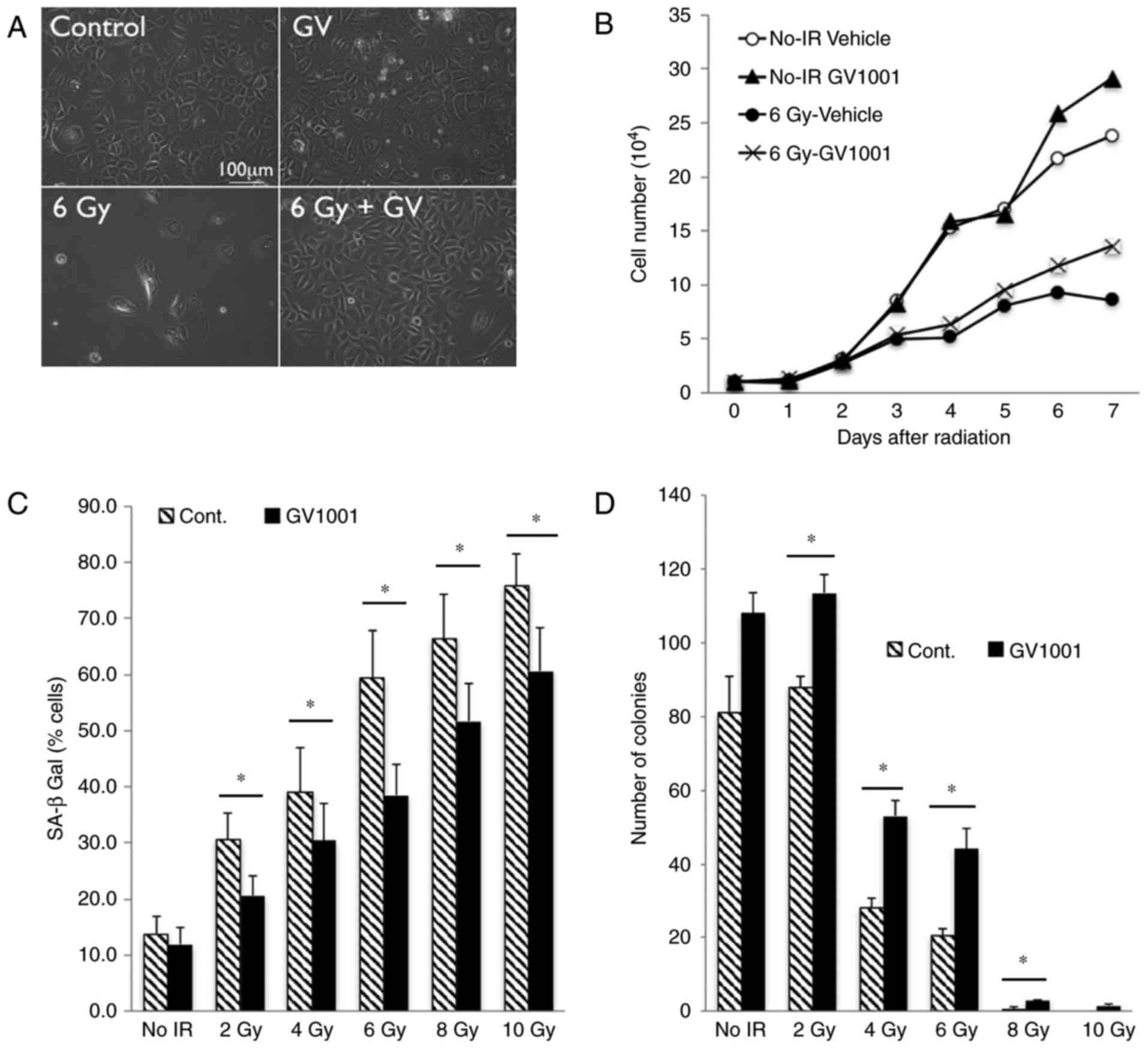
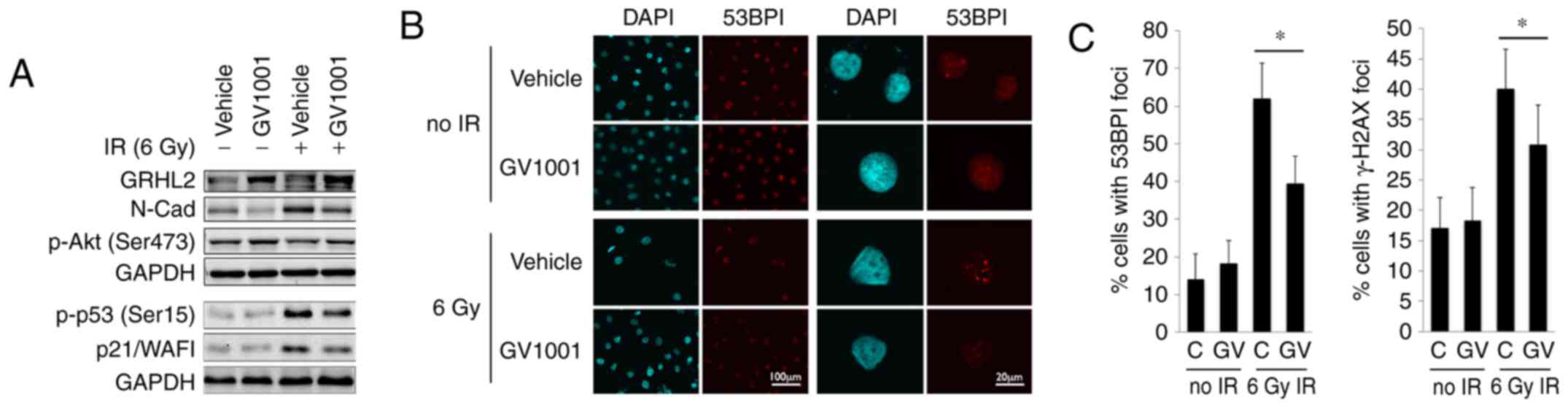
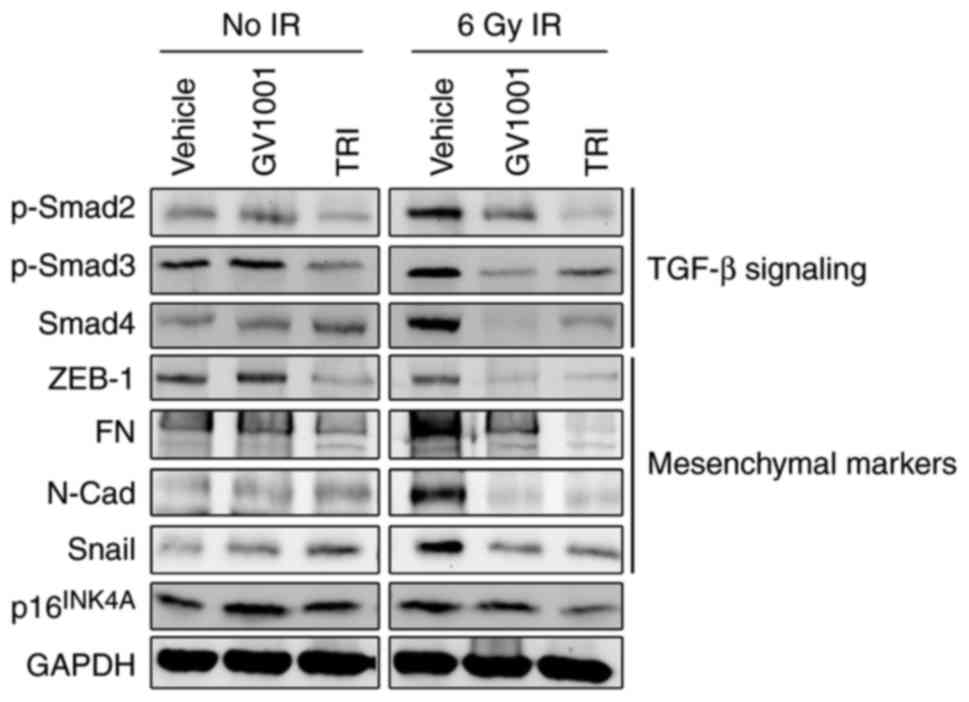
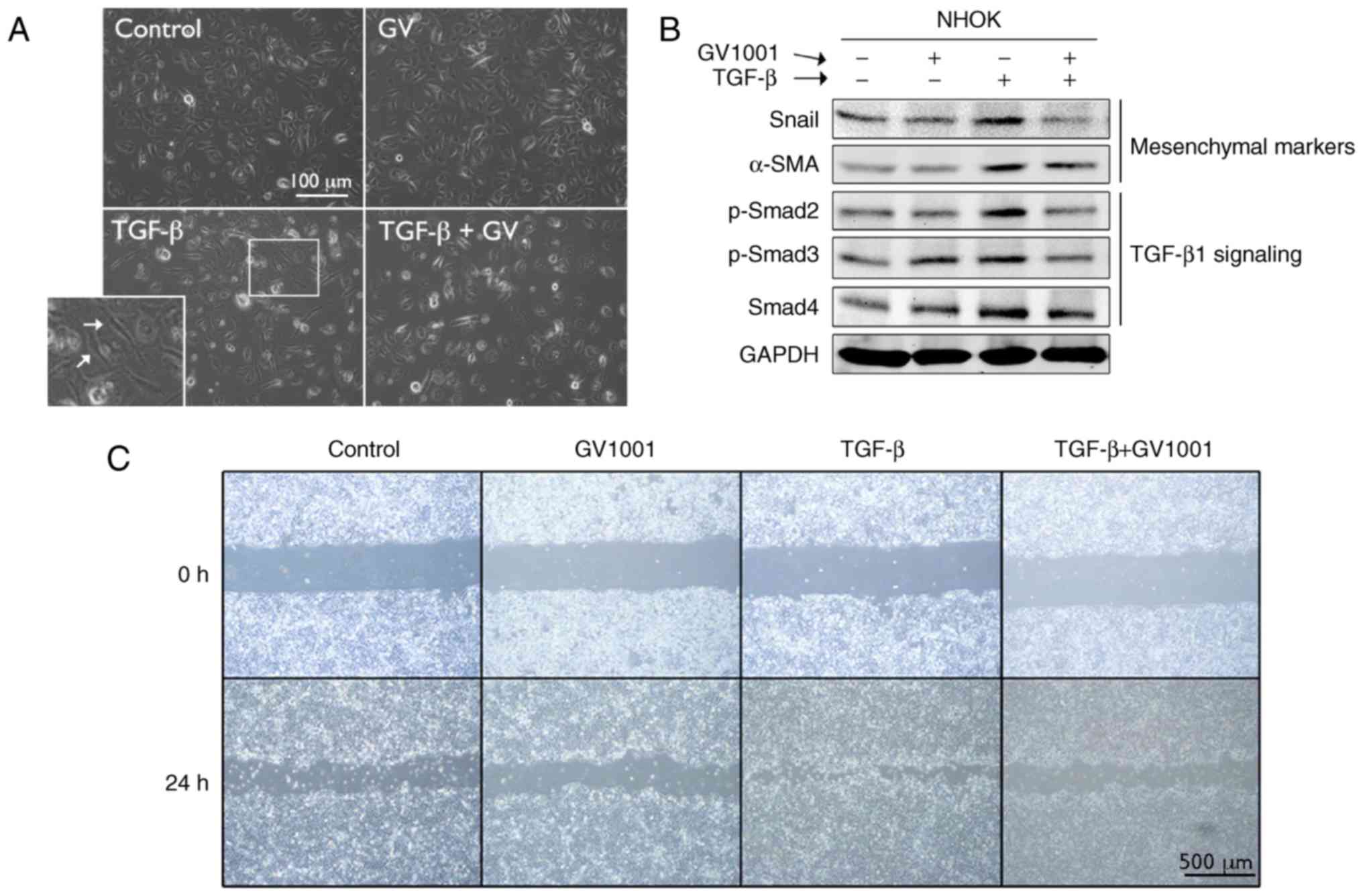
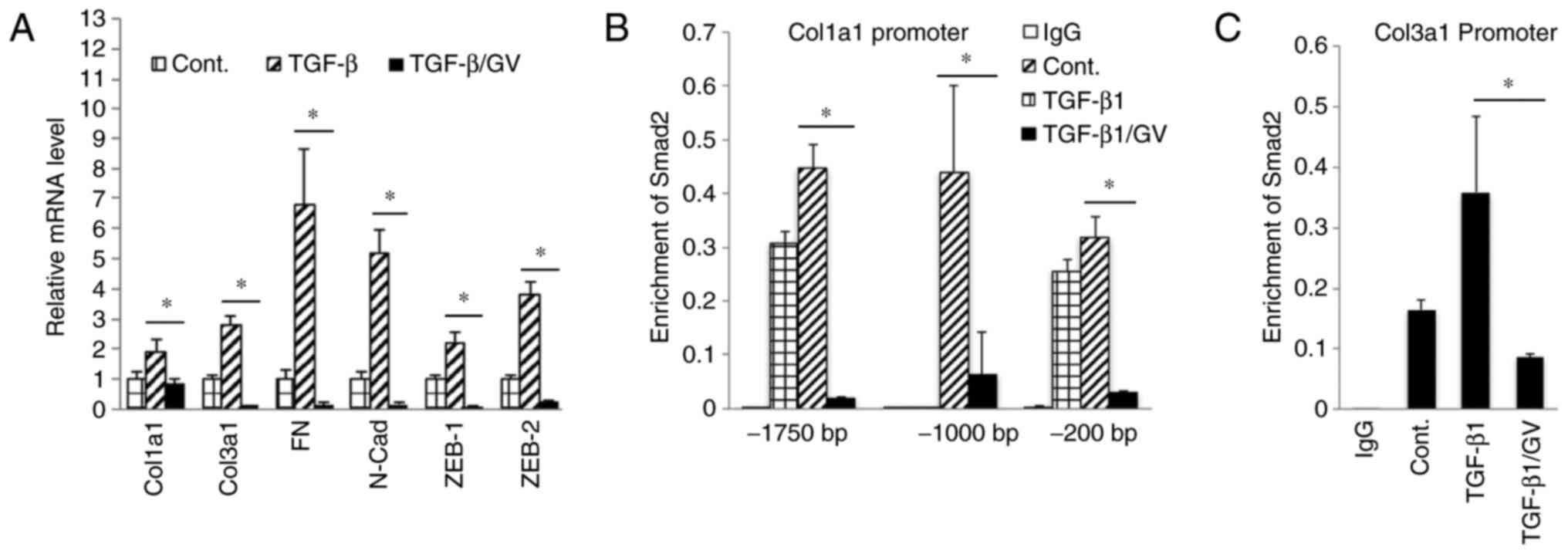
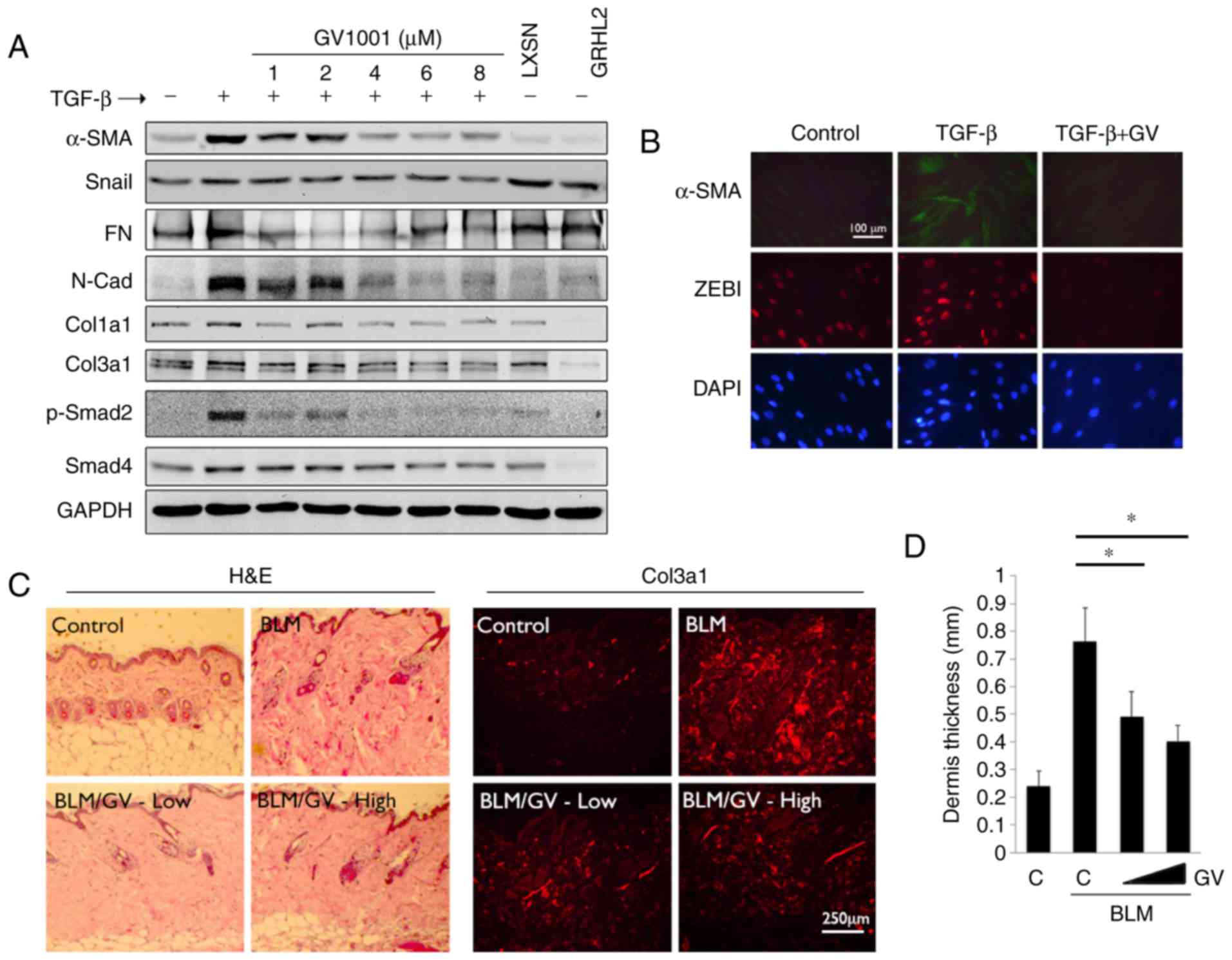
|
1
|
Kim HR, Christensen R and Park NH, Sapp P,
Kang MK and Park NH: Elevated expression of hTERT is associated
with dysplastic cell transformation during human oral
carcinogenesis in situ. Clin Cancer Res. 7:3079–3086.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley
CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL and Shay
JW: Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal
cells and cancer. Science. 266:2011–2015. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Greener M: Telomerase: The search for a
universal cancer vaccine. Mol Med Today. 6:2572000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brunsvig PF, Aamdal S, Gjertsen MK,
Kvalheim G, Markowski-Grimsrud CJ, Sve I, Dyrhaug M, Trachsel S,
Møller M, Eriksen JA and Gaudernack G: Telomerase peptide
vaccination: A phase I/II study in patients with non-small cell
lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 55:1553–1564. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bernhardt SL, Gjertsen MK, Trachsel S,
Møller M, Eriksen JA, Meo M, Buanes T and Gaudernack G: Telomerase
peptide vaccination of patients with non-resectable pancreatic
cancer: A dose escalating phase I/II study. Br J Cancer.
95:1474–1482. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kokhaei P, Palma M, Hansson L, Osterborg
A, Mellstedt H and Choudhury A: Telomerase (hTERT 611-626) serves
as a tumor antigen in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and
generates spontaneously antileukemic, cytotoxic T cells. Exp
Hematol. 35:297–304. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nicholls C, Li H, Wang JQ and Liu JP:
Molecular regulation of telomerase activity in aging. Protein Cell.
2:726–738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang JE, Kim HJ, Yi E, Jheon S and Kim K:
Reduction of ischaemia-reperfusion injury in a rat lung
transplantation model by low-concentration GV1001. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 50:972–979. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Choi J, Kim H, Kim Y, Jang M, Jeon J,
Hwang YI, Shon WJ, Song YW, Kang JS and Lee WJ: The
anti-inflammatory effect of GV1001 mediated by the downregulation
of ENO1-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Immune Netw.
15:291–303. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ko YJ, Kwon KY, Kum KY, Lee WC, Baek SH,
Kang MK and Shon WJ: The anti-inflammatory effect of human
telomerase-derived peptide on P. gingivalis
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokine production and its
mechanism in human dental pulp cells. Mediators Inflamm.
2015:3851272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim BK, Kim BR, Lee HJ, Lee SA and Kim BJ,
Kim H, Won YS, Shon WJ, Lee NR, Inn KS and Kim BJ:
Tumor-suppressive effect of a telomerase-derived peptide by
inhibiting hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-VEGF signaling axis.
Biomaterials. 35:2924–2933. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park JK, Kim Y, Kim H, Jeon J, Kim TW,
Park JH, Hwnag YI, Lee WJ and Kang JS: The anti-fibrotic effect of
GV1001 combined with gemcitabine on treatment of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:75081–75093. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim H, Choi MS, Inn KS and Kim BJ:
Inhibition of HIV-1 reactivation by a telomerase-derived peptide in
a HSP90-dependent manner. Sci Rep. 6:288962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee SA, Kim J, Sim J, Kim SG, Kook YH,
Park CG, Kim HR and Kim BJ: A telomerase-derived peptide regulates
reactive oxygen species and hepatitis C virus RNA replication in
HCV-infected cells via heat shock protein 90. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 471:156–162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park HH, Lee KY, Kim S, Lee JW, Choi NY,
Lee EH, Lee YJ, Lee SH and Koh SH: Novel vaccine peptide GV1001
effectively blocks β-amyloid toxicity by mimicking the
extra-telomeric functions of human telomerase reverse
transcriptase. Neurobiol Aging. 35:1255–1274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bitterman PB and Henke CA:
Fibroproliferative disorders. Chest. 99(3 Suppl): 81S–84S. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Judge JL, Owens KM, Pollock SJ, Woeller
CF, Thatcher TH, Williams JP, Phipps RP, Sime PJ and Kottmann RM:
Ionizing radiation induces myofibroblast differentiation via
lactate dehydrogenase. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
309:L879–L887. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Decologne N, Kolb M, Margetts PJ,
Menetrier F, Artur Y, Garrido C, Gauldie J, Camus P and Bonniaud P:
TGF-beta1 induces progressive pleural scarring and subpleural
fibrosis. J Immunol. 179:6043–6051. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Anscher MS, Crocker IR and Jirtle RL:
Jirtle, transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression in irradiated
liver. Radiat Res. 122:77–85. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Franko AJ, Sharplin J, Ghahary A and
Barcellos-Hoff MH: Immunohistochemical localization of transforming
growth factor beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the lungs of
fibrosis-prone and 'non-fibrosing' mice during the latent period
and early phase after irradiation. Radiat Res. 147:245–256. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang MK, Bibb C, Baluda MA, Rey O and Park
NH: In vitro replication and differentiation of normal human oral
keratinocytes. Exp Cell Res. 258:288–297. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dong Q, Oh JE, Chen W, Kim R, Kim RH, Shin
KH, McBride WH, Park NH and Kang MK: Radioprotective effects of
Bmi-1 involve epigenetic silencing of oxidase genes and enhanced
DNA repair in normal human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol.
131:1216–1225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Larionov A, Krause A and Miller W: A
standard curve based method for relative real time PCR data
processing. BMC Bioinformatics. 6:622005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen W, Xiao Liu Z, Oh JE, Shin KH, Kim
RH, Jiang M, Park NH and Kang MK: Grainyhead-like 2 (GRHL2)
inhibits keratinocyte differentiation through epigenetic mechanism.
Cell Death Dis. 3:e4502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen W, Dong Q, Shin KH, Kim RH, Oh JE,
Park NH and Kang MK: Grainyhead-like 2 enhances the human
telomerase reverse transcriptase gene expression by inhibiting DNA
methylation at the 5′-CpG island in normal human keratinocytes. J
Biol Chem. 285:40852–40863. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen W, Yi JK, Shimane T, Mehrazarin S,
Lin YL, Shin KH, Kim RH, Park NH and Kang MK: Grainyhead-like 2
regulates epithelial plasticity and stemness in oral cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 37:500–510. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cieply B, Farris J, Denvir J, Ford HL and
Frisch SM: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor suppression
are controlled by a reciprocal feedback loop between ZEB1 and
Grainyhead-like-2. Cancer Res. 73:6299–6309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma T, Zhao Y, Wei K, Yao G, Pan C, Liu B,
Xia Y, He Z, Qi X, Li Z, et al: MicroRNA-124 functions as a tumor
suppressor by regulating CDH2 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:1563–1574.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Holler M, Grottke A, Mueck K, Manes J,
Jücker M, Rodemann HP and Toulany M: Dual Targeting of Akt and
mTORC1 impairs repair of DNA double-strand breaks and increases
radiation sensitivity of human tumor cells. PLoS One.
11:e01547452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Borodkina A, Shatrova A, Abushik P,
Nikolsky N and Burova E: Interaction between ROS dependent DNA
damage, mitochondria and p38 MAPK underlies senescence of human
adult stem cells. Aging (Albany NY). 6:481–495. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Vandevoorde C, Vral A, Vandekerckhove B,
Philippé J and Thierens H: Radiation sensitivity of human CD34(+)
cells versus peripheral blood T lymphocytes of newborns and adults:
DNA Repair and Mutagenic Effects. Radiat Res. 185:580–590. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liakou E, Mavrogonatou E, Pratsinis H,
Rizou S, Evangelou K, Panagiotou PN, Karamanos NK, Gorgoulis VG and
Kletsas D: Ionizing radiation-mediated premature senescence and
paracrine interactions with cancer cells enhance the expression of
syndecan 1 in human breast stromal fibroblasts: The role of TGF-β.
Aging (Albany NY). 8:1650–1669. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chang YC, Tsai CH, Lai YL, Yu CC, Chi WY,
Li JJ and Chang WW: Arecoline-induced myofibroblast
transdifferentiation from human buccal mucosal fibroblasts is
mediated by ZEB1. J Cell Mol Med. 18:698–708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park HS, You GE, Yang KH, Kim JY, An S,
Song JY, Lee SJ, Lim YK and Nam SY: Role of AKT and ERK pathways in
controlling sensitivity to ionizing radiation and adaptive response
induced by low-dose radiation in human immune cells. Eur J Cell
Biol. 94:653–660. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park HH, Yu HJ, Kim S, Kim G, Choi NY, Lee
EH, Lee YJ, Yoon MY, Lee KY and Koh SH: Neural stem cells injured
by oxidative stress can be rejuvenated by GV1001, a novel peptide,
through scavenging free radicals and enhancing survival signals.
Neurotoxicology. 55:131–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mehrazarin S, Chen W, Oh JE, Liu ZX, Kang
KL, Yi JK, Kim RH, Shin KH, Park NH and Kang MK: The p63 gene is
regulated by grainyhead-like 2 (GRHL2) through reciprocal feedback
and determines the epithelial phenotype in human keratinocytes. J
Biol Chem. 290:19999–20008. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cieply B, Riley P IV, Pifer PM, Widmeyer
J, Addison JB, Ivanov AV, Denvir J and Frisch SM: Suppression of
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by Grainyhead-like-2. Cancer
Res. 72:2440–2453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Penke LR, Huang SK, White ES and
Peters-Golden M: Prostaglandin E2 inhibits α-smooth muscle actin
transcription during myofibroblast differentiation via distinct
mechanisms of modulation of serum response factor and
myocardin-related transcription factor-A. J Biol Chem.
289:17151–17162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hinz B: The role of myofibroblasts in
wound healing. Curr Res Transl Med. 64:171–177. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Willis BC, duBois RM and Borok Z:
Epithelial origin of myofibroblasts during fibrosis in the lung.
Proc Am Thorac Soc. 3:377–382. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M,
Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E, Chandraker A, Yuan X, Pu WT,
Roberts Ab, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:952–961. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Balli D, Ustiyan V, Zhang Y, Wang IC,
Masino AJ, Ren X, Whitsett JA, Kalinichenko VV and Kalin TV: Foxm1
transcription factor is required for lung fibrosis and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J. 32:231–244. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Saleh J, Figueiredo MA, Cherubini K and
Salum FG: Salivary hypofunction: An update on aetiology, diagnosis
and therapeutics. Arch Oral Biol. 60:242–255. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Fukui M, Ogawa Y, Shimmura S, Hatou S,
Ichihashi Y, Yaguchi S, Hirayama M, Kawakita T and Tsubota K:
Possible involvement of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
fibrosis associated with IgG4-related Mikulicz's disease. Mod
Rheumatol. 25:737–743. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|