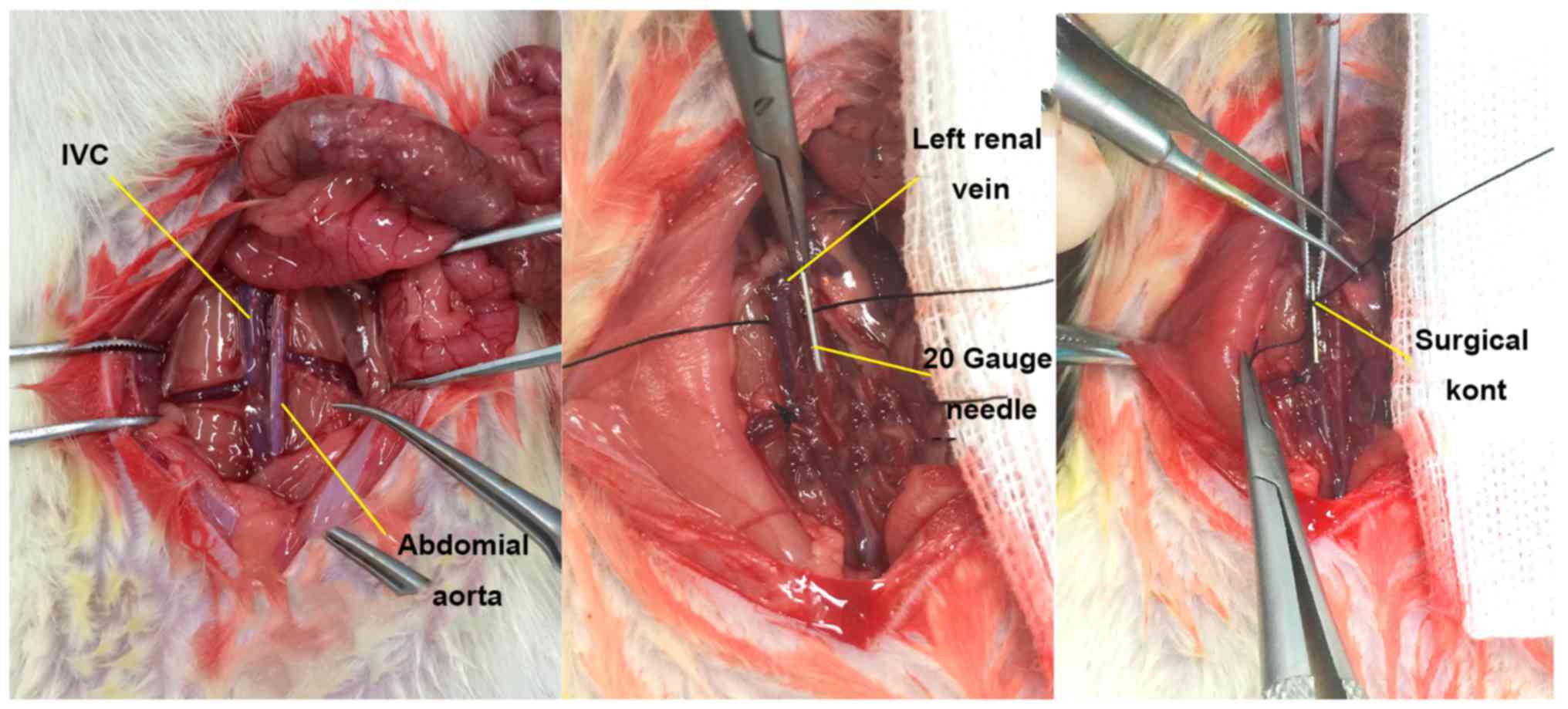
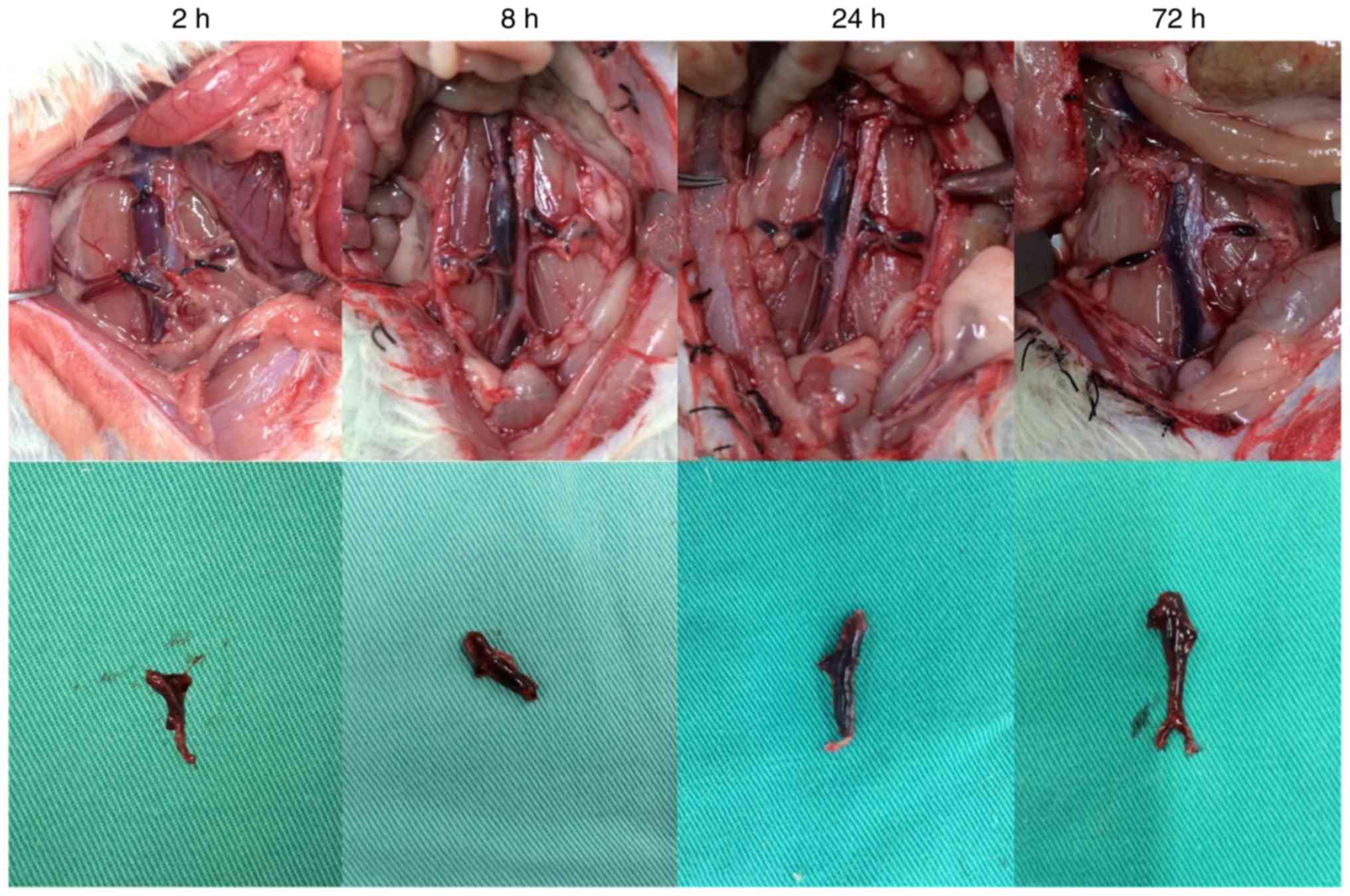
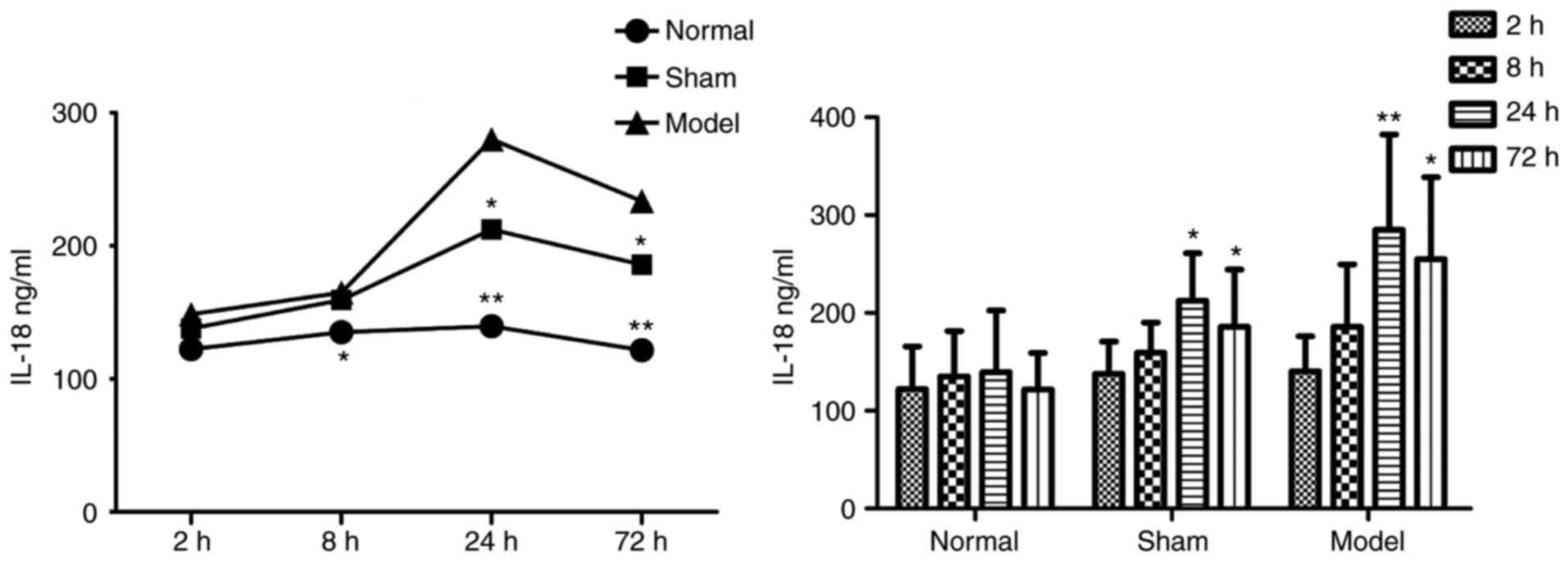
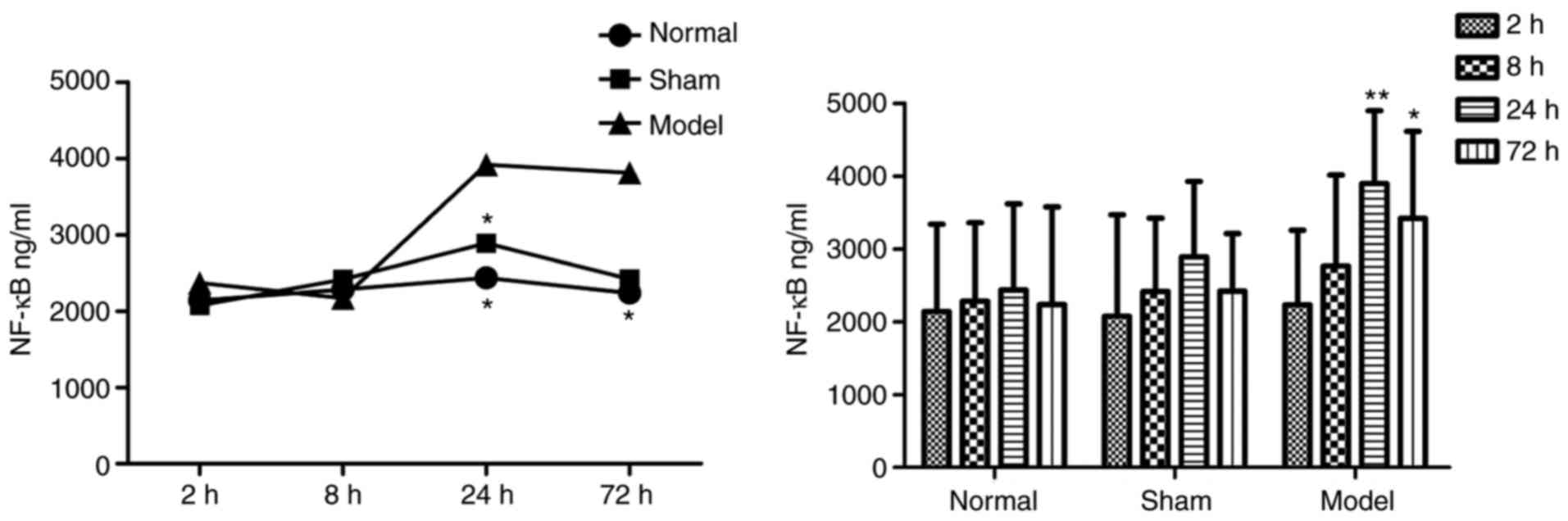
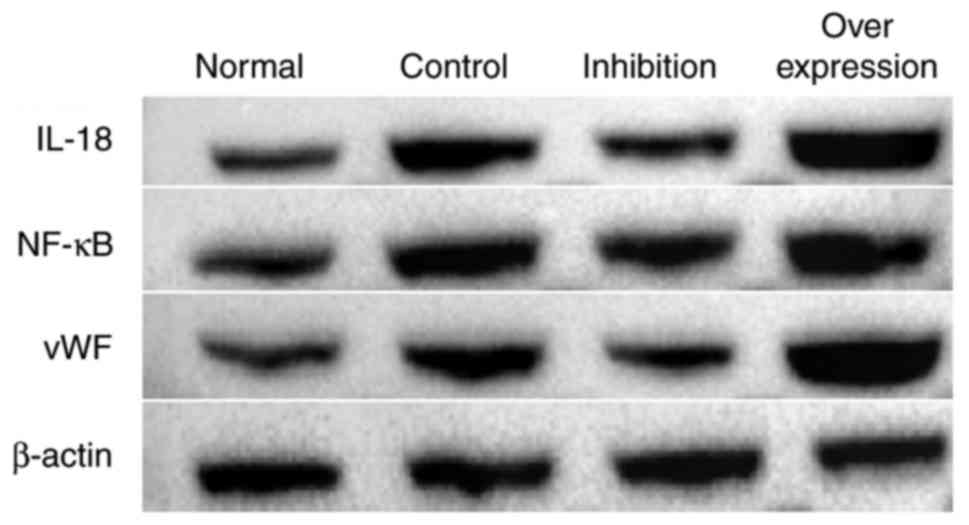
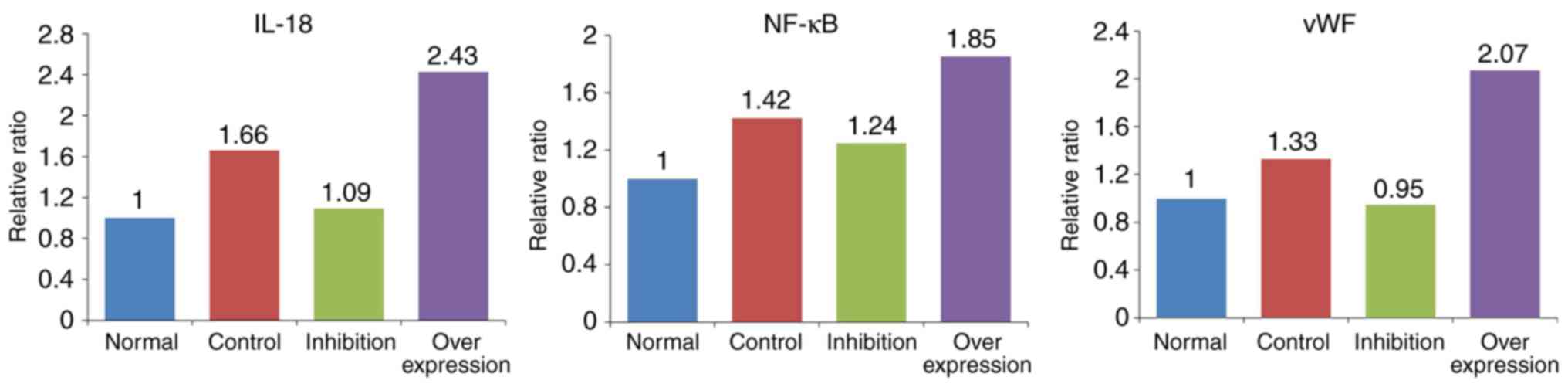
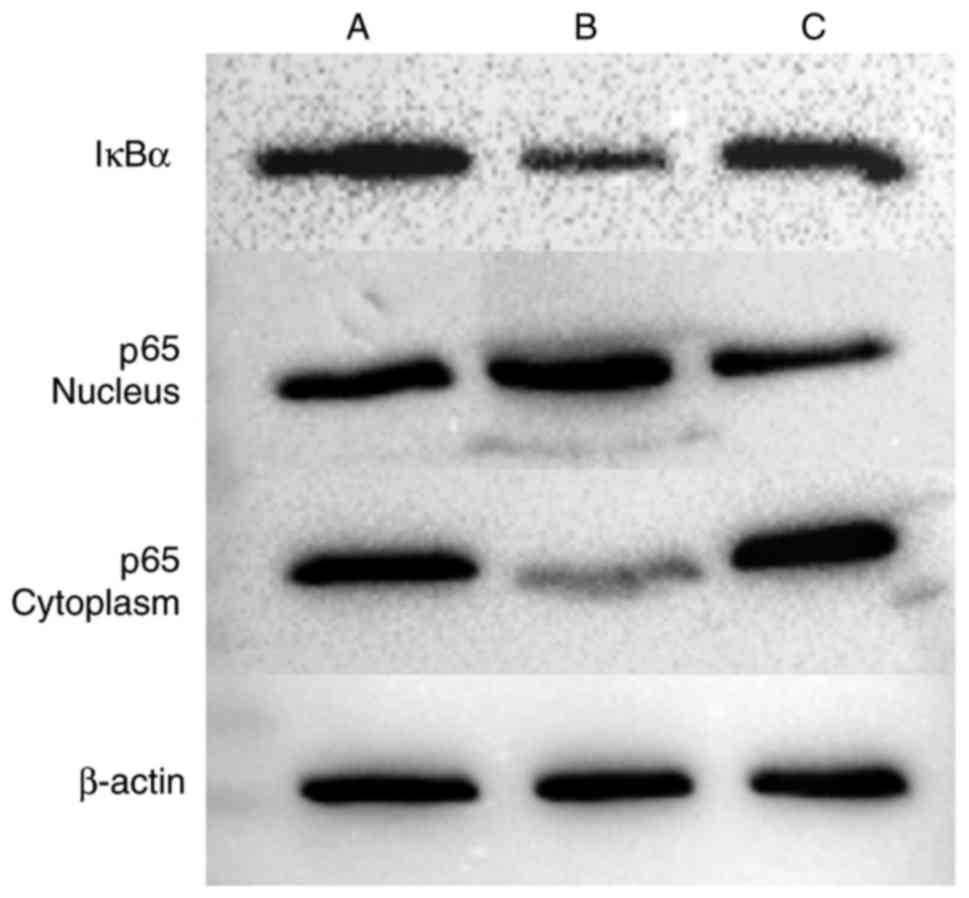
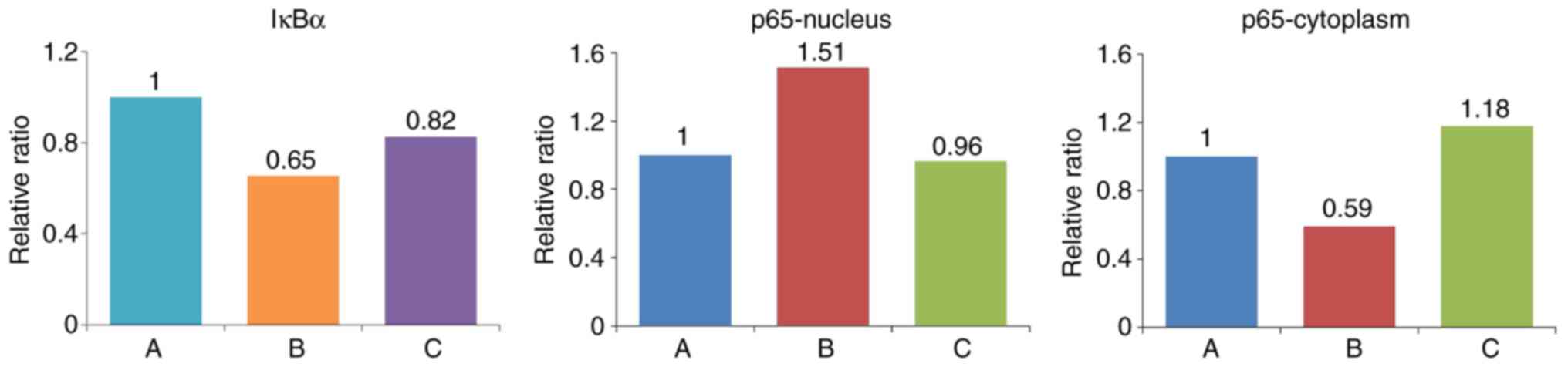
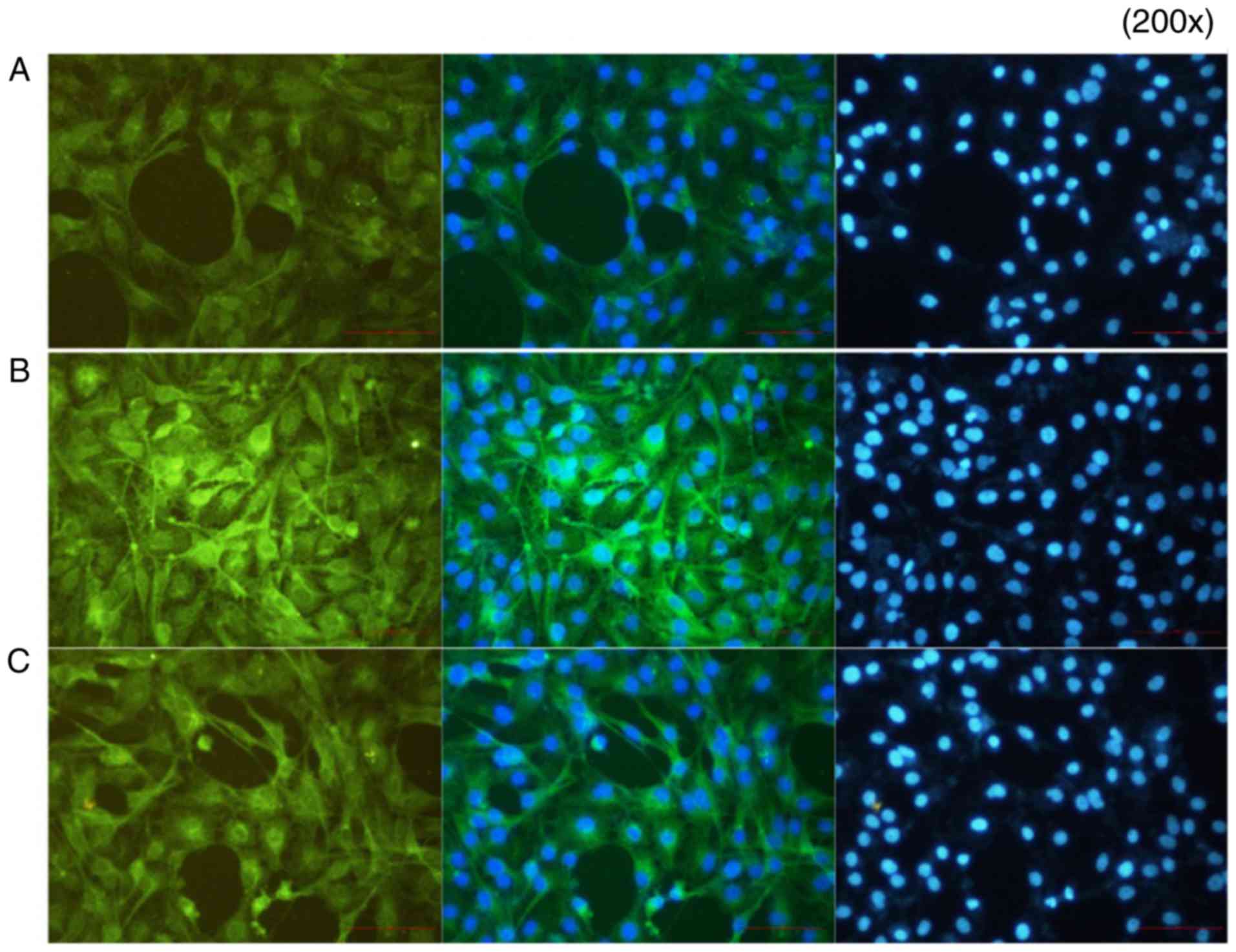
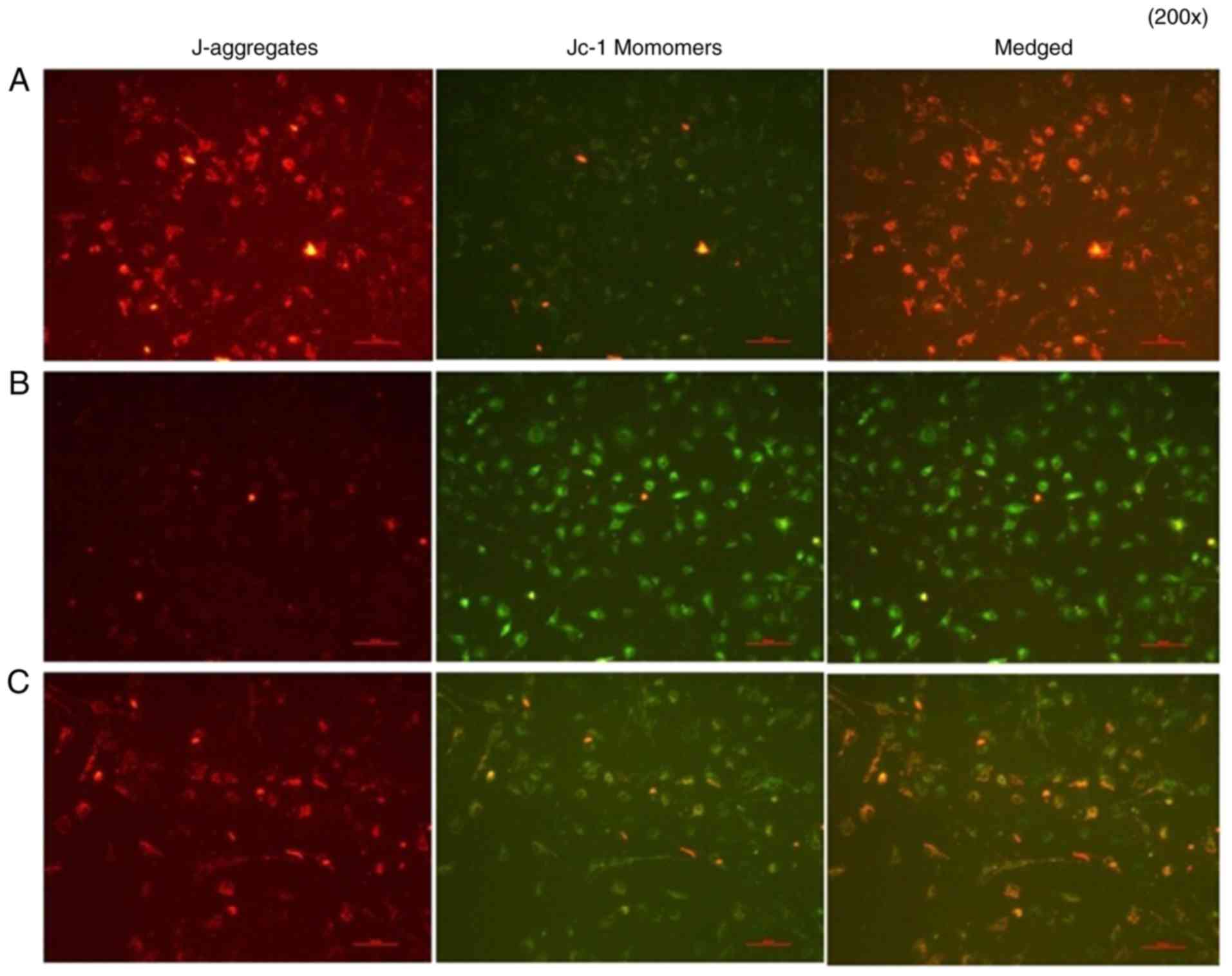
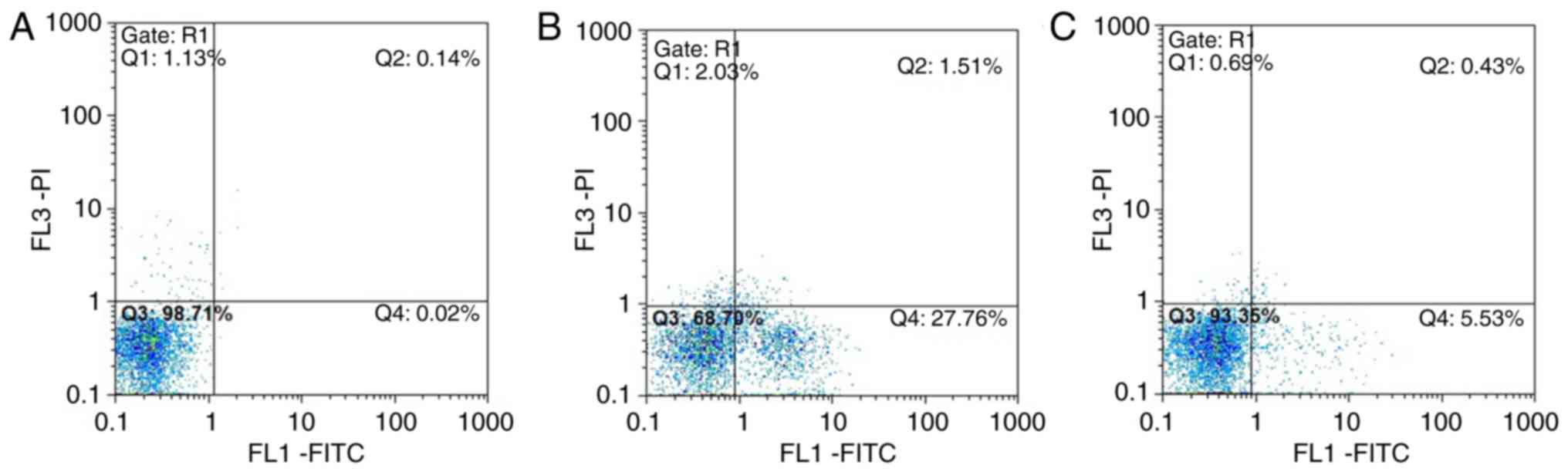
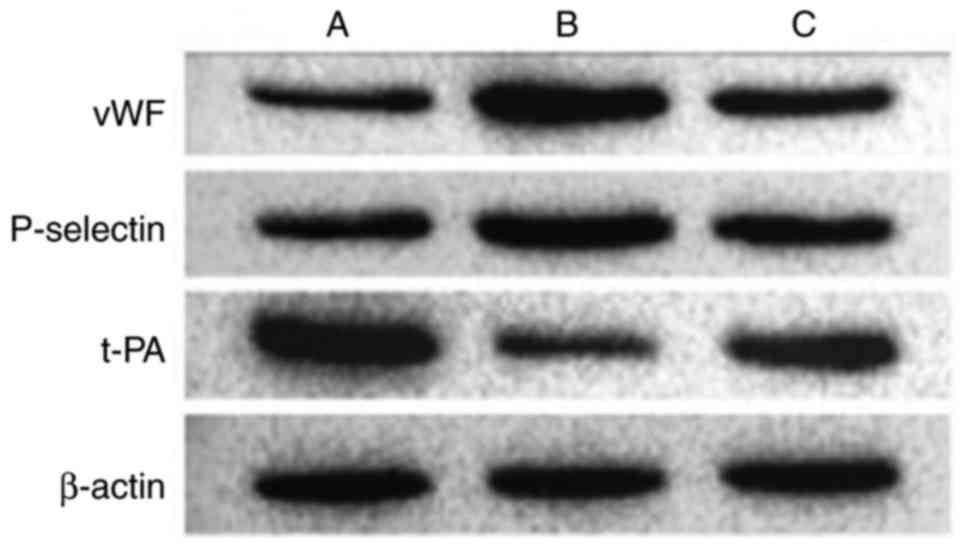
|
1
|
Downing LJ, Strieter RM, Kadell AM, Wilke
CA, Austin JC, Hare BD, Burdick MD, Greenfield LJ and Wakefield TW:
IL-10 regulates thrombus-induced vein wall inflammation and
thrombosis. J Immunol. 161:1471–1476. 1998.
|
|
2
|
Strukova S: Blood coagulation-dependent
inflammation. Coagulation-dependent inflammation and
inflammation-dependent thrombosis. Front Biosci. 11:59–80. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chandrasekar B, Vemula K, Surabhi RM,
Li-Weber M, Owen-Schaub LB, Jensen LE and Mummidi S: Activation of
intrinsic and extrinsic proapoptotic signaling pathways in
interleukin-18-mediated human cardiac endothelial cell death. J
Biol Chem. 279:20221–20233. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li YD, Ye BQ, Zheng SX, Wang JT, Wang JG,
Chen M, Liu JG, Pei XH, Wang LJ, Lin ZX, et al: NF-kappaB
transcription factor p50 critically regulates tissue factor in deep
vein thrombosis. J Biol Chem. 284:4473–4483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Brill A, Fuchs TA, Chauhan AK, Yang JJ, De
Meyer SF, Köllnberger M, Wakefield TW, Lämmle B, Massberg S and
Wagner DD: Von Willebrand factor-mediated platelet adhesion is
critical for deep vein thrombosis in mouse models. Blood.
117:1400–1407. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Myers DD, Hawley AE, Farris DM, Wrobleski
SK, Thanaporn P, Schaub RG, Wagner DD, Kumar A and Wakefield TW:
P-selectin and leukocyte microparticles are associated with venous
thrombogenesis. J Vasc Surg. 38:1075–1089. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Henke PK, Varga A, De S, Deatrick CB,
Eliason J, Arenberg DA, Sukheepod P, Thanaporn P, Kunkel SL,
Upchurch GR Jr and Wakefield TW: Deep vein thrombosis resolution is
modulated by monocyte CXCR2-mediated activity in a mouse model.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:1130–1137. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Morel JC, Park CC, Woods JM and Koch AE: A
novel role for interleukin-18 in adhesion molecule induction
through NF kappa B and phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase-dependent
signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 276:37069–37075. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S:
NF-kappaB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab.
13:11–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS and Ghosh S:
Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol. 12:695–708.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sen R: The origins of NF-κB. Nat Immunol.
12:686–688. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tobe M, Isobe Y, Tomizawa H, Nagasaki T,
Takahashi H and Hayashi H: A novel structural class of potent
inhibitors of NF-kappa B activation: Structure-activity
relationships and biological effects of 6-aminoquinazoline
derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem. 11:3869–3878. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Armstrong SJ, Wiberg M, Terenghi G and
Kingham PJ: Laminin activates NF-kappaB in Schwann cells to enhance
neurite outgrowth. Neurosci Lett. 439:42–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang RH, Strong JA and Zhang JM: NF-kappaB
mediated enhancement of potassium currents by the chemokine
CXCL1/growth related oncogene in small diameter rat sensory
neurons. Mol Pain. 5:262009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Blann AD and Lip GY: Virchow's triad
revisited: The importance of soluble coagulation factors, the
endothelium, and platelets. Thromb Res. 101:321–327. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pan J, Zhang SQ and Chen B: Interferon-γ
induces the apoptosis of vascular endothelial cell in vitro. J
Bengbu Med Coll. 30:388–389. 2005.
|
|
18
|
Choy JC, Granville DJ, Hunt DW and McManus
BM: Endothelial cell apoptosis: Biochemical characteristics and
potential implications for atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
33:1673–1690. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Blann AD: Plasma von Willebrand factor,
thrombosis, and the endothelium: The first 30 years. Thromb
Haemost. 95:49–55. 2006.
|
|
20
|
Jansson JH, Nilsson TK and Johnson O: Von
Willebrand factor in plasma: A novel risk factor for recurrent
myocardial infarction and death. Br Heart J. 66:351–355. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cortellaro M, Boschetti C, Cofrancesco E,
Zanussi C, Catalano M, de Gaetano G, Gabrielli L, Lombardi B,
Specchia G and Tavazzi L: The PLAT Study: Hemostatic function in
relation to atherothrombotic ischemic events in vascular disease
patients. Principal results. PLAT Study Group. Progetto Lombardo
Atero-Trombosi (PLAT) Study Group. Arterioscler Thromb.
12:1063–1070. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cambien B and Wagner DD: A new role in
hemostasis for the adhesion receptor P-selectin. Trends Mol Med.
10:179–186. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Furie B and Furie BC: Role of platelet
P-selectin and micropar-ticle PSGL-1 in thrombus formation. Trends
Mol Med. 10:171–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rosenbaum T, Rammos S, Kniemeyer HW and
Gobel U: Extended deep vein and inferior vena cava thrombosis in a
15-year-old boy: Successful lysis with recombinant tissue-type
plasminogen activator 2 weeks after onset of symptoms. Eur J
Pediatr. 152:978–980. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kruithof EK and Dunoyer-Geindre S: Human
tissue-type plas-minogen activator. Thromb Haemost. 112:243–254.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|