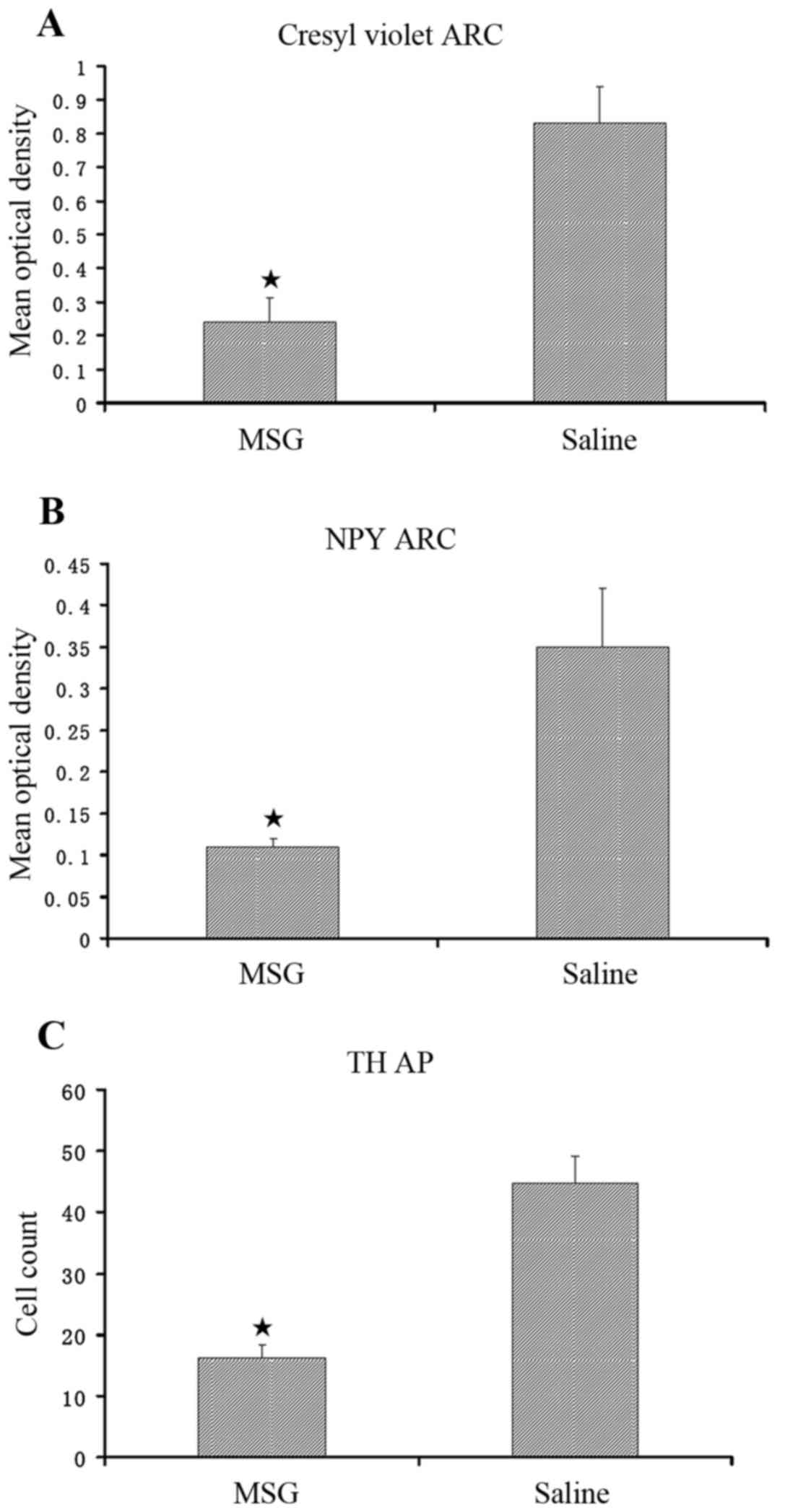
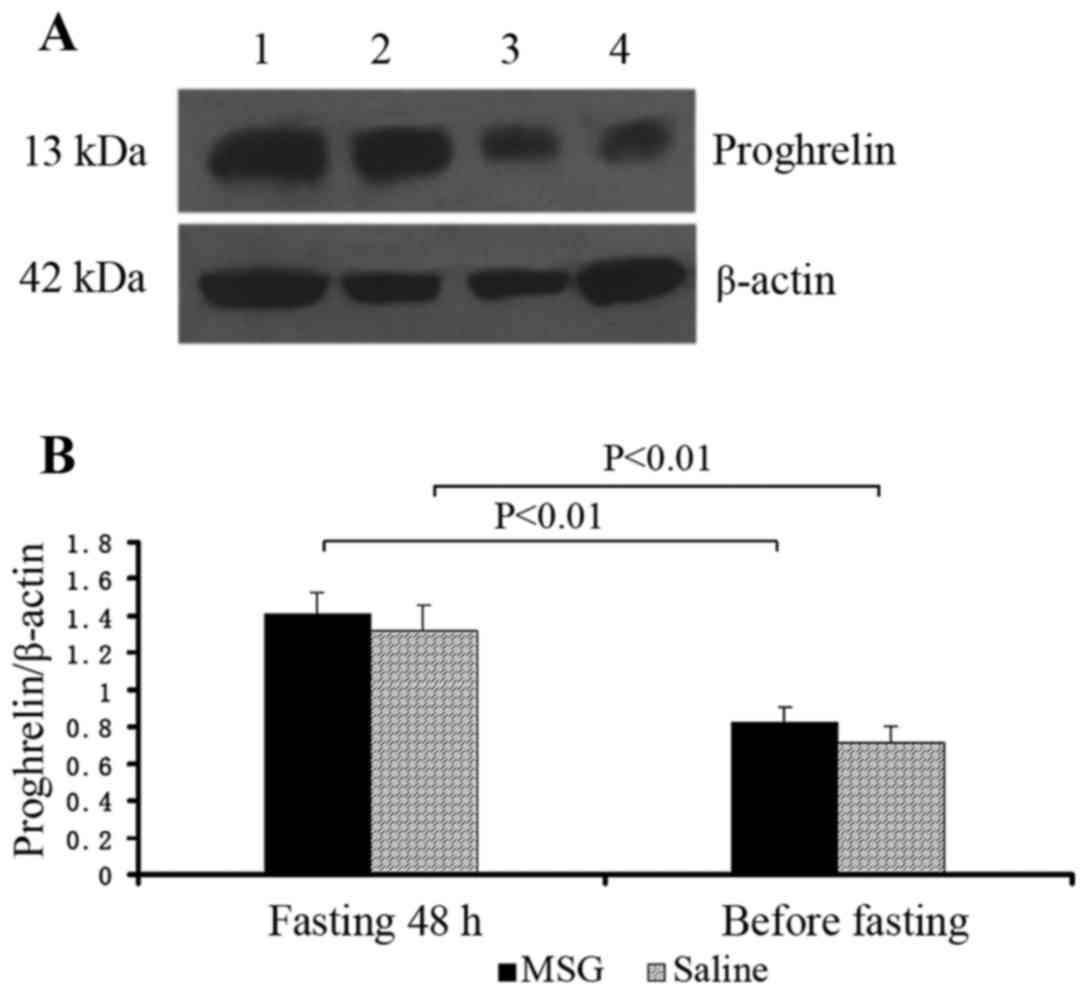
|
1
|
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M,
Matsuo H and Kangawa K: Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing
acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 402:656–660. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, Sawaguchi A,
Mondal MS, Suganuma T, Matsukura S, Kangawa K and Nakazato M:
Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is
synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the
gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology.
141:4255–4261. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mizutani M, Atsuchi K, Asakawa A, Matsuda
N, Fujimura M, Inui A, Kato I and Fujimiya M: Localization of acyl
ghrelin- and des-acyl ghrelin-immunoreactive cells in the rat
stomach and their responses to intragastric pH. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 297:G974–G980. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tschöp M, Weyer C, Tataranni PA,
Devanarayan V, Ravussin E and Heiman ML: Circulating ghrelin levels
are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes. 50:707–709. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jeon TY, Lee S, Kim HH, Kim YJ, Son HC,
Kim DH and Sim MS: Changes in plasma ghrelin concentration
immediately after gastrectomy in patients with early gastric
cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:5392–5396. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu S, Guan JL, Wang QP, Uehara K, Yamada
S, Goto N, Date Y, Nakazato M, Kojima M, Kangawa K, et al:
Immunocytochemical observation of ghrelin-containing neurons in the
rat arcuate nucleus. Neurosci Lett. 321:157–160. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cowley MA, Smith RG, Diano S, Tschöp M,
Pronchuk N, Grove KL, Strasburger CJ, Bidlingmaier M, Esterman M,
Heiman ML, et al: The distribution and mechanism of action of
ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit
regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron. 37:649–661. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley
RJ and Baskin DG: Central nervous system control of food intake.
Nature. 404:661–671. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abizaid A and Horvath TL: Brain circuits
regulating energy homeostasis. Regul Pept. 149:3–10. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang L, Saint-Pierre DH and Taché Y:
Peripheral ghrelin selectively increases Fos expression in
neuropeptide Y-synthesizing neurons in mouse hypothalamic arcuate
nucleus. Neurosci Lett. 325:47–51. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kamegai J, Tamura H, Shimizu T, Ishii S,
Sugihara H and Wakabayashi I: Chronic central infusion of ghrelin
increases hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and Agouti-related protein
mRNA levels and body weight in rats. Diabetes. 50:2438–2443. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tschöp M, Flora DB, Mayer JP and Heiman
ML: Hypophysectomy prevents ghrelin-induced adiposity and increases
gastric ghrelin secretion in rats. Obes Res. 10:991–999. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS,
Schmidova K, Wisse BE and Weigle DS: A preprandial rise in plasma
ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans.
Diabetes. 50:1714–1719. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tschöp M, Wawarta R, Riepl RL, Friedrich
S, Bidlingmaier M, Landgraf R and Folwaczny C: Post-prandial
decrease of circulating human ghrelin levels. J Endocrinol Invest.
24:RC19–RC21. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Williams DL and Cummings DE: Regulation of
ghrelin in physiologic and pathophysiologic states. J Nutr.
135:1320–1325. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Olney JW: Brain lesions, obesity, and
other disturbances in mice treated with monosodium glutamate.
Science. 164:719–721. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Perez VJ and Olney JW: Accumulation of
glutamic acid in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus of the
infant mouse followng subcutaneous administration of monosodium
glutamate. J Neurochem. 19:1777–1782. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takasaki Y: Studies on brain lesion by
administration of monosodium L-glutamate to mice. I. Brain lesions
in infant mice caused by administration of monosodium L-glutamate.
Toxicology. 9:293–305. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nikoletseas MM: Obesity in exercising,
hypophagic rats treated with monosodium glutamate. Physiol Behav.
19:767–773. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Small CJ, Liu YL, Stanley SA, Connoley IP,
Kennedy A, Stock MJ and Bloom SR: Chronic CNS administration of
Agouti-related protein (Agrp) reduces energy expenditure. Int J
Obes Relat Metab Disord. 27:530–533. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yasuda T, Masaki T, Kakuma T and
Yoshimatsu H: Centrally administered ghrelin suppresses sympathetic
nerve activity in brown adipose tissue of rats. Neurosci Lett.
349:75–78. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mercer JG, Moar KM, Ross AW, Hoggard N and
Morgan PJ: Photoperiod regulates arcuate nucleus POMC, AGRP, and
leptin receptor mRNA in Siberian hamster hypothalamus. Am J Physiol
Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 278:R271–R281. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ebihara K, Ogawa Y, Katsuura G, Numata Y,
Masuzaki H, Satoh N, Tamaki M, Yoshioka T, Hayase M, Matsuoka N, et
al: Involvement of agouti-related protein, an endogenous antagonist
of hypothalamic melanocortin receptor, in leptin action. Diabetes.
48:2028–2033. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kristensen P, Judge ME, Thim L, Ribel U,
Christjansen KN, Wulff BS, Clausen JT, Jensen PB, Madsen OD, Vrang
N, et al: Hypothalamic CART is a new anorectic peptide regulated by
leptin. Nature. 393:72–76. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bunyan J, Murrell EA and Shah PP: The
induction of obesity in rodents by means of monosodium glutamate.
Br J Nutr. 35:25–39. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bamshad M, Aoki VT, Adkison MG, Warren WS
and Bartness TJ: Central nervous system origins of the sympathetic
nervous system outflow to white adipose tissue. Am J Physiol.
275:R291–R299. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bowers RR, Festuccia WTL, Song CK, Shi H,
Migliorini RH and Bartness TJ: Sympathetic innervation of white
adipose tissue and its regulation of fat cell number. Am J Physiol
Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 286:R1167–R1175. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shi H and Bartness TJ: Neurochemical
phenotype of sympathetic nervous system outflow from brain to white
fat. Brain Res Bull. 54:375–385. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song CK and Bartness TJ: CNS sympathetic
outflow neurons to white fat that express MEL receptors may mediate
seasonal adiposity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
281:R666–R672. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Druce MR, Wren AM, Park AJ, Milton JE,
Patterson M, Frost G, Ghatei MA, Small C and Bloom SR: Ghrelin
increases food intake in obese as well as lean subjects. Int J
Obes. 29:1130–1136. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wren AM, Small CJ, Ward HL, Murphy KG,
Dakin CL, Taheri S, Kennedy AR, Roberts GH, Morgan DG, Ghatei MA,
et al: The novel hypothalamic peptide ghrelin stimulates food
intake and growth hormone secretion. Endocrinology. 141:4325–4328.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Davies JS, Kotokorpi P, Eccles SR, Barnes
SK, Tokarczuk PF, Allen SK, Whitworth HS, Guschina IA, Evans BA,
Mode A, et al: Ghrelin induces abdominal obesity via
GHS-R-dependent lipid retention. Mol Endocrinol. 23:914–924. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tschöp M, Smiley DL and Heiman ML: Ghrelin
induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 407:908–913. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cummings DE, Weigle DS, Frayo RS, Breen
PA, Ma MK, Dellinger EP and Purnell JQ: Plasma ghrelin levels after
diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med.
346:1623–1630. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stengel A, Goebel M, Wang L and Taché Y:
Ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and nesfatin-1 in gastric X/A-like cells:
Role as regulators of food intake and body weight. Peptides.
31:357–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Guan JL, Wang QP, Kageyama H, Takenoya F,
Kita T, Matsuoka T, Funahashi H and Shioda S: Synaptic interactions
between ghrelin- and neuropeptide Y-containing neurons in the rat
arcuate nucleus. Peptides. 24:1921–1928. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS,
Schmidova K, Wisse BE and Weigle DS: A preprandial rise in plasma
ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans.
Diabetes. 50:1714–1719. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Luquet S, Perez FA, Hnasko TS and Palmiter
RD: NPY/AgRP neurons are essential for feeding in adult mice but
can be ablated in neonates. Science. 310:683–685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Luquet S, Phillips CT and Palmiter RD:
NPY/AgRP neurons are not essential for feeding responses to
glucoprivation. Peptides. 28:214–225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Tamura H, Kamegai J, Shimizu T, Ishii S,
Sugihara H and Oikawa S: Ghrelin stimulates GH but not food intake
in arcuate nucleus ablated rats. Endocrinology. 143:3268–3275.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Faulconbridge LF, Grill HJ, Kaplan JM and
Daniels D: Caudal brainstem delivery of ghrelin induces fos
expression in the nucleus of the solitary tract, but not in the
arcuate or paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus. Brain Res.
1218:151–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen HY, Trumbauer ME, Chen AS, Weingarth
DT, Adams JR, Frazier EG, Shen Z, Marsh DJ, Feighner SD, Guan XM,
et al: Orexigenic action of peripheral ghrelin is mediated by
neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein. Endocrinology.
145:2607–2612. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ariyasu H, Takaya K, Tagami T, Ogawa Y,
Hosoda K, Akamizu T, Suda M, Koh T, Natsui K, Toyooka S, et al:
Stomach is a major source of circulating ghrelin, and feeding state
determines plasma ghrelin-like immunoreactivity levels in humans. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:4753–4758. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|