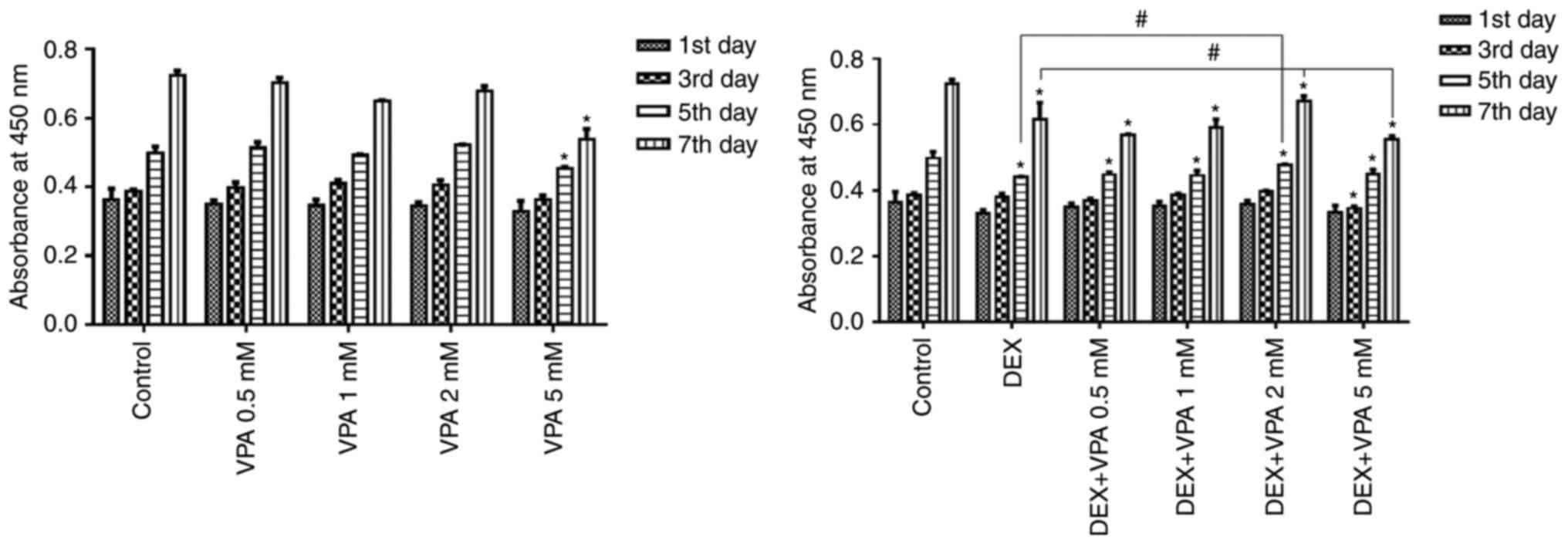
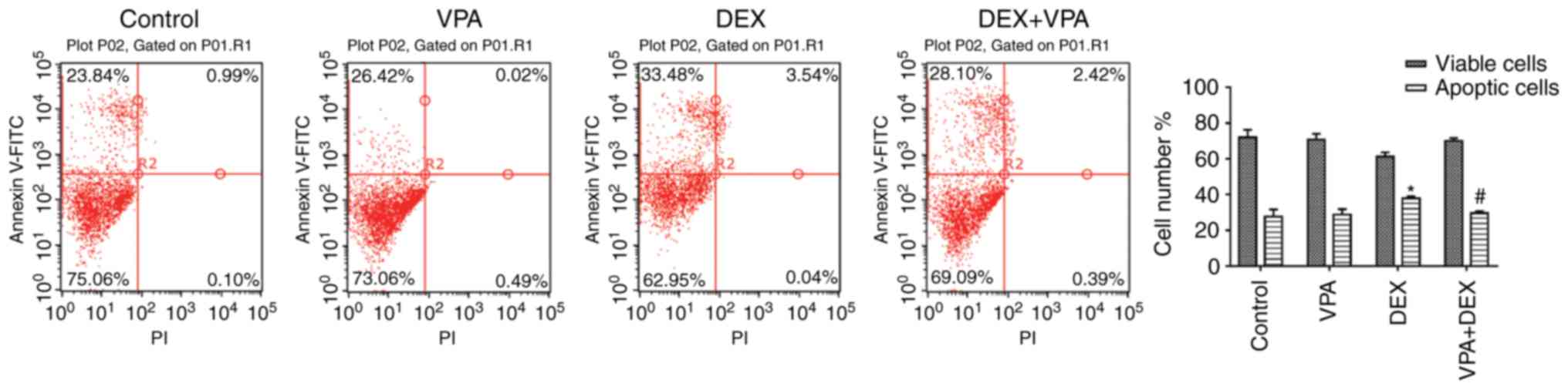
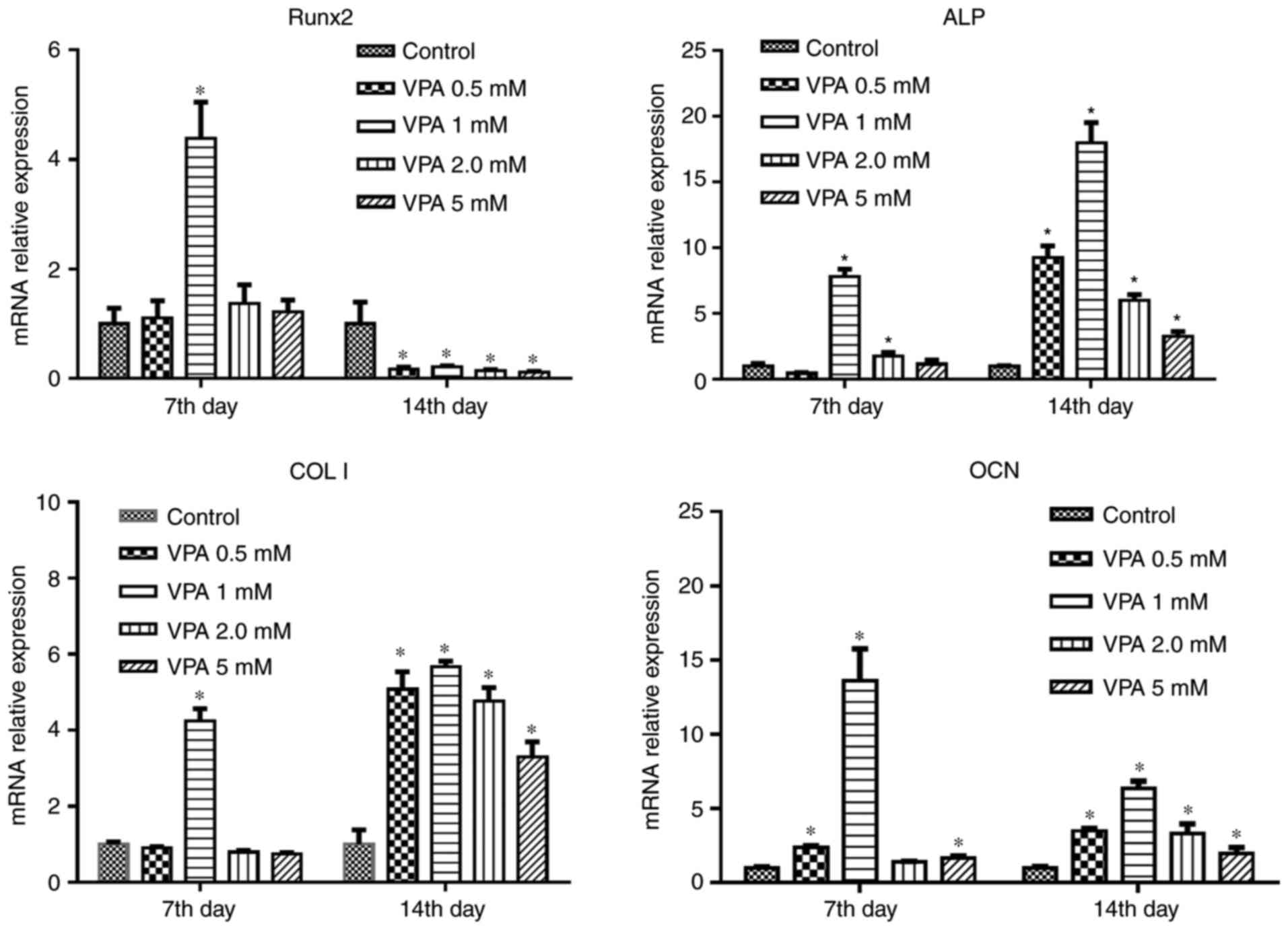
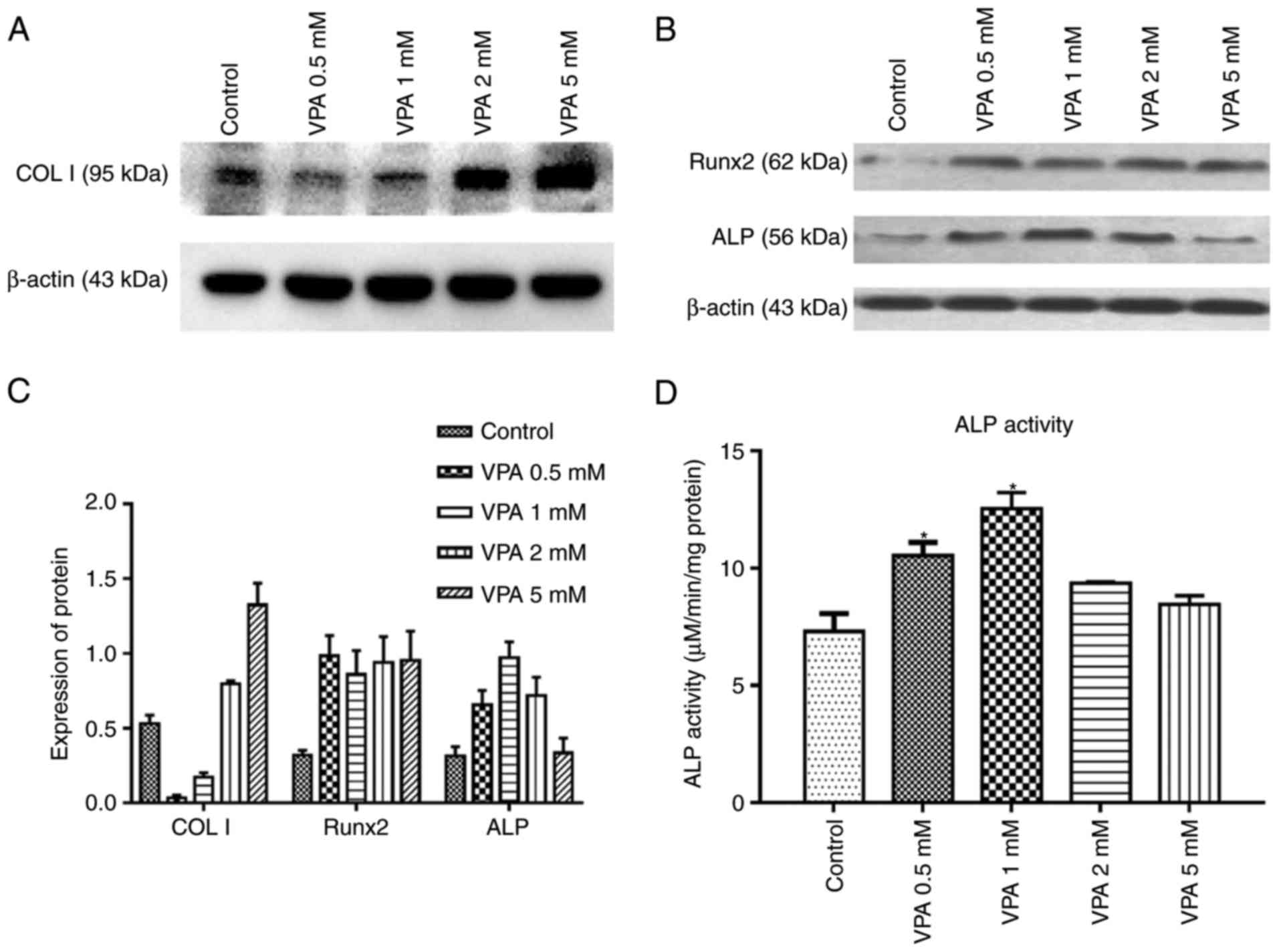
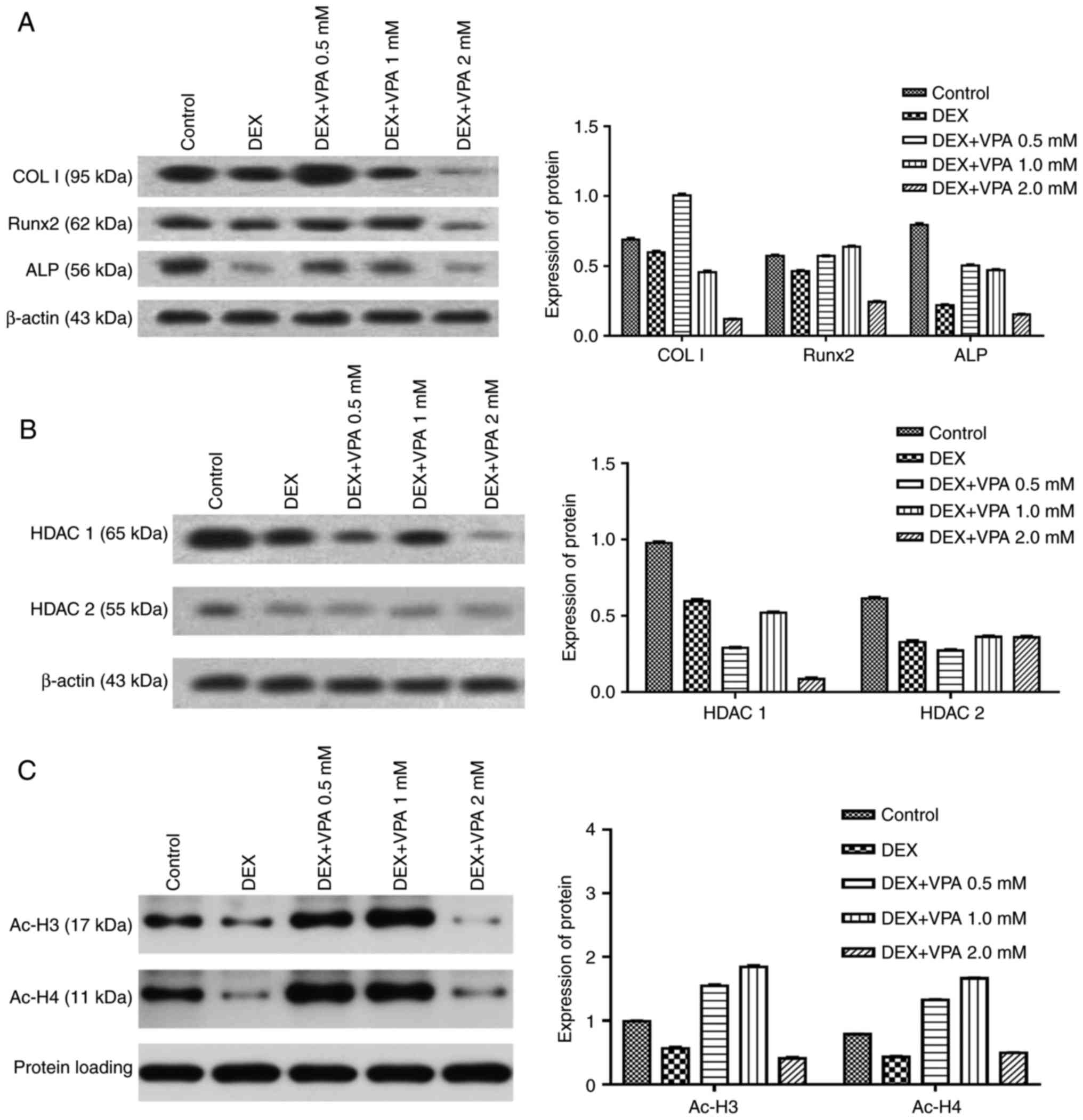
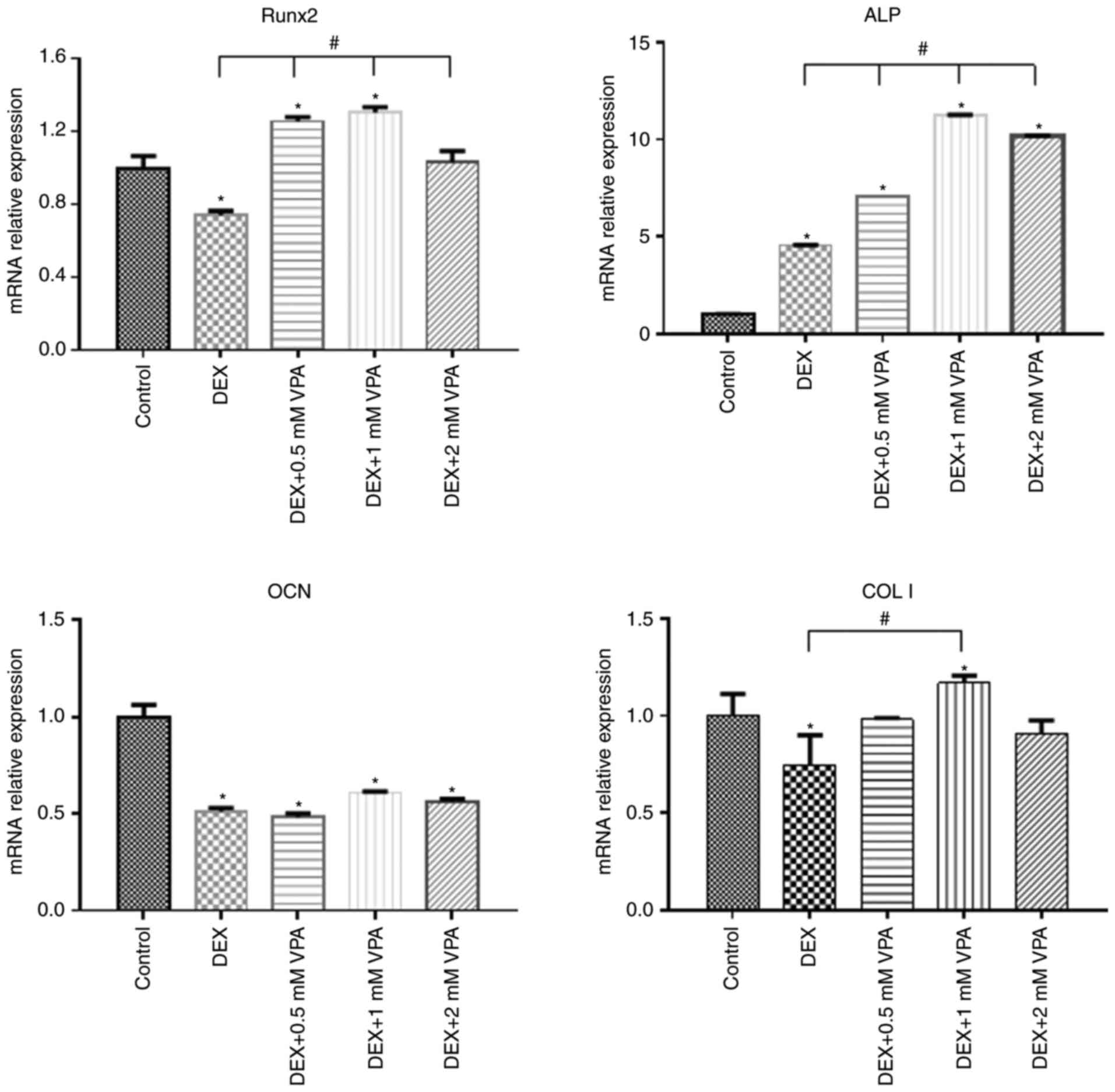
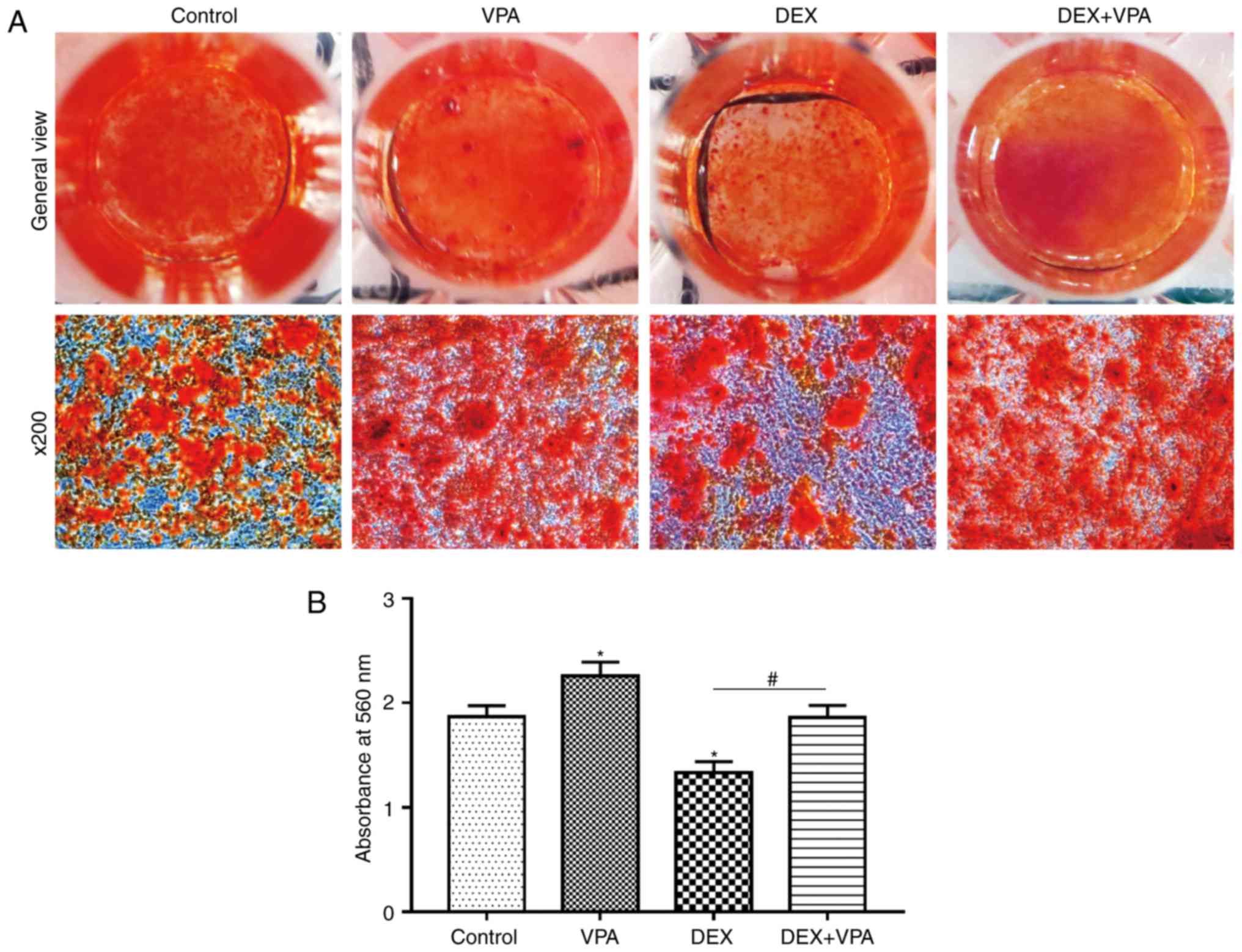
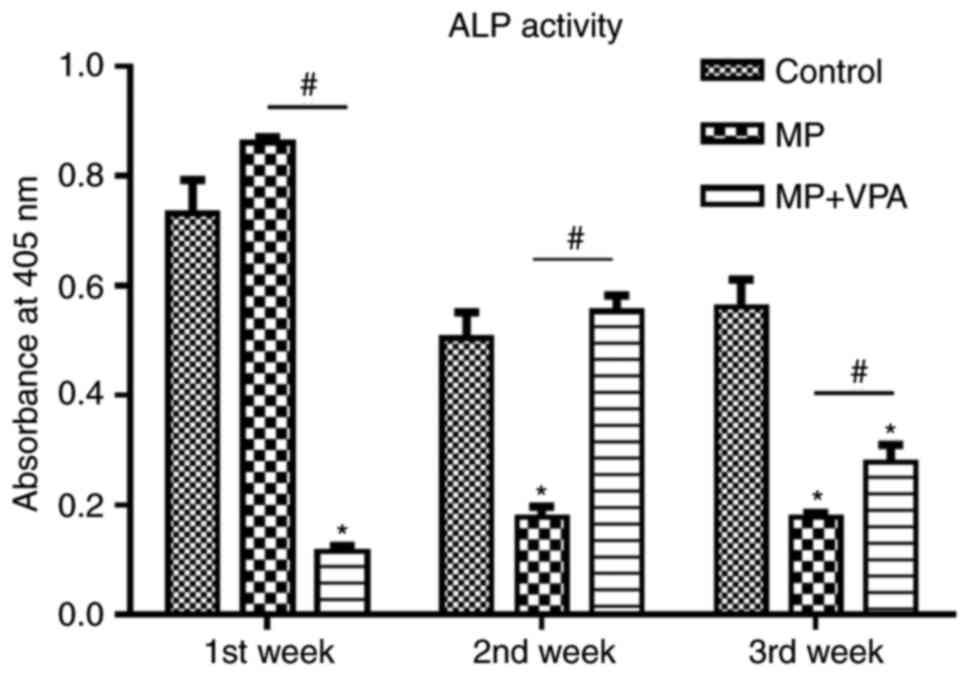
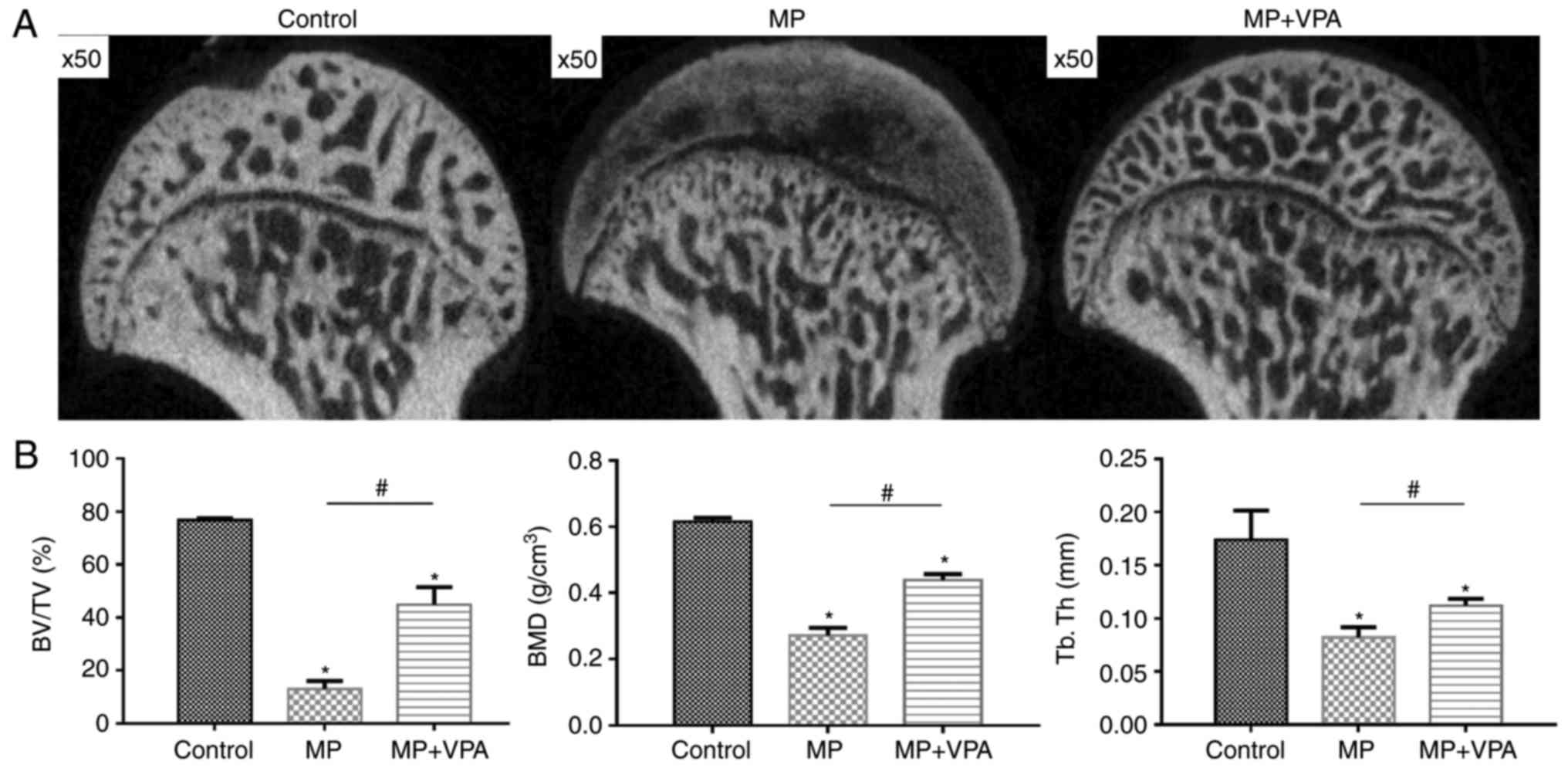
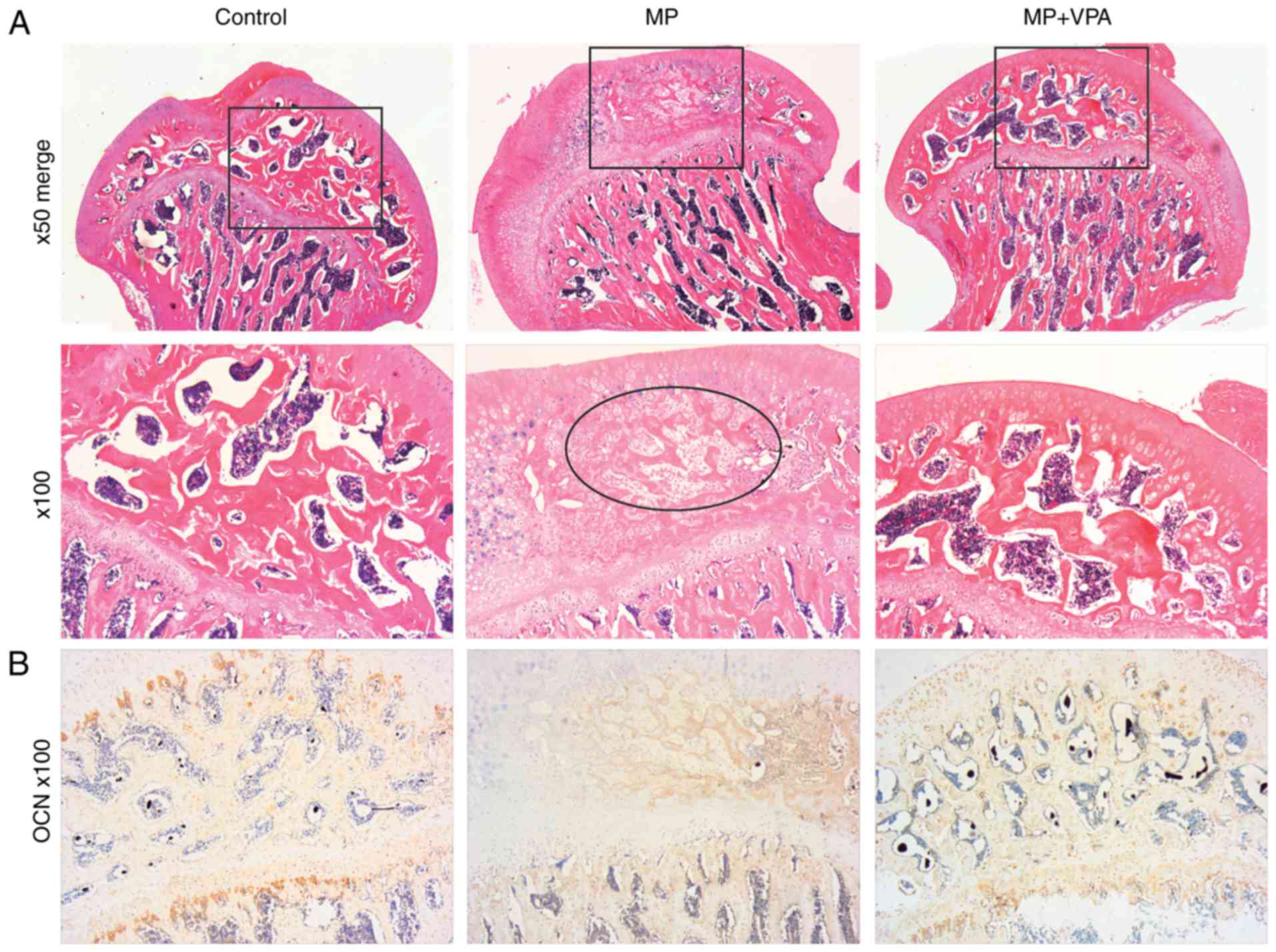
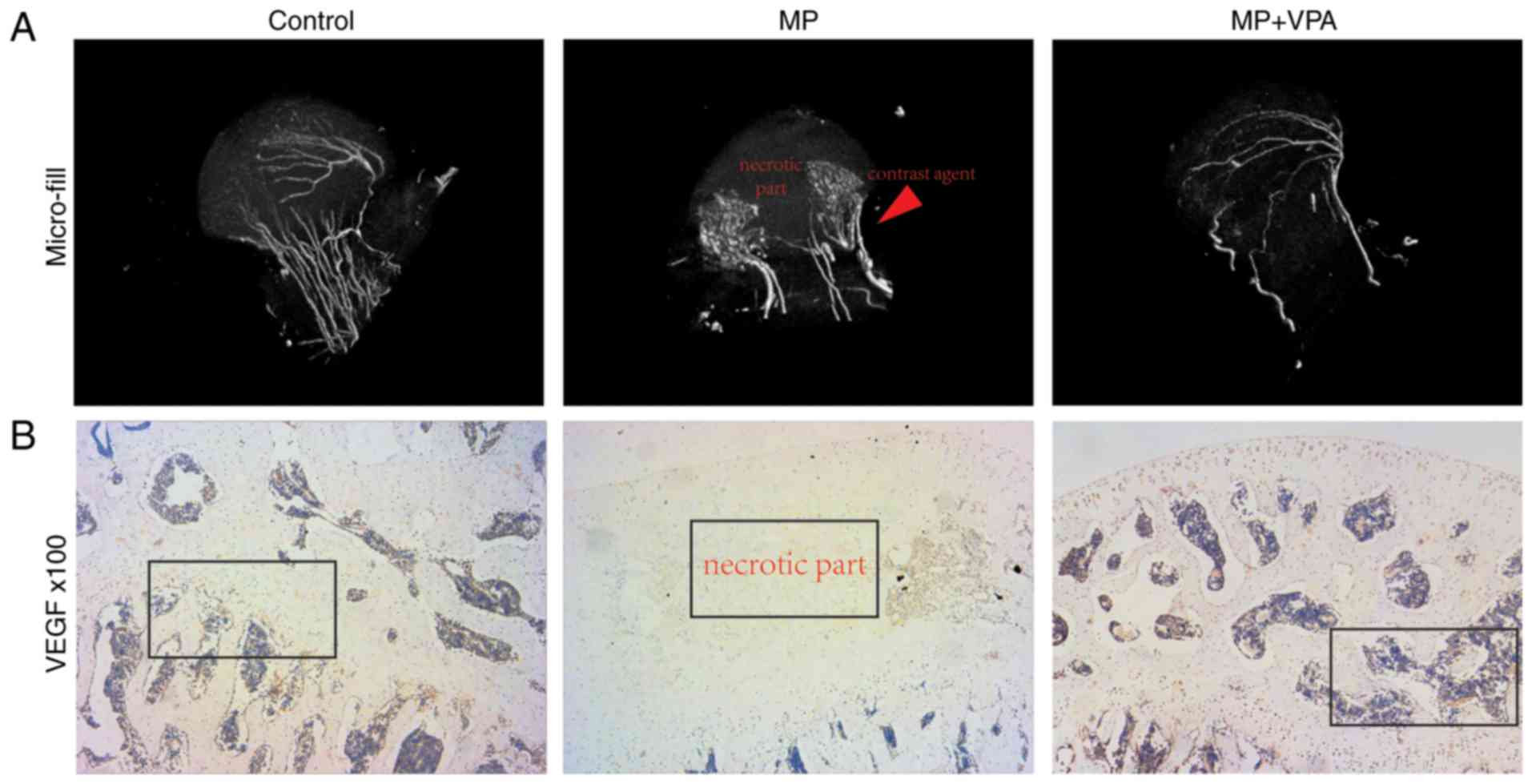
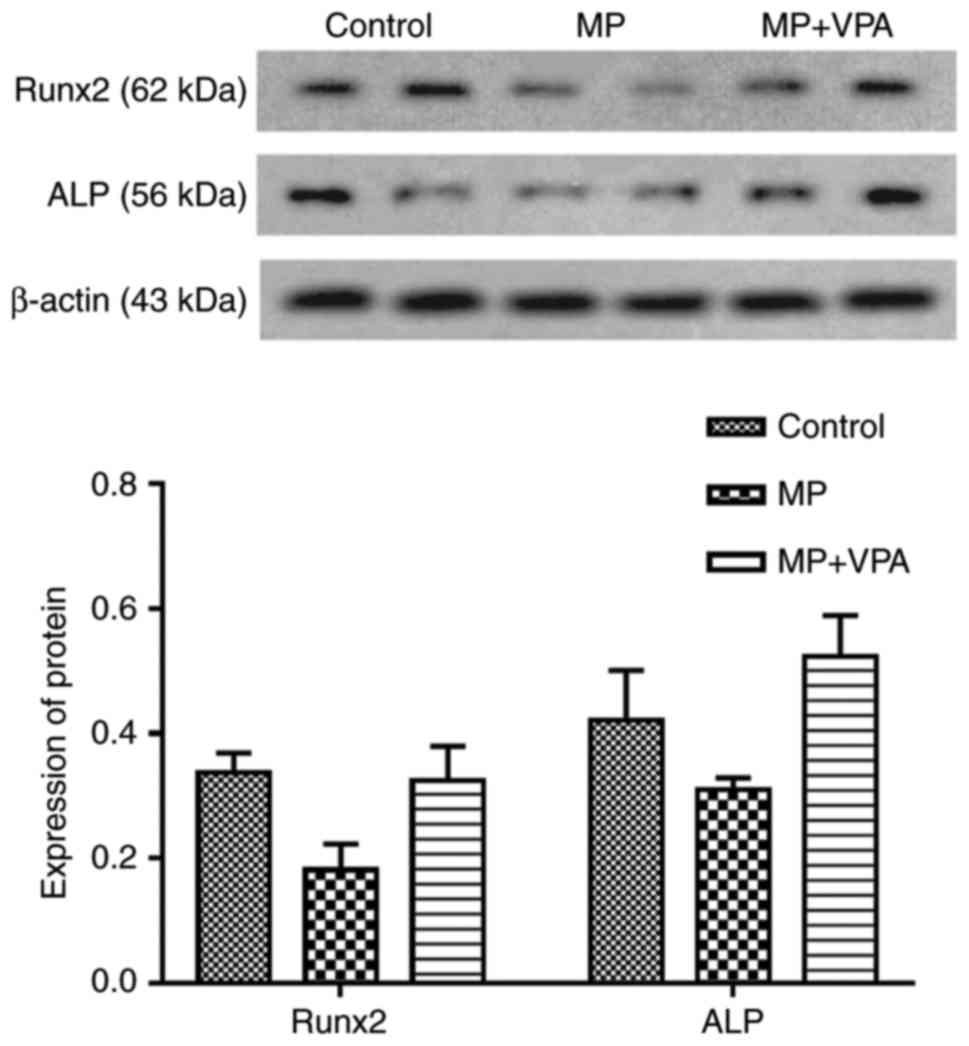
|
1
|
Assouline-Dayan Y, Chang C, Greenspan A,
Shoenfeld Y and Gershwin ME: Pathogenesis and natural history of
osteonecrosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 32:94–124. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mont MA, Jones LC and Hungerford DS:
Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Ten years later. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 88:1117–1132. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan G, Kang PD and Pei FX: Glucocorticoids
affect the metabolism of bone marrow stromal cells and lead to
osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A review. Chin Med J.
125:134–139. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tait AS, Butts CL and Sternberg EM: The
role of glucocorticoids and progestins in inflammatory, autoimmune,
and infectious disease. J Leukoc Biol. 84:924–931. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kirwan JR: The effect of glucocorticoids
on joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. The arthritis and
rheumatism council Low-dose glucocorticoid study group. N Engl J
Med. 333:142–146. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Salmon SE, Crowley JJ, Grogan TM, Finley
P, Pugh RP and Barlogie B: Combination chemotherapy,
glucocorticoids, and interferon alfa in the treatment of multiple
myeloma: A Southwest oncology group study. J Clin Oncol.
12:2405–2414. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hall ED and Braughler JM: Glucocorticoid
mechanisms in acute spinal cord injury: A review and therapeutic
rationale. Surg Neurol. 18:320–327. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mont MA, Zywiel MG, Marker DR, McGrath MS
and Delanois RE: The natural history of untreated asymptomatic
osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic literature review.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 92:2165–2170. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boss JH: Experimental models of
osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Sci. 9:533–534. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lavernia CJ, Sierra RJ and Grieco FR:
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.
7:250–261. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kerachian MA, Cournoyer D, Harvey EJ, Chow
TY, Bégin LR, Nahal A and Séguin C: New insights into the
pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis:
Microarray analysis of gene expression in a rat model. Arthritis
Res Ther. 12:R1242010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cenni E, Fotia C, Rustemi E, Yuasa K,
Caltavuturo G, Giunti A and Baldini N: Idiopathic and secondary
osteonecrosis of the femoral head show different thrombophilic
changes and normal or higher levels of platelet growth factors.
Acta Orthop. 82:42–49. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hernigou P, Beaujean F and Lambotte JC:
Decrease in the mesenchymal stem-cell pool in the proximal femur in
corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
81:349–355. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hernigou P and Beaujean F: Abnormalities
in the bone marrow of the iliac crest in patients who have
osteonecrosis secondary to corticosteroid therapy or alcohol abuse.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 79:1047–1053. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jia Y, Chu TW and Zhou Y: Repair process
in experimentally induced avascular necrosis of femoral head in
rabbits. Chongqing Med. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Takaoka K, Yoshioka T, Hosoya T, Ono K and
Takase T: The repair process in experimentally induced avascular
necrosis of the femoral head in dogs. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.
99:109–115. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Malizos KN, Quarles LD, Seaber AV, Rizk WS
and Urbaniak JR: An experimental canine model of osteonecrosis:
Characterization of the repair process. J Orthop Res. 11:350–357.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shapiro F, Connolly S, Zurakowski D,
Menezes N, Olear E, Jimenez M, Flynn E and Jaramillo D: Femoral
head deformation and repair following induction of ischemic
necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 91:2903–2914. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koromila T, Baniwal SK, Song YS, Martin A,
Xiong J and Frenkel B: Glucocorticoids antagonize RUNX2 during
osteoblast differentiation in cultures of ST2 pluripotent
mesenchymal cells. J Cell Biochem. 115:27–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
O'Brien CA, Jia D, Plotkin LI, Bellido T,
Powers CC, Stewart SA, Manolagas SC and Weinstein RS:
Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoblasts and osteocytes to
induce their apoptosis and reduce bone formation and strength.
Endocrinology. 145:1835–1841. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee JS, Lee JS, Roh HL, Kim CH, Jung JS
and Suh KT: Alterations in the differentiation ability of
mesenchymal stem cells in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis
of the femoral head: Comparative analysis according to the risk
factor. J Orthop Res. 24:604–609. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Houdek MT, Wyles CC, Packard BD, Terzic A,
Behfar A and Sierra RJ: Decreased osteogenic activity of
mesenchymal stem cells in patients with corticosteroid-induced
osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Arthroplasty. 31:893–898.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang BL, Sun W, Shi ZC, Lou JN, Zhang NF,
Shi SH, Guo WS, Cheng LM, Ye LY, Zhang WJ and Li ZR: Decreased
proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells in corticosteroid-induced
osteonecrosis of femoral head. Orthopedics. 31:4442008.
|
|
24
|
Zhou DA, Zheng HX, Wang CW, Shi D and Li
JJ: Influence of glucocorticoids on the osteogenic differentiation
of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. BMC
Musculoskeletal Disord. 15:2392014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang W, Yang N and Shi XM: Regulation of
mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation by
glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ). J Biol Chem.
283:4723–4729. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Waterhouse E: Intravenous valproate for
pediatric status epilepticus. Epilepsy Curr. 3:208–209. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Göttlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, Krämer OH,
Schimpf A, Giavara S, Sleeman JP, Lo Coco F, Nervi C, Pelicci PG
and Heinzel T: Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC
inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J.
20:6969–6978. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cho HH, Park HT, Kim YJ, Bae YC, Suh KT
and Jung JS: Induction of osteogenic differentiation of human
mesenchymal stem cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Cell
Biochem. 96:533–542. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN,
Kemp S and van Kuilenburg AB: Histone deacetylases (HDACs):
Characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J.
370:737–749. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Delcuve GP, Rastegar M and Davie JR:
Epigenetic control. J Cell Physiol. 219:243–250. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zheng QF, Wang HM, Wang ZF, Liu JY, Zhang
Q, Zhang L, Lu YH, You H and Jin GH: Reprogramming of histone
methylation controls the differentiation of monocytes into
macrophages. FEBS J. 284:1309–1323. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qin H, Zhao A, Zhang C and Fu X:
Epigenetic control of reprogramming and transdifferentiation by
histone modifications. Stem Cell Rev. 12:708–720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sepulveda H, Aguilar R, Prieto CP, Bustos
F, Aedo S, Lattus J, van Zundert B, Palma V and Montecino M:
Epigenetic signatures at the RUNX2-P1 and Sp7 gene promoters
control osteogenic lineage commitment of umbilical Cord-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 232:2519–2527. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shahbazian MD and Grunstein M: Functions
of site-specific histone acetylation and deacetylation. Annu Rev
Biochem. 76:75–100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hatakeyama Y, Hatakeyama J, Takahashi A,
Oka K, Tsuruga E, Inai T and Sawa Y: The effect of valproic Acid on
mesenchymal pluripotent cell proliferation and differentiation in
extracellular matrices. Drug Target Insights. 5:1–9. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Paino F, La Noce M, Tirino V, Naddeo P,
Desiderio V, Pirozzi G, De Rosa A, Laino L, Altucci L and Papaccio
G: Histone deacetylase inhibition with valproic acid downregulates
osteocalcin gene expression in human dental pulp stem cells and
osteoblasts: Evidence for HDAC2 involvement. Stem Cells.
32:279–289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Xu Y, Hammerick KE, James AW, Carre AL,
Leucht P, Giaccia AJ and Longaker MT: Inhibition of histone
deacetylase activity in reduced oxygen environment enhances the
osteogenesis of mouse adipose-derived stromal cells. Tissue Eng
Part A. 15:3697–3707. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee S, Park JR, Seo MS, Roh KH, Park SB,
Hwang JW, Sun B, Seo K, Lee YS, Kang SK, et al: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors decrease proliferation potential and multilineage
differentiation capability of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell
Prolif. 42:711–720. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rashid MM, Akiba Y, Akiba N, Kaku M and
Uoshima K: Effect of valproic acid on bone healing in rat.
IADR/AADR/CADR General Session and Exhibition. 2013.
|
|
40
|
Grose AW, Gardner MJ, Sussmann PS, Helfet
DL and Lorich DG: The surgical anatomy of the blood supply to the
femoral head: Description of the anastomosis between the medial
femoral circumflex and inferior gluteal arteries at the hip. J Bone
Joint Surg Br. 90:1298–1303. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zlotorowicz M and Czubak J: Vascular
anatomy and blood supply to the femoral head. Osteonecrosis. 19–25.
2014.
|
|
42
|
Li GY, Feng Y, Cheng TS, Yin JM and Zhang
CQ: Edaravone, a novel free radical scavenger, prevents
steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Rheumatology. 52:438–447.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen CH and Wang GJ: Alendronate in the
prevention of collapse of the femoral head in nontraumatic
osteonecrosis. Osteonecrosis. 7:265–271. 2014.
|
|
44
|
Nishida K, Yamamoto T, Motomura G,
Jingushi S and Iwamoto Y: Pitavastatin may reduce risk of
steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits: A preliminary
histological study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 466:1054–1058. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou D, Qi C, Chen YX, Zhu YJ, Sun TW,
Chen F and Zhang CQ: Comparative study of porous
hydroxyapatite/chitosan and whitlockite/chitosan scaffolds for bone
regeneration in calvarial defects. Int J Nanomedicine.
12:2673–2687. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Luo S, Yang Y, Chen J, Zhong Z, Huang H,
Zhang J and Cui L: Tanshinol stimulates bone formation and
attenuates dexamethasone-induced inhibition of osteogenesis in
larval zebrafish. J Orthopaedic Translation. 4:35–45. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Fujita T, Fukuyama R, Enomoto H and Komori
T: Dexamethasone inhibits insulin-induced chondrogenesis of ATDC5
cells by preventing PI3K-Akt signaling and DNA binding of Runx2. J
Cell Biochem. 93:374–83. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhang YL, Yin JH, Ding H, Zhang W, Zhang
CQ and Gao YS: Vitamin K2 prevents
glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats.
Int J Biol Sci. 12:347–358. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Guo SC, Tao SC, Yin WJ, Qi X, Sheng JG and
Zhang CQ: Exosomes from human synovial-derived mesenchymal stem
cells prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral
head in the rat. Int J Biol Sci. 12:1262–1272. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Siéssere S, Semprini M, Lopes RA, Sala MA
and Mattos MC: Morphological and morphometric alterations induced
by valproic acid on rat fetuses' Meckel's cartilage, lingual
musculature, and submandibular gland. Int J Morphol. 22:133–137.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Welbat JU, Chaisawang P,
Chaijaroonkhanarak W, Prachaney P, Pannangrong W, Sripanidkulchai B
and Wigmore P: Kaempferia parviflora extract ameliorates the
cognitive impairments and the reduction in cell proliferation
induced by valproic acid treatment in rats. Ann Anat. 206:7–13.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cho HH, Park HT, Kim YJ, Bae YC, Suh KT
and Jung JS: Induction of osteogenic differentiation of human
mesenchymal stem cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Cell
Biochem. 96:533–542. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jeon MJ, Kim JA, Kwon SH, Kim SW, Park KS,
Park SW, Kim SY and Shin CS: Activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma inhibits the Runx2-mediated
transcription of osteocalcin in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem.
278:23270–23277. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Morimoto E, Li M, Khalid AB, Krum SA,
Chimge NO and Frenkel B: Glucocorticoids Hijack Runx2 to stimulate
Wif1 for suppression of osteoblast growth and differentiation. J
Cell Physiol. 232:145–153. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Shi XM, Chutkan N, Hamrick MW and Isales
CM: Mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: An update.
Intech. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Marquez-Curtis LA, Qiu Y, Xu A and
Janowska-Wieczorek A: Migration, proliferation, and differentiation
of cord blood mesenchymal stromal cells treated with histone
deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid. Stem Cells Int.
2014:6104952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tomé M, López-Romero P, Albo C, Sepúlveda
JC, Fernández-Gutiérrez B, Dopazo A, Bernad A and González MA:
miR-335 orchestrates cell proliferation, migration and
differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ.
18:985–995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Ciciarello M, Zini R, Rossi L, Salvestrini
V, Ferrari D, Manfredini R and Lemoli RM: Extracellular purines
promote the differentiation of human bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells to the osteogenic and adipogenic lineages.
Stem Cells Dev. 22:1097–1111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Ding H, Wang T, Xu D, Cha B, Liu J and Li
Y: Dexamethasone-induced apoptosis of osteocytic and osteoblastic
cells is mediated by TAK1 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
460:157–163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim SM, Kim YG, Park JW, Lee JM and Suh
JY: The effects of dexamethasone on the apoptosis and osteogenic
differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal
Implant Sci. 43:168–176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pang J, Huang H, Zhang Q, et al: The
effect of dexamethasone on the proliferation and apoptosis of human
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Modern Med J China.
2008.
|
|
63
|
Gao B, Huang Q, Jie Q, Zhang HY, Wang L,
Guo YS, Sun Z, Wei BY, Han YH, Liu J, et al: Ginsenoside-Rb2
inhibits dexamethasone-induced apoptosis through promotion of
GPR120 induction in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
Stem Cells Dev. 24:781–790. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Komori T: Regulation of osteoblast
differentiation by Runx2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 658:43–49. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Rimando MG, Wu HH, Liu YA, Lee CW, Kuo SW,
Lo YP, Tseng KF, Liu YS and Lee OK: Glucocorticoid receptor and
Histone deacetylase 6 mediate the differential effect of
dexamethasone during osteogenesis of mesenchymal stromal cells
(MSCs). Sci Rep. 6:373712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Pujols L, Mullol J, Pérez M, Roca-Ferrer
J, Juan M, Xaubet A, Cidlowski JA and Picado C: Expression of the
human glucocorticoid receptor alpha and beta isoforms in human
respiratory epithelial cells and their regulation by dexamethasone.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 24:49–57. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li LB, Leung DY, Martin RJ and Goleva E:
Inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 expression by elevated
glucocorticoid receptor beta in steroid-resistant asthma. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 182:877–883. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Adcock IM: Glucocorticoid-regulated
transcription factors. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 14:211–219. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang YY, Li X, Qian SW, Guo L, Huang HY,
He Q, Liu Y, Ma CG and Tang QQ: Down-regulation of type I Runx2
mediated by dexamethasone is required for 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Mol
Endocrinol. 26:798–808. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Adcock IM, Cosio B, Tsaprouni L, Barnes PJ
and Ito K: Redox regulation of histone deacetylases and
glucocorticoid-mediated inhibition of the inflammatory response.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:144–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ito K, Yamamura S, Essilfie-Quaye S, Cosio
B, Ito M, Barnes PJ and Adcock IM: Histone deacetylase 2-mediated
deacetylation of the glucocorticoid receptor enables NF-kappaB
suppression. J Exp Med. 203:7–13. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Okazaki S, Nagoya S, Matsumoto H, Mizuo K,
Sasaki M, Watanabe S, Yamashita T and Inoue H: Development of
non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head requires toll-like
receptor 7 and 9 stimulations and is boosted by repression on
nuclear factor kappa B in rats. Lab Invest. 95:92–99. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Chen S, Li J, Peng H, Zhou J and Fang H:
Administration of erythropoietin exerts protective effects against
glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats.
Int J Mol Med. 33:840–848. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Han N, Yan ZQ, Guo CA, Shen F, Liu J, Shi
YX and Zhang ZY: Effect of rifampicin on the risk of
steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthop Surg.
2:124–133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Tseng MT, Hsieh SC, Shun CT, Lee KL, Pan
CL, Lin WM, Lin YH, Yu CL and Hsieh ST: Skin denervation and
cutaneous vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Brain.
129:977–985. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Suda S, Katsura K, Kanamaru T, Saito M and
Katayama Y: Valproic acid attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury in
the rat brain through inhibition of oxidative stress and
inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 707:26–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rao T, Wu F, Xing D, Peng Z, Ren D, Feng
W, Chen Y, Zhao Z, Wang H, Wang J, et al: Effects of valproic Acid
on axonal regeneration and recovery of motor function after
peripheral nerve injury in the rat. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2:17–24.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang Z, Qin X, Tong N, Zhao X, Gong Y,
Shi Y and Wu X: Valproic acid-mediated neuroprotection in retinal
ischemia injury via histone deacetylase inhibition and
transcriptional activation. Exp Eye Res. 94:98–108. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Hwabejire JO, Lu J, Liu B, Li Y, Halaweish
I and Alam HB: Valproic acid for the treatment of hemorrhagic
shock: A dose-optimization study. J Surg Res. 186:363–370. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Krishnamoorthy G, Karande S, Ahire N,
Mathew L and Kulkarni M: Bone metabolism alteration on
antiepileptic drug therapy. Indian J Pediatr. 76:377–383. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Lee HS, Lee CS, Jang JS, Lee JD and Um SM:
Changes of serum alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin during
fracture healing. J Korean Orthopaedic Association. 37:411–415.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Komnenou A, Karayannopoulou M,
Polizopoulou ZS, Constantinidis TC and Dessiris A: Correlation of
serum alkaline phosphatase activity with the healing process of
long bone fractures in dogs. Vet Clin Pathol. 34:35–38. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Floerkemeier T, Hirsch S, Budde S, Radtke
K, Thorey F, Windhagen H and von Lewinski G: Bone turnover markers
failed to predict the occurrence of osteonecrosis of the femoral
head: A preliminary study. J Clin Lab Anal. 26:55–60. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|