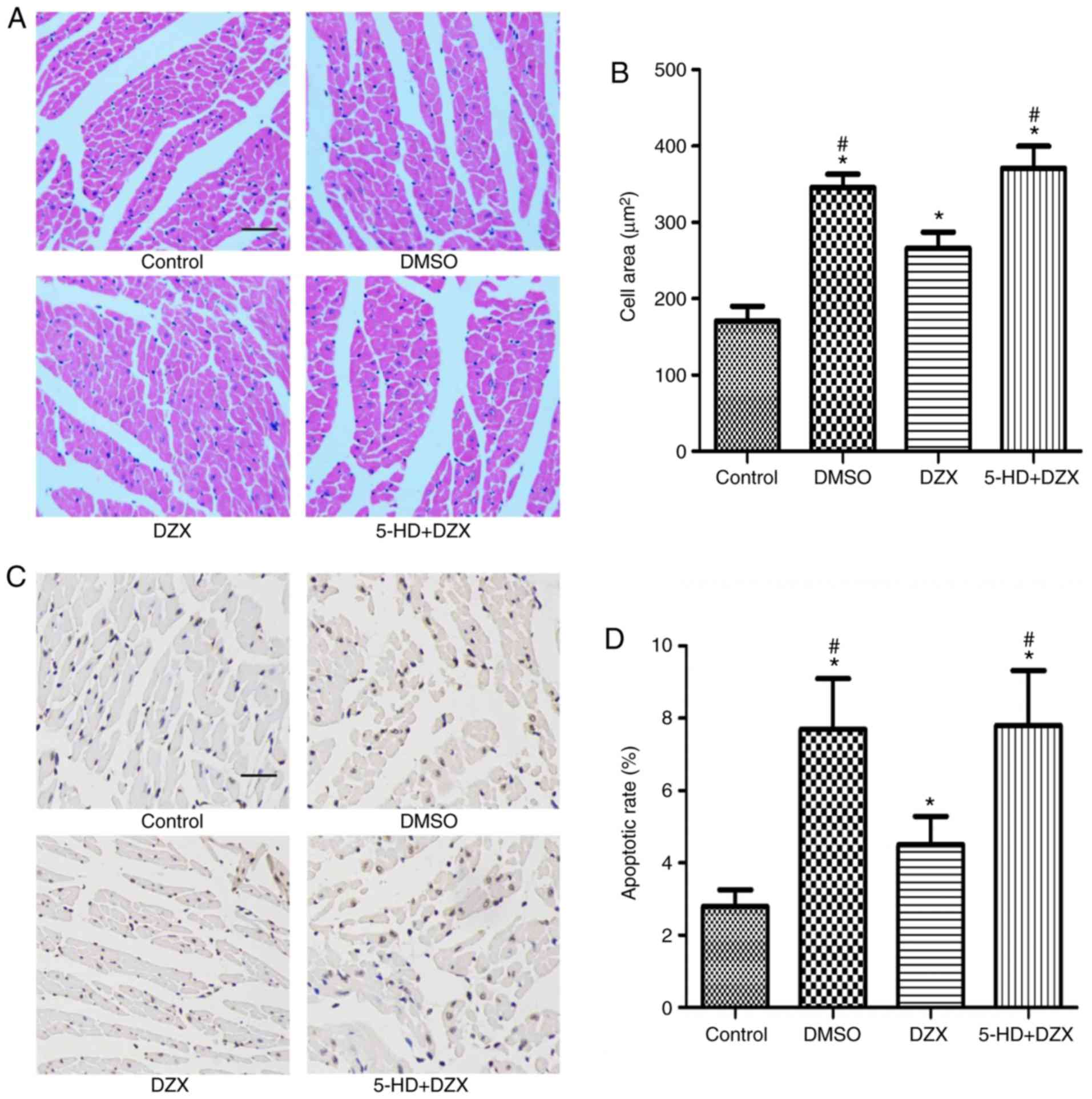
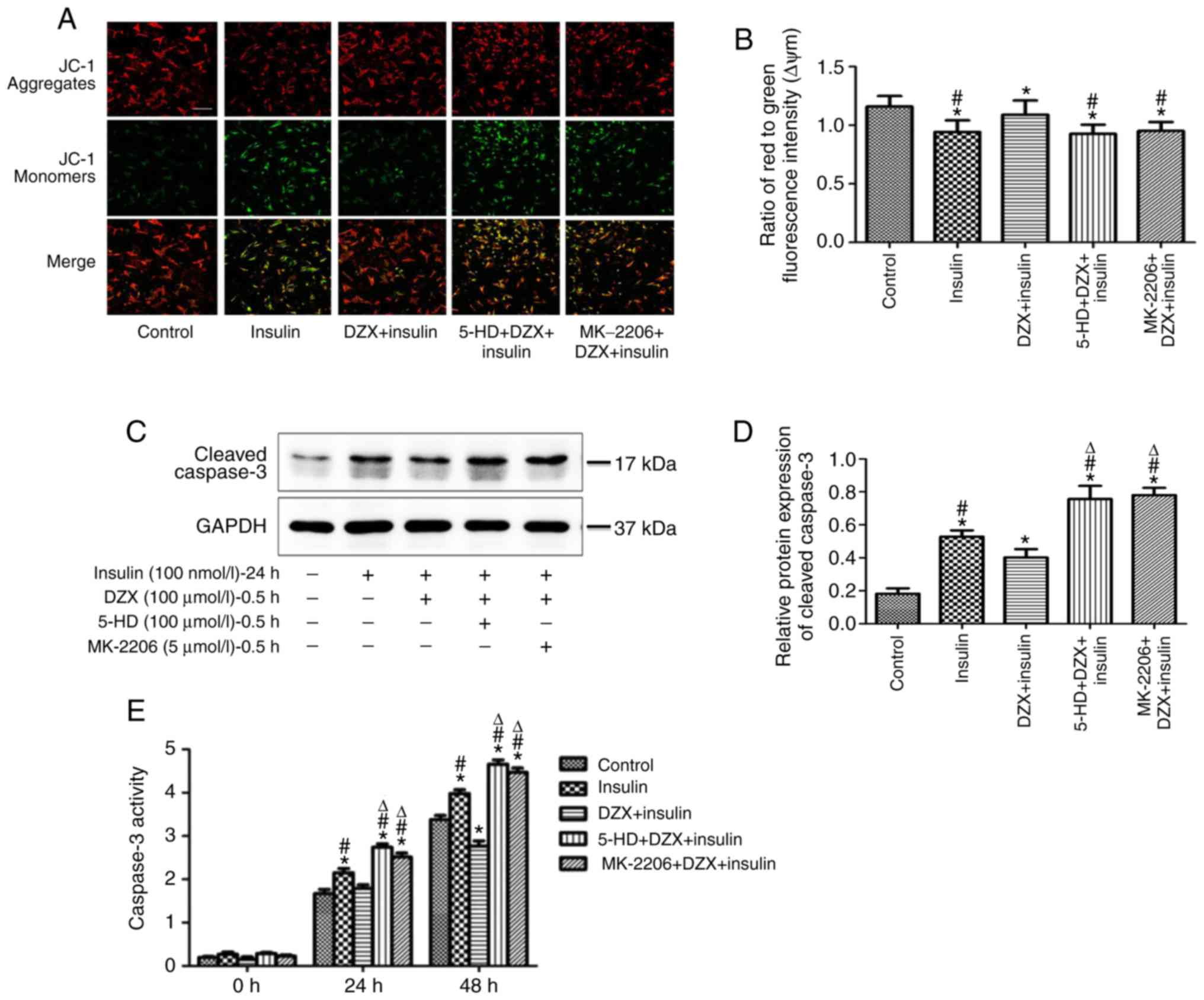
|
1
|
Cefalu WT, Buse JB, Tuomilehto J, Fleming
GA, Ferrannini E, Gerstein HC, Bennett PH, Ramachandran A, Raz I,
Rosenstock J and Kahn SE: Update and next steps for real-world
translation of interventions for type 2 diabetes prevention:
Reflections from a diabetes care editors' expert forum. Diabetes
Care. 39:1186–1201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bertoni AG, Hundley WG, Massing MW, Bonds
DE, Burke GL and Goff DC Jr: Heart failure prevalence, incidence,
and mortality in the elderly with diabetes. Diabetes Care.
27:699–703. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parrinello CM, Matsushita K, Woodward M,
Wagenknecht LE, Coresh J and Selvin E: Risk prediction of major
complications in individuals with diabetes: The atherosclerosis
risk in communities study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 18:899–906. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coll-de-Tuero G, Mata-Cases M,
Rodriguez-Poncelas A, Pepió JM, Roura P, Benito B and Franch-Nadal
J: Prevalence and associated variables in a random sample of 2642
patients of a Mediterranean area. BMC Nephrol. 13:872012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Demmer RT, Allison MA, Cai J, Kaplan RC,
Desai AA, Hurwitz BE, Newman JC, Shah SJ, Swett K, Talavera GA, et
al: Association of impaired glucose regulation and insulin
resistance with cardiac structure and function: Results from
ECHO-SOL (Echocardiographic Study of Latinos). Circ Cardiovasc
Imaging. 9:e0050322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nunes S, Soares E, Fernandes J, Viana S,
Carvalho E, Pereira FC and Reis F: Early cardiac changes in a rat
model of prediabetes: Brain natriuretic peptide overexpression
seems to be the best marker. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 12:442013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bugger H and Abel ED: Molecular mechanisms
of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetologia. 57:660–671. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huynh K, Bernardo BC, McMullen JR and
Ritchie RH: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and new treatment
strategies targeting antioxidant signaling pathways. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:375–415. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ernande L and Derumeaux G: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: Myth or reality. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 105:218–225.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pappachan JM, Varughese GI, Sriraman R and
Arunagirinathan G: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology,
diagnostic evaluation and management. World J Diabetes. 4:177–189.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Karnafel W: Diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Przegl Lek. 57(Suppl 4):
S9–S11. 2000.in Polish.
|
|
12
|
Guzun R, Kaambre T, Bagur R, Grichine A,
Usson Y, Varikmaa M, Anmann T, Tepp K, Timohhina N, Shevchuk I, et
al: Modular organization of cardiac energy metabolism: Energy
conversion, transfer and feedback regulation. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
213:84–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cuong DV, Kim N, Joo H, Youm JB, Chung JY,
Lee Y, Park WS, Kim E, Park YS and Han J: Subunit composition of
ATP-sensitive potassium channels in mitochondria of rat hearts.
Mitochondrion. 5:121–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Slocinska M, Lubawy J, Jarmuszkiewicz W
and Rosinski G: Evidences for an ATP-sensitive potassium channel
(KATP) in muscle and fat body mitochondria of insect. J Insect
Physiol. 59:1125–1132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Akao M, Ohler A, O'Rourke B and Marbán E:
Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels inhibit apoptosis
induced by oxidative stress in cardiac cells. Circ Res.
88:1267–1275. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Szydłowski M, Jabłońska E and Juszczyński
P: FOXO1 transcription factor: A critical effector of the PI3K-AKT
axis in B-cell development. Int Rev Immunol. 33:146–157. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tzivion G, Dobson M and Ramakrishnan G:
FoxO transcription factors; Regulation by AKT and 143-3 proteins.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1938–1945. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xin Z, Ma Z, Jiang S, Wang D, Fan C, Di S,
Hu W, Li T, She J and Yang Y: FOXOs in the impaired heart: New
therapeutic targets for cardiac diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:486–498. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Qi Y, Xu Z, Zhu Q, Thomas C, Kumar R, Feng
H, Dostal DE, White MF, Baker KM and Guo S: Myocardial loss of IRS1
and IRS2 causes heart failure and is controlled by p38alpha MAPK
during insulin resistance. Diabetes. 62:3887–3900. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kandula V, Kosuru R, Li H, Yan D, Zhu Q,
Lian Q, Ge RS, Xia Z and Irwin MG: Forkhead box transcription
factor 1: Role in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 15:442016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Palomer X, Salvadó L, Barroso E and
Vázquez-Carrera M: An overview of the crosstalk between
inflammatory processes and metabolic dysregulation during diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 168:3160–3172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xue Y, Xie N, Cao L, Zhao X, Jiang H and
Chi Z: Diazoxide preconditioning against seizure-induced oxidative
injury is via the PI3K/Akt pathway in epileptic rat. Neurosci Lett.
495:130–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grossini E, Molinari C, Caimmi PP, Uberti
F and Vacca G: Levosimendan induces NO production through p38 MAPK,
ERK and Akt in porcine coronary endothelial cells: Role for
mitochondrial K(ATP) channel. Br J Pharmacol. 156:250–261. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu J, Tian W, Ma X, Guo J, Shi Q, Jin Y,
Xi J and Xu Z: The molecular mechanism underlying morphine-induced
Akt activation: Roles of protein phosphatases and reactive oxygen
species. Cell Biochem Biophys. 61:303–311. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lemos Caldas FR, Rocha Leite IM, Tavarez
Filgueiras AB, de Figueiredo Júnior IL, Gomes Marques, de Sousa TA,
Martins PR, Kowaltowski AJ and Fernandes Facundo H: Mitochondrial
ATP-sensitive potassium channel opening inhibits
isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy by preventing oxidative
damage. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 65:393–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Diehl KH, Hull R, Morton D, Pfister R,
Rabemampianina Y, Smith D, Vidal JM and van de Vorstenbosch C;
European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries Association and
European Centre for the Validation of Alternative Methods: A good
practice guide to the administration of substances and removal of
blood, including routes and volumes. J Appl Toxicol. 21:15–23.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Spiers DE and Candas V: Relationship of
skin surface area to body mass in the immature rat: A
reexamination. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol.
56:240–243. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vidyasekar P, Shyamsunder P, Santhakumar
R, Arun R and Verma RS: A simplified protocol for the isolation and
culture of cardiomyocytes and progenitor cells from neonatal mouse
ventricles. Eur J Cell Biol. 94:444–452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ehler E, Moore-Morris T and Lange S:
Isolation and culture of neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. J Vis Exp.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xia Y, Javadov S, Gan TX, Pang T, Cook MA
and Karmazyn M: Distinct KATP channels mediate the antihypertrophic
effects of adenosine receptor activation in neonatal rat
ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320:14–21. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yang C, Zhang W, Liu X, Liang Y, Li P,
Zhang Y and Yuan Y: The influence of the single different radiation
dose and time on the microscopic structure and ultrastructure of
Balb/c mice]. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.
28:979–982. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
32
|
Zhu LA, Fang NY, Gao PJ, Jin X and Wang
HY: Differential expression of alpha-enolase in the normal and
pathological cardiac growth. Exp Mol Pathol. 87:27–31. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jian J, Xuan F, Qin F and Huang R: The
antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activities of the
Bauhinia Championii flavone are connected with protection against
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:1365–1375. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wei K, Liu L, Xie F, Hao X, Luo J and Min
S: Nerve growth factor protects the ischemic heart via attenuation
of the endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis by activation
of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Int J Med Sci. 12:83–91. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu Y, Zhu W, Wang Z, Yuan W, Sun Y, Liu H
and Du Z: Combinatorial microRNAs suppress hypoxia-induced
cardio-myocytes apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:921–932. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Liu X, Duan P, Hu X, Li R and Zhu Q:
Altered KATP channel subunits expression and vascular reactivity in
spontaneously hypertensive rats with age. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
68:143–149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang X, Jameel MN, Li Q, Mansoor A, Qiang
X, Swingen C, Panetta C and Zhang J: Stem cells for myocardial
repair with use of a transarterial catheter. Circulation. 120(Suppl
11): S238–S246. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ward ML and Crossman DJ: Mechanisms
underlying the impaired contractility of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
World J Cardiol. 6:577–584. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fuentes-Antrás J, Picatoste B,
Gómez-Hernández A, Egido J, Tuñón J and Lorenzo Ó: Updating
experimental models of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Diabetes Res.
2015:6567952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kadenbach B: Intrinsic and extrinsic
uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1604:77–94. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brand MD and Nicholls DG: Assessing
mitochondrial dysfunction in cells. Biochem J. 435:297–312. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gomez-Cabrera MC, Sanchis-Gomar F,
Garcia-Valles R, Pareja-Galeano H, Gambini J, Borras C and Viña J:
Mitochondria as sources and targets of damage in cellular aging.
Clin Chem Lab Med. 50:1287–1295. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kevelaitis E, Oubenaissa A, Mouas C,
Peynet J and Menasche P: Opening of mitochondrial potassium
channels: A new target for graft preservation strategies.
Transplantation. 70:576–578. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ali M, Mehmood A, Anjum MS, Tarrar MN,
Khan SN and Riazuddin S: Diazoxide preconditioning of endothelial
progenitor cells from streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic rats
improves their ability to repair diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell
Biochem. 410:267–279. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Monsalve M and Olmos Y: The complex
biology of FOXO. Curr Drug Targets. 12:1322–1350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Hou J and Shang YC:
The 'O' class: Crafting clinical care with FoxO transcription
factors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 665:242–260. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kim MY, Kim MJ, Yoon IS, Ahn JH, Lee SH,
Baik EJ, Moon CH and Jung YS: Diazoxide acts more as a PKC-epsilon
activator, and indirectly activates the mitochondrial K(ATP)
channel conferring cardioprotection against hypoxic injury. Br J
Pharmacol. 149:1059–1070. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Katoh H, Nishigaki N and Hayashi H:
Diazoxide opens the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and
alters Ca2+ transients in rat ventricular myocytes. Circulation.
105:2666–2671. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|