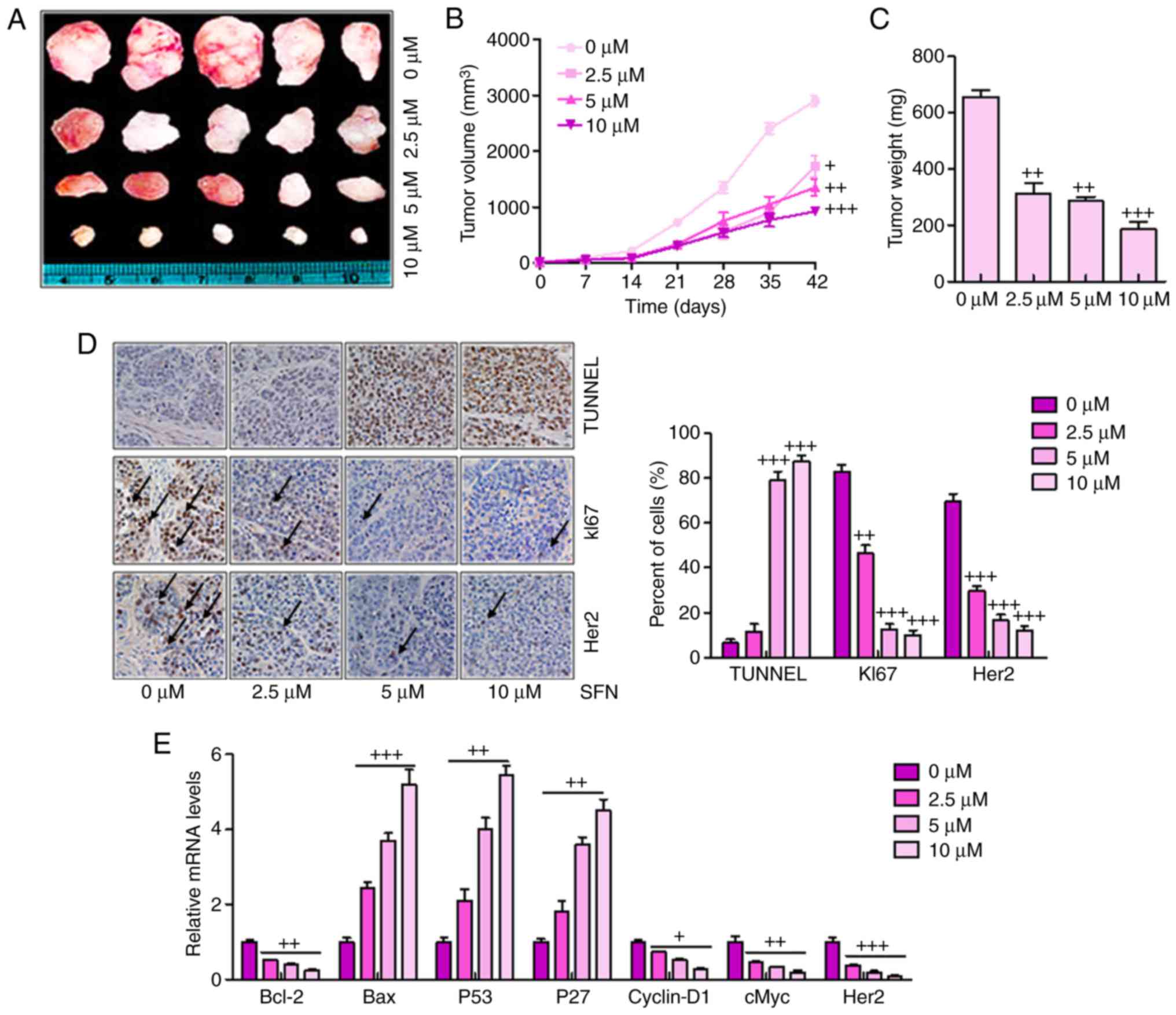
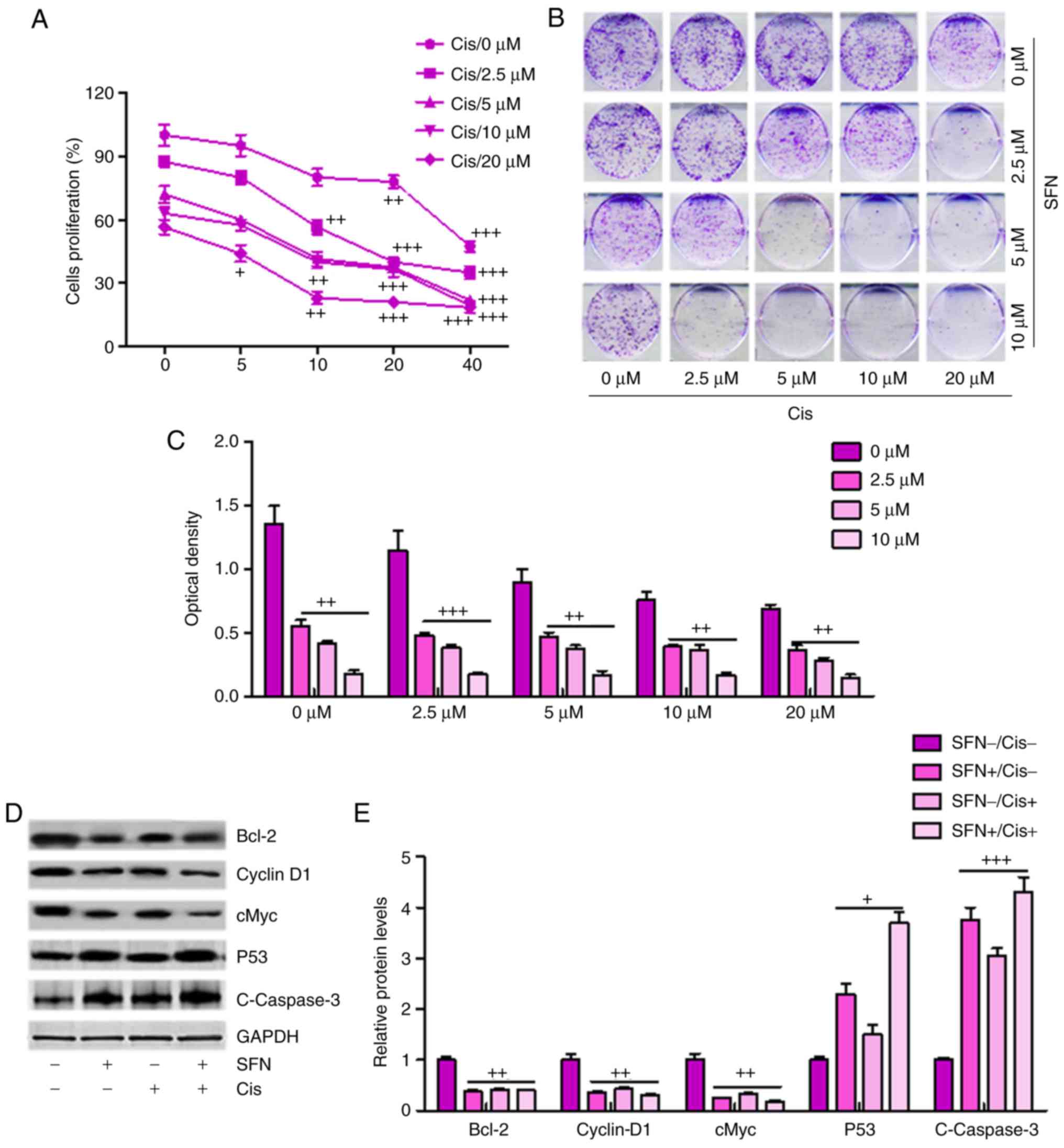
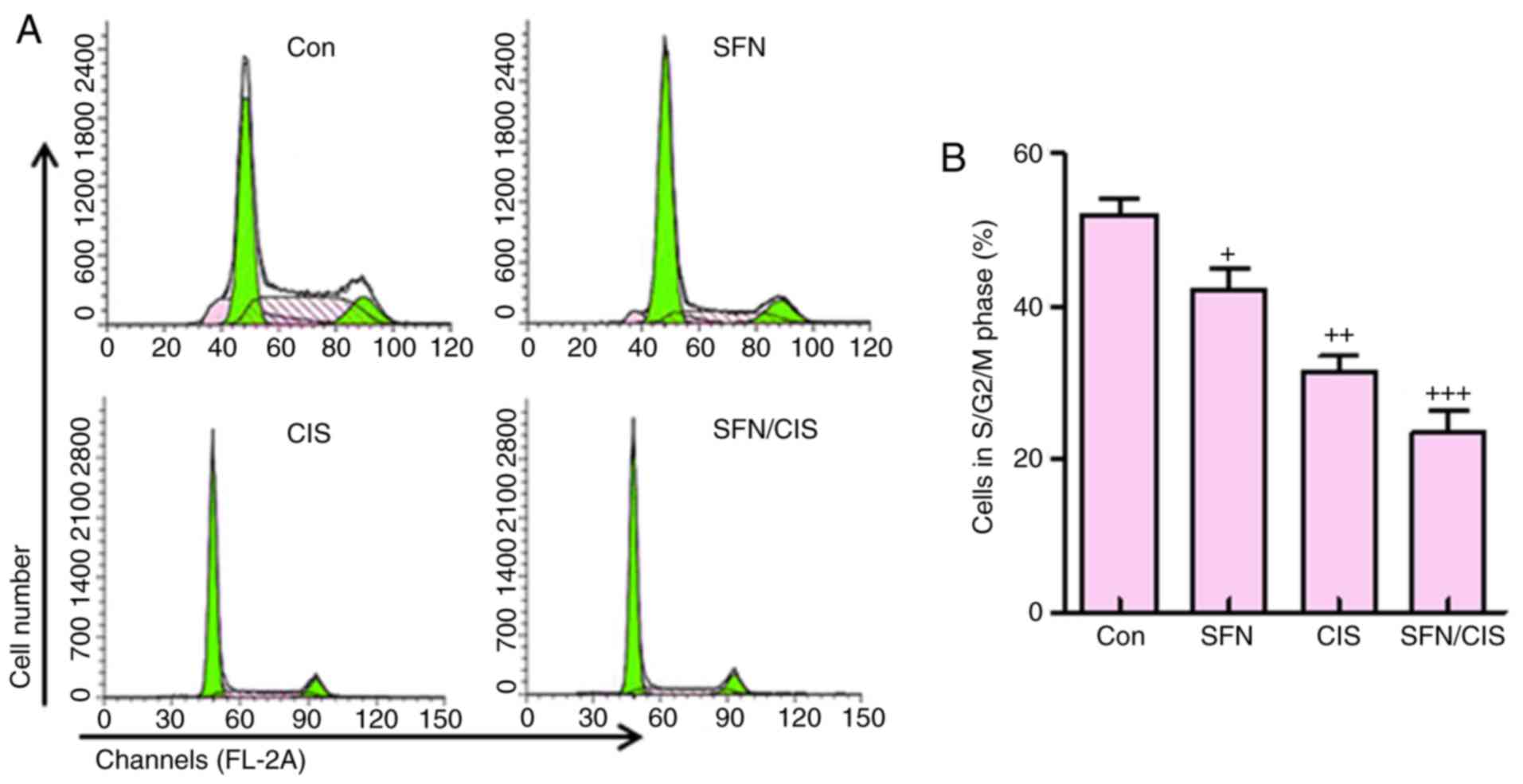
|
1
|
Kamieniak MM, Muñoz-Repeto I, Rico D,
Osorio A, Urioste M, García-Donas J, Hernando S, Robles-Díaz L and
Ramón Y: DNA copy number profiling reveals extensive genomic loss
in hereditary BRCA1 and BRCA2 ovarian carcinomas. Br J Cancer.
108:1732–1742. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pruthi S, Gostout BS and Lindor NM:
Identification and management of women with BRCA mutations or
hereditary predisposition for breast and ovarian cancer. Mayo Clin
Proc. 85:1111–1120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chester C, Dorigo O, Berek JS and Kohrt H:
Immunotherapeutic approaches to ovarian cancer treatment. J
Immunother Cancer. 3:72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gnjatic S, Ritter E, Büchler MW, Giese NA,
Brors B, Frei C, Murray A, Halama N, Zörnig I, Chen YT, et al:
Seromic profiling of ovarian and pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:5088–5093. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vaughan S, Coward JI, Bast RC Jr, Berchuck
A, Berek JS, Brenton JD, Coukos G, Crum CC, Drapkin R,
Etemadmoghadam D, et al: Rethinking ovarian cancer: Recommendations
for improving outcomes. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:719–725. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Frampton JE: Olaparib: A review of its use
as maintenance therapy in patients with ovarian cancer. BioDrugs.
29:143–150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okeke TC, Anyaehie UB and Ezenyeaku CC:
Premature menopause. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 3:90–95. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suppipat K, Park CS, Shen Y, Zhu X and
Lacorazza HD: Sulforaphane induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. PLoS One. 7:e512512012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Clarke JD, Dashwood RH and Ho E:
Multi-targeted prevention of cancer by sulforaphane. Cancer Lett.
269:291–304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Myzak MC, Hardin K, Wang R, Dashwood RH
and Ho E: Sulforaphane inhibits histone deacetylase activity in
BPH-1, LnCaP and PC-3 prostate epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis.
27:811–819. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ho E, Clarke JD and Dashwood RH: Dietary
sulforaphane a histone deacetylase inhibitor for cancer prevention.
J Nutr. 139:2393–2396. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su ZY, Zhang C, Lee JH, Shu L, Wu TY, Khor
TO, Conney AH, Lu YP and Kong AN: Requirement and epigenetics
reprogramming of Nrf2 in suppression of tumor promoter TPA-induced
mouse skin cell transformation by sulforaphane. Cancer Prev Res.
7:319–329. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Atwell LL, Hsu A, Wong CP, Stevens JF,
Bella D, Yu TW, Pereira CB, Löhr CV, Christensen JM, Dashwood RH,
et al: Absorption and chemopreventive targets of sulforaphane in
humans following consumption of broccoli sprouts or a
myrosinase-treated broccoli sprout extract. Mol Nutr Food Res.
59:424–433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Ho E, Beaver LM, Williams DE and Dashwood
RH: Dietary factors and epigenetic regulation for prostate cancer
prevention. Adv Nutr. 2:497–510. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Hsu A, Wong CP, Yu Z, Williams DE,
Dashwood RH and Ho E: Promoter de-methylation of cyclin D2 by
sulforaphane in prostate cancer cells. Clin Epigenet. 3:32011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li C, Zhou Y, Peng X, Du L, Tian H, Yang
G, Niu J and Wu W: Sulforaphane inhibits invasion via activating
ERK1/2 signaling in human glioblastoma U87MG and U373MG cells. PLoS
One. 9:e905202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fimognari C, Turrini E, Sestili P,
Calcabrini C, Carulli G, Fontanelli G, Rousseau M, Cantelli-Forti G
and Hrelia P: Antileukemic activity of sulforaphane in primary
blasts from patients affected by myelo- and lympho-proliferative
disorders and in hypoxic conditions. PLoS One. 9:e1019912014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sharma C, Sadrieh L, Priyani A, Ahmed M,
Hassan AH and Hussain A: Anti-carcinogenic effects of sulforaphane
in association with its apoptosis-inducing and anti-inflammatory
properties in human cervical cancer cells. Cancer Epidemiol.
35:272–278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ferreira de Oliveira JM, Remédios C,
Oliveira H, Pinto P, Pinho F, Pinho S, Costa M and Santos C:
Sulforaphane induces DNA damage and mitotic abnormalities in human
osteosarcoma MG-63 cells: Correlation with cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis. Nutr Cancer. 66:325–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tuefferd M, Couturier J, Penault-Llorca F,
Vincent-Salomon A, Broët P, Guastalla JP, Allouache D, Combe M,
Weber B, Pujade-Lauraine E, et al: HER2 status in ovarian
carcinomas: A multicenter GINECO study of 320 patients. PLoS One.
2:e11382007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang HS, Huh YM, Kim S and Lee DK:
Isolation of RNA aptamers targeting HER2-overexpressing breast
cancer cells using cell-SELEX. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 30:1827–1831.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen H, Landen CN, Li Y, Alvarez RD and
Tollefsbol TO: Epigallocatechin gallate and sulforaphane
combination treatment induce apoptosis in paclitaxel-resistant
ovarian cancer cells through hTERT and Bcl-2 down-regulation. Exp
Cell Res. 319:697–706. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu C, Shen G, Chen C, Gélinas C and Kong
AN: Suppression of NF-κB and NF-κB-regulated gene expression by
sulforaphane and PEITC through IjBa, IKK pathway in human prostate
cancer PC-3 cells. Oncogene. 24:4486–4495. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee WK and Kim SJ: Sulforaphane regulates
differentiation via PI-3K/AKT pathway in human chondrosarcoma cell
line, HTB-94 cells. Cancer Prev Res. 18:26–32. 2013.
|
|
26
|
Lubecka-Pietruszewska K, Kaufman-Szymczyk
A, Stefanska B, Cebula-Obrzut B, Smolewski P and
Fabianowska-Majewska K: Clofarabine, a novel adenosine analogue,
reactivates DNA methylation-silenced tumour suppressor genes and
inhibits cell growth in breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
723:276–287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Suh DH, Lee KH, Kim K, Kang S and Kim JW:
Major clinical research advances in gynecologic cancer in 2014. J
Gynecol Oncol. 26:156–167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mahajan N: Fertility preservation in
female cancer patients: An overview. J Hum Reprod Sci. 8:3–13.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kamieniak MM, Muñoz-Repeto I, Rico D,
Osorio A, Urioste M, García-Donas J, Hernando S, Robles-Díaz L,
Ramón Y, Cajal T, Cazorla A, et al: DNA copy number profiling
reveals extensive genomic loss in hereditary BRCA1 and BRCA2
ovarian carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 108:1732–1742. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Moyer V; The U.S. Preventive Services Task
Force: Risk assessment, genetic counseling, and genetic testing for
BRCA-related cancer in women: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force
recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 160:271–281. 2014.
|
|
31
|
Jablonska K, Pula B, Zemla A, Kobierzycki
C, Kedzia W, Nowak-Markwitz E, Spaczynski M, Zabel M,
Podhorska-Okolow M and Dziegiel P: Expression of the MT1 melatonin
receptor in ovarian cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 15:23074–23089.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dexheimer TS, Daekyu S and Hurley LH:
Deconvoluting the structural and drug-recognition complexity of the
G-quadruplex-forming region upstream of the bcl-2 P1 promoter. J Am
Chem Soc. 128:5404–5415. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen T and Wong Y: Selenocystine induces
reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 63:105–113. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kallifatidis G, Rausch V, Baumann B, Apel
A, Beckermann BM, Groth A, Mattern J, Li Z, Kolb A, Moldenhauer G,
et al: Sulforaphane targets pancreatic tumour-initiating cells by
NF-κB-induced antiapoptotic signaling. Gut. 58:949–963. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ju W, Wang X, Shi H, Chen W, Belinsky SA
and Lin Y: A critical role of luteolin-induced reactive oxygen
species in blockage of tumor necrosis factor-activated nuclear
factor κB pathway and sensitization of apoptosis in lung cancer
cells. Mol Pharmacol. 71:1381–1388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bardeesy N, Aguirre AJ, Chu GC, Cheng KH,
Lopez LV, Hezel AF, Feng B, Brennan C, Weissleder R, Mahmood U, et
al: Both p16Ink4a and the p19Arf-p53 pathway
constrain progression of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in the mouse.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:5947–5952. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Psyrri A, Bamias A, Yu Z, Weinberger PM,
Kassar M, Markakis S, Kowalski D, Efstathiou E, Camp RL, Rimm DL,
et al: Subcellular localization and protein levels of
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 independently predict for
survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
11:8384–8390. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou X, Zhang Z, Yang X, Chen W and Zhang
P: Inhibition of cyclin D1 expression by cyclin D1 shRNAs in human
oral squamous cell carcinoma cells is associated with increased
cisplatin chemosensitivity. Int J Cancer. 124:483–489. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Biliran H Jr, Wang Y, Banerjee S, Xu H,
Heng H, Thakur A, Bollig A, Sarkar FH and Liao JD: Overexpression
of cyclin D1 promotes tumor cell growth and confers resistance to
cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in an elastase-myc
transgene-expressing pancreatic tumor cell line. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6075–6086. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luo H, Rankin GO, Juliano N, Jiang BH and
Chen YC: Kaempferol inhibits VEGF expression and in vitro
angiogenesis through a novel ERK-NFκB-cMyc-p21 pathway. Food Chem.
130:321–328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen T and Wong YS: Selenocystine induces
S-phase arrest and apoptosis in human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7
cells by modulating ERK and Akt phosphorylation. J Agric Food Chem.
56:10574–10581. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|