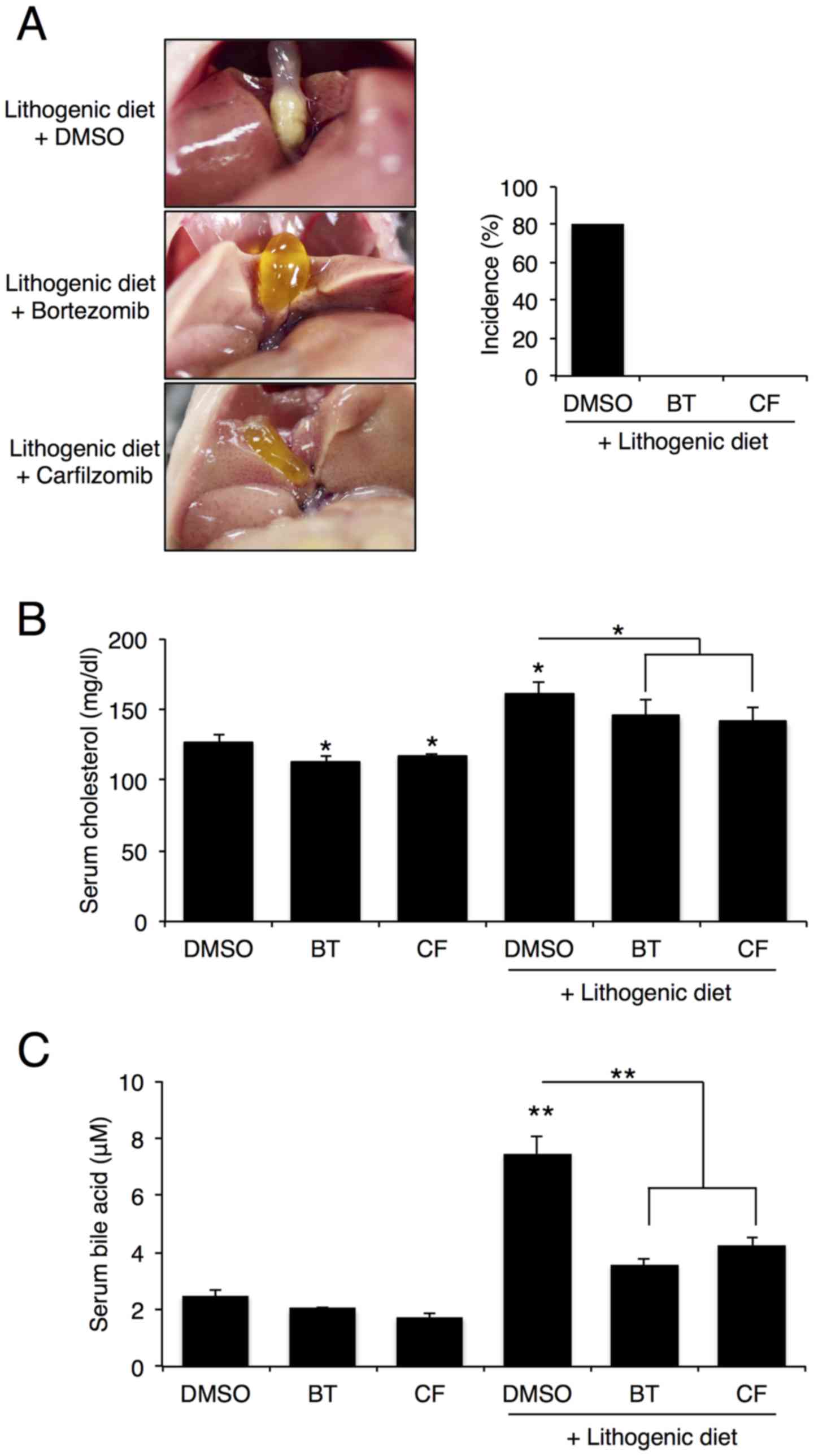
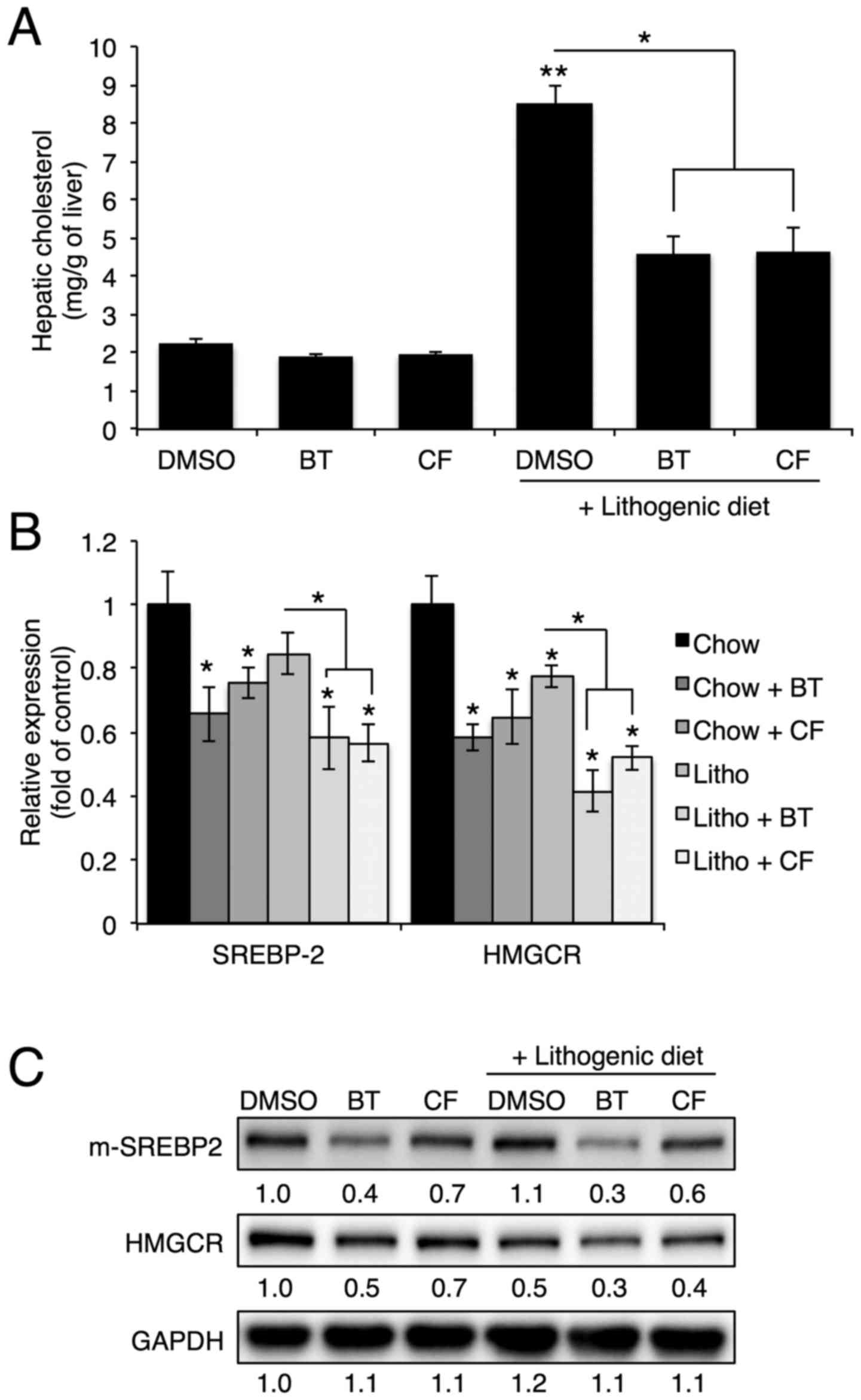
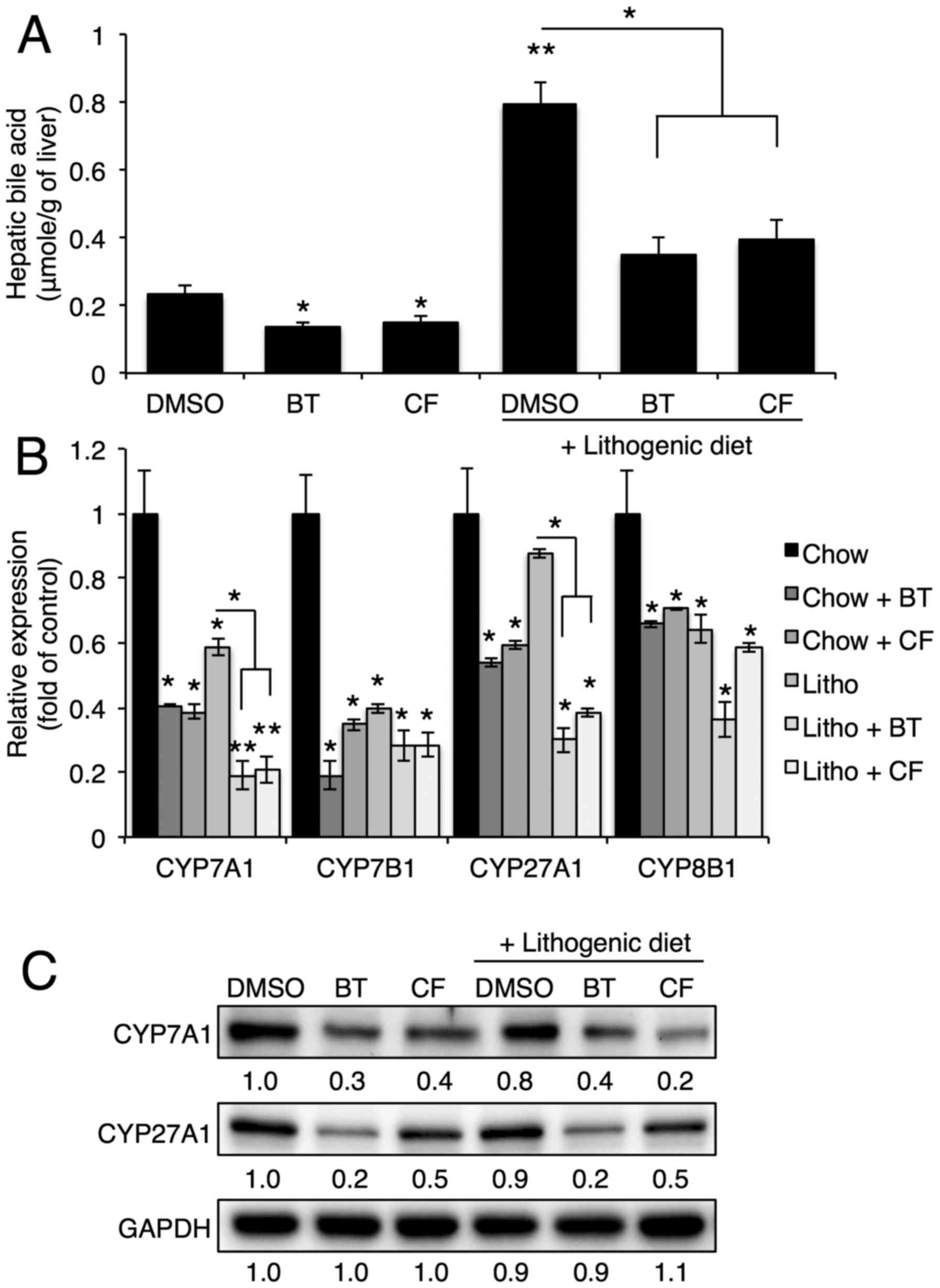
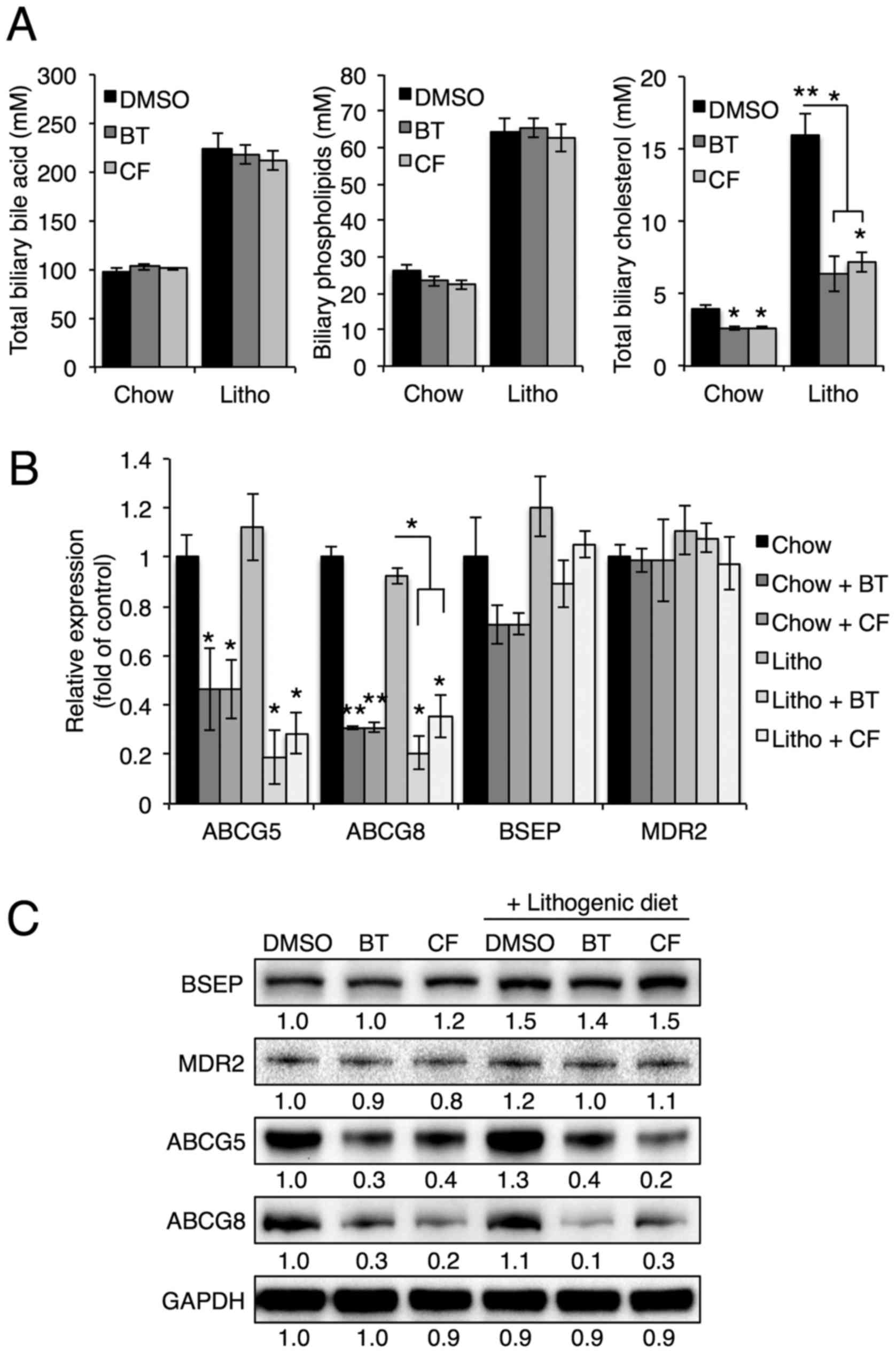
|
1
|
Stinton LM and Shaffer EA: Epidemiology of
gallbladder disease: cholelithiasis and cancer. Gut Liver.
6:172–187. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kosters A, Jirsa M and Groen AK: Genetic
background of cholesterol gallstone disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1637:1–19. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Portincasa P, Moschetta A and Palasciano
G: Cholesterol gallstone disease. Lancet. 368:230–239. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tao R, Xiong X, DePinho RA, Deng CX and
Dong XC: Hepatic SREBP-2 and cholesterol biosynthesis are regulated
by FoxO3 and Sirt6. J Lipid Res. 54:2745–2753. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chiang JY: Bile acids: regulation of
synthesis. J Lipid Res. 50:1955–1966. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Van Erpecum KJ: Pathogenesis of
cholesterol and pigment gallstones: an update. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 35:281–287. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ahmed MH, Hamad MA, Routh C and Connolly
V: Statins as potential treatment for cholesterol gallstones: an
attempt to understand the underlying mechanism of actions. Expert
Opin Pharmacother. 12:2673–2681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Merzon E, Weiss NS, Lustman AJ, Elhayani
A, Dresner J and Vinker S: Statin administration and risk of
cholecystectomy: a population-based case-control study. Expert Opin
Drug Saf. 9:539–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cariati A and Piromalli E: Limits and
perspective of oral therapy with statins and aspirin for the
prevention of symptomatic cholesterol gallstone disease. Expert
Opin Pharmacother. 13:1223–1227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kotb MA: Molecular mechanisms of
ursodeoxycholic acid toxicity & side effects: ursodeoxycholic
acid freezes regeneration & induces hibernation mode. Int J Mol
Sci. 13:8882–8914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Adams J, Palombella VJ and Elliott PJ:
Proteasome inhibition: a new strategy in cancer treatment. Invest
New Drugs. 18:109–121. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Field-Smith A, Morgan GJ and Davies FE:
Bortezomib (Velca-detrade mark) in the treatment of multiple
myeloma. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2:271–279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Oliva J, French SW, Li J and Bardag-Gorce
F: Proteasome inhibitor treatment reduced fatty acid,
triacylglycerol and cholesterol synthesis. Exp Mol Pathol.
93:26–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Anan A, Baskin-Bey ES, Isomoto H, Mott JL,
Bronk SF, Albrecht JH and Gores GJ: Proteasome inhibition
attenuates hepatic injury in the bile duct-ligated mouse. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 291:G709–G716. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park WJ, Kim SY, Kim YR and Park JW:
Bortezomib alleviates drug-induced liver injury by regulating
CYP2E1 gene transcription. Int J Mol Med. 37:613–622. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nawrocki ST, Carew JS, Pino MS, Highshaw
RA, Dunner K Jr, Huang P, Abbruzzese JL and McConkey DJ: Bortezomib
sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res. 65:11658–11666. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Codony-Servat J, Tapia MA, Bosch M, Oliva
C, Domingo-Domenech J, Mellado B, Rolfe M, Ross JS, Gascon P,
Rovira A, et al: Differential cellular and molecular effects of
bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor, in human breast cancer cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 5:665–675. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kondagunta GV, Drucker B, Schwartz L,
Bacik J, Marion S, Russo P, Mazumdar M and Motzer RJ: Phase II
trial of bortezomib for patients with advanced renal cell
carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 22:3720–3725. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Papandreou CN, Daliani DD, Nix D, Yang H,
Madden T, Wang X, Pien CS, Millikan RE, Tu SM, Pagliaro L, et al:
Phase I trial of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in patients
with advanced solid tumors with observations in
androgen-independent prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:2108–2121.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dick LR and Fleming PE: Building on
bortezomib: second-generation proteasome inhibitors as anti-cancer
therapy. Drug Discov Today. 15:243–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wooton-Kee CR, Coy DJ, Athippozhy AT, Zhao
T, Jones BR and Vore M: Mechanisms for increased expression of
cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (Cyp7a1) in lactating rats.
Hepatology. 51:277–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gupta S, Stravitz RT, Dent P and Hylemon
PB: Down-regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) gene
expression by bile acids in primary rat hepatocytes is mediated by
the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. J Biol Chem. 276:15816–15822.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stroup D: Kinase/phosphatase regulation of
CYP7A1. Front Biosci. 10:1678–1692. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Repa JJ, Berge KE, Pomajzl C, Richardson
JA, Hobbs H and Mangelsdorf DJ: Regulation of ATP-binding cassette
sterol transporters ABCG5 and ABCG8 by the liver X receptors alpha
and beta. J Biol Chem. 277:18793–18800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamazaki Y, Yasui K, Hashizume T, Suto A,
Mori A, Murata Y, Yamaguchi M, Ikari A and Sugatani J: Involvement
of a cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent signal in the
diet-induced canalicular trafficking of adenosine
triphosphate-binding cassette transporter g5/g8. Hepatology.
62:1215–1226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moschetta A, Bookout AL and Mangelsdorf
DJ: Prevention of cholesterol gallstone disease by FXR agonists in
a mouse model. Nat Med. 10:1352–1358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bertolotti M, Gabbi C, Anzivino C, Carulli
L and Carulli N: Changes in bile acid synthesis in gallstone
disease: cause, consequence, or neither? Hepatology. 46:1664–1665.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li T, Jahan A and Chiang JY: Bile acids
and cytokines inhibit the human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase
gene via the JNK/c-jun pathway in human liver cells. Hepatology.
43:1202–1210. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Qi Y, Tian B, Chen D, Gao H, Xi C,
Xing Y and Yuan Z: Maternal protein restriction induces alterations
in hepatic tumor necrosis factor-α/CYP7A1 signaling and disorders
regulation of cholesterol metabolism in the adult rat offspring. J
Clin Biochem Nutr. 55:40–47. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Choi CH, Lee BH, Ahn SG and Oh SH:
Proteasome inhibition-induced p38 MAPK/ERK signaling regulates
autophagy and apoptosis through the dual phosphorylation of
glycogen synthase kinase 3β. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
418:759–764. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang HQ, Liu BQ, Gao YY, Meng X, Guan Y,
Zhang HY and Du ZX: Inhibition of the JNK signalling pathway
enhances proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis of kidney cancer
cells by suppression of BAG3 expression. Br J Pharmacol.
158:1405–1412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Uppal H, Zhai Y, Gangopadhyay A, Khadem S,
Ren S, Moser JA and Xie W: Activation of liver X receptor
sensitizes mice to gallbladder cholesterol crystallization.
Hepatology. 47:1331–1342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang F, Hu Y, Huang P, Toleman CA,
Paterson AJ and Kudlow JE: Proteasome function is regulated by
cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase through phosphorylation of
Rpt6. J Biol Chem. 282:22460–22471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hegde AN, Goldberg AL and Schwartz JH:
Regulatory subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinases are degraded
after conjugation to ubiquitin: a molecular mechanism underlying
long-term synaptic plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:7436–7440. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin JT, Chang WC, Chen HM, Lai HL, Chen
CY, Tao MH and Chern Y: Regulation of feedback between protein
kinase A and the proteasome system worsens Huntington's disease.
Mol Cell Biol. 33:1073–1084. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Takenokuchi M, Miyamoto K, Saigo K and
Taniguchi T: Bortezomib causes ER stress-related death of acute
promyelocytic leukemia cells through excessive accumulation of
PML-RARA. Anticancer Res. 35:3307–3316. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meregalli C, Carozzi VA, Sala B, Chiorazzi
A, Canta A, Oggioni N, Rodriguez-Menendez V, Ballarini E, Ceresa C,
Nicolini G, et al: Bortezomib-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in
human multiple myeloma-bearing mice. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.
29:115–124. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu G, Friggeri A, Yang Y, Park Y-J,
Tsuruta Y and Abraham E: miR-147, a microRNA that is induced upon
Toll-like receptor stimulation, regulates murine macrophage
inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:15819–15824.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|