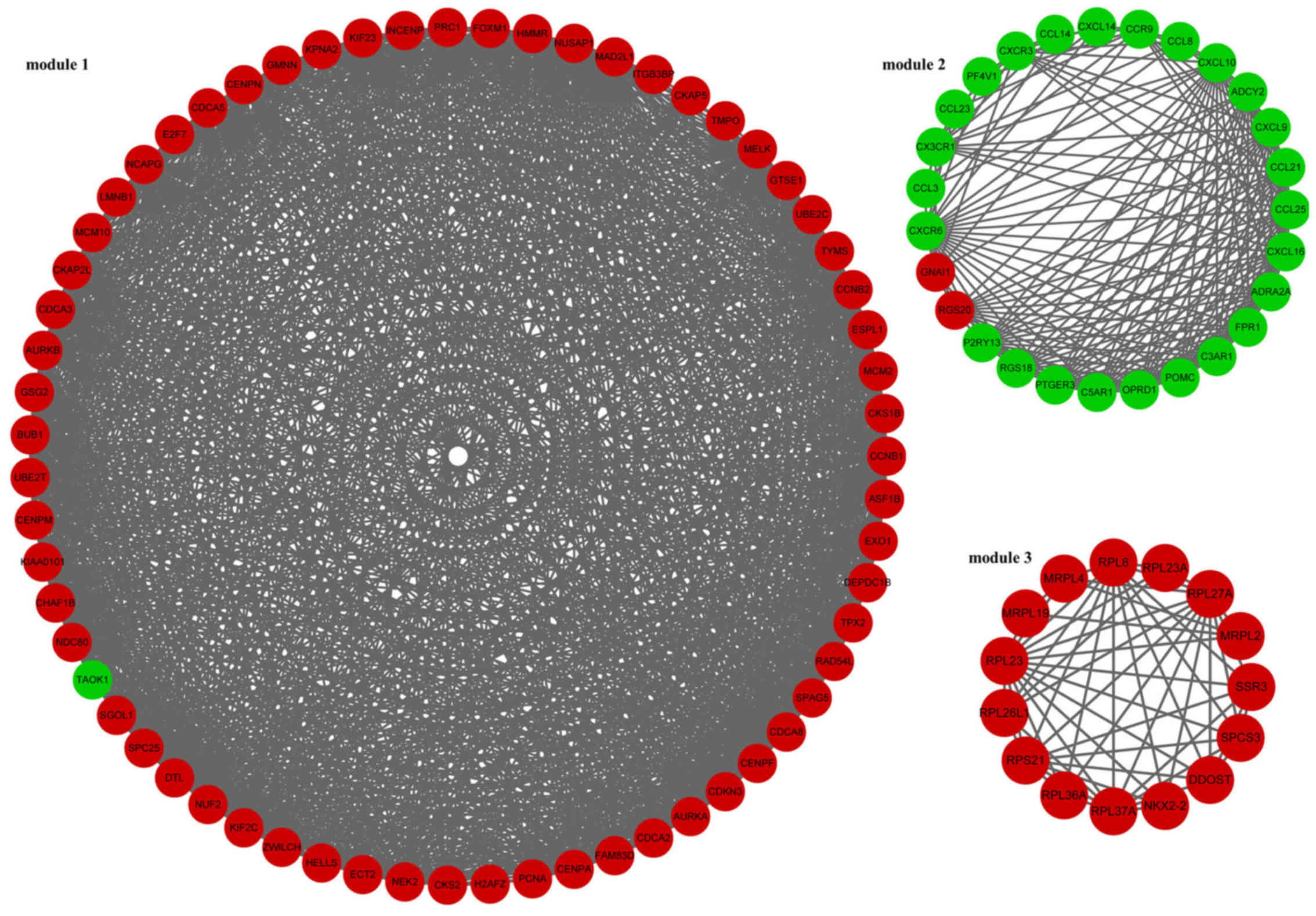
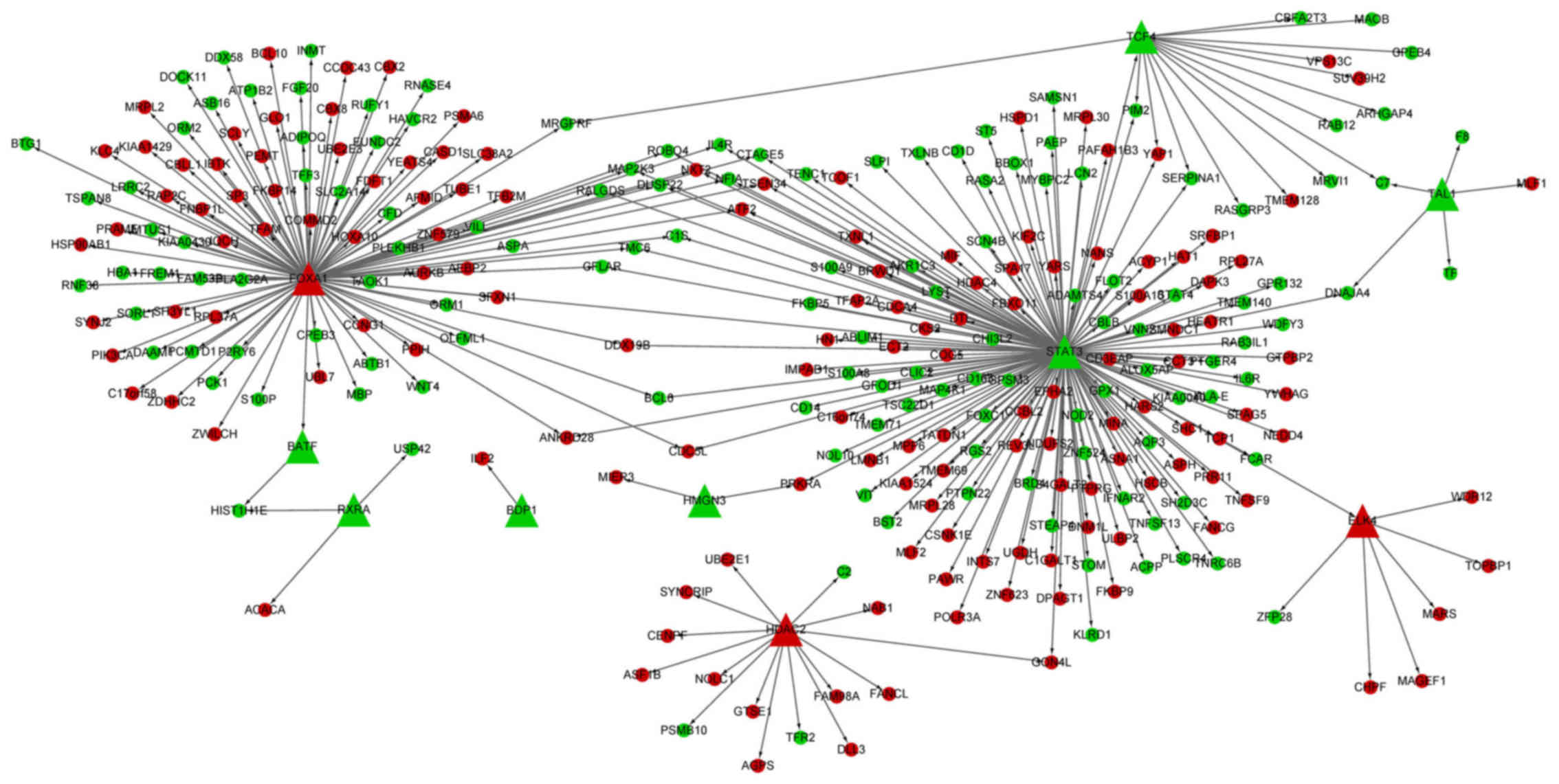
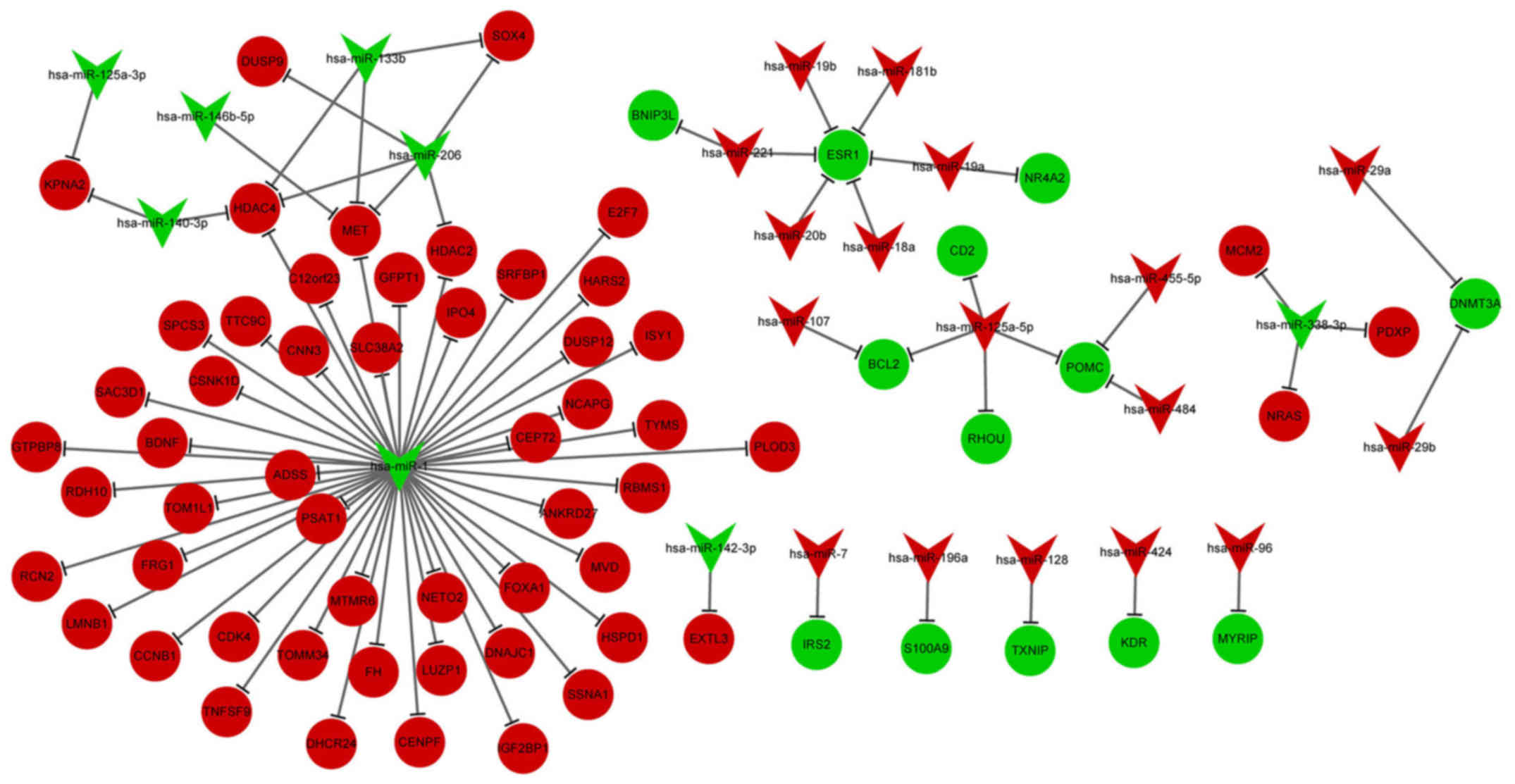
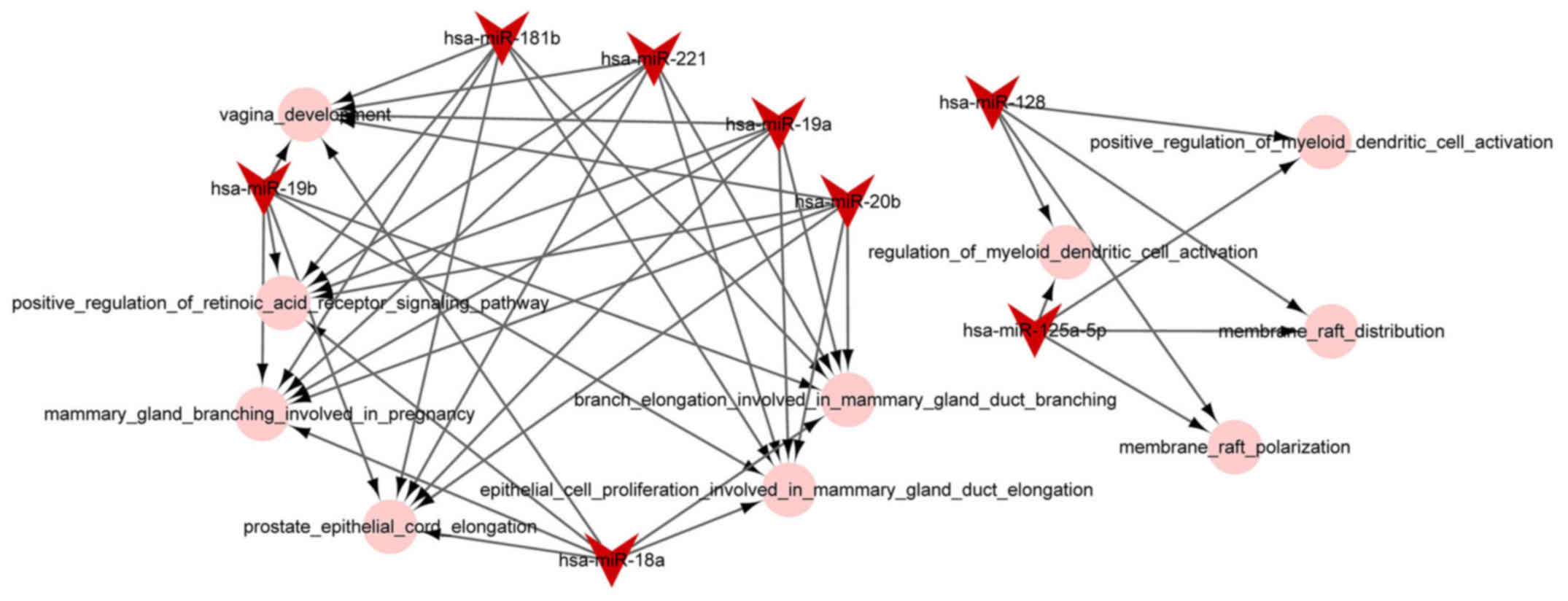
|
1
|
Wittig JC, Bickels J, Priebat D, Jelinek
J, Kellar-Graney K, Shmookler B and Malawer MM: Osteosarcoma: A
multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam
Physician. 65:1123–1132. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Pediatric and Adolescent Osteosarcoma. Springer;
pp. 3–13. 2010
|
|
3
|
Stiller CA, Bielack SS, Jundt G and
Steliarova-Foucher E: Bone tumours in European children and
adolescents, 1978–1997. Report from the Automated Childhood Cancer
Information System project. Eur J Cancer. 42:2124–2135. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stiller CA, Craft AW and Corazziari I;
EUROCARE Working Group: Survival of children with bone sarcoma in
Europe since 1978: Results from the EUROCARE study. Eur J Cancer.
37:760–766. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maire G, Yoshimoto M, Chilton-MacNeill S,
Thorner PS, Zielenska M and Squire JA: Recurrent RECQL4 imbalance
and increased gene expression levels are associated with structural
chromosomal instability in sporadic osteosarcoma. Neoplasia.
11:260–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou H, Randall RL, Brothman AR, Maxwell
T, Coffin CM and Goldsby RE: Her-2/neu expression in osteosarcoma
increases risk of lung metastasis and can be associated with gene
amplification. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 25:27–32. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sadikovic B, Thorner P, Chilton-Macneill
S, Martin JW, Cervigne NK, Squire J and Zielenska M: Expression
analysis of genes associated with human osteosarcoma tumors shows
correlation of RUNX2 overexpression with poor response to
chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 10:2022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gamberi G, Benassi MS, Bohling T,
Ragazzini P, Molendini L, Sollazzo MR, Pompetti F, Merli M,
Magagnoli G, Balladelli A, et al: C-myc and c-fos in human
osteosarcoma: Prognostic value of mRNA and protein expression.
Oncology. 55:556–563. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu XY, Lu Y, Zhao YJ, Jaeweon K, Kang J,
Xiao-Nan L, Ge G, Meyer R, Perlaky L, Hicks J, et al: Cell cycle
regulator gene CDC5L, a potential target for 6p12-21 amplicon in
osteosarcoma. Mol Cancer Res. 6:937–946. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
de Nigris F, Botti C, de Chiara A,
Rossiello R, Apice G, Fazioli F, Fiorito C, Sica V and Napoli C:
Expression of transcription factor Yin Yang 1 in human
osteosarcomas. Eur J Cancer. 42:2420–2424. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cao Y, Zhou Z, de Crombrugghe B, Nakashima
K, Guan H, Duan X, Jia SF and Kleinerman ES: Osterix, a
transcription factor for osteoblast differentiation, mediates
antitumor activity in murine osteosarcoma. Cancer Res.
65:1124–1128. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Osaki M, Takeshita F, Sugimoto Y, Kosaka
N, Yamamoto Y, Yoshioka Y, Kobayashi E, Yamada T, Kawai A, Inoue T,
et al: MicroRNA-143 regulates human osteosarcoma metastasis by
regulating matrix metalloprotease-13 expression. Mol Ther.
19:1123–1130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang H, Cai X, Wang Y, Tang H, Tong D and
Ji F: microRNA-143, downregulated in osteosarcoma, promotes
apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol
Rep. 24:1363–1369. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Duan Z, Choy E, Harmon D, Liu X, Susa M,
Mankin H and Hornicek F: MicroRNA-199a-3p is downregulated in human
osteosarcoma and regulates cell proliferation and migration. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:1337–1345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ziyan W, Shuhua Y, Xiufang W and Xiaoyun
L: MicroRNA-21 is involved in osteosarcoma cell invasion and
migration. Med Oncol. 28:1469–1474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yan K, Gao J, Yang T, Ma Q, Qiu X, Fan Q
and Ma B: MicroRNA-34a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
7:e337782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Namløs HM, Meza-Zepeda LA, Barøy T,
Østensen IH, Kresse SH, Kuijjer ML, Serra M, Bürger H,
Cleton-Jansen AM and Myklebost O: Modulation of the osteosarcoma
expression phenotype by microRNAs. PLoS One. 7:e480862012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Smyth GK: Limma: linear models for
microarray data. Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Springer; pp. 397–420. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhao M, Sun J and Zhao Z: TSGene: A web
resource for tumor suppressor genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D970–D976. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Chen JS, Hung WS, Chan HH, Tsai SJ and Sun
HS: In silico identification of oncogenic potential of fyn-related
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics. 29:420–427.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Boyle EI, Weng S, Gollub J, Jin H,
Botstein D, Cherry JM and Sherlock G: GO:TermFinder - open source
software for accessing Gene Ontology information and finding
significantly enriched Gene Ontology terms associated with a list
of genes. Bioinformatics. 20:3710–3715. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Furumichi M, Tanabe M
and Hirakawa M: KEGG for representation and analysis of molecular
networks involving diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:D355–D360. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering
C, et al: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks, with
increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Data Mining in Proteomics. Springer; pp. 291–303.
2011
|
|
25
|
Nepusz T, Yu H and Paccanaro A: Detecting
overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction
networks. Nat Methods. 9:471–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fujita PA, Rhead B, Zweig AS, Hinrichs AS,
Karolchik D, Cline MS, Goldman M, Barber GP, Clawson H, Coelho A,
et al: The UCSC genome browser database: Update 2011. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D876–D882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D105–D110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk - database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
'walking' the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu L, Liu S, Guo W, Zhang B, Liang Y and
Feng Q: Upregulation of Mad2 facilitates in vivo and in vitro
osteosarcoma progression. Oncol Rep. 28:2170–2176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu L, Guo W, Zhao S, Tang J and Liu J:
Knockdown of Mad2 induces osteosarcoma cell apoptosis-involved
Rad21 cleavage. J Orthop Sci. 16:814–820. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang Z, Jiang J, Yang H, Ge Z, Wang Q,
Zhang L, Wu C and Wang J: Silencing of Aurora kinase A by RNA
interference inhibits tumor growth in human osteosarcoma cells by
inducing apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep.
31:1249–1254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu LH, Li H, Li JP, Zhong H, Zhang HC,
Chen J and Xiao T: miR-125b suppresses the proliferation and
migration of osteosarcoma cells through downregulation of STAT3.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 416:31–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ryu K, Choy E, Yang C, Susa M, Hornicek
FJ, Mankin H and Duan Z: Activation of signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) pathway in osteosarcoma cells
and overexpression of phosphorylated-Stat3 correlates with poor
prognosis. J Orthop Res. 28:971–978. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang YC, Zheng LH, Ma BA, Zhou Y, Zhang
MH, Zhang DZ and Fan QY: Clinical value of signal transducers and
activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) gene expression in human
osteosarcoma. Acta Histochem. 113:402–408. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Novello C, Pazzaglia L, Cingolani C, Conti
A, Quattrini I, Manara MC, Tognon M, Picci P and Benassi MS: miRNA
expression profile in human osteosarcoma: Role of miR-1 and
miR-133b in proliferation and cell cycle control. Int J Oncol.
42:667–675. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shen L, Chen XD and Zhang YH: MicroRNA-128
promotes proliferation in osteosarcoma cells by downregulating
PTEN. Tumour Biol. 35:2069–2074. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sonaglio V, de Carvalho AC, Toledo SR,
Salinas-Souza C, Carvalho AL, Petrilli AS, de Camargo B and Vettore
AL: Aberrant DNA methylation of ESR1 and p14ARF genes could be
useful as prognostic indicators in osteosarcoma. Onco Targets Ther.
6:713–723. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kimura R, Ishikawa C, Rokkaku T, Janknecht
R and Mori N: Phosphorylated c-Jun and Fra-1 induce matrix
metalloproteinase-1 and thereby regulate invasion activity of 143B
osteosarcoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1543–1553. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|