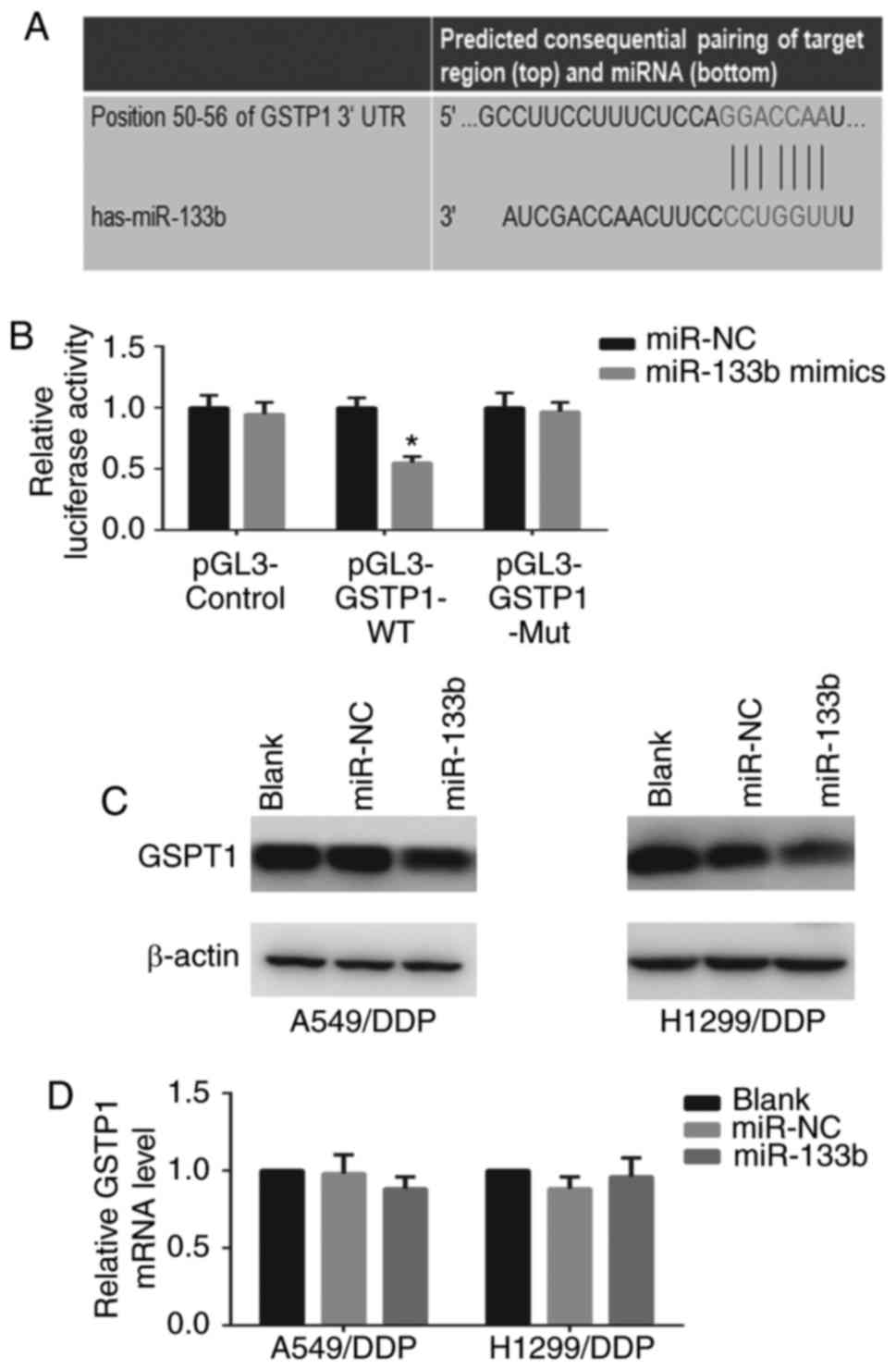
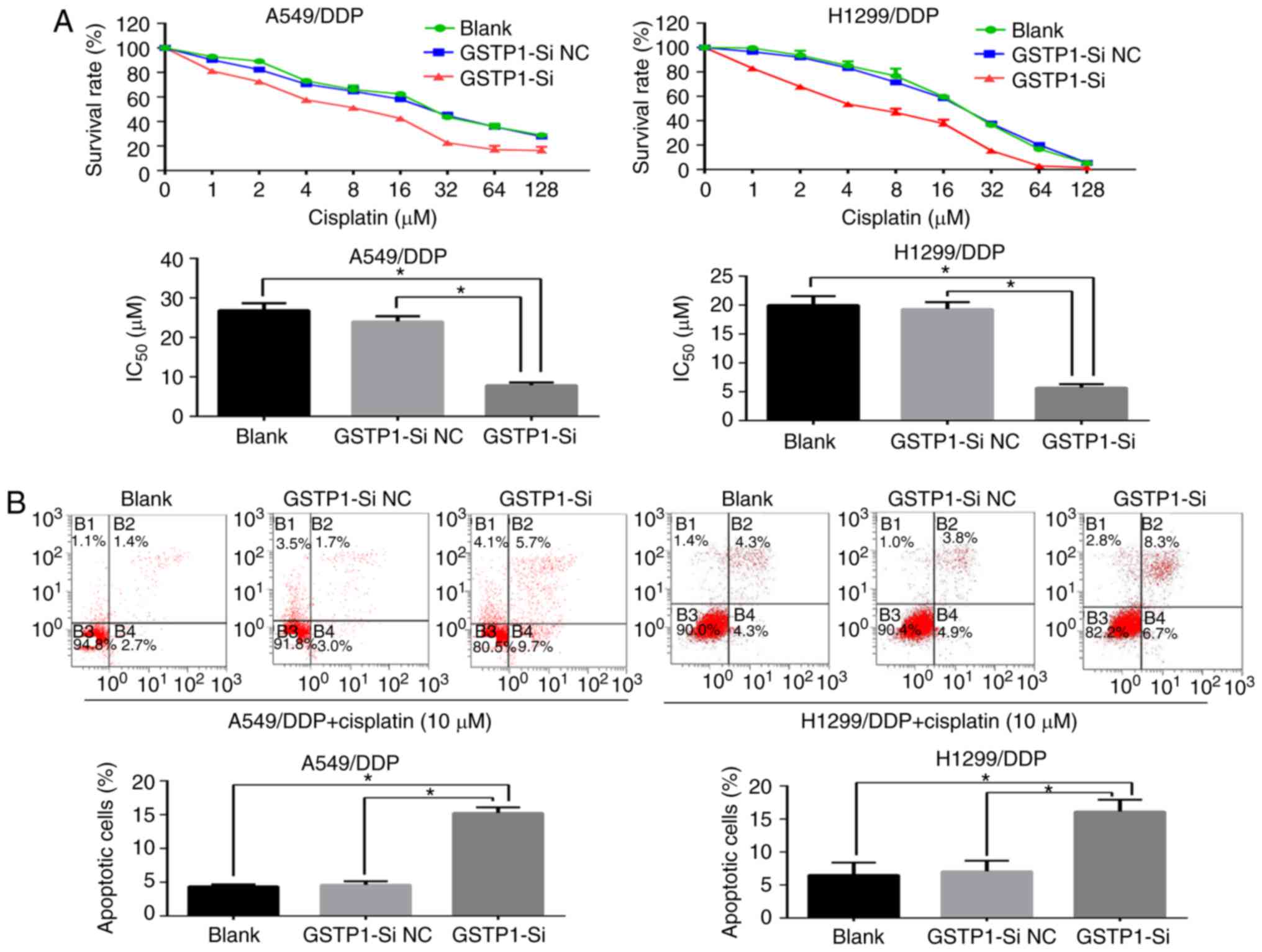
|
1
|
Travis WD, Travis LB and Devesa SS: Lung
cancer. Cancer. 75(1 Suppl): S191–S202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S,
Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, et
al: Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal
growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase
3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 11:121–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Oliver TG, Mercer KL, Sayles LC, Burke JR,
Mendus D, Lovejoy KS, Cheng MH, Subramanian A, Mu D, Powers S, et
al: Chronic cisplatin treatment promotes enhanced damage repair and
tumor progression in a mouse model of lung cancer. Genes Dev.
24:837–52. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ardizzoni A, Boni L, Tiseo M, Fossella FV,
Schiller JH, Paesmans M, Radosavljevic D, Paccagnella A, Zatloukal
P, Mazzanti P, et al: Cisplatin-versus carboplatin-based
chemotherapy in first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer: An individual patient data meta-analysis. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 99:847–857. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tan XL, Moyer AM, Fridley BL, Schaid DJ,
Niu N, Batzler AJ, Jenkins GD, Abo RP, Li L, Cunningham JM, et al:
Genetic variation predicting cisplatin cytotoxicity associated with
overall survival in lung cancer patients receiving platinum-based
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 17:5801–5811. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cortés-Sempere M, de Miguel MP, Pernía O,
Rodriguez C, de Castro Carpeño J, Nistal M, Conde E, López-Ríos F,
Belda-Iniesta C, Perona R and Ibanez de Caceres I: IGFBP-3
methylation-derived deficiency mediates the resistance to cisplatin
through the activation of the IGFIR/Akt pathway in non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncogene. 32:1274–1283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Orellana EA and Kasinski AL: MicroRNAs in
cancer: A historical perspective on the path from discovery to
therapy. Cancers (Basel). 7:1388–1405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chitwood DH and Timmermans MC: Small RNAs
are on the move. Nature. 467:415–419. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhai H and Ju J: Implications of microRNAs
in colorectal cancer development, diagnosis, prognosis, and
therapeutics. Front Genet. 2:000782011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao JJ, Chu ZB, Hu Y, Lin J, Wang Z,
Jiang M, Chen M, Wang X, Kang Y, Zhou Y, et al: Targeting the
miR-221-222/PUMA/BAK/BAX pathway abrogates dexamethasone resistance
in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 75:4384–4397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma J, Fang B, Zeng F, Ma C, Pang H, Cheng
L, Shi Y, Wang H, Yin B, Xia J, et al: Down-regulation of miR-223
reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant
pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:1740–1749. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao Y, Huang J, Zhang L, Qu Y, Li J, Yu
B, Yan M, Yu Y, Liu B and Zhu Z: MiR-133b is frequently decreased
in gastric cancer and its overexpression reduces the metastatic
potential of gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 14:342014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tao J, Wu D, Xu B, Qian W, Li P, Lu Q, Yin
C and Zhang W: microRNA-133 inhibits cell proliferation, migration
and invasion in prostate cancer cells by targeting the epidermal
growth factor receptor. Oncol Rep. 27:1967–1975. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Akçakaya P, Ekelund S, Kolosenko I,
Caramuta S, Ozata DM, Xie H, Lindforss U, Olivecrona H and Lui WO:
miR-185 and miR-133b deregulation is associated with overall
survival and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
9:311–318. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Liu L, Shao X, Gao W, Zhang Z, Liu P, Wang
R, Huang P, Yin Y and Shu Y: MicroRNA-133b inhibits the growth of
non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting the epidermal growth factor
receptor. FEBS J. 279:3800–3812. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
MacDonagh L, Gray SG, Finn SP, Cuffe S,
O’Byrne KJ and Barr MP: The emerging role of microRNAs in
resistance to lung cancer treatments. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:160–169.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen S, Jiao JW, Sun KX, Zong ZH and Zhao
Y: MicroRNA-133b targets glutathione S-transferase π expression to
increase ovarian cancer cell sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs.
Drug Des Dev Ther. 9:5225–5235. 2015.
|
|
21
|
Zhou J, Lv L, Lin C, Hu G, Guo Y, Wu M,
Tian B and Li X: Combinational treatment with microRNA 133b and
cetuximab has increased inhibitory effects on the growth and
invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulating EGFR. Mol Med
Rep. 12:5407–5414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin W, Dong P, Ma C, Mitchelson K, Deng T,
Zhang L, Sun Y, Feng X, Ding Y, Lu X, et al: MicroRNA-133b is a key
promoter of cervical carcinoma development through the activation
of the ERK and AKT1 pathways. Oncogene. 31:4067–4075. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mendell JT: MiRiad roles for the miR-17-92
cluster in development and disease. Cell. 133:217–222. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Singh S: Cytoprotective and regulatory
functions of glutathione S-transferases in cancer cell
proliferation and cell death. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 75:1–15.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schnekenburger M, Karius T and Diederich
M: Regulation of epigenetic traits of the glutathione S-transferase
P1 gene: From detoxification toward cancer prevention and
diagnosis. Front Pharmacol. 5:1702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Louie SM, Grossman EA, Crawford LA, Ding
L, Camarda R, Huffman TR, Miyamoto DK, Goga A, Weerapana E and
Nomura DK: GSTP1 is a driver of triple-negative breast cancer cell
metabolism and pathogenicity. Cell Chem Biol. 23:567–578. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Townsend DM and Tew KD: The role of
glutathione-S-transferase in anti-cancer drug resistance. Oncogene.
22:7369–7375. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Depeille P, Cuq P, Passagne I, Evrard A
and Vian L: Combined effects of GSTP1 and MRP1 in melanoma drug
resistance. Br J Cancer. 93:216–223. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sau A, Filomeni G, Pezzola S, D’Aguanno S,
Tregno FP, Urbani A, Serra M, Pasello M, Picci P, Federici G and
Caccuri AM: Targeting GSTP1-1 induces JNK activation and leads to
apoptosis in cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant human osteosarcoma
cell lines. Mol Biosyst. 8:994–1006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sawers L, Ferguson MJ, Ihrig BR, Young HC,
Chakravarty P, Wolf CR and Smith G: Glutathione S-transferase P1
(GSTP1) directly influences platinum drug chemosensitivity in
ovarian tumour cell lines. Br J Cancer. 111:1150–1158. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Holley SL, Fryer AA, Haycock JW, Grubb SE,
Strange RC and Hoban PR: Differential effects of glutathione
S-transferase pi (GSTP1) haplotypes on cell proliferation and
apoptosis. Carcinogenesis. 28:2268–2273. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|