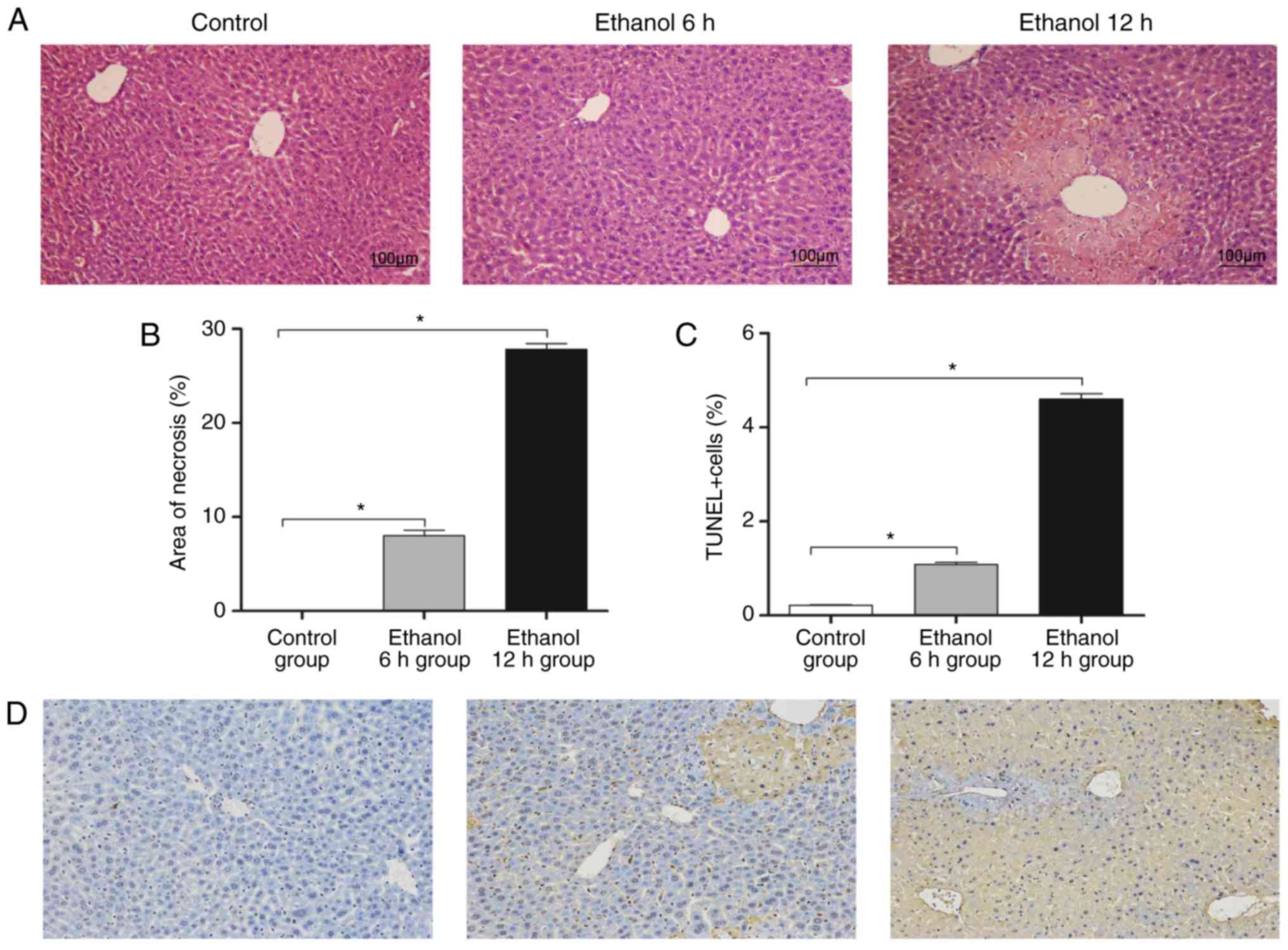
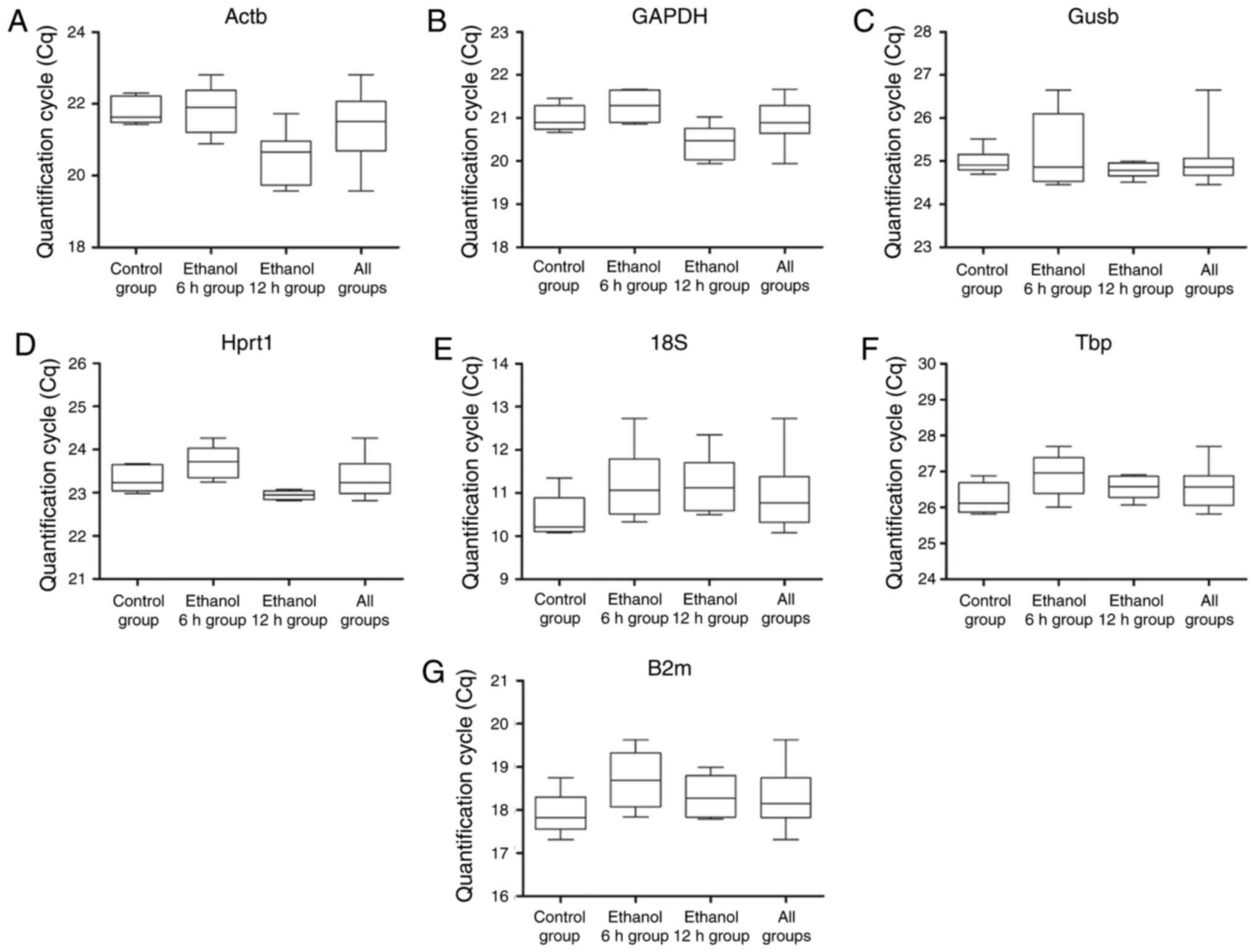
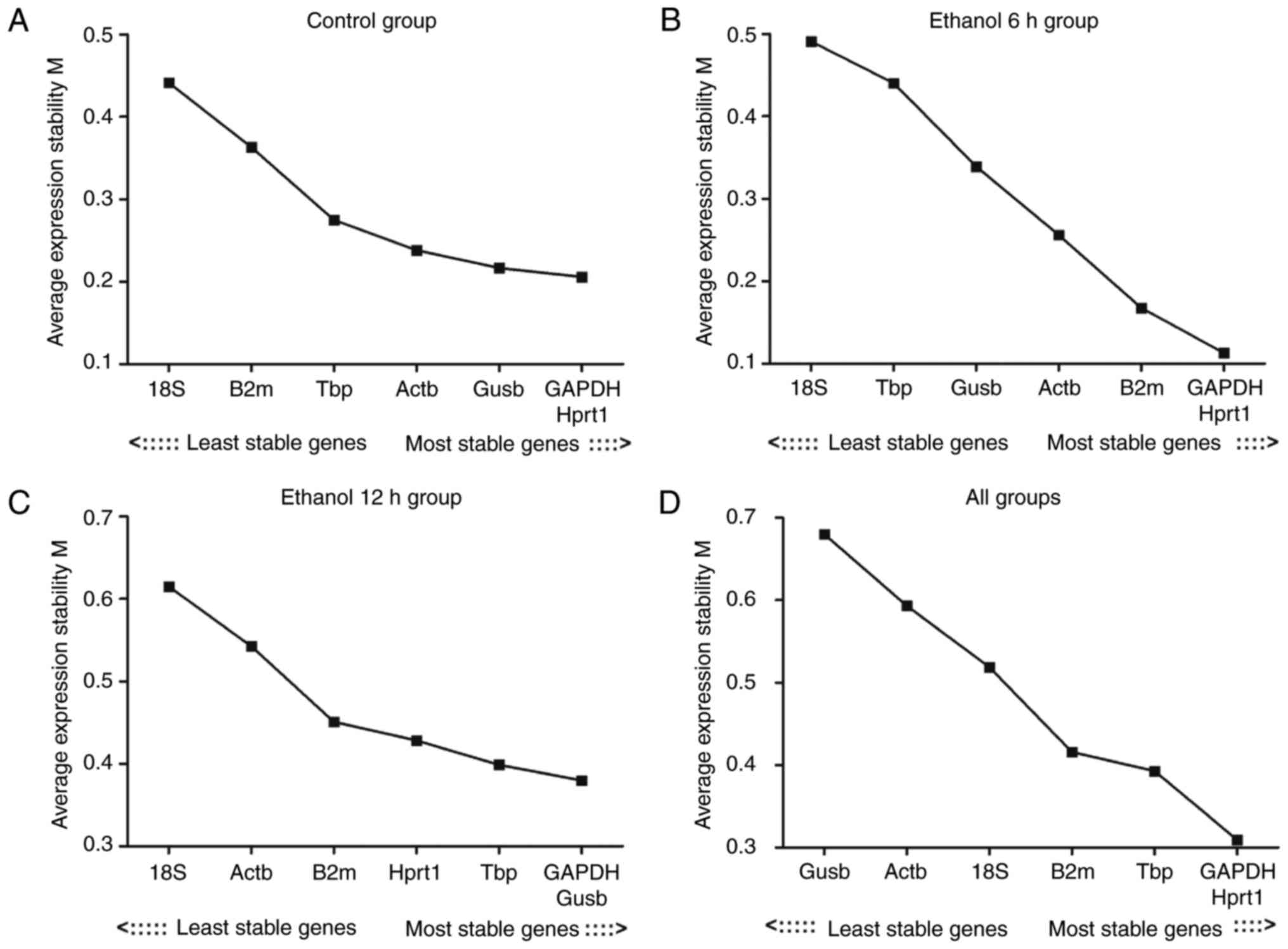
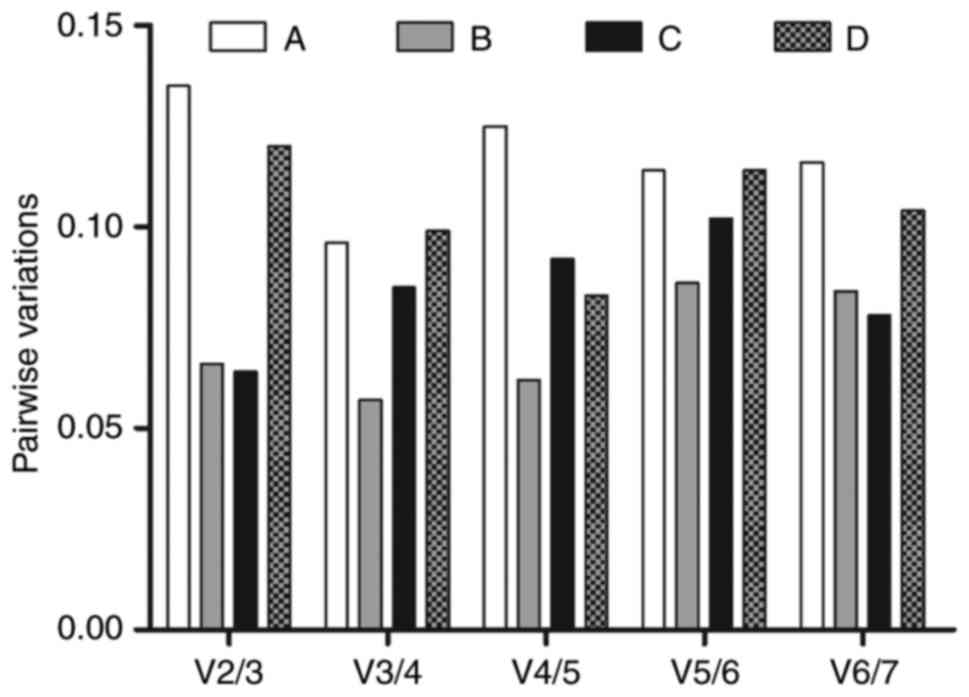
|
1
|
Massey VL and Arteel GE: Acute
alcohol-induced liver injury. Front Physiol. 3:1932012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gonçalves JL, Lacerda-Queiroz N, Sabino
JFL, Marques PE, Galvão I, Gamba CO, Cassali GD, de Carvalho LM, da
Silva E, Silva DA, Versiani A, et al: Evaluating the effects of
refined carbohydrate and fat diets with acute ethanol consumption
using a mouse model of alcoholic liver injury. J Nutr Biochem.
39:93–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sugimoto K and Takei Y: Pathogenesis of
alcoholic liver disease. Hepatol Res. 47:70–79. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chang B, Xu MJ, Zhou Z, Cai Y, Li M, Wang
W, Feng D, Bertola A, Wang H, Kunos G and Gao B: Short- or
long-term high-fat diet feeding plus acute ethanol binge
synergistically induce acute liver injury in mice: An important
role for CXCL1. Hepatology. 62:1070–1085. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song BJ, Abdelmegeed MA, Henderson LE, Yoo
SH, Wan J, Purohit V, Hardwick JP and Moon KH: Increased
nitroxidative stress promotes mitochondrial dysfunction in
alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2013:7810502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujita N and Takei Y: Alcohol consumption
and metabolic syndrome. Hepatol Res. 41:287–295. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang JJ, Meng X, Li Y, Zhou Y, Xu DP, Li
S and Li HB: Effects of melatonin on liver injuries and diseases.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:E6732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chacko KR and Reinus J: Spectrum of
alcoholic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 20:419–427. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsuchiya M, Ji C, Kosyk O, Shymonyak S,
Melnyk S, Kono H, Tryndyak V, Muskhelishvili L, Pogribny IP,
Kaplowitz N and Rusyn I: Interstrain differences in liver injury
and one-carbon metabolism in alcohol-fed mice. Hepatology.
56:130–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Halsted CH: B-Vitamin dependent methionine
metabolism and alcoholic liver disease. Clin Chem Lab Med.
51:457–465. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nolan T, Hands RE and Bustin SA:
Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc.
1:1559–1582. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Derveaux S, Vandesompele J and Hellemans
J: How to do successful gene expression analysis using real-time
PCR. Methods. 50:227–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ballester M, Cordon R and Folch JM: DAG
expression: High-throughput gene expression analysis of real-time
PCR data using standard curves for relative quantification. PloS
One. 8:e803852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lardizabal MN, Nocito AL, Daniele SM,
Ornella LA, Palatnik JF and Veggi LM: Reference genes for real-time
PCR quantification of microRNAs and messenger RNAs in rat models of
hepatotoxicity. PLoS One. 7:e363232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hernández AH, Curi R and Salazar LA:
Selection of reference genes for expression analyses in liver of
rats with impaired glucose metabolism. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:3946–3954. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu XY, Shen YB, Fu JJ, Lu LQ and Li JL:
Determination of reference microRNAs for relative quantification in
grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol.
36:374–382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Matouskova P, Bartikova H, Bousova I,
Hanusova V, Szotakova B and Skalova L: Reference genes for
real-time PCR quantification of messenger RNAs and microRNAs in
mouse model of obesity. PLoS One. 9:e860332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Castonguay Y, Michaud J and Dubé MP:
Reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of environmentally and
developmentally regulated gene expression in alfalfa. Am J Plant
Sci. 6:132–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F,
Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A and Speleman F: Accurate
normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric
averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol.
3:RESEARCH00342002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andersen CL, Jensen JL and Ørntoft TF:
Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-pcr
data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes
suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data
sets. Cancer Res. 64:5245–5250. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C and
Neuvians TP: Determination of stable housekeeping genes,
differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity:
BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations.
Biotechnol Lett. 26:509–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tatsumi K, Ohashi K, Taminishi S, Okano T,
Yoshioka A and Shima M: Reference gene selection for real-time
RT-PCR in regenerating mouse livers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
374:106–110. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji C: New insights into the pathogenesis
of alcohol-induced ER stress and liver diseases. Int J Hepatol.
2014:5137872014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C (T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ferlini A and Rimessi P: Exon skipping
quantification by real-time PCR. Methods Mol Biol. 867:189–199.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao X, Huang X, Zhou Z and Lin X: An
improvement of the 2ˆ(−delta delta CT) method for quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat
Bioinforma Biomath. 3:71–85. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ji C and Kaplowitz N: ER stress: Can the
liver cope? J Hepatol. 45:321–333. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Malhi H and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol. 54:795–809. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lai CW, Otero JH, Hendershot LM and Snapp
E: ERdj4 protein is a soluble endoplasmic reticulum (ER) DnaJ
family protein that interacts with ER-associated degradation
machinery. J Biol Chem. 287:7969–7978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang SB, Shi Q, Xu Y, Xie WL, Zhang J,
Tian C, Guo Y, Wang K, Zhang BY, Chen C, et al: Protein disulfide
isomerase regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and the apoptotic
process during prion infection and PrP mutant-induced cytotoxicity.
PLoS One. 7:e382212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peletto S, Bertuzzi S, Campanella C,
Modesto P, Maniaci MG, Bellino C, Ariello D, Quasso A, Caramelli M
and Acutis PL: Evaluation of internal reference genes for
quantitative expression analysis by real-time PCR in ovine whole
blood. Int J Mol Sci. 12:7732–7747. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans
J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL,
et al: The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of
quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 55:611–622.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lacerda AL, Fonseca LN, Blawid R, Boiteux
LS, Ribeiro SG and Brasileiro AC: Reference gene selection for qPCR
analysis in tomato-bipartite begomovirus interaction and validation
in additional tomato-virus pathosystems. PLoS One. 10:e01368202015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang X, Ding L and Sandford AJ: Selection
of reference genes for gene expression studies in human neutrophils
by real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol. 6:42005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nelissen K, Smeets K, Mulder M, Hendriks
JJ and Ameloot M: Selection of reference genes for gene expression
studies in rat oligodendrocytes using quantitative real time PCR. J
Neurosci Methods. 187:78–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li H, Chen C, Yao H, Li X, Yang N, Qiao J,
Xu K and Zeng L: Identification of suitable reference genes for
mRNA studies in bone marrow in a mouse model of hematopoietic stem
cell transplantation. Transplant Proc. 48:2826–2832. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin P, Lan X, Chen F, Yang Y, Jin Y and
Wang A: Reference gene selection for real-time quantitative PCR
analysis of the mouse uterus in the peri-implantation period. PLoS
One. 8:e624622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stephens AS, Stephens SR and Morrison NA:
Internal control genes for quantitative RT-PCR expression analysis
in mouse osteoblasts, osteoclasts and macrophages. BMC Res Notes.
4:4102011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Klein C, Rutllant J and Troedsson MH:
Expression stability of putative reference genes in equine
endometrial, testicular, and conceptus tissues. BMC Res Notes.
4:1202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Valadan R, Hedayatizadeh-Omran A,
Alhosseini-Abyazani MN, Amjadi O, Rafiei A, Tehrani M and
Alizadeh-Navaei R: Data supporting the design and evaluation of a
universal primer pair for pseudogene-free amplification of HPRT1 in
real-time PCR. Data Brief. 4:384–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Valadan R, Amjadi O, Tehrani M, Rafiei A,
Hedayatizadeh-Omran A and Alizadeh-Navaei R: Pseudogene-free
amplification of HPRT1 in quantitative reverse transcriptase
polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 485:46–48. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zainuddin A, Chua KH, Abdul Rahim N and
Makpol S: Effect of experimental treatment on GAPDH mRNA expression
as a housekeeping gene in human diploid fibroblasts. BMC Mol Biol.
11:592010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bonefeld BE, Elfving B and Wegener G:
Reference genes for normalization: A study of rat brain tissue.
Synapse. 62:302–309. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|