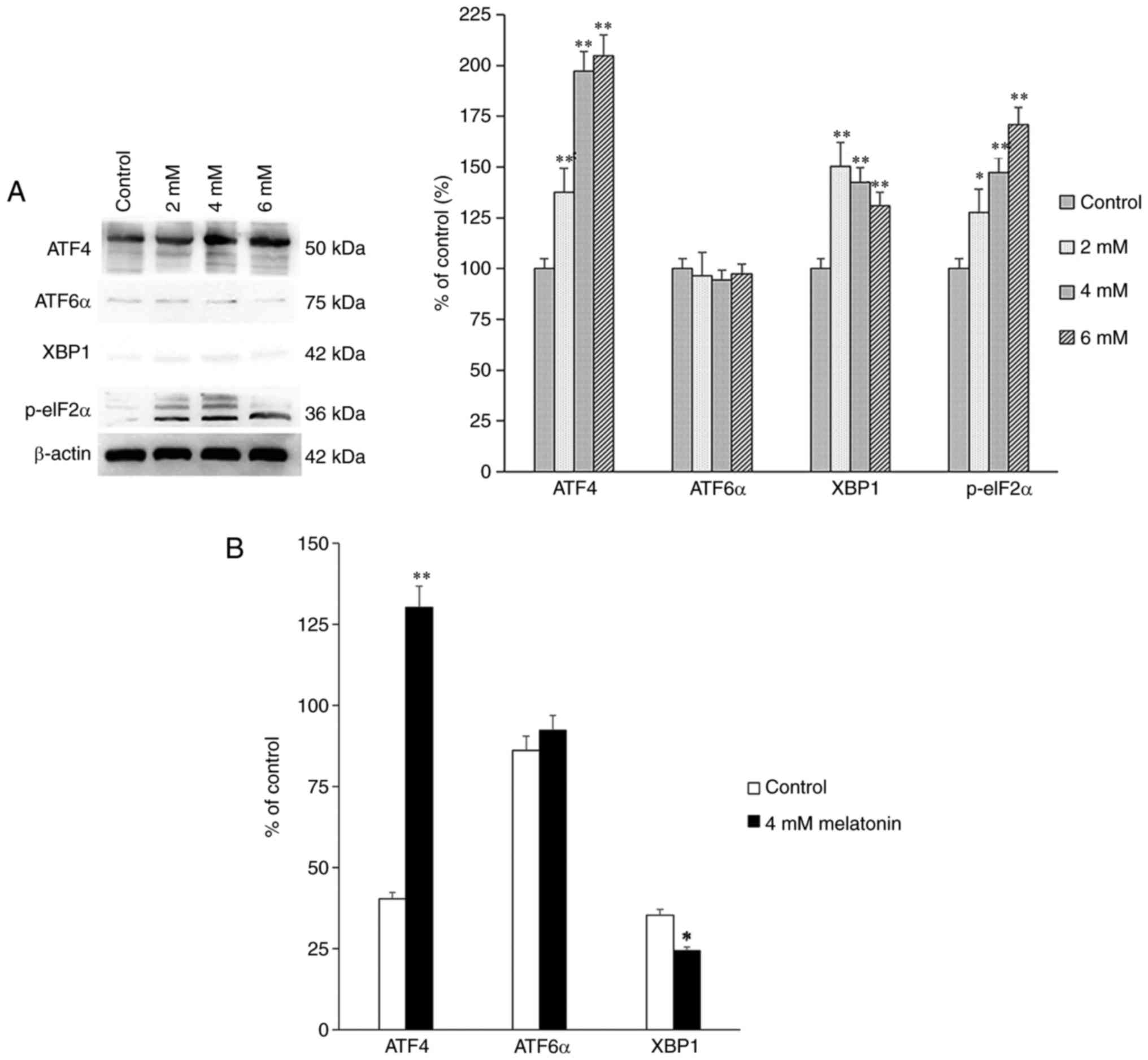
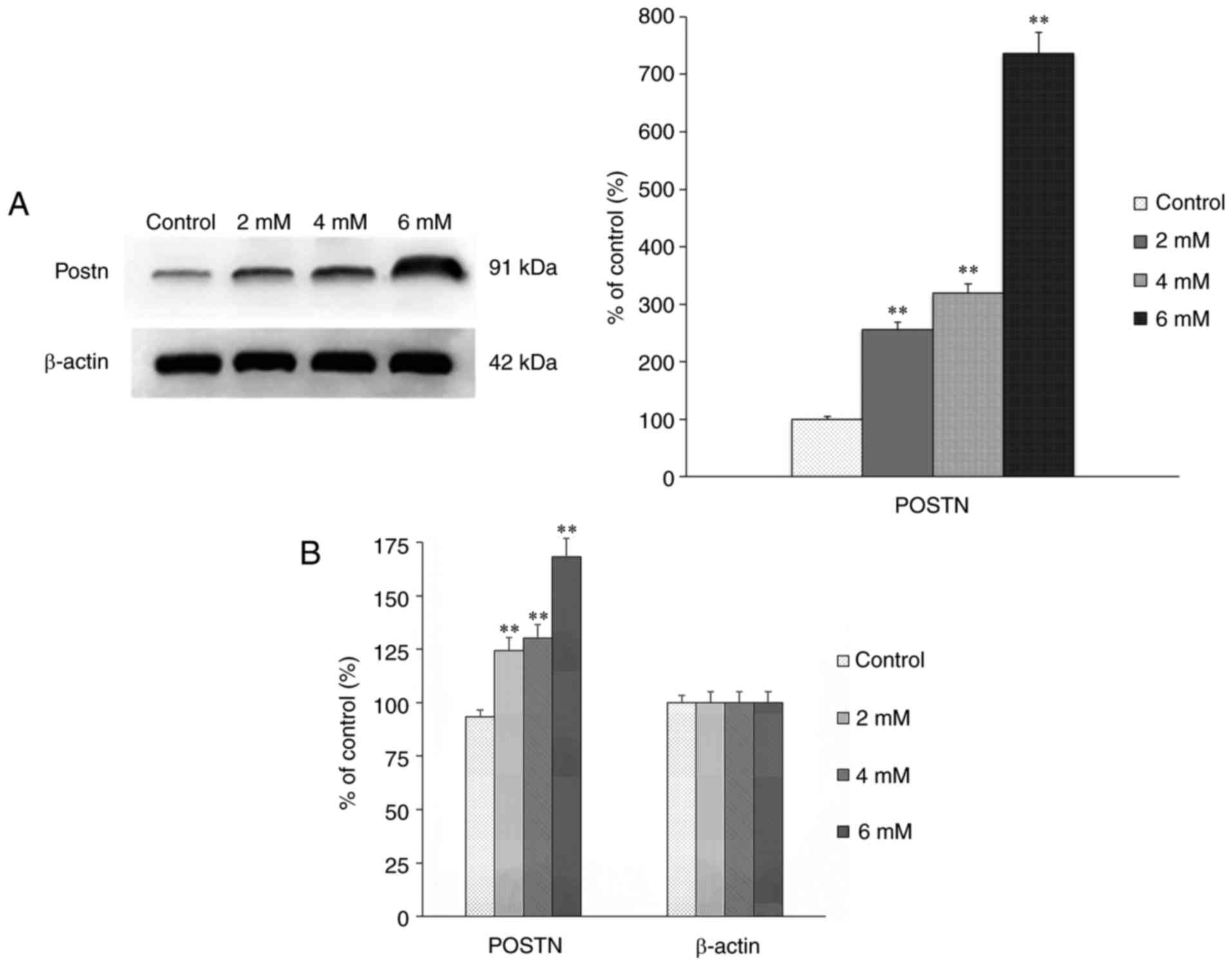
|
1
|
Thillard MJ: Deformations de la colonne
vertebrale consecutives à l'épiphysectomie chez le poussin. Extrait
C R Assoc Anat. 46:22–26. 1959.In French.
|
|
2
|
Liu L, Zhu Y, Xu Y and Reiter RJ:
Melatonin delays cell proliferation by inducing G1 and G2/M phase
arrest in a human osteoblastic cell line hFOB 1.19. J Pineal Res.
50:222–231. 2011.
|
|
3
|
Liu L, Zhu Y, Xu Y and Reiter RJ:
Prevention of ERK activation involves melatonin-induced G(1) and
G(2)/M phase arrest in the human osteoblastic cell line hFOB 1.19.
J Pineal Res. 53:60–66. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Moreira AJ, Ordoñez R, Cerski CT, Picada
JN, García-Palomo A, Marroni NP, Mauriz JL and González-Gallego J:
Melatonin activates endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in
rats with diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. PLoS
One. 10:e01445172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zha L, Fan L, Sun G, Wang H, Ma T, Zhong F
and Wei W: Melatonin sensitizes human hepatoma cells to endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Pineal Res. 52:322–331. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wongprayoon P and Govitrapong P: Melatonin
protects sh-sy5y neuronal cells against methamphetamine-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptotic cell death. Neurotox
Res. 31:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Espino J, Bejarano I, Paredes SD, Barriga
C, Reiter RJ, Pariente JA and Rodríguez AB: Melatonin is able to
delay endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in leukocytes
from elderly humans. AGE (Dordr). 33:497–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yi L, Zongyuan Y, Cheng G, Lingyun Z,
Guilian Y and Wei G: Quercetin enhances apoptotic effect of tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in
ovarian cancer cells through reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediated
CCAAT enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP)-death
receptor 5 pathway. Cancer Sci. 105:520–527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He L, Jang JH, Choi HG, Lee SM, Nan MH,
Jeong SJ, Dong Z, Kwon YT, Lee KS, Lee KW, et al: Oligomycin a
enhances apoptotic effect of TRAIL through CHOP-mediated death
receptor 5 expression. Mol Carcinog. 52:85–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiong SB, Mu TY, Wang GW and Jiang X:
Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in ma mMals. Protein Cell.
5:737–749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Faitova J, Krekac D, Hrstka R and Vojtesek
B: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
11:488–505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Phal HL: Signal transduction from the
endoplasmic reticulum to the cell nucleus. Physiol Rev. 79:683–701.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Espenshade PJ: SREBPs: Sterol-regulated
transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 15:973–976. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Davenport EL, Morgan GJ and Davies FE:
Untangling the unfolded protein response. Cell Cycle. 7:865–869.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Malhotra JD and Kaufman RJ: The
endoplasmic reticulum and the unfolded protein response. Semin Cell
DevBiol. 18:716–731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gupta S, Deepti A, Deegan S, Lisbona F,
Hetz C and Samali A: HSP72 protects cells from ER stress-induced
apoptosis via enhancement of IRE1alpha-XBP1 signaling through a
physical interaction. PLoS Biol. 8:e10004102010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Long ZS: Expression and significance of
CHOP related ERS after acute spinal cord injury in rats. Chin J
Spine Spinal Cord. 19:458–463. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
19
|
Szegezdi E, Duffy A, O'Mahoney ME, Logue
SE, Mylotte LA, O'brien T and Samali A: ER stress contributes to
ischemia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 349:1406–1411. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Takeda K, Shimozono R, Noguchi T, Umeda T,
Morimoto Y, Naguro I, Tobiume K, Saitoh M, Matsuzawa A and Ichijo
H: Apoptosis signal-regulation kinase (ASK) 2 functions as a
mitogen-activated protein kinase in a heteromeric complex with
ASK1. J Biol Chem. 282:7522–7531. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li F, Guo Y, Sun S, Jiang X, Tang B, Wang
Q and Wang L: Free cholesterol-induced macrophage apoptosis is
mediated by inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha-regulated activation
of Jun N-terminal kinase. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai.
40:226–234. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matsuzawa A, Saegusa K, Noguchi T,
Sadamitsu C, Nishitoh H, Nagai S, Koyasu S, Matsumoto K, Takeda K
and Ichijo H: Ros-dependent activation of the TRAF6-ASK1-p38
pathway is selectively required for TLR4-mediated innate immunity.
Nat Immunol. 6:587–592. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hoersch S and Andrade-Navarro MA:
Periostin shows increased evolutionary plasticity in its
alternatively spliced region. BMC Evol Biol. 10:302010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morra L and Moch H: Periostin expression
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: A review and an
update. Virchows Arch. 459:465–475. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Merle B, Bouet G, Rousseau JC, Bertholon C
and Garnero P: Periostin and transforming growth factor β-induced
protein (TGF βIp) are both expressed by osteoblasts and
osteoclasts. Cell Biol Int. 38:398–404. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Subramaniam M, Jalal SM, Rickard DJ,
Harris SA, Bolander ME and Spelsberg TC: Further characterization
of human fetal osteoblastic hFOB 1.19 and hFOB/ER alpha cells: Bone
formation in vivo and karyotype analysis using multicolor
fluorescent in situ hybridization. J Cell Biochem. 87:9–15. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pizarro JG, Yeste-Velasco M, Esparza JL,
Verdaguer E, Pallàs M, Camins A and Folch J: The antiproliferative
activity of melatonin in B65 rat dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells
is related to the downregulation of cell cycle-related genes. J
Pineal Res. 45:8–16. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reiter RJ, Tan DX and Fuentes-Broto L:
Melatonin: A multi-tasking molecule. Prog Brain Res. 181:127–151.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Akbarzadeh M, Rahbarghazi R, Nabat E,
Movassaghpour AA, Shanehbandi D, Faramarzian Azimi Maragheh B,
Matluobi D, Barazvan B, Kazemi M, Samadi N and Nouri M: The impact
of different extracellular matrices on melatonin effect in
proliferation and stemness properties of ovarian cancer cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 87:288–295. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bavithra S, Selvakumar K, Sundareswaran L
and Arunakaran J: Neuroprotective effect of melatonin against pcbs
induced behavioural, molecular and histological changes in cerebral
cortex of adult male wistar rats. Neurochem Res. 42:428–438. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Khan S, Adhikari JS, Rizvi MA and
Chaudhury NK: Melatonin attenuates 60 Co γ-ray-induced
hematopoietic, immunological and gastrointestinal injuries in
C57BL/6 male mice. Environ Toxicol. 32:501–518. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Satomura K, Tobiume S, Tokuyama R,
Yamasaki Y, Kudoh K, Maeda E and Nagayama M: Melatonin at
pharmacological doses enhances human osteoblastic differentiation
in vitro and promotes mouse cortical bone formation in vivo. J
Pineal Res. 42:231–239. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Man GC, Wang WW, Yeung BH, Lee SK, Ng BK,
Hung WY, Wong JH, Ng TB, Qiu Y and Cheng JC: Abnormal proliferation
and differentiation of osteoblasts from girls with adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis to melatonin. J Pineal Res. 49:69–77.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nakade O, Koyama H, Ariji H, Yajima A and
Kaku T: Melatonin stimulates proliferation and type I collagen
synthesis in human bone cells in vitro. J Pineal Res. 27:106–110.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sanchez-Hidalgo M, Lu Z, Tan DX, Maldonado
MD, Reiter RJ and Gregerman RI: Melatonin inhibits fatty
acid-induced triglyceride accumulation in ROS17/2.8 cells:
Implications for osteoblast differentiation and osteoporosis. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 292:R2208–R2215. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Anelli T and Sitia R: Protein quality
control in the early secretory pathway. EMBO J. 27:315–327. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pizzo P and Pozzan T:
Mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum choreography: Structure and
signaling dynamics. Trends Cell Biol. 17:511–517. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hamamura K and Yokota H: Stress to
endoplasmic reticulum of mouse osteoblasts induces apoptosis and
transcriptional activation for bone remodeling. FEBS Lett.
581:1769–1774. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wysokinski D, Pawlowska E and Blasiak J:
RUNX2: A master bone growth regulator that may be involved in the
DNA damage response. DNA Cell Biol. 34:305–315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yu SH and Hong A: Runx2 promotes
osteogenic differentiating C2C12 cells through inhibiting
macroautophagy. Chin J Pathophysiol. 29:481–487. 2013.In
Chinese.
|
|
42
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fernández A, Ordóñez R, Reiter RJ,
González-Gallego J and Mauriz JL: Melatonin and endoplasmic
reticulum stress: Relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal
Res. 59:292–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang HM and Zhang Y: Melatonin: A
well-documented antioxidant with conditional pro-oxidant actions. J
Pineal Res. 57:131–146. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Brown MK and Naidoo N: The UPR and the
anti-oxidant response: Relevance to sleep and sleep loss. Mol
Neurobiol. 42:103–113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bizzarri M, Proietti S, Cucina A and
Reiter RJ: Molecular mechanisms of the pro-apoptotic actions of
melatonin in cancer: A review. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
17:1483–1496. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tabas I and Ron D: Integrating the
mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Nat Cell Biol. 13:184–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li Y, Guo Y, Tang J, Jiang J and Chen Z:
New insights into the roles of CHOP-induced apoptosis in ER stress.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 46:629–640. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fu HY, Okada K, Liao Y, Tsukamoto O,
Isomura T, Asai M, Sawada T, Okuda K, Asano Y, Sanada S, et al:
Ablation of C/EBP homologous protein attenuates endoplasmic
reticulum-mediated apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction induced by
pressure overload. Circulation. 122:361–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hoersch S and Andrade-Navarro MA:
Periostin shows increased evolutionary plasticity in its
alternatively spliced region. BMC Evol Biol. 10:302010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lai E, Teodoro T and Volchuk A:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Signaling the unfolded protein
response. Physiology (Bethesda). 22:193–201. 2007.
|
|
52
|
Morra L and Moch H: Periostin expression
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: A review and an
update. Virchows Arch. 459:465–475. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Erkan M, Kleeff J, Gorbachevski A, Reiser
C, Mitkus T, Esposito I, Giese T, Büchler MW, Giese NA and Friess
H: Periostin creates a tumor-supportive microenvironment in the
pancreas by sustaining fibrogenic stellate cell activity.
Gastroenterology. 132:1447–1464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tai IT, Dai M and Chen LB: Periostin
induction in tumor cell line explants and inhibition of in vitro
cell growth by anti-periostin antibodies. Carcinogenesis.
26:908–915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gillan L, Matei D, Fishman DA, Gerbin CS,
Karlan BY and Chang DD: Periostin secreted by epithelial ovarian
carcinoma is a ligand for alpha(V)beta(3) and alpha(V)beta(5)
integrins and promotes cell motility. Cancer Res. 62:5358–5364.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kudo Y, Ogawa I, Kitajima S, Kitagawa M,
Kawai H, Gaffney PM, Miyauchi M and Takata T: Periostin promotes
invasion and anchorage-independent growth in the metastatic process
of head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 66:6928–6935. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Siriwardena BS, Kudo Y, Ogawa I, Kitagawa
M, Kitajima S, Hatano H, Tilakaratne WM, Miyauchi M and Takata T:
Periostin is frequently overexpressed and enhances invasion and
angiogenesis in oral cancer. Br J Cancer. 95:1396–1403. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shao R, Bao S, Bai X, Blanchette C,
Anderson RM, Dang T, Gishizky ML, Marks JR and Wang XF: Acquired
expression of periostin by human breast cancers promotes tumor
angiogenesis through up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 2 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 24:3992–4003. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li B, Wang L and Chi B: Upregulation of
periostin prevents p53-mediated apoptosis in SGC-7901 gastric
cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. 40:1677–1683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Aukkarasongsup P, Haruyama N, Matsumoto T,
Shiga M and Moriyama K: Periostin inhibits hypoxia-induced
apoptosis in human periodontal ligament cells via TGF-β signaling.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:126–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Luo JH, Zhou J and Gao Y: Correlation
between periostin and SNCG and esophageal cancer invasion,
infiltration and apoptosis. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:516–519. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Stansfield WE, Andersen NM, Tang RH and
Selzman CH: Periostin is a novel factor in cardiac remodeling after
experimental and clinical unloading of the failing heart. Ann
Thorac Surg. 88:1916–1921. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|