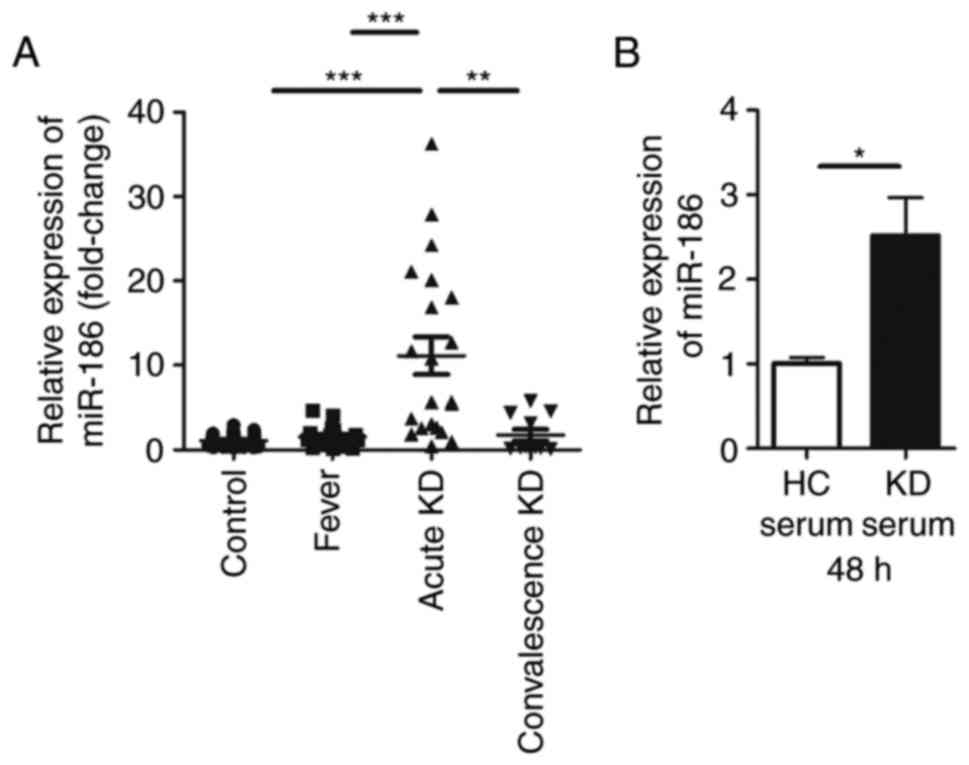
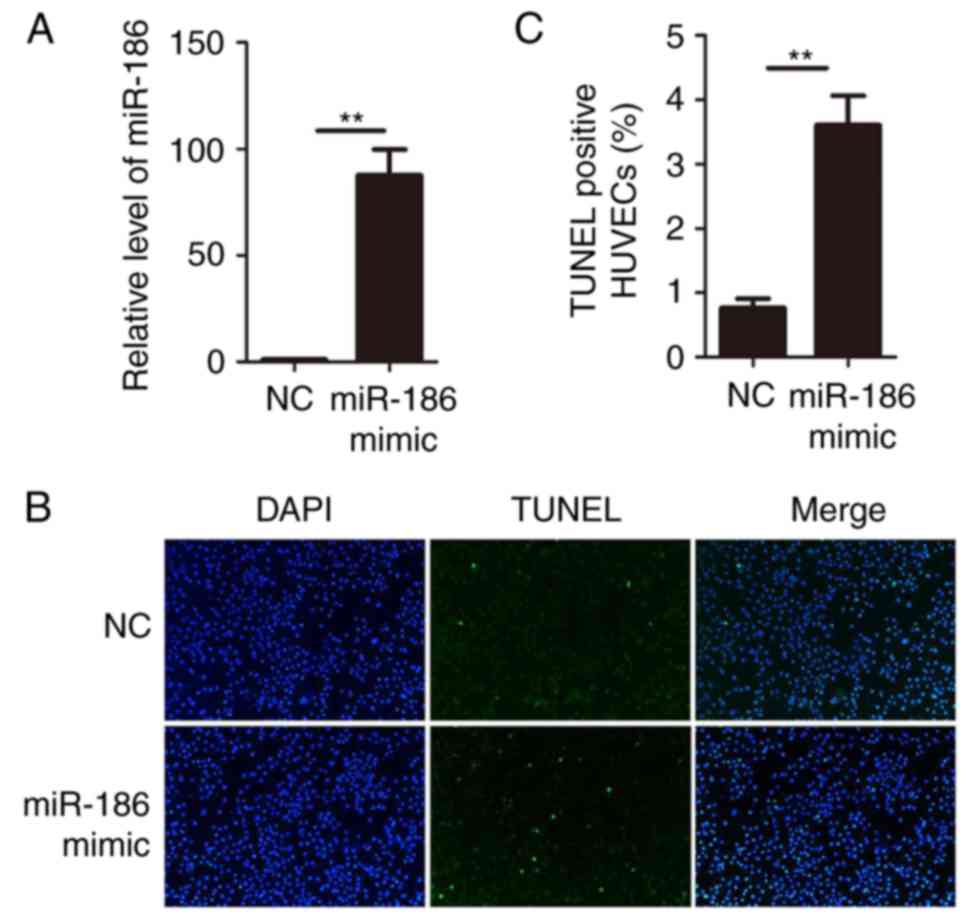
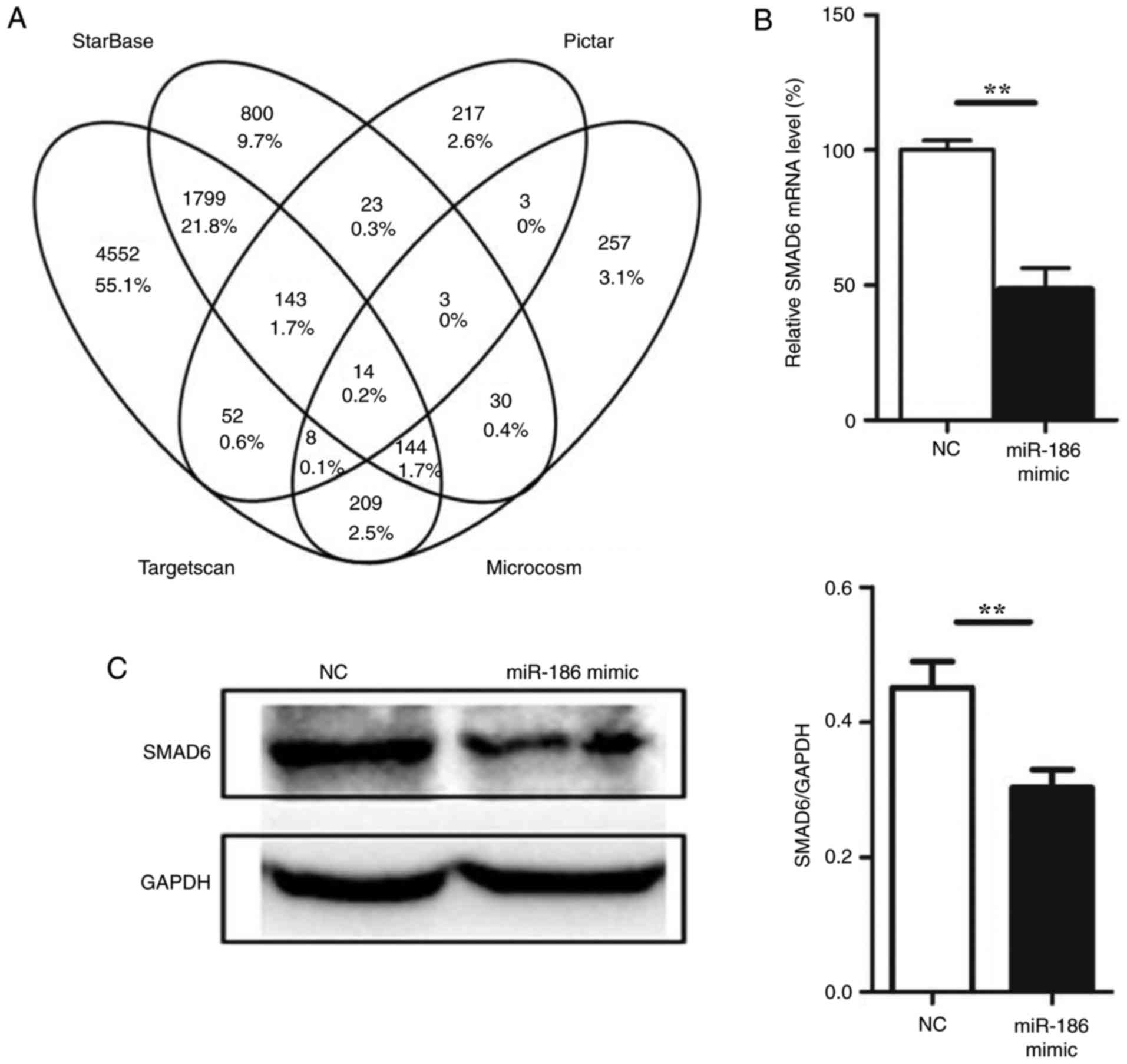
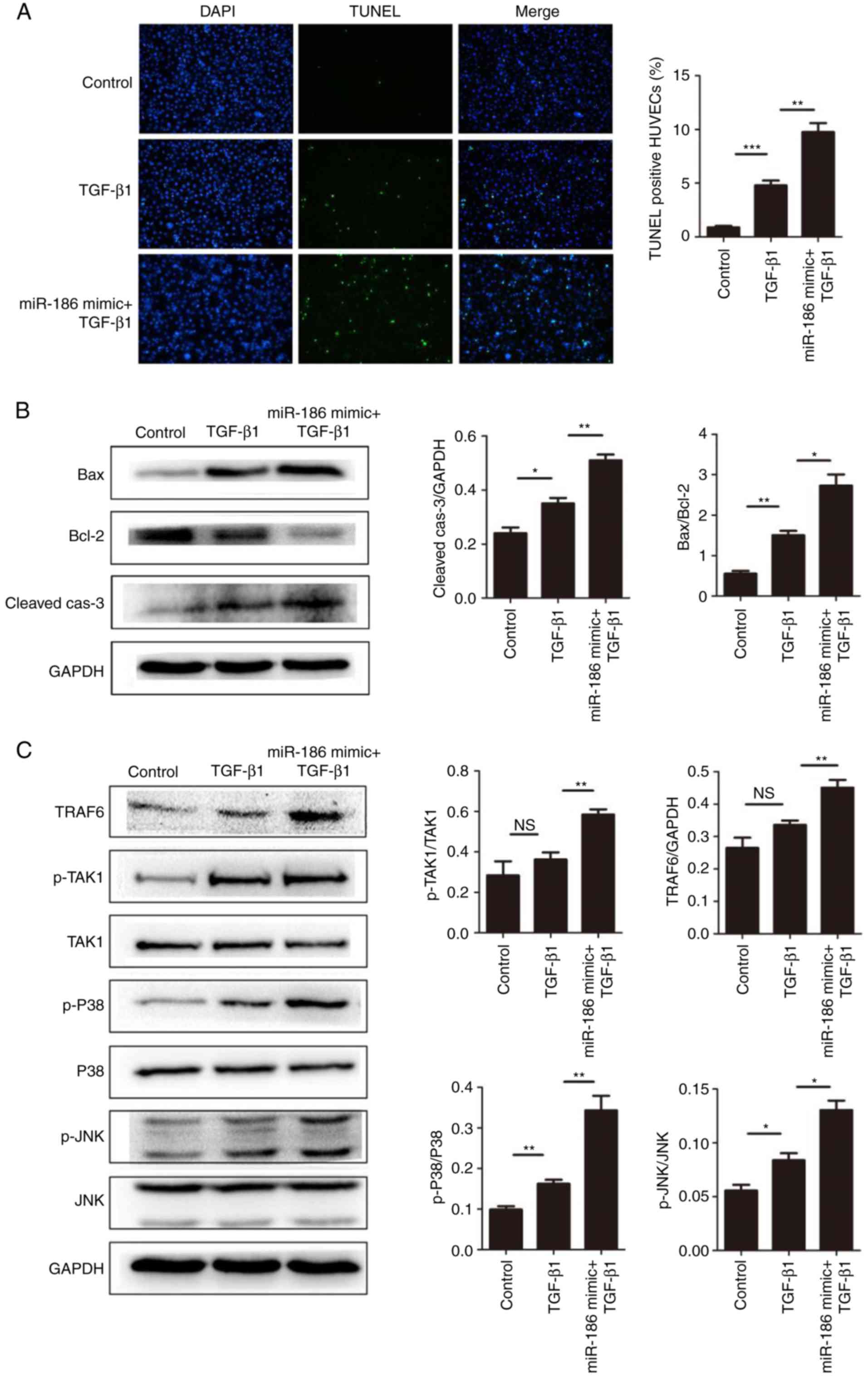
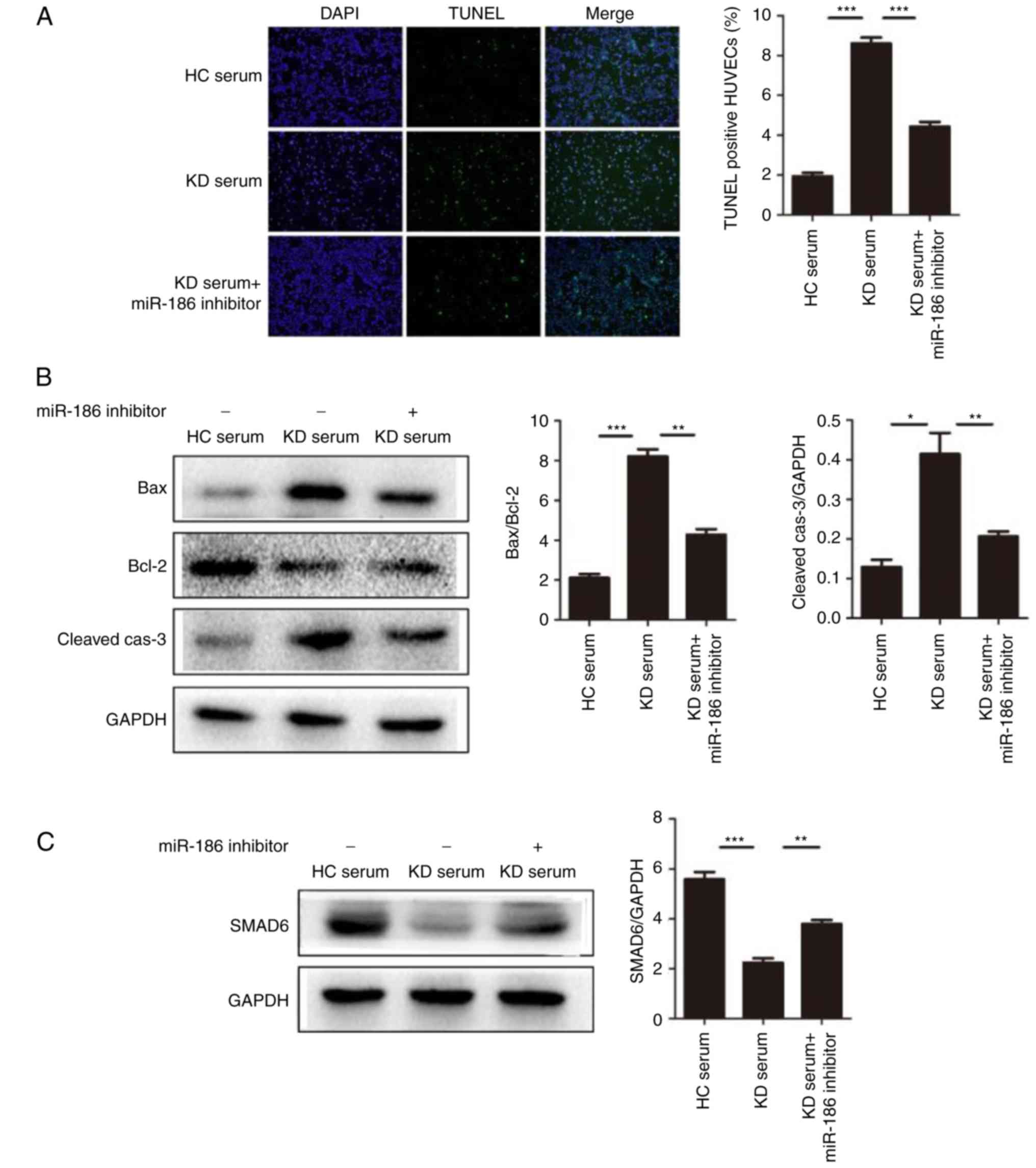
|
1
|
Newburger JW, Takahashi M and Burns JC:
Kawasaki Disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 67:1738–1749. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gordon JB, Kahn AM and Burns JC: When
children with Kawasaki disease grow up: Myocardial and vascular
complications in adulthood. J Am Coll Cardiol. 54:1911–1920. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kato H, Sugimura T, Akagi T, Sato N,
Hashino K, Maeno Y, Kazue T, Eto G and Yamakawa R: Long-term
consequences of Kawasaki disease. A 10- to 21-year follow-up study
of 594 patients. Circulation. 94:1379–1385. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS,
Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, Colan SD, Duffy CE, Fulton DR, Glode
MP, et al: A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as
compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki
syndrome. N Engl J Med. 324:1633–1639. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leung DY, Cotran RS, Kurt-Jones E, Burns
JC, Newburger JW and Pober JS: Endothelial cell activation and high
interleukin-1 secretion in the pathogenesis of acute Kawasaki
disease. Lancet. 2:1298–1302. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amano S, Hazama F and Hamashima Y:
Pathology of Kawasaki disease: I. Pathology and morphogenesis of
the vascular changes. Jpn Circ J. 43:633–643. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arkin A: A Clinical and pathological study
of periarteritis nodosa: A report of five cases, one histologically
healed. Am J Pathol. 6:401–426.5. 1930.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shah V, Christov G, Mukasa T, Brogan KS,
Wade A, Eleftheriou D, Levin M, Tulloh RM, Almeida B, Dillon MJ, et
al: Cardiovascular status after Kawasaki disease in the UK. Heart.
101:1646–1655. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsuda E, Hamaoka K, Suzuki H, Sakazaki H,
Murakami Y, Nakagawa M, Takasugi H and Yoshibayashi M: A survey of
the 3-decade outcome for patients with giant aneurysms caused by
Kawasaki disease. Am Heart J. 167:249–258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liang M: MicroRNA: A new entrance to the
broad paradigm of systems molecular medicine. Physiol Genomics.
38:113–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yun KW, Lee JY, Yun SW, Lim IS and Choi
ES: Elevated serum level of microRNA (miRNA)-200c and miRNA-371-5p
in children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 35:745–752.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shimizu C, Kim J, Stepanowsky P, Trinh C,
Lau HD, Akers JC, Chen C, Kanegaye JT, Tremoulet A, Ohno-Machado L
and Burns JC: Differential expression of miR-145 in children with
Kawasaki disease. PLoS One. 8:e581592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rowley AH, Pink AJ, Reindel R, Innocentini
N, Baker SC, Shulman ST and Kim KY: A study of cardiovascular miRNA
biomarkers for Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J.
33:1296–1299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rong X, Jia L, Hong L, Pan L, Xue X, Zhang
C, Lu J, Jin Z, Qiu H, Wu R and Chu M: Serum miR-92a-3p as a new
potential biomarker for diagnosis of Kawasaki disease with coronary
artery lesions. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 10:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
He M, Chen Z, Martin M, Zhang J, Sangwung
P, Woo B, Tremoulet AH, Shimizu C, Jain MK, Burns JC and Shyy JY:
miR-483 targeting of CTGF suppresses endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition: Therapeutic implications in Kawasaki disease. Circ Res.
120:354–365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Chu M, Wu R, Qin S, Hua W, Shan Z, Rong X,
Zeng J, Hong L, Sun Y, Liu Y, et al: Bone marrow-derived
microRNA-223 works as an endocrine genetic signal in vascular
endothelial cells and participates in vascular injury from Kawasaki
disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 6:pii: e0048782017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cao C, Sun D, Zhang L and Song L: miR-186
affects the proliferation, invasion and migration of human gastric
cancer by inhibition of Twist1. Oncotarget. 7:79956–79963. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong Y, Jin X, Sun Z, Zhao Y and Song X:
MiR-186 inhibited migration of NSCLC via targeting cdc42 and
effecting EMT process. Mol Cells. 40:195–201. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW,
Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, Baker AL, Jackson MA, Takahashi M,
Shah PB, et al: Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of
Kawasaki disease: A scientific statement for health professionals
from the American heart association. Circulation. 135:e927–e999.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Higashi K, Terai M, Hamada H, Honda T,
Kanazawa M and Kohno Y: Impairment of angiogenic activity in the
serum from patients with coronary aneurysms due to Kawasaki
disease. Circ J. 71:1052–1059. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tian J, Lv HT, An XJ, Ling N and Xu F:
Endothelial microparticles induce vascular endothelial cell injury
in children with Kawasaki disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:1814–1818. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
He JH, Han ZP, Zou MX, Wang L, Lv YB, Zhou
JB, Cao MR and Li YG: Analyzing the LncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA
regulatory network in prostate cancer with bioinformatics software.
J Comput Biol. 2017.Epub ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang JH, Li JH, Shao P, Zhou H, Chen YQ
and Qu LH: starBase: A database for exploring microRNA-mRNA
interaction maps from Argonaute CLIP-Seq and Degradome-Seq data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D202–D209. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vlachos IS, Paraskevopoulou MD, Karagkouni
D, Georgakilas G, Vergoulis T, Kanellos I, Anastasopoulos IL,
Maniou S, Karathanou K, Kalfakakou D, et al: DIANA-TarBase v7.0:
Indexing more than half a million experimentally supported miRNA:
mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D153–D159. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Jung SM, Lee JH, Park J, Oh YS, Lee SK,
Park JS, Lee YS, Kim JH, Lee JY, Bae YS, et al: Smad6 inhibits
non-canonical TGF-β1 signalling by recruiting the deubiquitinase
A20 to TRAF6. Nat Commun. 4:25622013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lee MK, Pardoux C, Hall MC, Lee PS,
Warburton D, Qing J, Smith SM and Derynck R: TGF-beta activates Erk
MAP kinase signalling through direct phosphorylation of ShcA. EMBO
J. 26:3957–3967. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hua X, Xiao Y, Pan W, Li M, Huang X, Liao
Z, Xian Q and Yu L: miR-186 inhibits cell proliferation of prostate
cancer by targeting GOLPH3. Am J Cancer Res. 6:1650–1660.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Z, Zhang G, Yu W, Gao N and Peng J:
miR-186 inhibits cell proliferation in multiple myeloma by
repressing Jagged1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:692–697. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang KJ, Zhao X, Liu YZ, Zeng QT, Mao XB,
Li SN, Zhang M, Jiang C, Zhou Y, Qian C, et al: Circulating
miR-19b-3p, miR-134-5p and miR-186-5p are promising novel
biomarkers for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 38:1015–1029. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Davignon J and Ganz P: Role of endothelial
dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 109(Suppl 1):
III27–III32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Horio E, Kadomatsu T, Miyata K, Arai Y,
Hosokawa K, Doi Y, Ninomiya T, Horiguchi H, Endo M, Tabata M, et
al: Role of endothelial cell-derived angptl2 in vascular
inflammation leading to endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis
progression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:790–800. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hartopo AB and Setianto BY: Coronary
artery sequel of Kawasaki disease in adulthood, a concern for
internists and cardiologists. Acta Med Indones. 45:69–75.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Z, Jiang J, Tian L, Li X, Chen J, Li S,
Li C and Yang Z: A plasma mir-125a-5p as a novel biomarker for
Kawasaki disease and induces apoptosis in HUVECs. PLoS One.
12:e01754072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ruiz-Ortega M, Rodriguez-Vita J,
Sanchez-Lopez E, Carvajal G and Egido J: TGF-beta signaling in
vascular fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res. 74:196–206. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu C, Chen F, Han X, Xu H and Wang Y:
Role of TGF-β1/p38 MAPK pathway in hepatitis B virus-induced
tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:7923–7930. 2014.
|
|
40
|
Wei J, Li Z, Chen W, Ma C, Zhan F, Wu W
and Peng Y: AEG-1 participates in TGF-beta1-induced EMT through p38
MAPK activation. Cell Biol Int. 37:1016–1021. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Malik S, Suchal K, Khan SI, Bhatia J,
Kishore K, Dinda AK and Arya DS: Apigenin ameliorates
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats via
MAPK/NF-κB/TNF-α and TGF-β1/MAPK/fibronectin pathways. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 2:F414–F422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hyman KM, Seghezzi G, Pintucci G, Stellari
G, Kim JH, Grossi EA, Galloway AC and Mignatti P: Transforming
growth factor-beta1 induces apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells
by activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Surgery.
132:173–179. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ferrari G, Terushkin V, Wolff MJ, Zhang X,
Valacca C, Poggio P, Pintucci G and Mignatti P: TGF-β1 induces
endothelial cell apoptosis by shifting VEGF activation of p38
(MAPK) from the prosurvival p38β to proapoptotic p38α. Mol Cancer
Res. 10:605–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pollman MJ, Naumovski L and Gibbons GH:
Vascular cell apoptosis: Cell type-specific modulation by
transforming growth factor-beta1 in endothelial cells versus smooth
muscle cells. Circulation. 99:2019–2026. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tsukada T, Eguchi K, Migita K, Kawabe Y,
Kawakami A, Matsuoka N, Takashima H, Mizokami A and Nagataki S:
Transforming growth factor beta 1 induces apoptotic cell death in
cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells with down-regulated
expression of bcl-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 210:1076–1082.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shimizu C, Jain S, Davila S, Hibberd ML,
Lin KO, Molkara D, Frazer JR, Sun S, Baker AL, Newburger JW, et al:
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway in patients with
Kawasaki disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 4:16–25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Shimizu C, Oharaseki T, Takahashi K,
Kottek A, Franco A and Burns JC: The role of TGF-β and
myofibroblasts in the arteritis of Kawasaki disease. Hum Pathol.
44:189–198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|