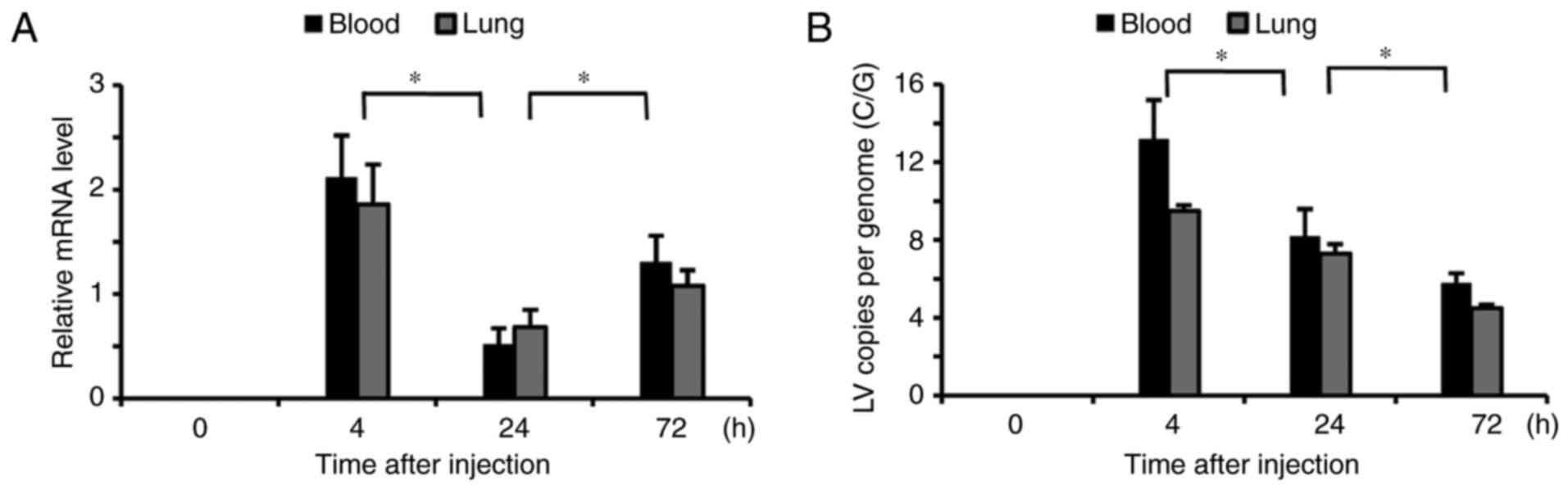
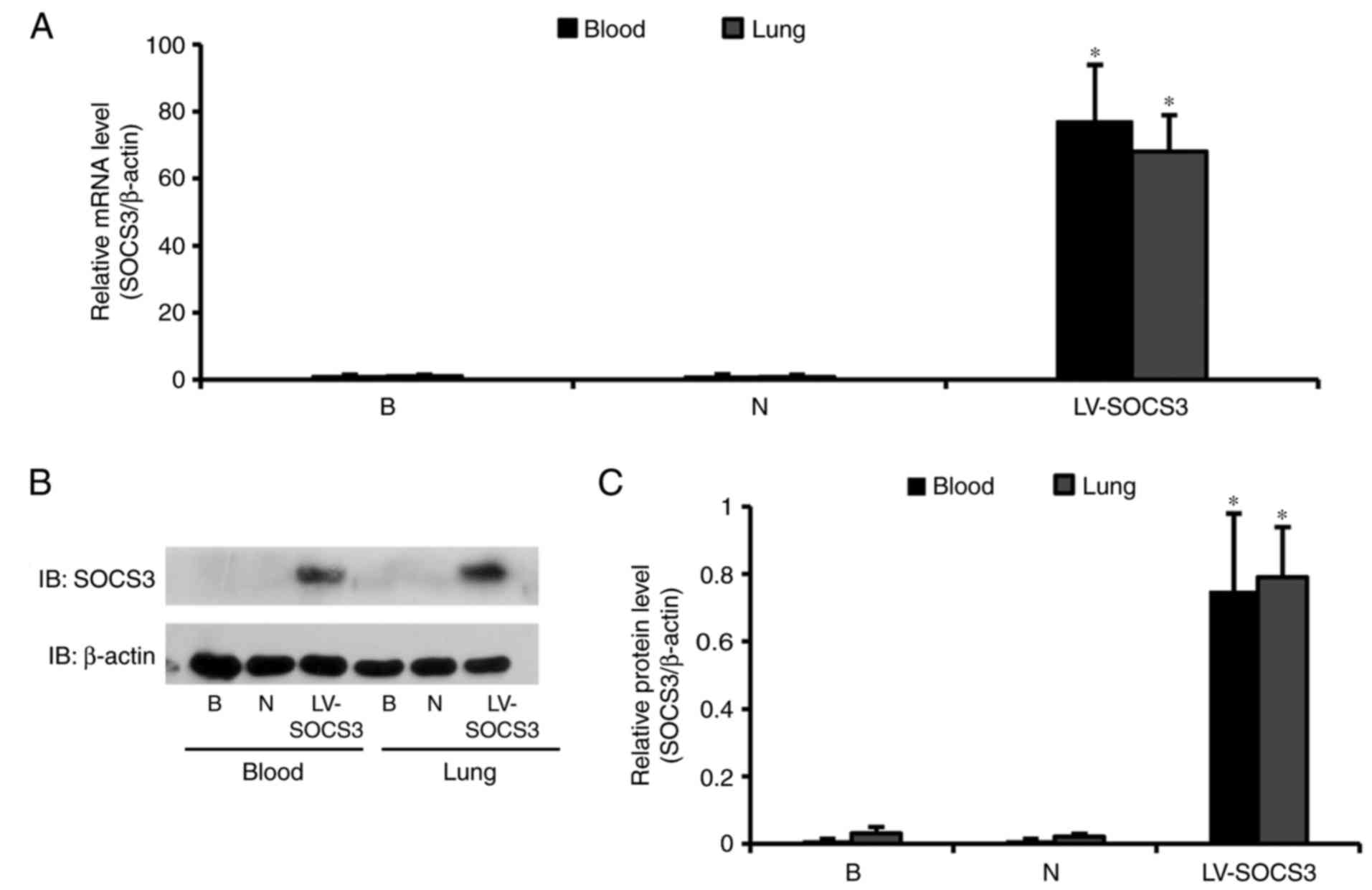
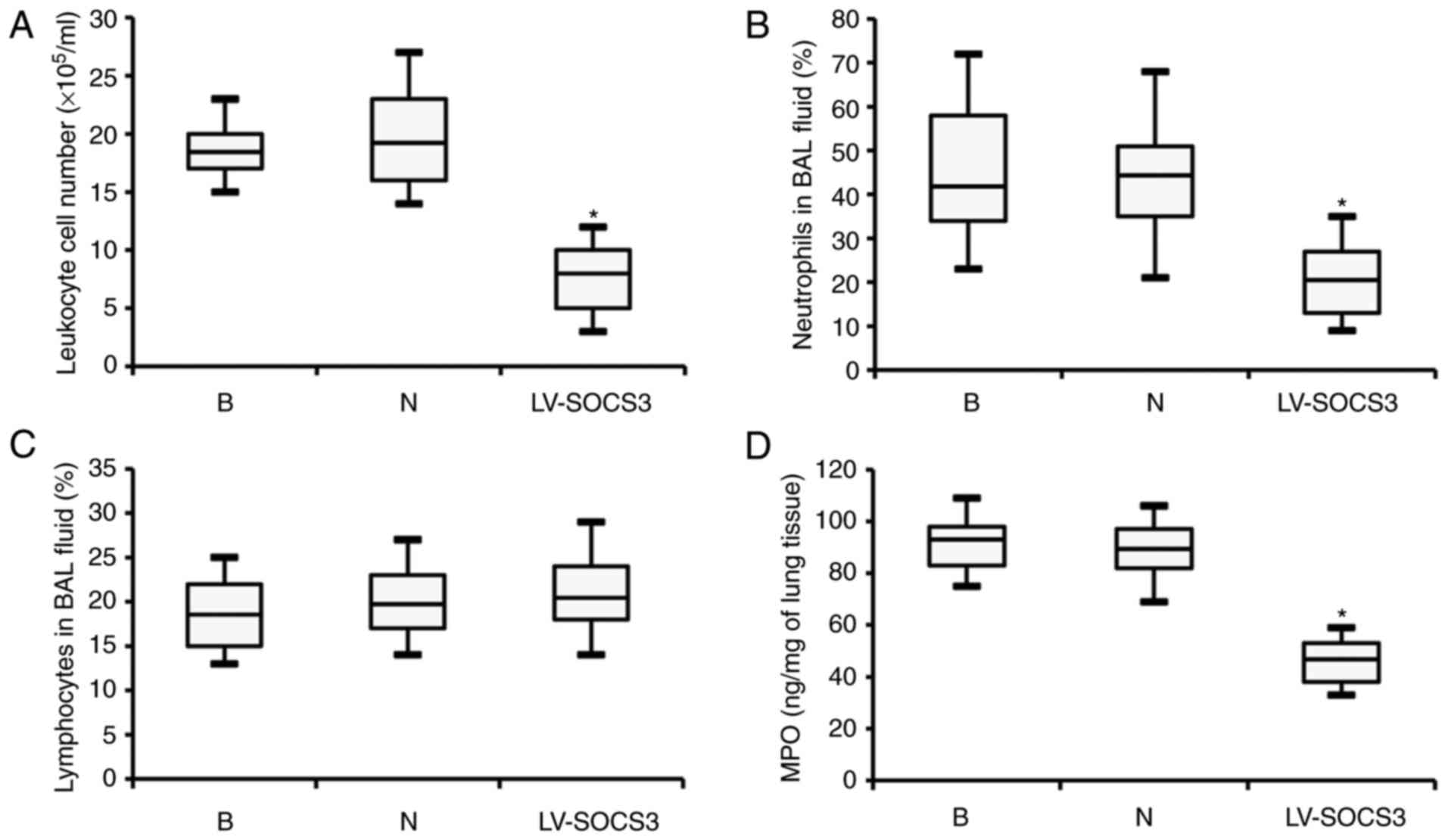
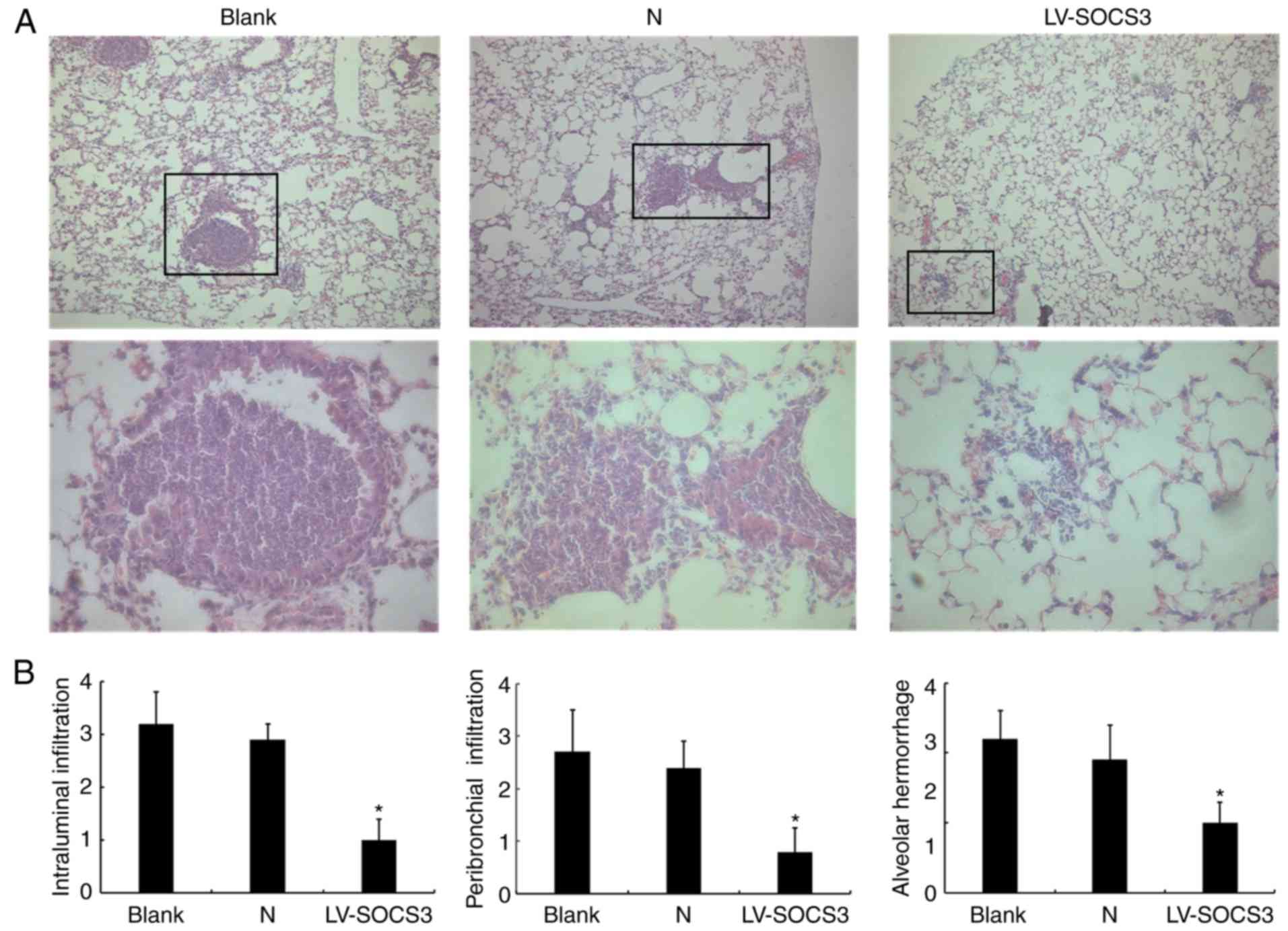
|
1
|
Hengzhuang W, Song Z, Ciofu O, Onsøyen E,
Rye PD and Høiby N: OligoG CF-5/20 disruption of mucoid Pseudomonas
aeruginosa biofilm in a murine lung infection model. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 60:2620–2626. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mayer-Hamblett N, Kloster M, Rosenfeld M,
Gibson RL, Retsch-Bogart GZ, Emerson J, Thompson V and Ramsey BW:
Impact of sustained eradication of new pseudomonas aeruginosa
infection on long-term outcomes in cystic fibrosis. Clin Infect
Dis. 61:707–715. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharma G, Rao S, Bansal A, Dang S, Gupta S
and Gabrani R: Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm: Potential
therapeutic targets. Biologicals. 42:1–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Darch SE, McNally A, Harrison F, Corander
J, Barr HL, Paszkiewicz K, Holden S, Fogarty A, Crusz SA and Diggle
SP: Recombination is a key driver of genomic and phenotypic
diversity in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa population during cystic
fibrosis infection. Sci Rep. 5:76492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Armstrong DS, Hook SM, Jamsen KM, Nixon
GM, Carzino R, Carlin JB, Robertson CF and Grimwood K: Lower airway
inflammation in infants with cystic fibrosis detected by newborn
screening. Pediatr Pulmonol. 40:500–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Regamey N, Tsartsali L, Hilliard TN, Fuchs
O, Tan HL, Zhu J, Qiu YS, Alton EW, Jeffery PK, Bush A and Davies
JC: Distinct patterns of inflammation in the airway lumen and
bronchial mucosa of children with cystic fibrosis. Thorax.
67:164–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kolls JK: CD4+ T-cell subsets
and host defense in the lung. Immunol Rev. 252:156–163. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ,
Locksley RM and Stockinger B: TGFbeta in the context of an
inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of
IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 24:179–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mangan PR, Harrington LE, O'Quinn DB,
Helms WS, Bullard DC, Elson CO, Hatton RD, Wahl SM, Schoeb TR and
Weaver CT: Transforming growth factor-β induces development of the
TH17 lineage. Nature. 441:231–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang XO, Pappu BP, Nurieva R, Akimzhanov
A, Kang HS, Chung Y, Li M, Shah B, Panopoulos AD, Schluns KS, et
al: T helper 17 lineage differentiation is programmed by orphan
nuclear receptors ROR alpha and ROR gamma. Immunity. 28:29–39.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ivanov II, Mckenzie BS, Liang Z, Tadokoro
CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, Cua DJ and Littman DR: The orphan
nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of
proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell.
126:1121–1133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kolls JK and Lindén A: Interleukin-17
family members and inflammation. Immunity. 21:467–476. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lubberts E: The role of IL-17 and family
members in the pathogenesis of arthritis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs.
4:572–577. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dubin PJ and Kolls JK: IL-23 mediates
inflammatory responses to mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung
infection in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
292:L519–L528. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Linossi EM, Babon JJ, Hilton DJ and
Nicholson SE: Suppression of cytokine signaling: The SOCS
prespective. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:241–248. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshimura A and Yasukawa H: JAK's SOCS: A
mechanism of inhibition. Immunity. 36:157–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Ren S, Qu X, Ge C, Cheng K and Zhao
RC: Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit Th17 cells differentiation via
IFN-γ-mediated SOCS3 activation. Immunol Res. 61:219–229. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tanaka K, Ichiyama K, Hashimoto M, Yoshida
H, Takimoto T, Takaesu G, Torisu T, Hanada T, Yasukawa H, Fukuyama
S, et al: Loss of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 in helper T
cells leads to defective Th17 differentiation by enhancing
antagonistic effects of IFN-gamma on STAT3 and Smads. J Immunol.
180:3746–3756. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Z, Laurence A, Kanno Y,
Pacher-Zavisin M, Zhu BM, Tato C, Yoshimura A, Hennighausen L and
O'Shea JJ: Selective regulatory function of Socs3 in the formation
of IL-17-secreting T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:8137–8142.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van Heeckeren AM and Schluchter MD: Murine
models of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. Lab Anim.
36:291–312. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brown BD, Venneri MA, Zingale A, Sergi
Sergi L and Naldini L: Endogenous microRNA regulation suppresses
transgene expression in hematopoietic lineages and enables stable
gene transfer. Nat Med. 12:585–591. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dalpke A and Heeg K: Suppressors of
cytokine signaling proteins in innate and adaptive immune
responses. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. 51:91–103. 2003.
|
|
24
|
Carow B and Rottenberg ME: SOCS3, a major
regulator of infection and inflammation. Front Immunol. 5:582014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Khader SA, Pearl JE, Sakamoto K, Gilmartin
L, Bell GK, Jelley-Gibbs DM, Ghilardi N, deSauvage F and Cooper AM:
IL-23 compensates for the absence of IL-12p70 and is essential for
the IL-17 response during tuberculosis but is dispensable for
protection and antigen-specific IFN-gamma responses if IL-12p70 is
available. J Immunol. 175:788–795. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nguyen-Jackson H, Panopoulos AD, Zhang H,
Li HS and Watowich SS: STAT3 controls the neutrophil migratory
response to CXCR2 ligands by direct activation of G-CSF-induced
CXCR2 expression and via modulation of CXCR2 signal transduction.
Blood. 115:3354–3363. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu D and Qu CK: Protein tyrosine
phosphatases in the JAK/STAT pathway. Front Biosci. 13:4925–4932.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shuai K and Liu B: Regulation of JAK-STAT
signalling in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:900–911. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shouda T, Yoshida T, Hanada T, Wakioka T,
Oishi M, Miyoshi K, Komiya S, Kosai K, Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, et
al: Induction of the cytokine signal regulator SOCS3/CIS3 as a
therapeutic strategy for treating inflammatory arthritis. J Clin
Invest. 108:1781–1788. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suzuki A, Hanada T, Mitsuyama K, Yoshida
T, Kamizono S, Hoshino T, Kubo M, Yamashita A, Okabe M, Takeda K,
et al: Cis3/Socs3/Ssi3 plays a negative regulatory role in STAT3
activation and intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 193:471–481.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Harris TJ, Grosso JF, Yen HR, Xin H,
Kortylewski M, Albesiano E, Hipkiss EL, Getnet D, Goldberg MV,
Maris CH, et al: Cutting edge: An in vivo requirement for STAT3
signaling in TH17 development and TH17-dependent autoimmunity. J
Immunol. 179:4313–4317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ernst M, Najdovska M, Grail D,
Lundgren-May T, Buchert M, Tye H, Matthews VB, Armes J, Bhathal PS,
Hughes NR, et al: STAT3 and STAT1 mediate IL-11-dependent and
inflammation- associated gastric tumorigenesis in gp130 receptor
mutant mice. J Clin Invest. 118:1727–1738. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brender C, Tannahill GM, Jenkins BJ,
Fletcher J, Columbus R, Saris CJ, Ernst M, Nicola NA, Hilton DJ,
Alexander WS and Starr R: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3
regulates CD8 T-cell proliferation by inhibition of interleukins 6
and 27. Blood. 110:2528–2536. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moseley TA, Haudenschild DR, Rose L and
Reddi AH: Interleukin-17 family and IL-17 receptors. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 14:155–174. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ye P, Garvey PB, Zhang P, Nelson S, Bagby
G, Summer WR, Schwarzenberger P, Shellito JE and Kolls JK:
Interleukin-17 and lung host defense against Klebsiella pneumoniae
infection. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 25:335–340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Happel KI, Zheng M, Young E, Quinton LJ,
Lockhart E, Ramsay AJ, Shellito JE, Schurr JR, Bagby GJ, Nelson S
and Kolls JK: Cutting edge: Roles of Toll-like receptor 4 and IL-23
in IL-17 expression in response to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection.
J Immunol. 170:4432–4436. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lindén A and Adachi M: Neutrophilic airway
inflammation and IL-17. Allergy. 57:769–775. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|