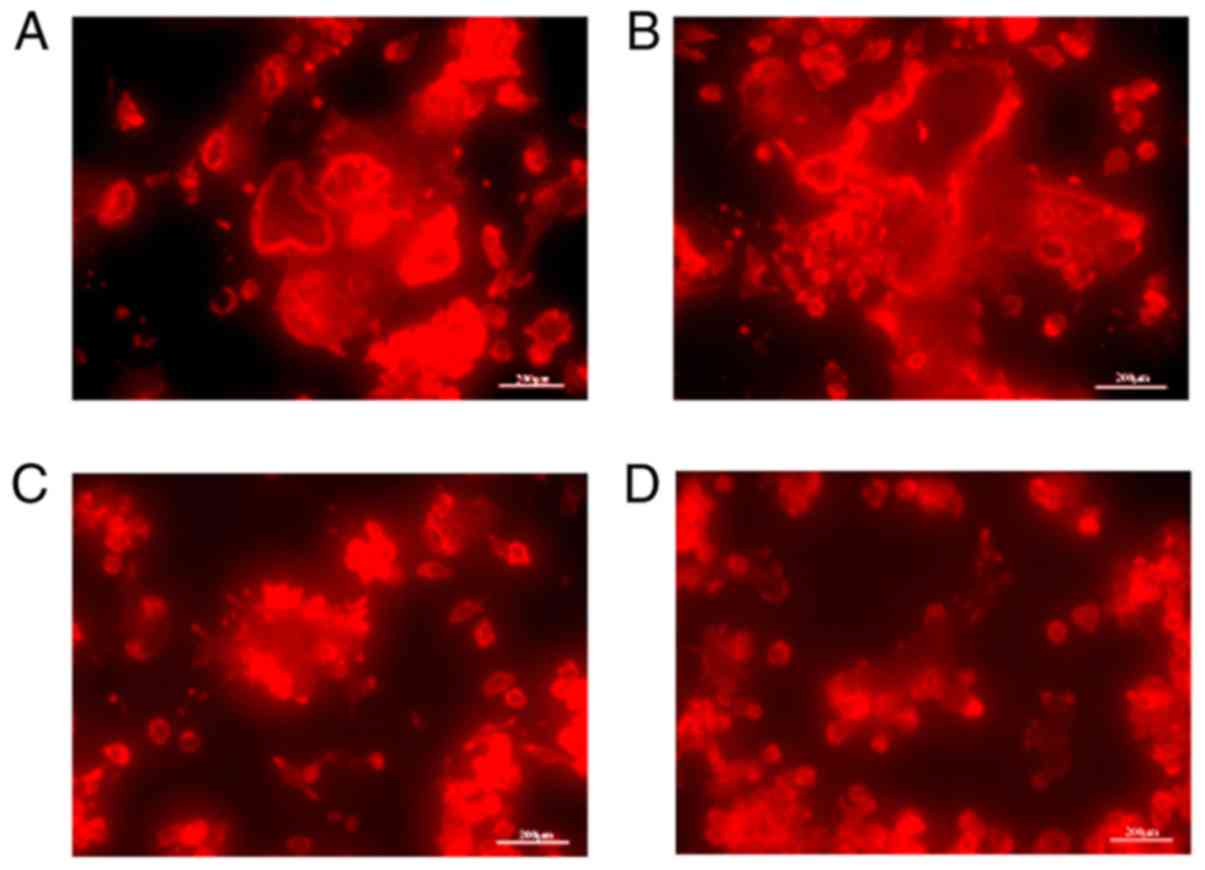
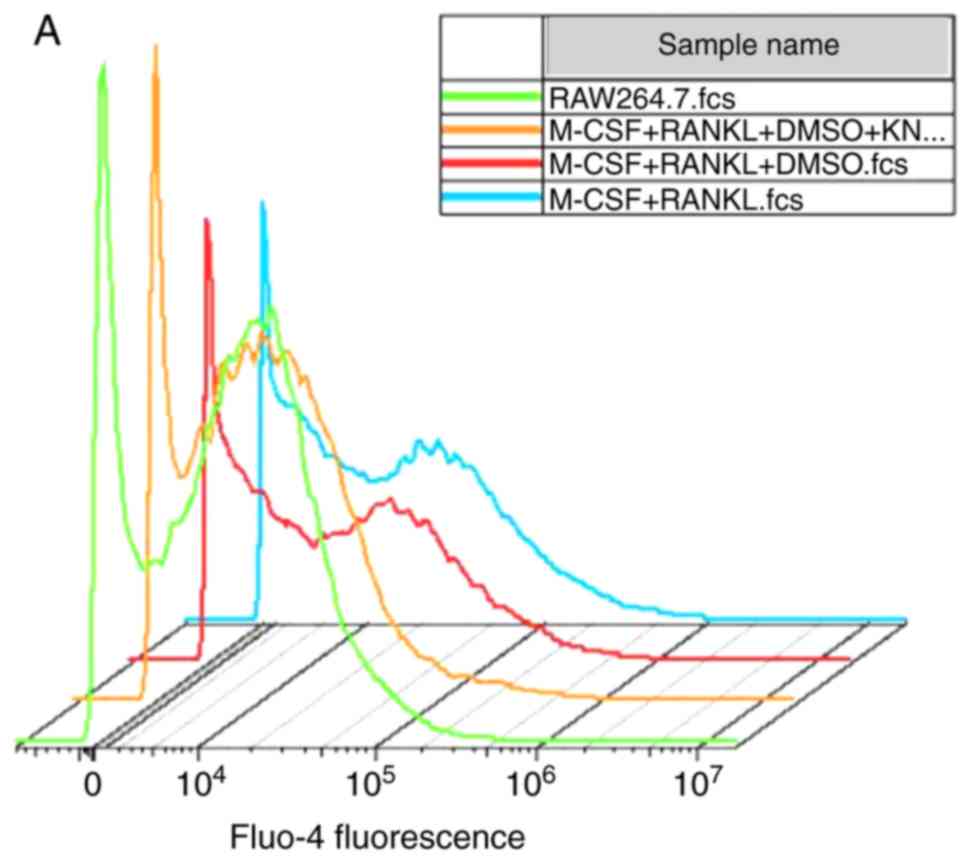
|
1
|
Kikuta J and Ishii M: Intravital bone
imaging: osteoclast. Clin Calcium. 28:211–216. 2018.In
Japanese.
|
|
2
|
Verma SK, Leikin E, Melikov K, Gebert C,
Kram V, Young MF, Uygur B and Chernomordik LV: Cell-surface
phosphatidylserine regulates osteoclast precursor fusion. J Biol
Chem. 293:254–270. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cafiero C, Gigante M, Brunetti G, Simone
S, Chaoul N, Oranger A, Ranieri E, Colucci S, Pertosa GB, Grano M
and Gesualdo L: Inflammation induces osteoclast differentiation
from peripheral mononuclear cells in chronic kidney disease
patients: Crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 33:65–75. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tanaka S, Nakamura I, Inoue J, Oda H and
Nakamura K: Signal transduction pathways regulating osteoclast
differentiation and function. J Bone Miner Metab. 21:123–133. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blair HC, Robinson LJ and Zaidi M:
Osteoclast signalling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
328:728–738. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Del Fattore A, Teti A and Rucci N:
Osteoclast receptors and signaling. Arch Biochem Biophys.
473:147–160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seales EC, Micoli KJ and McDonald JM:
Calmodulin is a critical regulator of osteoclastic differentiation,
function, and survival. J Cell Biochem. 97:45–55. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD and Roderick HL:
Calcium signalling: Dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 4:517–529. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wagner E: Functions of AP1 (Fos/Jun) in
bone development. Ann Rheum Dis. 61:ii40–ii42. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Linseman DA, Bartley CM, Le SS, Laessig
TA, Bouchard RJ, Meintzer MK, Li M and Heidenreich KA: Inactivation
of the myocyte enhancer factor-2 repressor histone deacetylase-5 by
endogenous Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent kinase II promotes
depolarization-mediated cerebellar granule neuron survival. J Biol
Chem. 278:41472–41481. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yao CH, Zhang P and Zhang L: Differential
protein and mRNA expression of CaMKs during osteoclastogenesis and
its functional implications. Biochem Cell Biol. 90:532–539. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sato K, Suematsu A, Nakashima T,
Takemoto-Kimura S, Aoki K, Morishita Y, Asahara H, Ohya K,
Yamaguchi A, Takai T, et al: Regulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the CaMK-CREB pathway. Nat Med.
12:1410–1416. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang EJ, Ha J, Huang H, Kim HJ, Woo JH,
Lee Y, Lee ZH, Kim JH and Kim HH: The JNK-dependent CaMK pathway
restrains the reversion of committed cells during osteoclast
differentiation. J Cell Sci. 121:2555–2564. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bone HG, McClung MR, Roux C, Recker RR,
Eisman JA, Verbruggen N, Hustad CM, DaSilva C, Santora AC and Ince
BA: Odanacatib, a cathepsin-K inhibitor for osteoporosis: A
two-year study in postmenopausal women with low bone density. J
Bone Miner Res. 25:937–947. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Stoch S and Wagner J: Cathepsin K
inhibitors: A novel target for osteoporosis therapy. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 83:172–176. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Missbach M, Jeschke M, Feyen J, Müller K,
Glatt M, Green J and Susa M: A novel inhibitor of the tyrosine
kinase Src suppresses phosphorylation of its major cellular
substrates and reduces bone resorption in vitro and in rodent
models in vivo. Bone. 24:437–449. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fu YX, Gu JH, Wang Y, Yuan Y, Liu XZ, Bian
JC and Liu ZP: Involvement of the Ca2+ signaling pathway
in osteoprotegerin inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and
maturation. J Vet Sci. 16:151–156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Fu YX, Gu JH, Zhang YR, Tong XS, Zhao HY,
Yuan Y, Liu XZ, Bian JC and Liu ZP: Osteoprotegerin influences the
bone resorption activity of osteoclast. Int J Mol Med.
31:1411–1417. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−delta delta C(t)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ono T and Nakashima T: Recent advances in
osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 149:325–341. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pixley FJ and Stanley ER: CSF-1 regulation
of the wandering macrophage: Complexity in action. Trends Cell
Biol. 14:628–638. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ross FP and Teitelbaum SL: avb3 and
macrophage colony-stimulating factor: Partners in osteoclast
biology. Immunol Rev. 208:88–105. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arai F, Miyamoto T, Ohneda O, Inada T,
Sudo T, Brasel K, Miyata T, Anderson DM and Suda T: Commitment and
differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential
expression of c-Fms and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB
(RANK) receptors. J Exp Med. 190:1741–1754. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S,
et al: Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates
osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Negishi-Koga T and Takayanagi H:
Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling is an essential axis of osteoclast
differentiation. Immunol Rev. 231:241–256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lorenzo J, Horowitz M and Choi Y:
Osteoimmunology: Interactions of the bone and immune system. Endocr
Rev. 29:403–440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zeng X, Zhang Y, Wang S, Wang K, Tao L,
Zou M, Chen N, Xu J, Liu S and Li X: Artesunate suppresses
RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through inhibition of
PLCγ1-Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling pathway and prevents
ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Biochem Pharmacol. 124:57–68. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Soysa NS, Alles N, Aoki K and Ohya K:
Osteoclast formation and differentiation: An overview. J Med Dent
Sci. 59:65–74. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saltel F, Chabadel A, Bonnelye E and
Jurdic P: Actin cytoskeletal organisation in osteoclasts: A model
to decipher transmigration and matrix degradation. Eur J Cell Biol.
87:459–468. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dolmetsch RE, Lewis RS, Goodnow CC and
Healy JI: Differential activation of transcription factors induced
by Ca2+ response amplitude and duration. Nature.
386:855–858. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dolmetsch RE, Xu K and Lewis RS: Calcium
oscillations increase the efficiency and specificity of gene
expression. Nature. 392:933–936. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tomida T, Hirose K, Takizawa A, Shibasaki
F and Iino M: NFAT functions as a working memory of Ca2+
signals in decoding Ca2+ oscillation. EMBO J.
22:3825–3832. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Koga T, Matsui Y, Asagiri M, Kodama T, De
Crombrugghe B, Nakashima K and Takayanagi H: NFAT and Osterix
cooperatively regulate bone formation. Nat Med. 11:880–885. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hofbauer LC, Neubauer A and Heufelder AE:
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and
osteoprotegerin: Potential implications for the pathogenesis and
treatment of malignant bone diseases. Cancer. 92:460–470. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Price CP, Kirwan A and Vader C:
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase as a marker of bone resorption.
Clin Chem. 41:641–643. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vaananen HK, Zhao H, Mulari M and Halleen
JM: The cell biology of osteoclast function. J Cell Sci.
113:377–381. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lehenkari P, Hentunen TA, Laitala-Leinonen
T, Tuukkanen J and Väänänen HK: Carbonic anhydrase II plays a major
role in osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by effecting
the steady state intracellular pH and Ca2+. Exp Cell
Res. 242:128–137. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Teitelbaum SL, Tondravi MM and Ross FP:
Osteoclasts, macrophages, and the molecular mechanisms of bone
resorption. J Leuk Biol. 61:381–388. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kusano K, Miyaura C, Inada M, Tamura T,
Ito A, Nagase H, Kamoi K and Suda T: Regulation of matrix
metalloproteinases (MMP-2, -3, -9, and -13) by interleukin-1 and
interleukin-6 in mouse calvaria: Association of MMP induction with
bone resorption. Endocrinology. 139:1338–1345. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wagner EF and Eferl R: Fos/AP-1 proteins
in bone and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 208:126–140. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ikeda F, Nishimura R, Matsubara T, Tanaka
S, Inoue J, Reddy SV, Hata K, Yamashita K, Hiraga T, Watanabe T, et
al: Critical roles of c-Jun signaling in regulation of NFAT family
and RANKL-regulated osteoclast differentiation. J Clin Invest.
114:475–484. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Takayanagi H: The role of NFAT in
osteoclast formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1116:227–237. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|