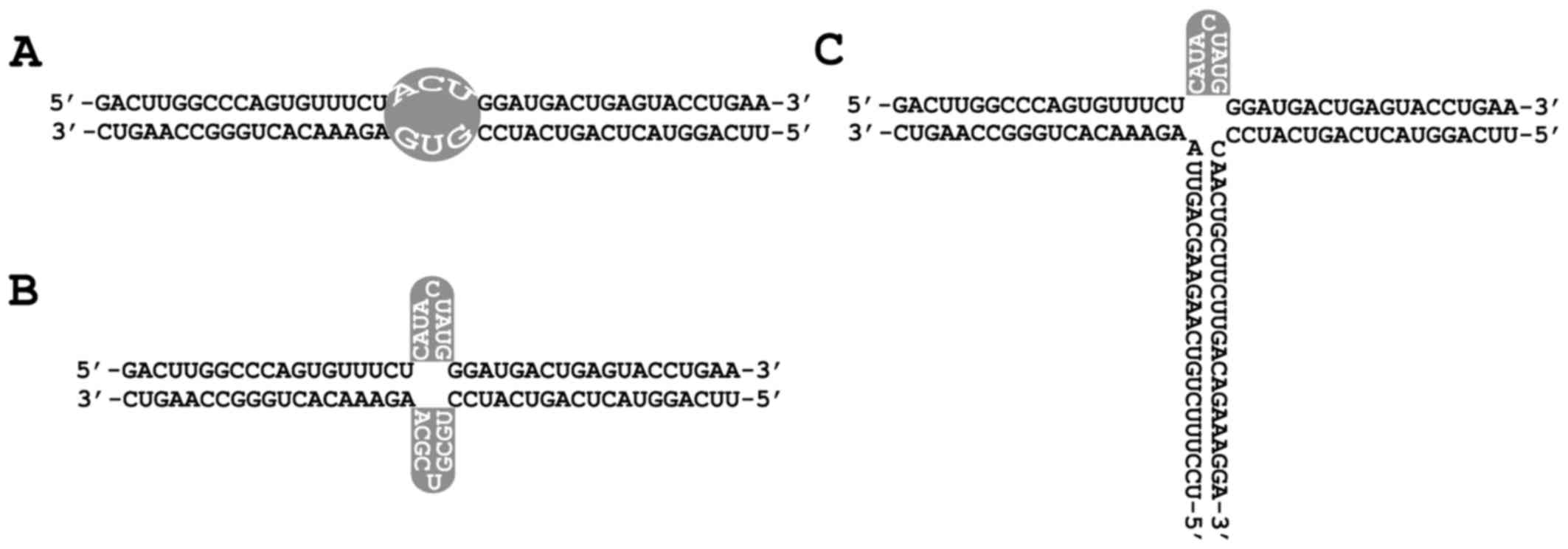
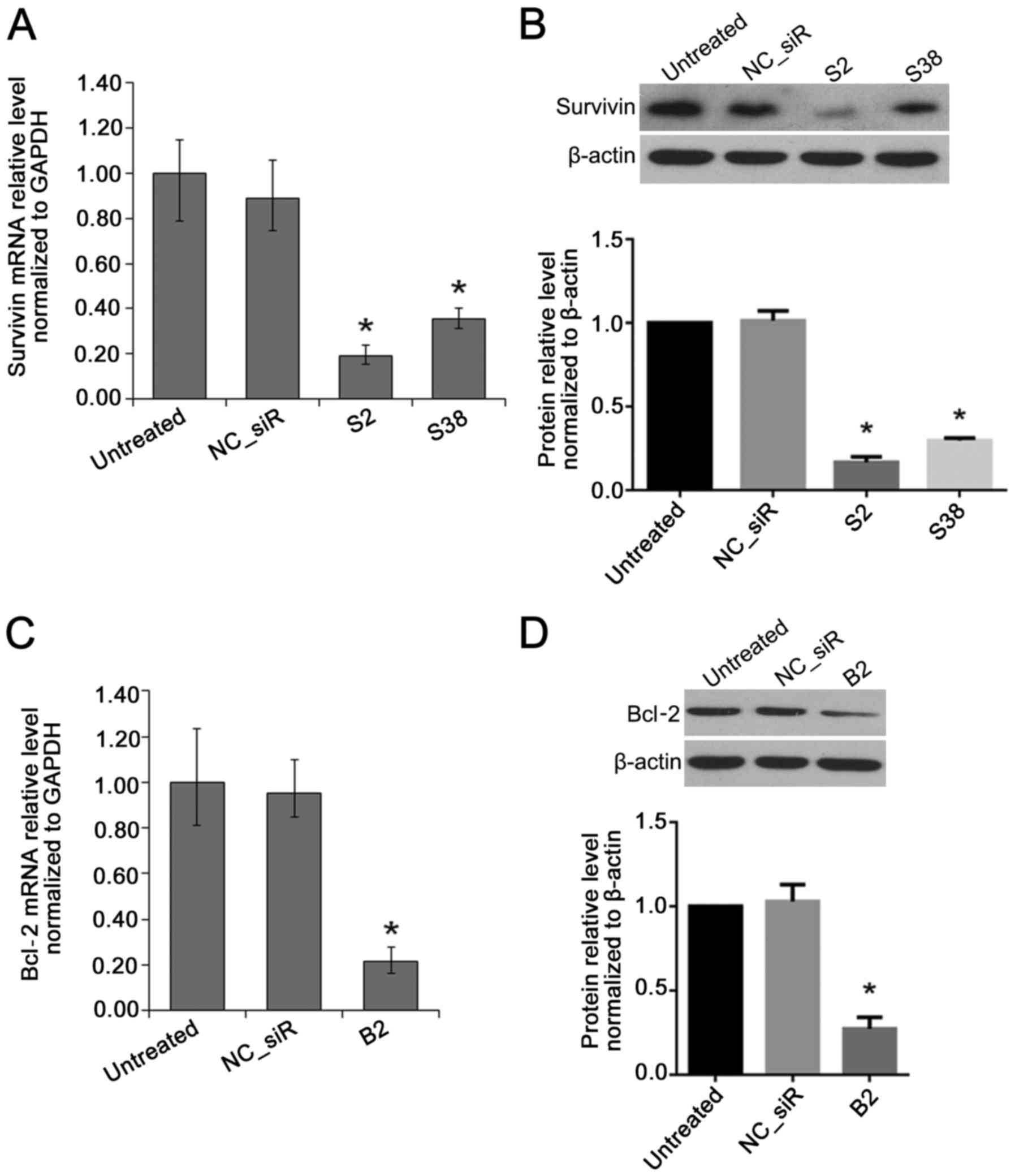
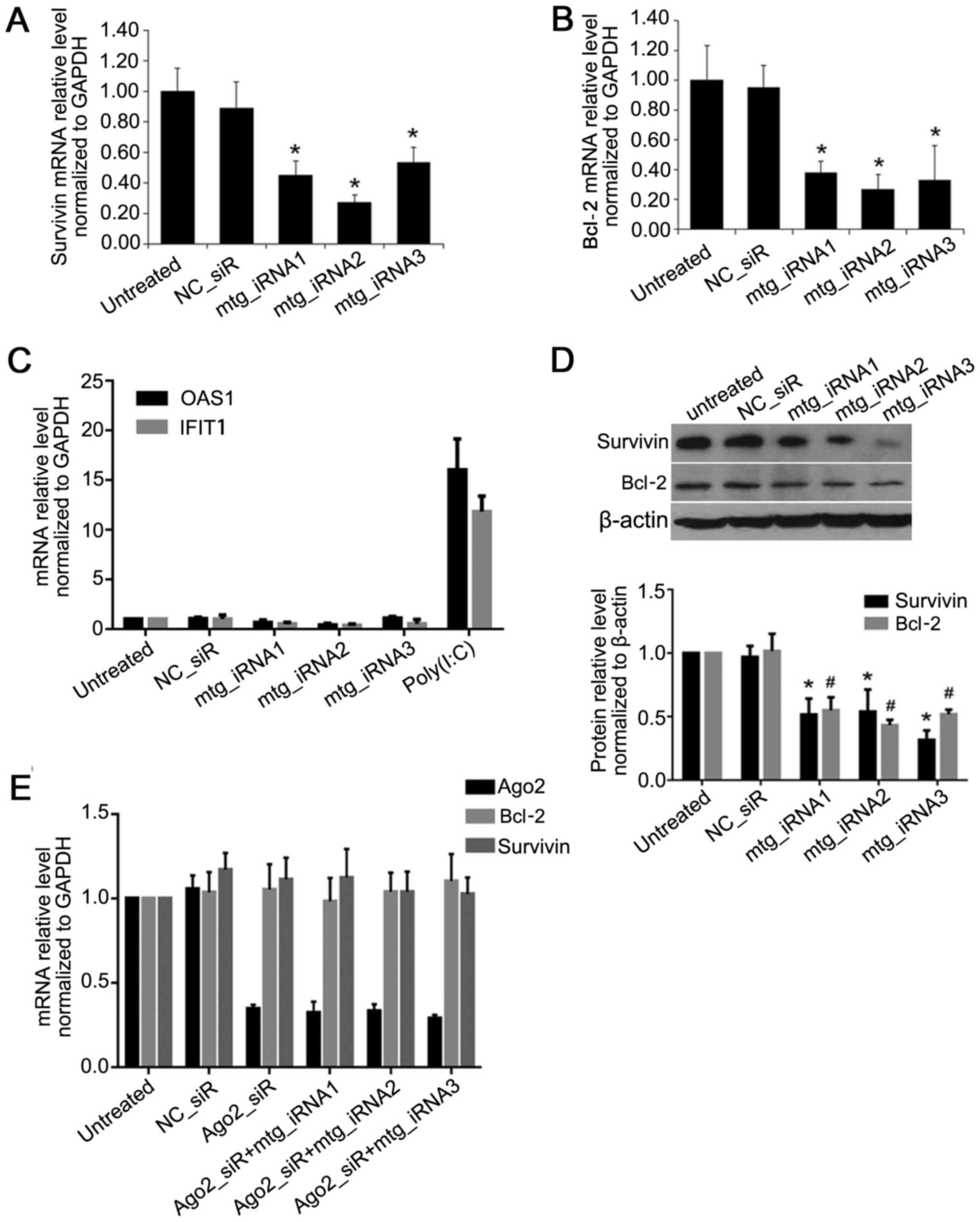
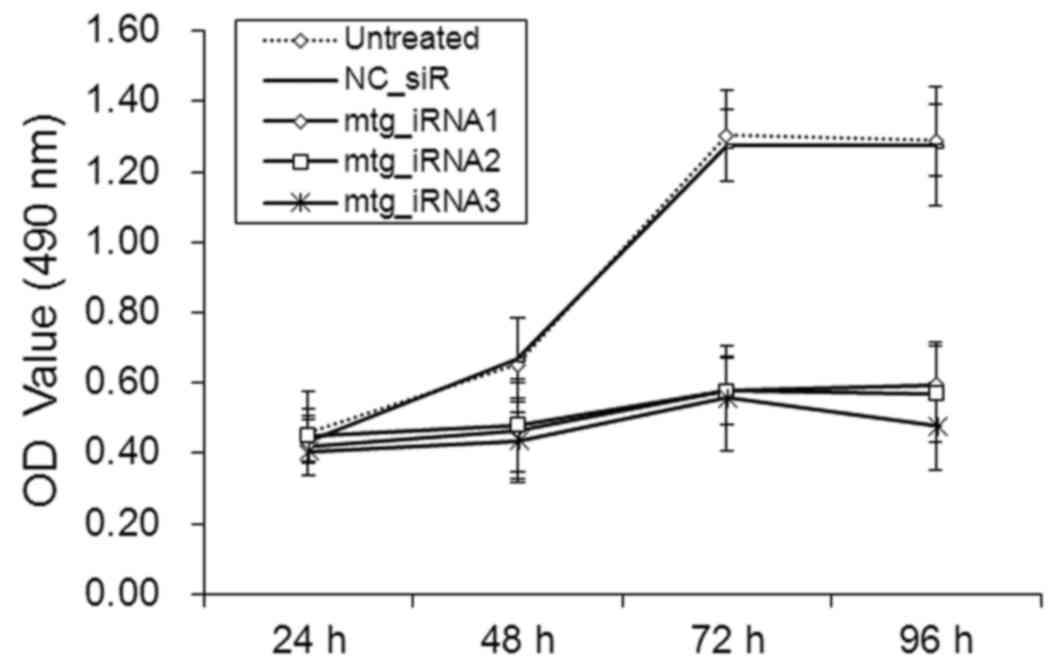
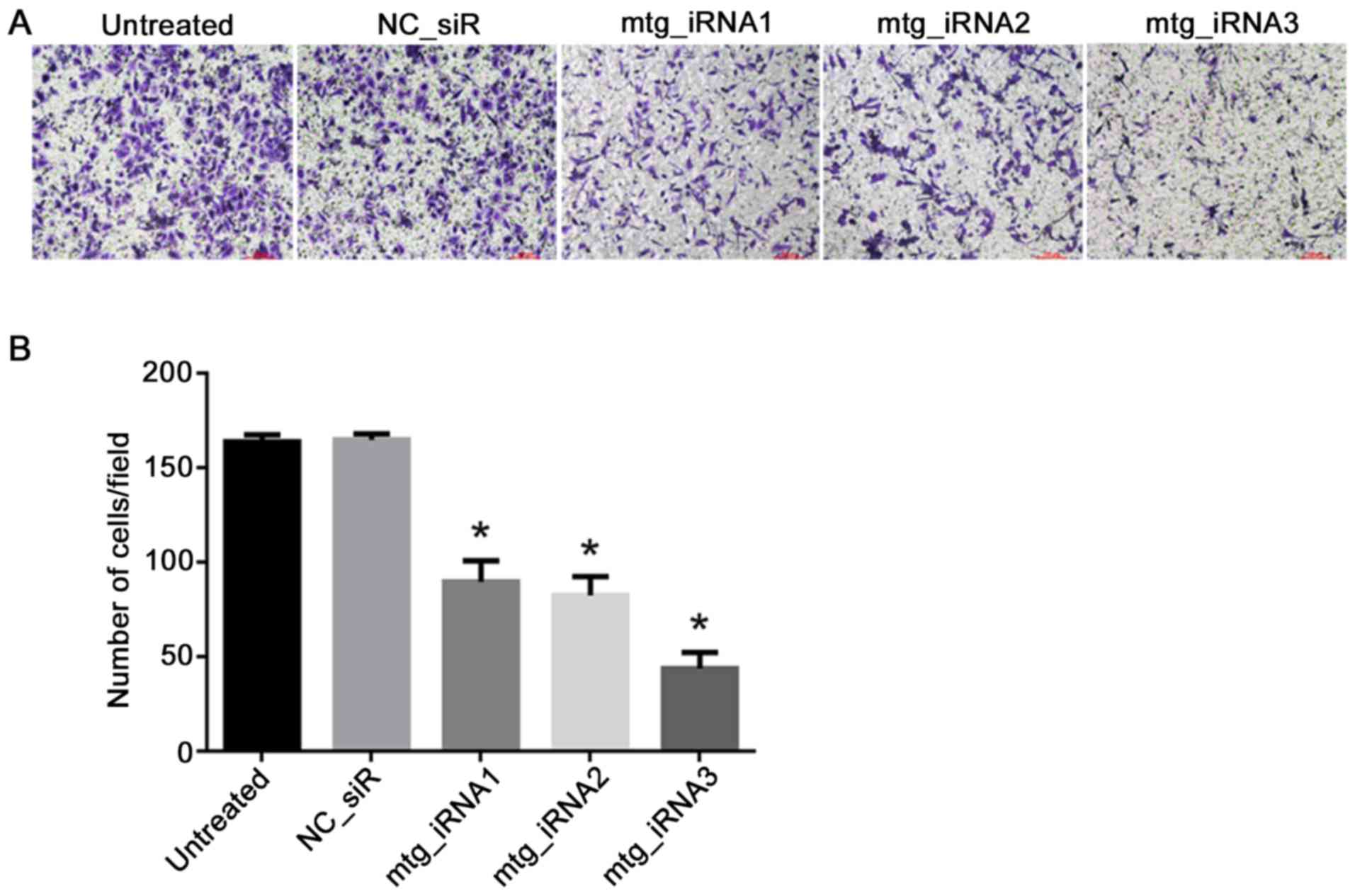
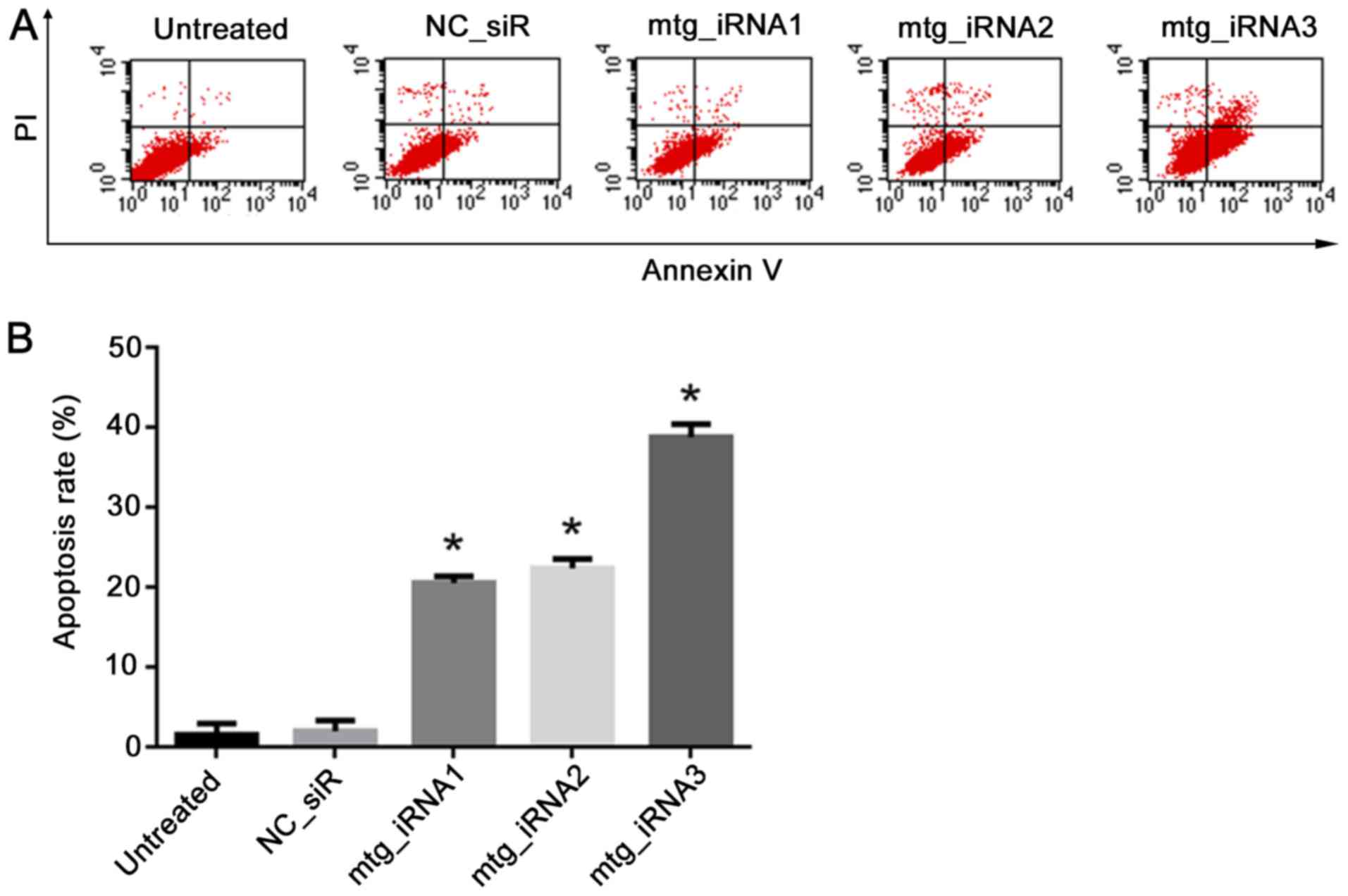
|
1
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA,
Driver SE and Mello CC: Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chendrimada TP, Gregory RI, Kumaraswamy E,
Norman J, Cooch N, Nishikura K and Shiekhattar R: TRBP recruits the
Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing.
Nature. 436:740–744. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hammond SM, Bernstein E, Beach D and
Hannon GJ: An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional
gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature. 404:293–296. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W and Tuschl T: RNA
interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev.
15:188–200. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Shi X, Zhang X, Wang L, Luo J,
Xing G, Deng R, Yang H, Li J, Wang A, et al: Porcine reproductive
and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) inhibits RNA-mediated gene
silencing by targeting Ago-2. Viruses. 7:5539–5552. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nikitenko NA, Speiseder T, Lam E, Rubtsov
PM, Tonaeva KhD, Borzenok SA, Dobner T and Prassolov VS: Regulation
of human adenovirus replication by RNA interference. Acta Naturae.
7:100–107. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tai W, Qin B and Cheng K: Inhibition of
breast cancer cell growth and invasiveness by dual silencing of
HER-2 and VEGF. Mol Pharm. 7:543–556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shahzad MM, Lu C, Lee JW, Stone RL, Mitra
R, Mangala LS, Lu Y, Baggerly KA, Danes CG, Nick AM, et al: Dual
targeting of EphA2 and FAK in ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther.
8:1027–1034. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim DH, Behlke MA, Rose SD, Chang MS, Choi
S and Rossi JJ: Synthetic dsRNA Dicer substrates enhance RNAi
potency and efficacy. Nat Biotechnol. 23:222–226. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tabernero J, Shapiro GI, LoRusso PM,
Cervantes A, Schwartz GK, Weiss GJ, Paz-Ares L, Cho DC, Infante JR,
Alsina M, et al: First-in-humans trial of an RNA interference
therapeutic targeting VEGF and KSP in cancer patients with liver
involvement. Cancer Discov. 3:406–417. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Coelho T, Adams D, Silva A, Lozeron P,
Hawkins PN, Mant T, Perez J, Chiesa J, Warrington S, Tranter E, et
al: Safety and efficacy of RNAi therapy for transthyretin
amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 369:819–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zimmermann GR, Lehár J and Keith CT:
Multi-target therapeutics: When the whole is greater than the sum
of the parts. Drug Discov Today. 12:34–42. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li T, Wu M, Zhu YY, Chen J and Chen L:
Development of RNA interference-based therapeutics and application
of multi-target small interfering RNAs. Nucleic Acid Ther.
24:302–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boyapalle S, Xu W, Raulji P, Mohapatra S
and Mohapatra SS: A multiple siRNA-based anti-HIV/SHIV microbicide
shows protection in both in vitro and in vivo models. PLoS One.
10:e01352882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takeshita F and Ochiya T: Therapeutic
potential of RNA interference against cancer. Cancer Sci.
97:689–696. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aigner A: Applications of RNA
interference: Current state and prospects for siRNA-based
strategies in vivo. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 76:9–21. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Davidson BL and McCray PB Jr: Current
prospects for RNA interference-based therapies. Nat Rev Genet.
12:329–340. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peng W, Chen J, Qin Y, Yang Z and Zhu YY:
Long double-stranded multiplex siRNAs for dual genes silencing.
Nucleic Acid Ther. 23:281–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li T, Zhu YY, Chen L, Sun Y, Yuan J,
Graham M and French P: Size unbiased representative enzymatically
generated RNAi (SURER) library and application for RNAi therapeutic
screens. Nucleic Acid Ther. 25:35–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chang CI, Kang HS, Ban C, Kim S and Lee
DK: Dual-target gene silencing by using long, synthetic siRNA
duplexes without triggering antiviral responses. Mol Cells.
27:689–695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rice RR, Muirhead AN, Harrison BT,
Kassianos AJ, Sedlak PL, Maugeri NJ, Goss PJ, Davey JR, James DE
and Graham MW: Simple, robust strategies for generating
DNA-directed RNA interference constructs. Methods Enzymol.
392:405–419. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shin D, Lee H, Kim SI, Yoon Y and Kim M:
Optimization of linear double-stranded RNA for the production of
multiple siRNAs targeting hepatitis C virus. RNA. 15:898–910. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aviñó A and Ocampo SM: Perales and JC
Eritja R: Branched RNA: A new architecture for RNA interference. J
Nucleic Acids. 5869352011.
|
|
25
|
Verdecia MA, Huang H, Dutil E, Kaiser DA,
Hunter T and Noel JP: Structure of the human anti-apoptotic protein
survivin reveals a dimeric arrangement. Nat Struct Biol. 7:602–608.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC
and Croce CM: Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B
cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science.
226:1097–1099. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cleary ML, Smith SD and Sklar J: Cloning
and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid
bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18)
translocation. Cell. 47:19–28. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W,
Yalcin A, Weber K and Tuschl T: Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs
mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature.
411:494–498. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Palchetti S, Starace D, De Cesaris P,
Filippini A, Ziparo E and Riccioli A: Transfected poly(I:C)
activates different dsRNA receptors, leading to apoptosis or
immunoadjuvant response in androgen-independent prostate cancer
cells. J Biol Chem. 290:5470–5483. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|