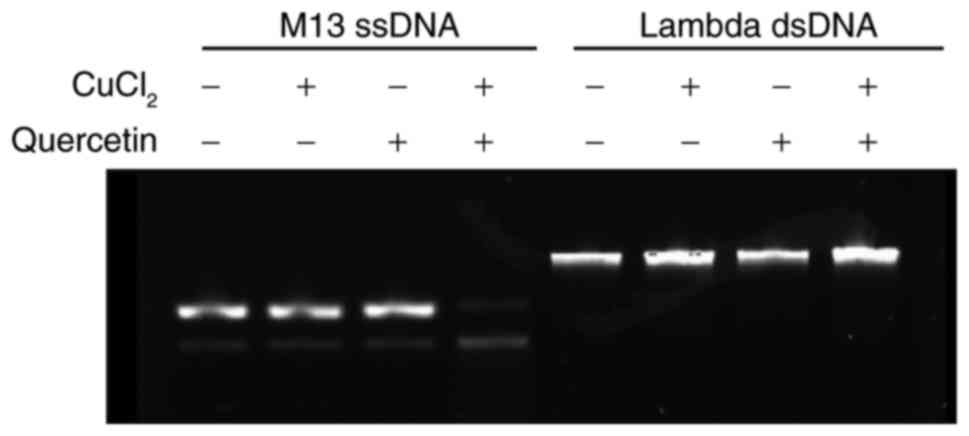
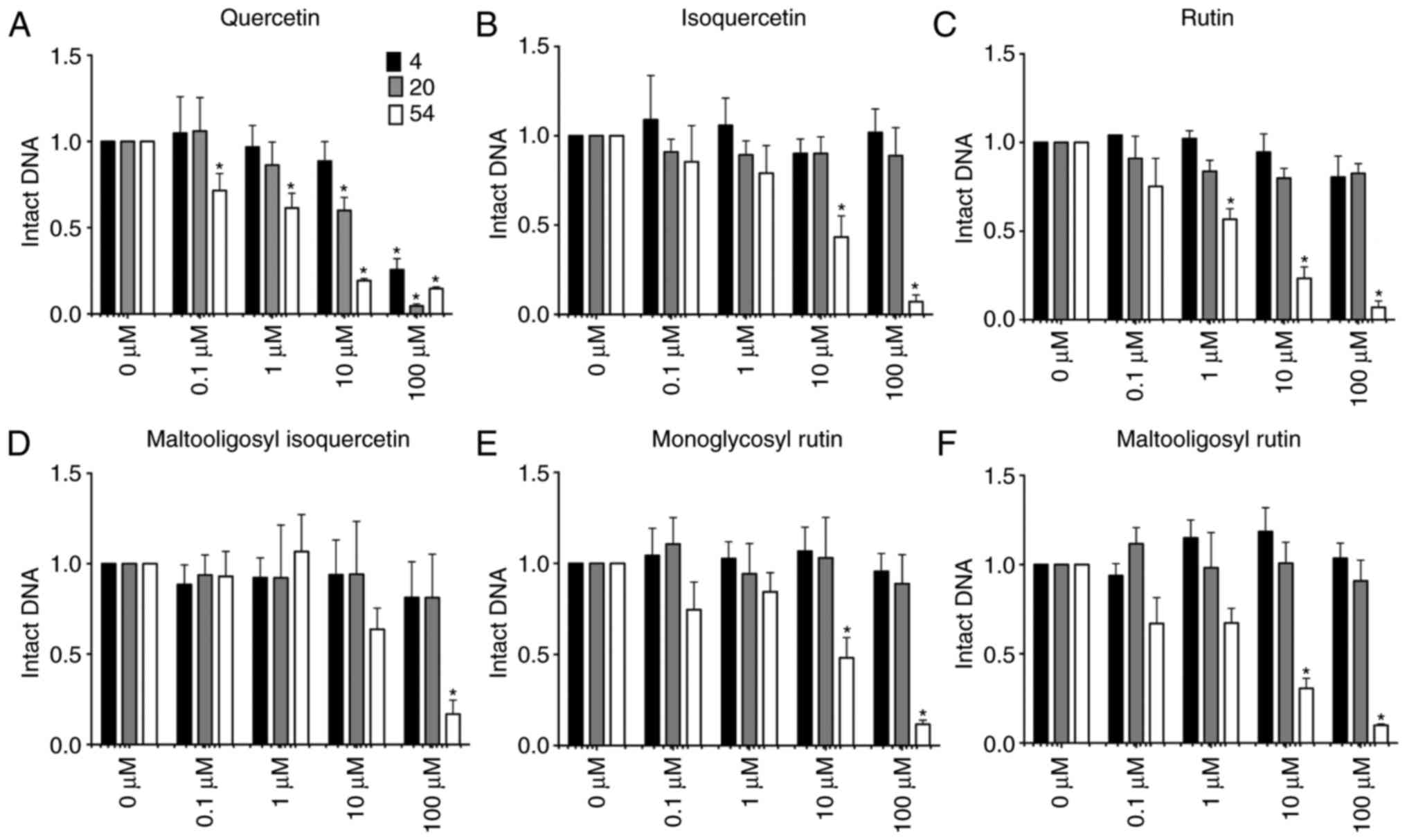
|
1
|
Havsteen BH: The biochemistry and medical
significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol Ther. 96:67–202. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yao LH, Jiang YM, Shi J, Tomás-Barberán
FA, Datta N, Singanusong R and Chen SS: Flavonoids in food and
their health benefits. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 59:113–122. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Amin A and Buratovich M: The anti-cancer
charm of flavonoids: A cup-of-tea will do! Recent Pat Anticancer
Drug Discov. 2:109–117. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yu H, Haskins JS, Su C, Allum A, Haskins
AH, Salinas VA, Sunada S, Inoue T, Aizawa Y, Uesaka M and Kato TA:
In vitro screening of radioprotective properties in the novel
glucosylated flavonoids. Int J Mol Med. 38:1525–1530. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Maeda J, Roybal EJ, Brents CA, Uesaka M,
Aizawa Y and Kato TA: Natural and glucosyl flavonoids inhibit
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity and induce synthetic lethality
in BRCA mutant cells. Oncol Rep. 31:551–556. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Engen A, Maeda J, Wozniak DE, Brents CA,
Bell JJ, Uesaka M, Aizawa Y and Kato TA: Induction of cytotoxic and
genotoxic responses by natural and novel quercetin glycosides.
Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 784–785:15–22. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gaspar J, Rodrigues A, Laires A, Silva F,
Costa S, Monteiro MJ, Monteiro C and Rueff J: On the mechanisms of
genotoxicity and metabolism of quercetin. Mutagenesis. 9:445–449.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bjeldanes LF and Chang GW: Mutagenic
activity of quercetin and related compounds. Science. 197:577–578.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brown JP and Dietrich PS: Mutagenicity of
plant flavonols in the Salmonella/mammalian microsome test:
Activation of flavonol glycosides by mixed glycosidases from rat
cecal bacteria and other sources. Mutat Res. 66:223–240. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
MacGregor JT and Jurd L: Mutagenicity of
plant flavonoids: Structural requirements for mutagenic activity in
Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 54:297–309. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rahman A, Shahabuddin, Hadi SM, Parish JH
and Ainley K: Strand scission in DNA induced by quercetin and
Cu(II): Role of Cu(I) and oxygen free radicals. Carcinogenesis.
10:1833–1839. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rahman A, Fazal F, Greensill J, Ainley K,
Parish JH and Hadi SM: Strand scission in DNA induced by dietary
flavonoids: Role of Cu(I) and oxygen free radicals and biological
consequences of scission. Mol Cell Biochem. 111:3–9. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y and Guo M: Studies on transition
metal-quercetin complexes using electrospray ionization tandem mass
spectrometry. Molecules. 20:8583–8594. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pekal A, Biesaga M and Pyrzynska K:
Interaction of quercetin with copper ions: Complexation, oxidation
and reactivity towards radicals. Biometals. 24:41–49. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ríha M, Karlícková J, Filipský T, Jahodár
L, Hrdina R and Mladenka P: In vitro copper-chelating properties of
flavonoids. Free Radic Biol Med. 75(Suppl 1): S462014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cherrak SA, Mokhtari-Soulimane N,
Berroukeche F, Bensenane B, Cherbonnel A, Merzouk H and Elhabiri M:
In vitro antioxidant versus metal ion chelating properties of
flavonoids: A structure-activity investigation. PLoS One.
11:e01655752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bukhari SB, Memon S, Mahroof-Tahir M and
Bhanger MI: Synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity
copper-quercetin complex. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc.
71:1901–1906. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yoshino M, Haneda M, Naruse M and Murakami
K: Prooxidant activity of flavonoids: Copper-dependent strand
breaks and the formation of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in DNA. Mol
Genet Metab. 68:468–472. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ahsan H and Hadi SM: Strand scission in
DNA induced by curcumin in the presence of Cu(II). Cancer Lett.
124:23–30. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ohashi Y, Yoshinaga K and Yoshioka H and
Yoshioka H: Kinetic analysis of the effect of (-)-epigallocatechin
gallate on the DNA scission induced by Fe(II). Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 66:770–776. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar S and Pandey AK: Chemistry and
biological activities of flavonoids: An overview.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2013:1627502013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yamashita N, Tanemura H and Kawanishi S:
Mechanism of oxidative DNA damage induced by quercetin in the
presence of Cu(II). Mutat Res. 425:107–115. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carver JH, Carrano AV and MacGregor JT:
Genetic effects of the flavonols quercetin, kaempferol, and
galangin on Chinese hamster ovary cells in vitro. Mutat Res.
113:45–60. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen JW, Zhu ZQ, Hu TX and Zhu DY:
Structure-activity relationship of natural flavonoids in hydroxyl
radical-scavenging effects. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 23:667–672.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|