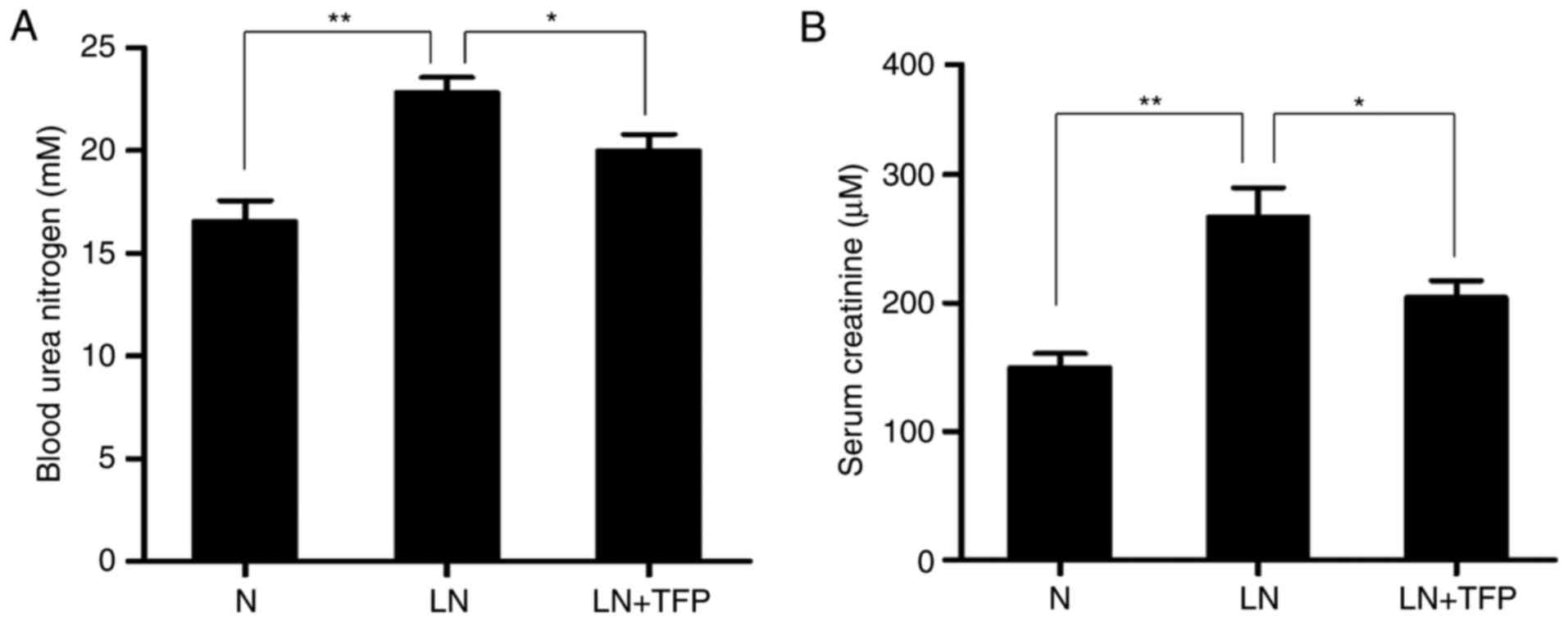
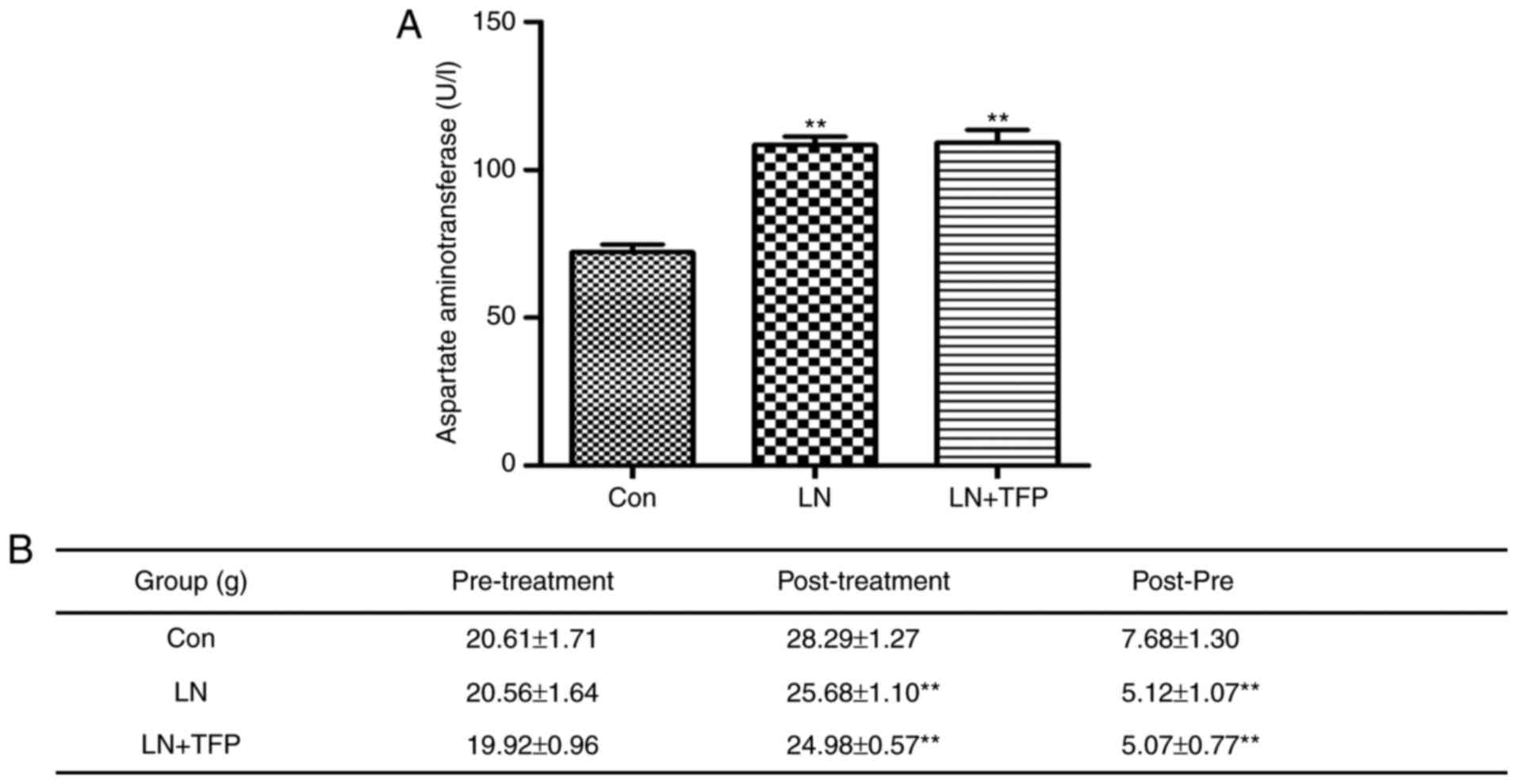
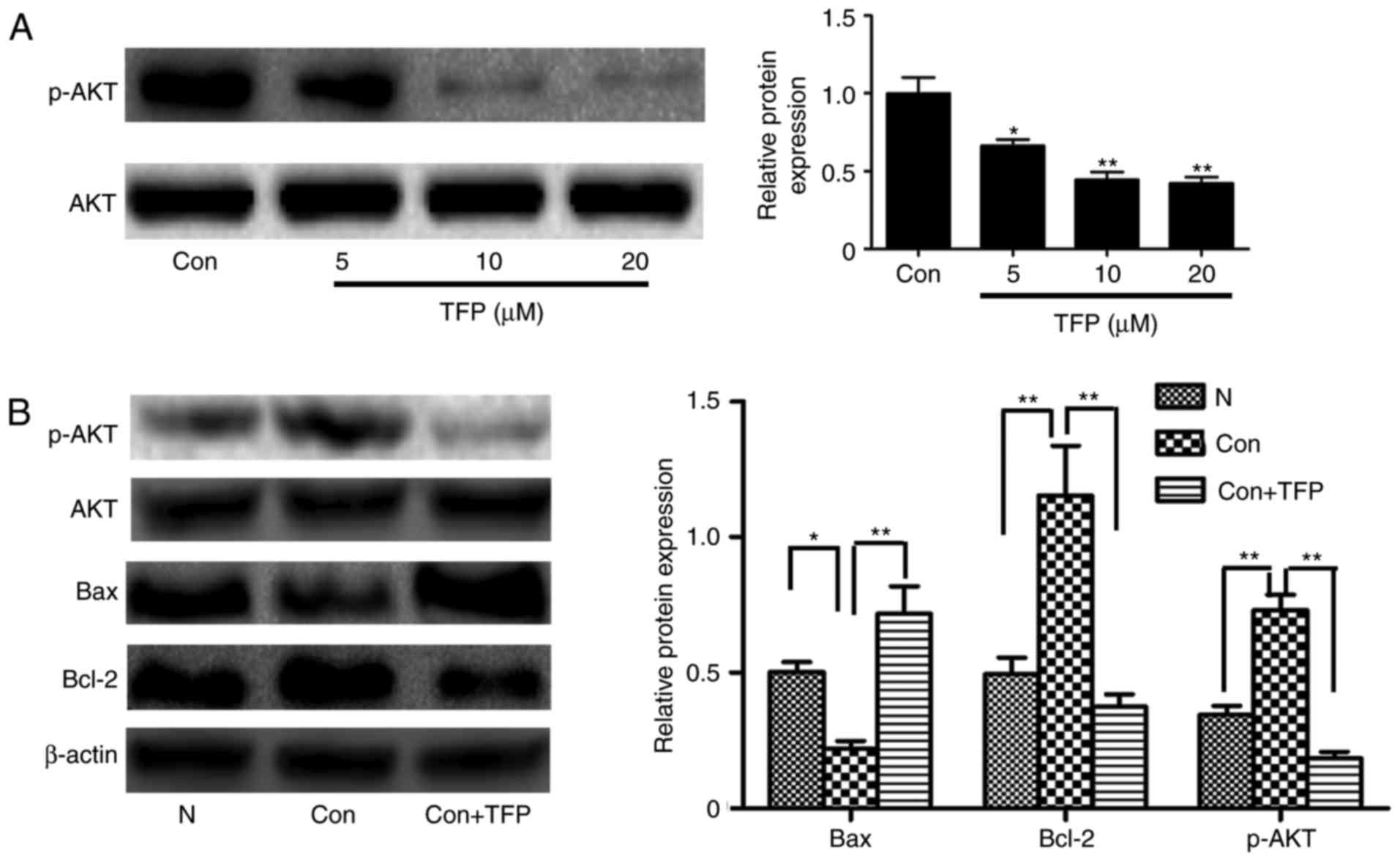
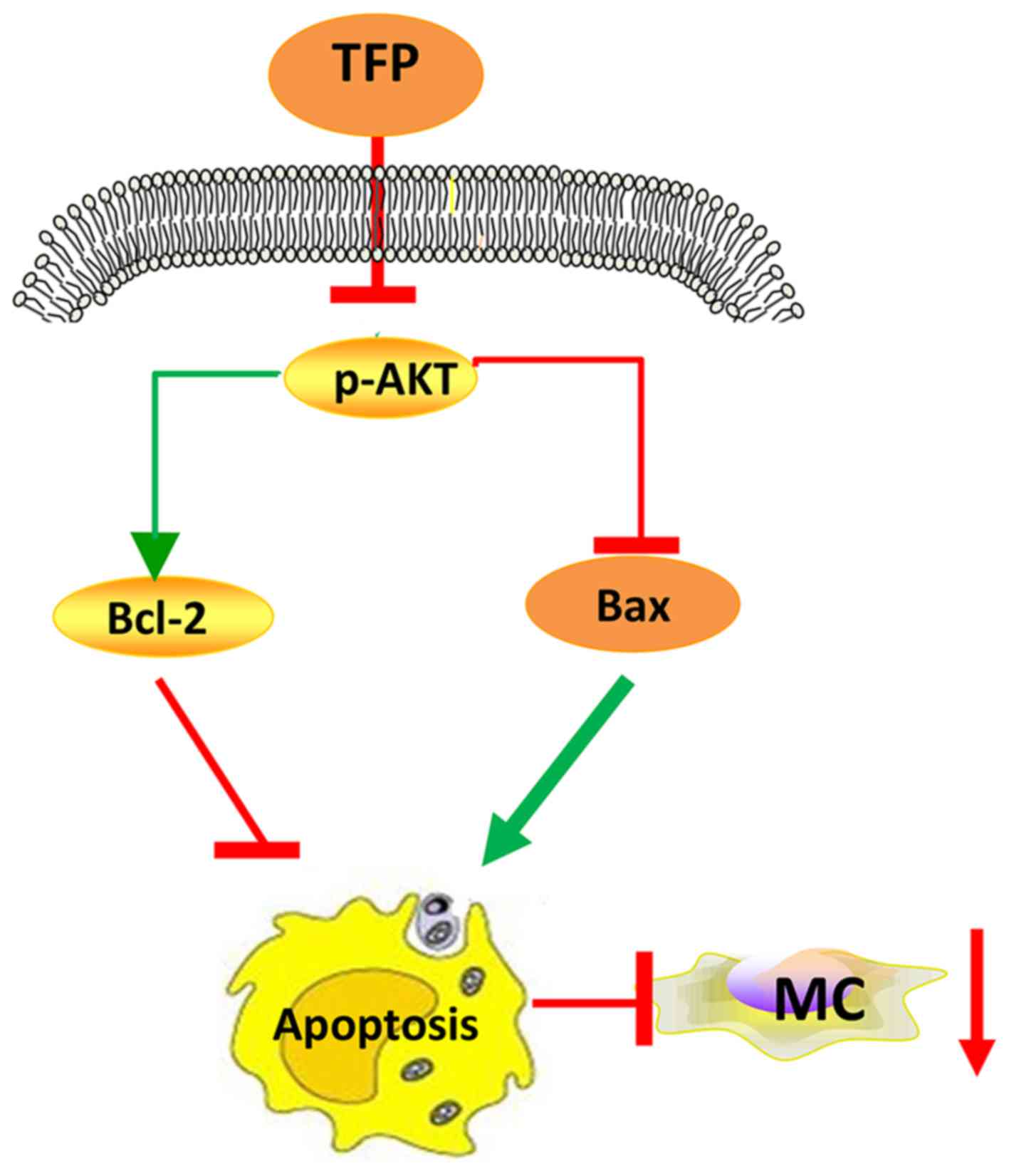
|
1
|
Badr KF, Murray JJ, Breyer MD, Takahashi
K, Inagami T and Harris RC: Mesangial cell, glomerular and renal
vascular responses to endothelin in the rat kidney. Elucidation of
signal transduction pathways. J Clin Invest. 83:336–342. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wyatt RJ and Julian BA: IgA nephropathy. N
Engl J Med. 368:2402–2414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grassmann A, Gioberge S, Moeller S and
Brown G: ESRD patients in 2004: Global overview of patient numbers,
treatment modalities and associated trends. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 20:2587–2593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matsumoto K, Yoshikai Y, Asano T, Himeno
K, Iwasaki A and Nomoto K: Defect in negative selection in lpr
donor-derived T cells differentiating in non-lpr host thymus. J Exp
Med. 173:127–136. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sugiyama N, Nakashima H, Yoshimura T,
Sadanaga A, Shimizu S, Masutani K, Igawa T, Akahoshi M, Miyake K,
Takeda A, et al: Amelioration of human lupus-like phenotypes in
MRL/lpr mice by overexpression of interleukin 27 receptor alpha
(WSX-1). Ann Rheum Dis. 67:1461–1467. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lamoureux JL, Watson LC, Cherrier M, Skog
P, Nemazee D and Feeney AJ: Reduced receptor editing in lupus-prone
MRL/lpr mice. J Exp Med. 204:2853–2864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA and Lowe SW:
Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell.
108:153–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brunelle JK and Letai A: Control of
mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J Cell Sci.
122:437–441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Uda S, Yoshimura A, Sugenoya Y, Inui K,
Taira T and Ideura T: Mesangial proliferative nephritis in man is
associated with increased expression of the cell survival factor,
Bcl-2. Am J Nephrol. 18:291–295. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhuan B, Ding Y, Zhang H and Yu Y: Effects
of Xueniaoting powder and S-9 on apoptosis and expression of bax
and bcl-2 in glomerular mesangial cells. Shenzhen J Integ Trad Chin
Western Med. 13:447–456. 2003.
|
|
12
|
Zhuan B, Ding Y and Wu L: Effects of
shenbining on apoptosis and experssion of bax and Bcl-2 in the
kidney of mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Chin J Integ
Trad Western Nephrol. 4:316–318. 2003.
|
|
13
|
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA
and Sugimoto C: PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: Size matters. Oncogene.
22:8983–8998. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao T, Furnari F and Newton AC: PHLPP: A
phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates Akt, promotes apoptosis,
and suppresses tumor growth. Mol Cell. 18:13–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gong AJ, Gong LL, Yao WC, Ge N, Lu LX and
Liang H: Aplysin induces apoptosis in glioma cells through
HSP90/AKT pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:639–644. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen WS, Xu PZ, Gottlob K, Chen ML, Sokol
K, Shiyanova T, Roninson I, Weng W, Suzuki R, Tobe K, et al: Growth
retardation and increased apoptosis in mice with homozygous
disruption of the Akt1 gene. Genes Dev. 15:2203–2208. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stylianou K, Petrakis I, Mavroeidi V,
Stratakis S, Vardaki E, Perakis K, Stratigis S, Passam A,
Papadogiorgaki E, Giannakakis K, et al: The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway
is activated in murine lupus nephritis and downregulated by
rapamycin. Nephrol Dialy Transplant. 26:498–508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gulino A, Barrera G, Vacca A, Farina A,
Ferretti C, Screpanti I, Dianzani MU and Frati L: Calmodulin
antagonism and growth-inhibiting activity of triphenylethylene
antiestrogens in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
46:6274–6278. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen QY, Wu LJ, Wu YQ, Lu GH, Jiang ZY,
Zhan JW, Jie Y and Zhou JY: Molecular mechanism of trifluoperazine
induces apoptosis in human A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. Mol
Med Rep. 2:811–817. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Polischouk AG, Holgersson A, Zong D,
Stenerlöw B, Karlsson HL, Möller L, Viktorsson K and Lewensohn R:
The antipsychotic drug trifluoperazine inhibits DNA repair and
sensitizes non small cell lung carcinoma cells to DNA double-strand
break induced cell death. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2303–2309. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yeh CT, Wu AT, Chang PM, Chen KY, Yang CN,
Yang SC, Ho CC, Chen CC, Kuo YL, Lee PY, et al: Trifluoperazine, an
antipsychotic agent, inhibits cancer stem cell growth and overcomes
drug resistance of lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
186:1180–1188. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Delarue F, Virone A, Hagege J, Lacave R,
Peraldi MN, Adida C, Rondeau E, Feunteun J and Sraer JD: Stable
cell line of T-SV40 immortalized human glomerular visceral
epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 40:906–912. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Savill J, Mooney A and Hughes J: Apoptosis
and renal scarring. Kidney Int Suppl. 54:S14–S17. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hong SH, Lee MY, Shin KS and Kang SJ:
Perphenazine and trifluoperazine induce mitochondria-mediated cell
death in SH-SY5Y cells. Animal Cells Syst. 16:20–26. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cui JH, Qiao Q, Guo Y, Zhang YQ, Cheng H,
He FR and Zhang J: Increased apoptosis and expression of FasL, Bax
and caspase-3 in human lupus nephritis class II and IV. J Nephrol.
25:255–261. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim AH, Khursigara G, Sun X, Franke TF and
Chao MV: Akt phosphorylates and negatively regulates apoptosis
signal-regulating kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol. 21:893–901. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Majumder PK and Sellers WR: Akt-regulated
pathways in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 24:7465–7474. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shimamura H, Terada Y, Okado T, Tanaka H,
Inoshita S and Sasaki S: The PI3-kinase-Akt pathway promotes
mesangial cell survival and inhibits apoptosis in vitro via
NF-kappa B and Bad. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:1427–1434. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Franke TF, Yang SI, Chan TO, Datta K,
Kazlauskas A, Morrison DK, Kaplan DR and Tsichlis PN: The protein
kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the
PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell. 81:727–736.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Howland RH: Trifluoperazine: A sprightly
old drug. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv. 54:20–22. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|