|
1
|
Grossman AW and Broderick JP: Advances and
challenges in treatment and prevention of ischemic stroke. Ann
Neurol. 74:363–372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, Robey PG
and Shi S: Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro
and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:13625–13630. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nosrat IV, Widenfalk J, Olson L and Nosrat
CA: Dental pulp cells produce neurotrophic factors, interact with
trigeminal neurons in vitro, and rescue motoneurons after spinal
cord injury. Dev Biol. 238:120–132. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Király M, Kádár K, Horváthy DB, Nardai P,
Rácz GZ, Lacza Z, Varga G and Gerber G: Integration of neuronally
predifferentiated human dental pulp stem cells into rat brain in
vivo. Neurochem Int. 59:371–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fang CZ, Yang YJ, Wang QH, Yao Y, Zhang XY
and He XH: Intraventricular injection of human dental pulp stem
cells improves hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. PLoS
One. 8:e667482013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nosrat IV, Smith CA, Mullally P, Olson L
and Nosrat CA: Dental pulp cells provide neurotrophic support for
dopaminergic neurons and differentiate into neurons in vitro;
implications for tissue engineering and repair in the nervous
system. Eur J Neurosci. 19:2388–2398. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Apel C, Forlenza OV, de Paula VJ, Talib
LL, Denecke B, Eduardo CP and Gattaz WF: The neuroprotective effect
of dental pulp cells in models of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 116:71–78. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee HJ, Lim IJ, Lee MC and Kim SU: Human
neural stem cells genetically modified to overexpress brain-derived
neurotrophic factor promote functional recovery and neuroprotection
in a mouse stroke model. J Neurosci Res. 88:3282–3294. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han Q, Li B, Feng H, Xiao Z, Chen B, Zhao
Y, Huang J and Dai J: The promotion of cerebral ischemia recovery
in rats by laminin-binding BDNF. Biomaterials. 32:5077–5085. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cotman CW and Berchtold NC: Exercise: A
behavioral intervention to enhance brain health and plasticity.
Trends Neurosci. 25:295–301. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kokaia Z, Andsberg G, Yan Q and Lindvall
O: Rapid alterations of BDNF protein levels in the rat brain after
focal ischemia: Evidence for increased synthesis and anterograde
axonal transport. Exp Neurol. 154:289–301. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Schäbitz WR, Schwab S, Spranger M and
Hacke W: Intraventricular brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces
infarct size after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 17:500–506. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamashita K, Wiessner C, Lindholm D,
Thoenen H and Hossmann KA: Post-occlusion treatment with BDNF
reduces infarct size in a model of permanent occlusion of the
middle cerebral artery in rat. Metab Brain Dis. 12:271–280. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kurozumi K, Nakamura K, Tamiya T, Kawano
Y, Kobune M, Hirai S, Uchida H, Sasaki K, Ito Y, Kato K, et al:
BDNF gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells promote functional
recovery and reduce infarct size in the rat middle cerebral artery
occlusion model. Mol Ther. 9:189–197. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nomura T, Honmou O, Harada K, Houkin K,
Hamada H and Kocsis JD: I.V. infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic
factor gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells protects against
injury in a cerebral ischemia model in adult rat. Neuroscience.
136:161–169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang DJ, Lee N, Choi C, Jeon I, Oh SH,
Shin DA, Hwang TS, Lee HJ, Kim SU, Moon H, et al: Therapeutic
effect of BDNF-overexpressing human neural stem cells (HB1.F3.BDNF)
in a rodent model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Cell
Transplant. 22:1441–1452. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ellis KM, O'Carroll DC, Lewis MD, Rychkov
GY and Koblar SA: Neurogenic potential of dental pulp stem cells
isolated from murine incisors. Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:302014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang XF, Yuan SJ and Yang C: Effects of
total flavonoids from Drynaria fortunei on the proliferation and
osteogenic differentiation of rat dental pulp stem cells. Mol Med
Rep. 6:547–552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hata M, Omi M, Kobayashi Y, Nakamura N,
Tosaki T, Miyabe M, Kojima N, Kubo K, Ozawa S, Maeda H, et al:
Transplantation of cultured dental pulp stem cells into the
skeletal muscles ameliorated diabetic polyneuropathy: Therapeutic
plausibility of freshly isolated and cryopreserved dental pulp stem
cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:1622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Lu D, Lu M
and Chopp M: Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of
bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke.
32:1005–1011. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
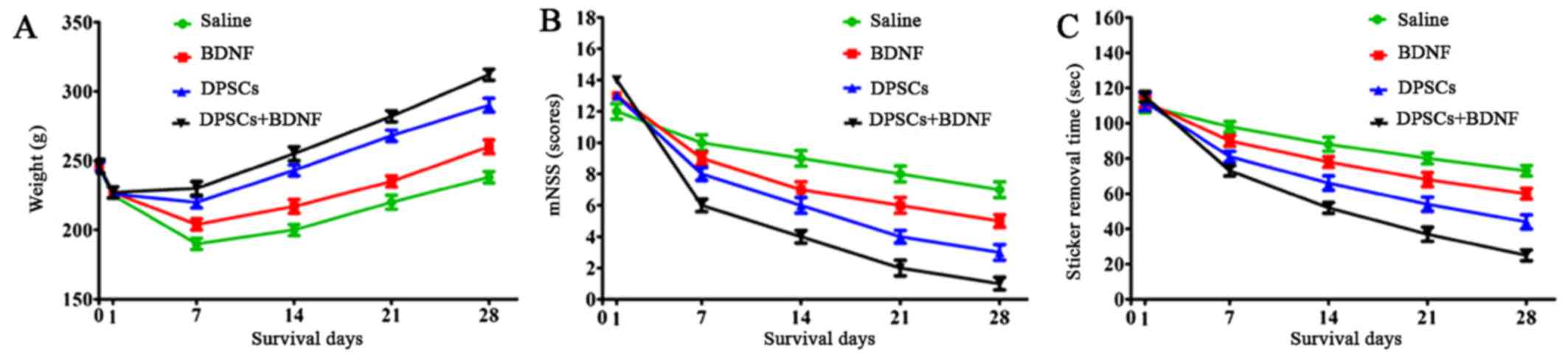
Reglodi D, Tamás A and Lengvári I:
Examination of sensorimotor performance following middle cerebral
artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res Bull. 59:459–466. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Winderlich JN, Kremer KL and Koblar SA:
Adult human dental pulp stem cells promote blood-brain barrier
permeability through vascular endothelial growth factor-α
expression. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 36:1087–1097. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
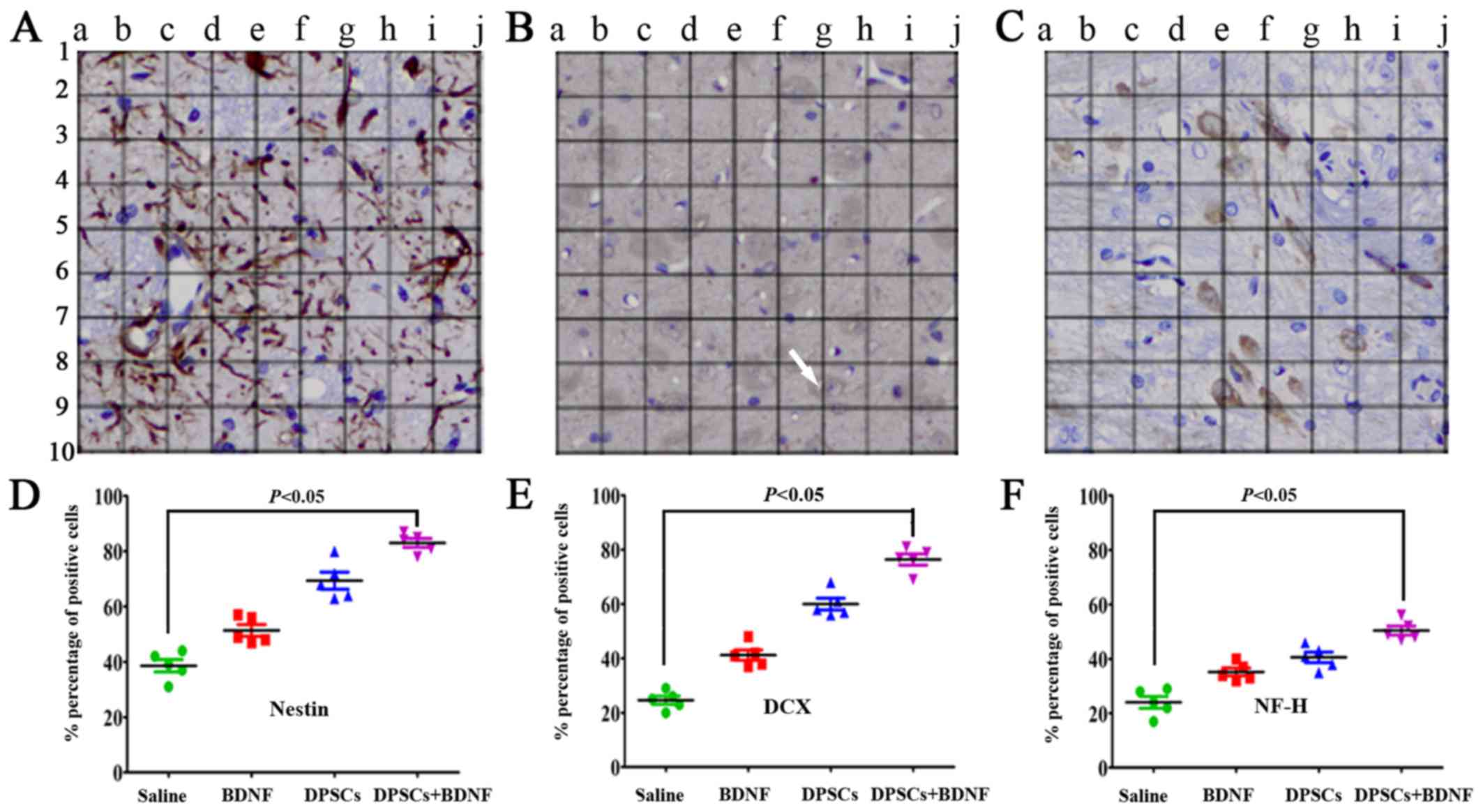
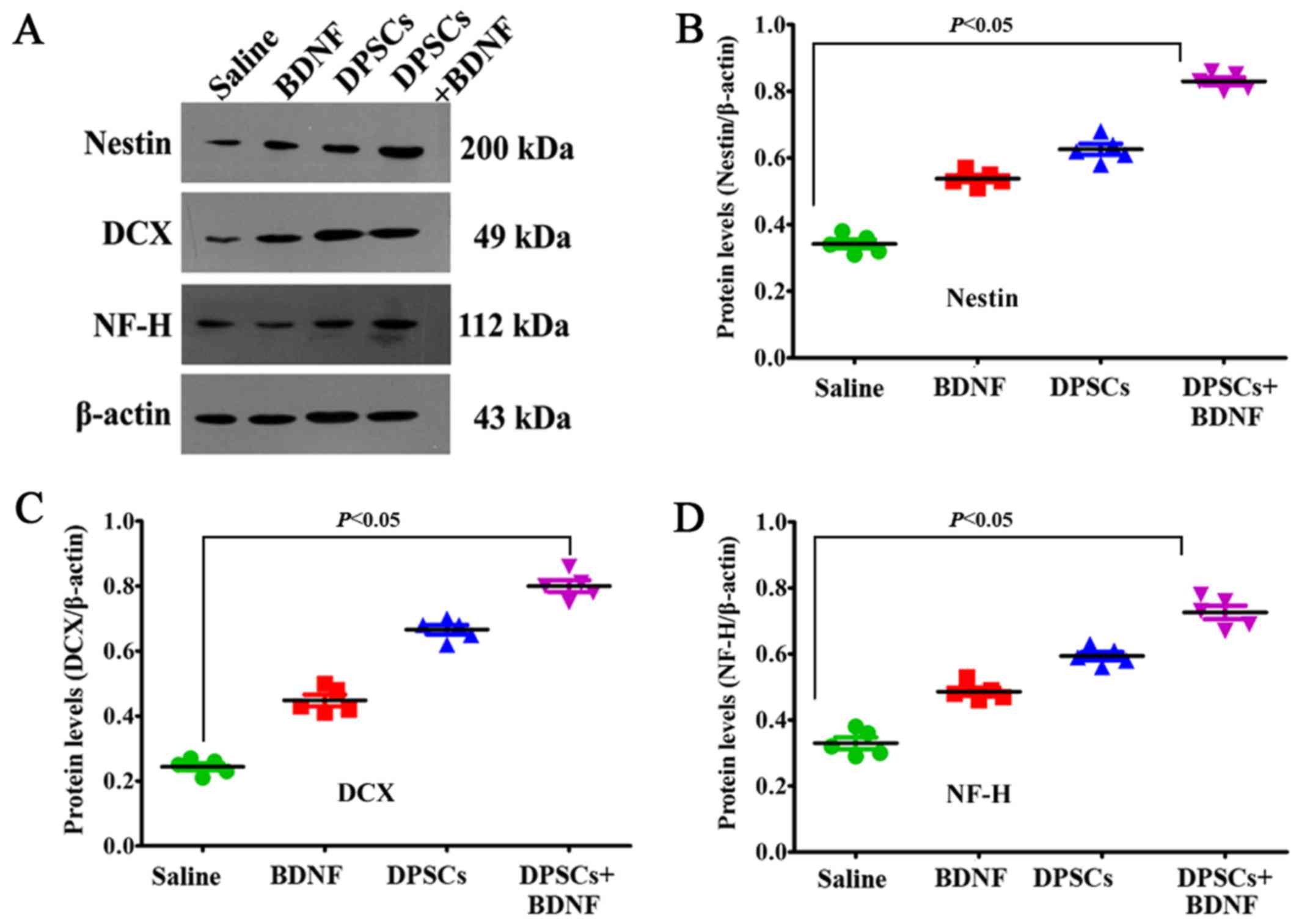
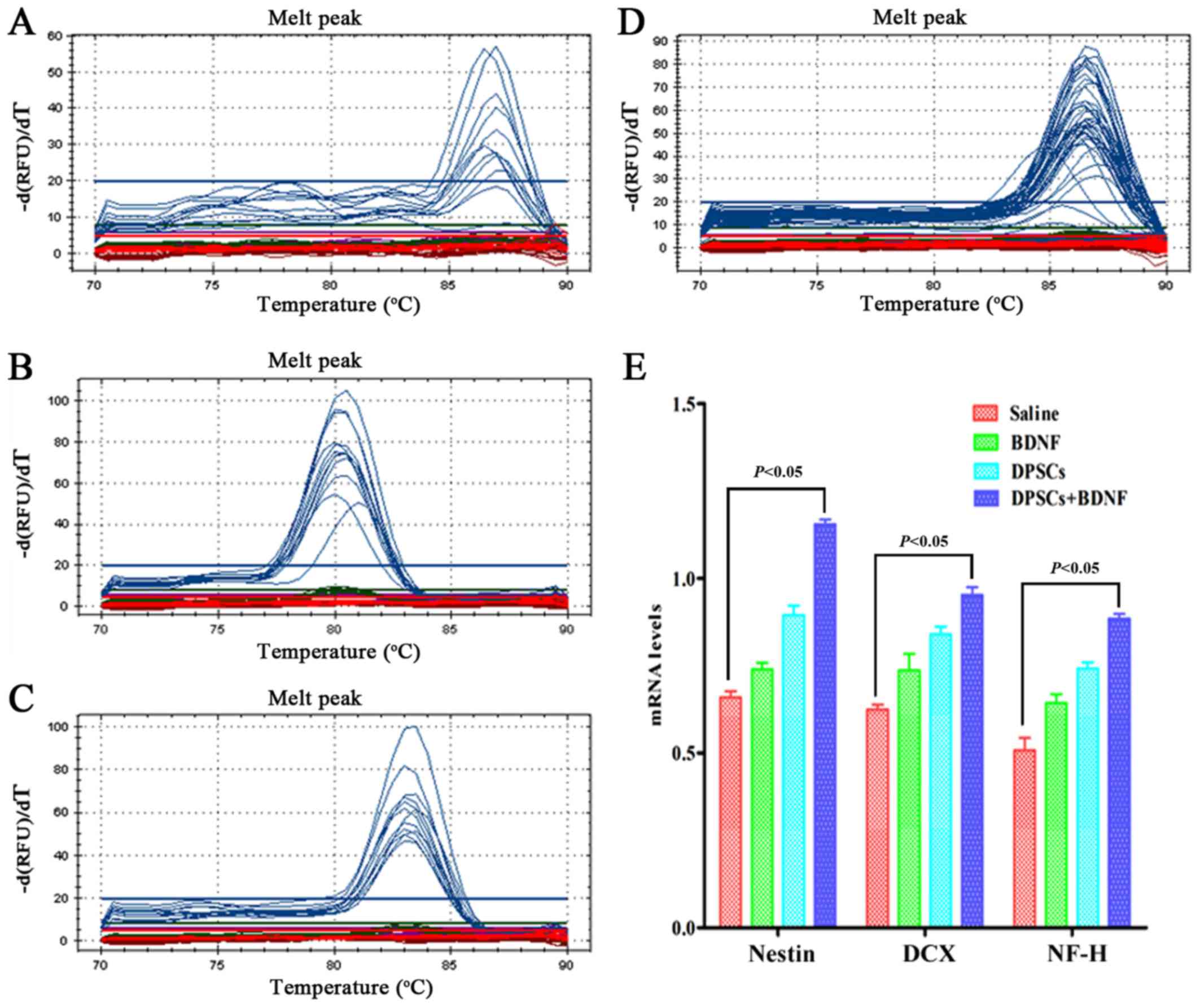
Michalczyk K and Ziman M: Nestin structure
and predicted function in cellular cytoskeletal organisation.
Histol Histopathol. 20:665–671. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Couillard-Despres S, Winner B, Schaubeck
S, Aigner R, Vroemen M, Weidner N, Bogdahn U, Winkler J, Kuhn HG
and Aigner L: Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect
neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci. 21:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen SJ, Chang CM, Tsai SK, Chang YL, Chou
SJ, Huang SS, Tai LK, Chen YC, Ku HH, Li HY, et al: Functional
improvement of focal cerebral ischemia injury by subdural
transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cells with fibrin glue.
Stem Cells Dev. 19:1757–1767. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tae-Hoon L and Yoon-Seok L:
Transplantation of mouse embryonic stem cell after middle cerebral
artery occlusion. Acta Cir Bras. 27:333–339. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang L, Wong S, Snyder EY, Hamblin MH and
Lee JP: Human neural stem cells rapidly ameliorate symptomatic
inflammation in early-stage ischemic-reperfusion cerebral injury.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:1292014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mitkari B, Kerkelä E, Nystedt J, Korhonen
M, Mikkonen V, Huhtala T and Jolkkonen J: Intra-arterial infusion
of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells results in
transient localization in the brain after cerebral ischemia in
rats. Exp Neurol. 239:158–162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yamagata M, Yamamoto A, Kako E, Kaneko N,
Matsubara K, Sakai K, Sawamoto K and Ueda M: Human dental
pulp-derived stem cells protect against hypoxic-ischemic brain
injury in neonatal mice. Stroke. 44:551–4. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang XM, Du F, Yang D, Yu CJ, Huang XN,
Liu W and Fu J: Transplanted bone marrow stem cells relocate to
infarct penumbra and co-express endogenous proliferative and
immature neuronal markers in a mouse model of ischemic cerebral
stroke. BMC Neurosci. 11:1382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rosenkranz K, Kumbruch S, Lebermann K,
Marschner K, Jensen A, Dermietzel R and Meier C: The chemokine
SDF-1/CXCL12 contributes to the 'homing' of umbilical cord blood
cells to a hypoxic-ischemic lesion in the rat brain. J Neurosci
Res. 88:1223–1233. 2010.
|
|
33
|
Miller JT, Bartley JH, Wimborne HJ, Walker
AL, Hess DC, Hill WD and Carroll JE: The neuroblast and angioblast
chemotaxic factor SDF-1 (CXCL12) expression is briefly up regulated
by reactive astrocytes in brain following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic
injury. BMC Neurosci. 6:632005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hill WD, Hess DC, Martin-Studdard A,
Carothers JJ, Zheng J, Hale D, Maeda M, Fagan SC, Carroll JE and
Conway SJ: SDF-1 (CXCL12) is upregulated in the ischemic penumbra
following stroke: Association with bone marrow cell homing to
injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 63:84–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li M, Sun X, Ma L, Jin L, Zhang W, Xiao M
and Yu Q: SDF-1/CXCR4 axis induces human dental pulp stem cell
migration through FAK/PI3K/Akt and GSK3β/β-catenin pathways. Sci
Rep. 7:401612017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang XM, Du F, Yang D, Wang R, Yu CJ,
Huang XN, Hu HY, Liu W and Fu J: Granulocyte colony-stimulating
factor increases the therapeutic efficacy of bone marrow
mononuclear cell transplantation in cerebral ischemia in mice. BMC
Neurosci. 12:612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kvinnsland IH, Luukko K, Fristad I,
Kettunen P, Jackson DL, Fjeld K, von Bartheld CS and Byers MR:
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) from adult rat
tooth serves a distinct population of large-sized trigeminal
neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 19:2089–2098. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang Y, Wei N, Zhu J, Lu T, Chen Z, Xu G
and Liu X: Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on local
inflammation in experimental stroke of rat. Mediators Inflamm.
2010:3724232010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Melvin NR and Sutherland RJ: Quantitative
caveats of standard immunohistochemical procedures: Implications
for optical disector-based designs. J Histochem Cytochem.
58:577–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|