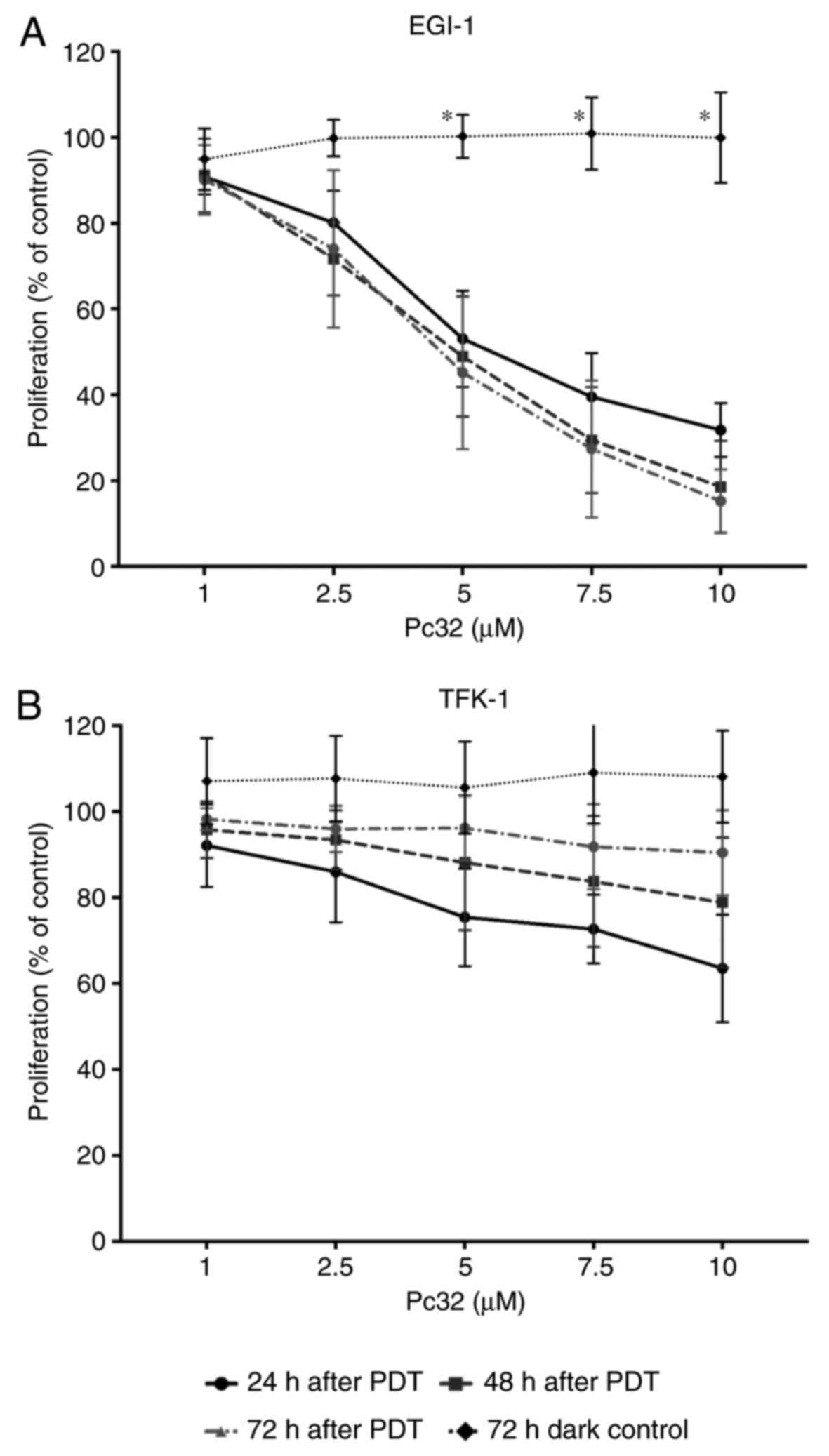
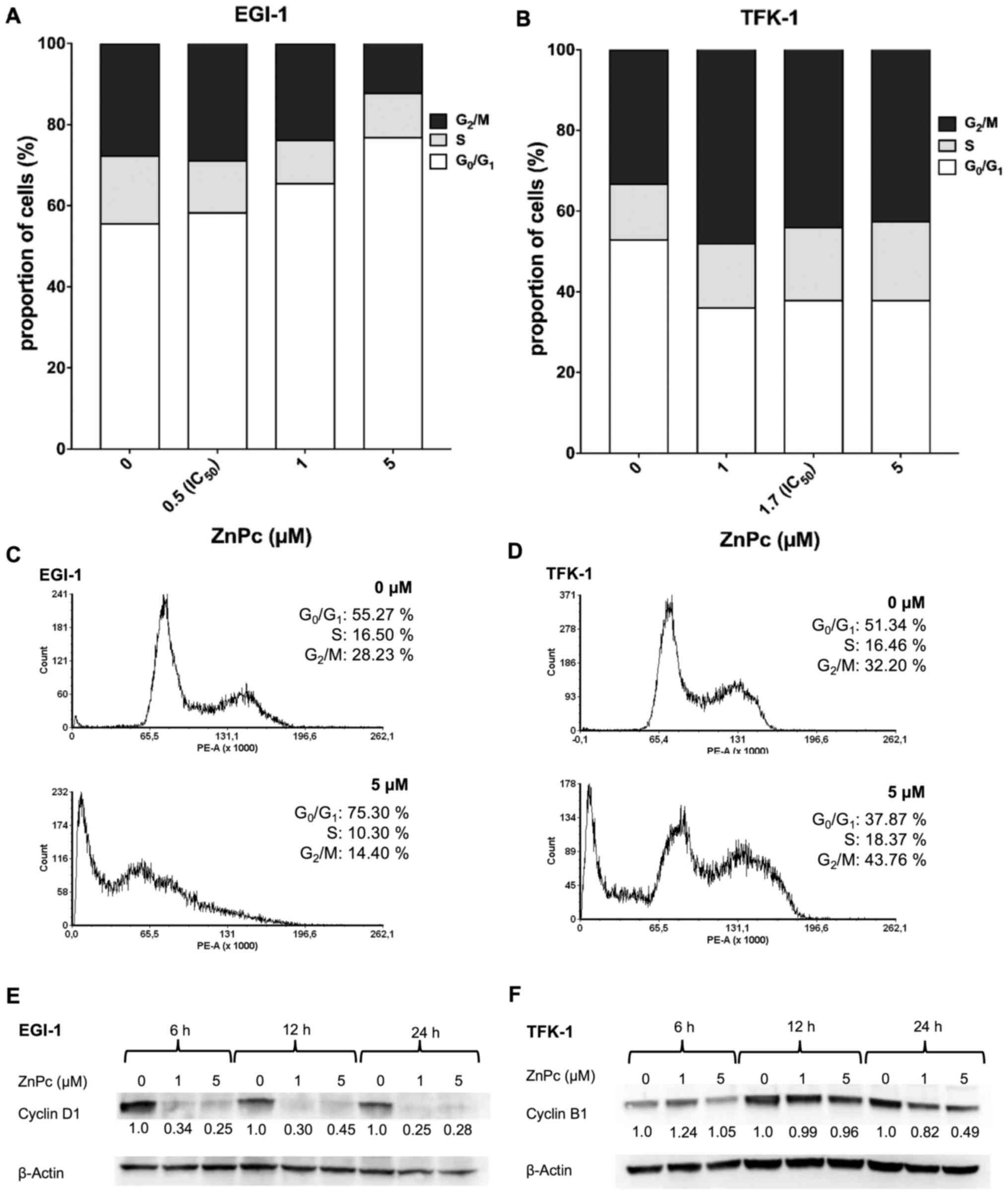
|
1
|
Aljiffry M, Walsh MJ and Molinari M:
Advances in diagnosis, treatment and palliation of
cholangiocarcinoma: 1990–2009. World J Gastroenterol. 15:4240–4262.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bergquist A and Von Seth E: Epidemiology
of cholangiocarcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
29:221–232. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baradari V, Höpfner M, Huether A, Schuppan
D and Scherübl H: Histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 alone or
combined with bortezomib or sorafenib exhibits strong
antiproliferative action in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:4458–4466. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Doherty B, Nambudiri VE and Palmer WC:
Update on the diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Curr
Gastroenterol Rep. 19:22017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, Dematteo RP, Gonen M,
Burke EC, Bodniewicz BSJ, Youssef BAM, Klimstra D and Blumgart LH:
Staging, resectability, and outcome in 225 patients with hilar
cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 234:507–517. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ortner ME, Caca K, Berr F, Liebetruth J,
Mansmann U, Huster D, Voderholzer W, Schachschal G, Mössner J and
Lochs H: Successful photodynamic therapy for nonresectable.
cholangiocarcinoma: A randomized prospective study.
Gastroenterology. 5085:1355–1363. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Moole H, Tathireddy H, Dharmapuri S, Moole
V, Boddireddy R, Yedama P, Dharmapuri S, Uppu A, Bondalapati N and
Duvvuri A: Success of photodynamic therapy in palliating patients
with nonresectable cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 23:1278–1288. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ortner M: Photodynamic therapy in
cholangiocarcinoma: An overview. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther.
1:85–92. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abu-hamda EM and Baron TH: Endoscopic
management of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 24:165–175.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dolmans DE, Fukumura D and Jain RK:
Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:380–387. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Witzigmann H, Berr F, Ringel U, Caca K,
Uhlmann D, Schoppmeyer K, Tannapfel A, Wittekind C, Mossner J,
Hauss J and Wiedmann M: Surgical and palliative management and
outcome in 184 patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg.
244:230–239. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zoepf T, Jakobs R, Arnold J, Apel D and
Riemann JF: Palliation of nonresectable bile duct cancer: Improved
survival after photodynamic therapy. Am J Gastroenterol.
100:2426–2430. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prasad GA, Wang KK, Baron TH, Buttar NS,
Wongkeesong LM, Roberts LR, LeRoy AJ, Lutzke LS and Borkenhagen LS:
Factors associated with increased survival after photodynamic
therapy for cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
5:743–748. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee TY, Cheon YK, Shim CS and Cho YD:
Photodynamic therapy prolongs metal stent patency in patients with
unresectable hilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
18:5589–5594. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McCaughan JS Jr, Mertens BF, Cho C,
Barabash RD and Payton HW: Photodynamic therapy to treat tumors of
the extrahepatic biliary ducts. A case report Arch Surg.
126:111–113. 1991.
|
|
16
|
Allison RR, Zervos E and Sibata CH:
Cholangiocarcinoma: An emerging indication for photodynamic
therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 6:84–92. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Allison RR and Sibata CH: Oncologic
photodynamic therapy photosensitizers: A clinical review.
Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 7:61–75. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bonnett R: Photosensitizers of the
porphyrin and phthalocyanine series for photodynamic therapy. Chem
Soc Rev. 24:1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Josefsen LB and Boyle RW: Photodynamic
therapy: Novel third-generation photosensitizers one step closer?
Br J Pharmacol. 154:1–3. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang Z, Shao J, Yang T, Wang J and Jia L:
Pharmaceutical development, composition and quantitative analysis
of phthalocyanine as the photosensitizer for cancer photodynamic
therapy. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 87:98–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Neagu M, Constantin C, Tampa M, Matei C,
Lupu A, Manole E, Ion RM, Fenga C and Tsatsakis AM: Toxicological
and efficacy assessment of post-transition metal (Indium)
phthalocyanine for photodynamic therapy in neuroblastoma.
Oncotarget. 7:69718–69732. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Agostinis P, Berg K, Cengel KA, Foster TH,
Girotti AW, Gollnick SO, Hahn SM, Hamblin MR, Juzeniene A, Kessel
D, et al: Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:250–281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ochsner M: Light scattering of human skin:
A comparison between Zinc(II)-phthalocyanine and photofrin II. J
Photochem Photobiol B. 32:3–9. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yslas EI, Prucca C, Romanini S, Durantini
EN, Bertuzzi M and Rivarola V: Biodistribution and phototherapeutic
properties of Zinc(II) 2,9,16,23-tetrakis (methoxy) phthalocyanine
s. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 6:62–70. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kuzyniak W, Ermilov EA, Atilla D, Gürek
AG, Nitzsche B, Derkow K, Hoffmann B, Steinemann G, Ahsen V and
Höpfner M: Tetra-triethyleneoxysulfonyl substituted zinc
phthalocyanine for photodynamic cancer therapy. Photodiagnosis
Photodyn Ther. 13:148–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu W, Chen N, Jin H, Huang J, Wei J, Bao
J, Li C, Liu Y, Li X and Wang A: Intravenous repeated-dose toxicity
study of ZnPcS2P2-based-photodynamic therapy in beagle dogs. Regul
Toxicol Pharmacol. 47:221–231. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Atilla D, Saydan N, Durmus M, Gürek AG,
Khan T, Rück A, Walt H, Nyokong T and Ahsen V: Synthesis and
photodynamic potential of tetra- and octa-triethyleneoxysulfonyl
substituted zinc phthalocyanines. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem.
186:298–307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Scherdin G, Garbrecht M and Klouche M: In
vitro interaction of á-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) and human
recombinant interferon-a (rIFN-a) on human cancer cell lines.
Immunobiology. 175:1–143. 1987.
|
|
29
|
Saijyo S, Kudo T, Suzuki M, Katayose Y,
Shinoda M, Muto T, Fukuhara K, Suzuki T and Matsuno S:
Establishment of a new extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma cell line,
TFK-1. Tohoku J Exp Med. 177:61–71. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nitzsche B, Gloesenkamp C, Schrader M,
Ocker M, Preissner R, Lein M, Zakrzewicz A, Hoffmann B and Höpfner
M: Novel compounds with antiangiogenic and antiproliferative
potency for growth control of testicular germ cell tumours. Br J
Cancer. 103:18–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cai Y, Xia Q, Su Q, Luo R, Sun Y, Shi Y
and Jiang W: MTOR inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) induces apoptotic,
not autophagic cell death, in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Int J Mol Med. 31:904–912. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gloesenkamp C, Nitzsche B, Lim AR, Normant
E, Vosburgh E, Schrader M, Ocker M, Scherübl H and Höpfner M: Heat
shock protein 90 is a promising target for effective growth
inhibition of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Int J Oncol.
40:1659–1667. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Höpfner M, Baradari V, Huether A, Schöfl C
and Scherübl H: The insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 is a
promising target for novel treatment approaches in neuroendocrine
gastrointestinal tumours. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13:135–149. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rodrigues JR, Charris J, Camacho J,
Barazarte A, Gamboa N, Nitzsche B, Höpfner M, Lein M, Jung K and
Abramjuk C:
N'-Formyl-2-(5-nitrothiophen-2-yl)benzothiazole-6-carbohydrazide as
a potential anti-tumour agent for prostate cancer in experimental
studies. J Pharm Pharmacol. 65:411–422. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Krysko DV, Vanden Berghe T, D'Herde K and
Vandenabeele P: Apoptosis and necrosis: Detection, discrimination
and phagocytosis. Methods. 44:205–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kuzyniak W, Schmidt J, Glac W, Berkholz J,
Steinemann G, Hoffmann B, Ermilov EA, Gürek AG, Ahsen V, Nitzsche B
and Höpfner M: Novel zinc phthalocyanine as a promising
photosensitizer for photodynamic treatment of esophageal cancer.
Int J Oncol. 50:953–963. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mfouo-tynga I and Abrahamse H: Cell death
pathways and phthalocyanine as an efficient agent for photodynamic
cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 16:10228–10241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roskoski R Jr: ERK1/2 MAP kinases:
Structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 66:105–143.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Höpfner M, Maaser K, Theiss A, Lenz M,
Sutter AP, Kashtan H, von Lampe B, Riecken EO, Zeitz M and Scherübl
H: Hypericin activated by an incoherent light source has
photodynamic effects on esophageal cancer cells. Int J Colorectal
Dis. 18:239–247. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Whitacre CM, Feyes DK, Satoh T, Grossmann
J, Mulvihill JW, Mukhtar H and Oleinick NL: Photodynamic therapy
with the phthalocyanine photosensitizer pc 4 of SW480 human colon
cancer xenografts in athymic mice 1. Clin Cancer Res. 6:2021–2027.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nanashima A, Isomoto H, Abo T, Nonaka T,
Morisaki T, Arai J, Takagi K, Ohnita K, Shoji H, Urabe S, et al:
How to access photodynamic therapy for bile duct carcinoma. Ann
Transl Med. 2:232014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Oniszczuk A, Wojtunik-Kulesza KA,
Oniszczuk T and Kasprzak K: The potential of photodynamic therapy
(PDT)-experimental investigations and clinical use. Biomed
Pharmacother. 83:912–929. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
van Straten D, Mashayekhi V, de Bruijn H,
Oliveira S and Robinson D: Oncologic photodynamic therapy: Basic
principles, current clinical status and future directions. Cancers
(Basel). 9:E192017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Fabris C, Valduga G, Miotto G, Borsetto L,
Jori G, Garbisa S and Reddi E: Photosensitization with Zinc (II)
phthalocyanine as a switch in the decision between apoptosis and
necrosis. Cancer Res. 61:7495–7500. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Morgan J, Potter WR and Oseroff AR:
Comparison of photodynamic targets in a carcinoma cell line and its
mitochondrial DNA-deficient derivative. Photochem Photobiol.
71:747–57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Oleinick NL, Morris RL and Belichenko I:
The role of apoptosis in response to photodynamic therapy: What,
where, why, and how. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 1:1–21. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Rodriguez ME, Zhang P, Azizuddin K, Delos
Santos GB, Chiu SM, Xue LY, Berlin JC, Peng X, Wu H, Lam M, et al:
Structural factors and mechanisms underlying the improved
photodynamic cell killing with Silicon phthalocyanine
photosensitizers directed to lysosomes v/s mitochondria. Photochem
Photobiol. 85:1189–1200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Tynga IM, Houreld NN and Abrahamse H: The
primary subcellular localization of Zinc phthalocyanine and its
cellular impact on viability, proliferation and structure of breast
cancer cells (MCF-7). J Photochem Photobiol B. 120:171–176. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Shao J, Dai Y, Zhao W, Xie J, Xue J, Ye J
and Jia L: Intracellular distribution and mechanisms of actions of
photosensitizer Zinc (II)-phthalocyanine solubilized in Cremophor
EL against human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells q. Cancer
Lett. 330:49–56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Biology C, Marino J, García MC, Furmento
VA, Blank VC, Awruch J and Roguin LP: Lysosomal and mitochondrial
permeabilization mediates zinc (II) cationic phthalocyanine
phototoxicity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2553–2562. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Challa S and Chan FK: Going up in flames:
Necrotic cell injury and inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci.
67:3241–3253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lam M, Oleinick NL and Nieminen A:
Photodynamic therapy-induced apoptosis in epidermoid carcinoma
cells. J Biol Chem. 276:47379–47386. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tampa M, Matei C, Popescu S, Georgescu S
and Neagu M: Zinc trisulphonated phthalocyanine used in
photodynamic therapy of dysplastic oral keratinocytes. Rev Chim.
64:639–645. 2013.
|
|
54
|
Dickson MA and Schwartz GK: Development of
cell-cycle inhibitors for cancer therapy. Drug Dev Contemp Oncol.
16:36–43. 2009.
|
|
55
|
Gabrielli B, Brooks K and Pavey S:
Defective cell cycle checkpoints as targets for anti-cancer
therapies. Front Pharmacol. 3:92012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Resnitzky D and Reed SI: Different roles
for cyclins D1 and E in regulation of the G1-to-S transition. Mol
Cell Biol. 15:3463–3469. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gupta SC, Hevia D, Patchva S, Park B, Koh
W and Aggarwal BB: Upsides and downsides of reactive oxygen species
for cancer: The roles of reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis,
prevention, and therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1295–1322. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Rezaei PF, Fouladdel S, Ghaffari SM, Amin
G and Azizi E: Induction of G1 cell cycle arrest and cyclin D1
down-regulation in response to pericarp extract of Baneh in human
breast cancer T47D cells. DARU. 20:1012012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Su C, Lin J, Chen G, Lin W and Chung J:
Down-regulation of Cdc25c, CDK1 and cyclin B1 and up-regulation of
wee1 by curcumin promotes human colon cancer colo 205 cell entry
into G2/M-phase of cell cycle. Cancer Gen Proteomics. 3:55–62.
2006.
|
|
60
|
Huether A, Höpfner M, Baradari V, Schuppan
D and Scherübl H: Sorafenib alone or as combination therapy for
growth control of cholangiocarcinoma. Biochem Pharmacol.
73:1308–1317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Levine AJ: P53, the cellular gatekeeper
for growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Caca K, Feisthammel J, Klee K, Tannapfel
A, Witzigmann H, Wittekind C, Mössner J and Berr F: Inactivation of
the INK4a/ARF locus and p53 in sporadic extrahepatic bile duct
cancers and bile tract cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer. 97:481–488.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis: An organizing
principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:273–286. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Thelen A, Scholz A, Weichert W, Wiedenmann
B, Neuhaus P, Gessner R, Benckert C and Jonas S: Tumor-associated
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis correlate with progression of
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 105:1123–1132.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|