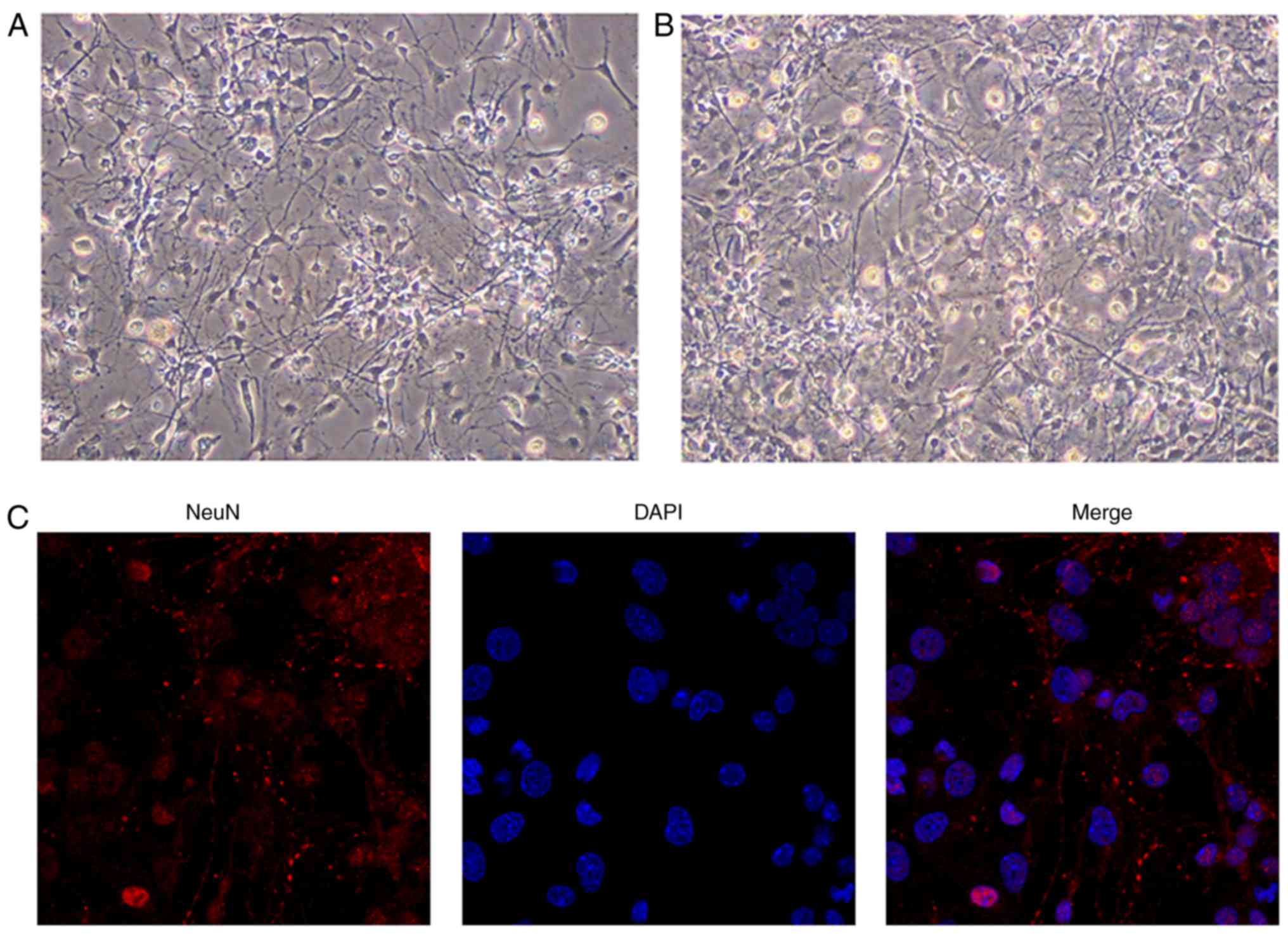
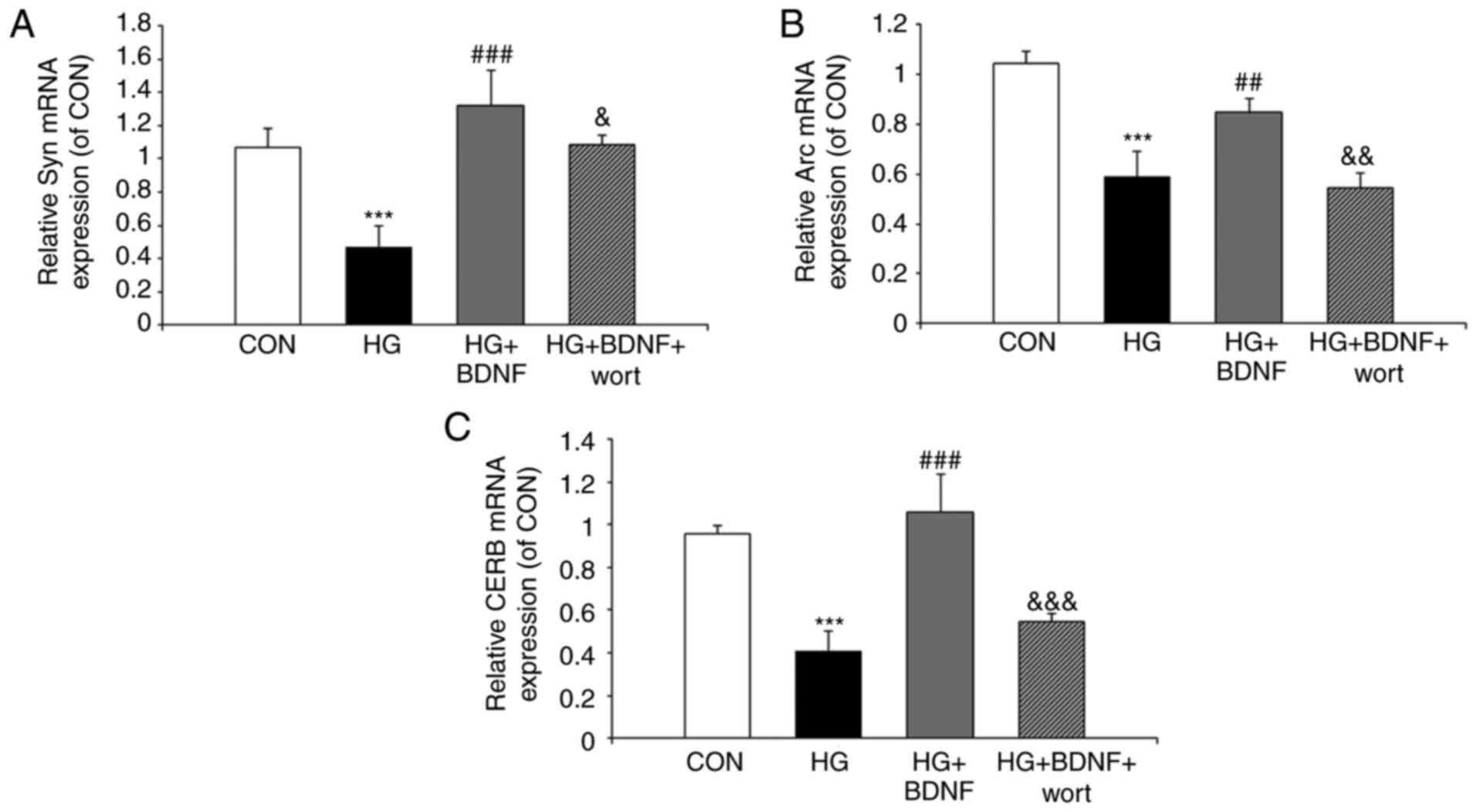
|
1
|
Alam U, Asghar O, Azmi S and Malik RA:
General aspects of diabetes mellitus. Handb Clin Neurol.
126:211–222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shekhar S, Wang S, Mims PN,
Gonzalez-Fernandez E, Zhang C, He X, Liu CY, Lv W, Wang Y, Huang J
and Fan F: Impaired cerebral Autoregulation-A common neurovascular
pathway in diabetes may play a critical role in diabetes-related
Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Res Diabetes Obes J. 2:pii:
5555872017.
|
|
3
|
Ninomiya T: Diabetes mellitus and
dementia. Curr Diab Rep. 14:4872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bitel CL, Kasinathan C, Kaswala RH, Klein
WL and Frederikse PH: Amyloid-β and tau pathology of Alzheimer’s
disease induced by diabetes in a rabbit animal model. J Alzheimers
Dis. 32:291–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sima AA: Encephalopathies: The emerging
diabetic complications. Acta Diabetol. 47:279–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen S, Liu AR, An FM, Yao WB and Gao XD:
Amelioration of neurodegenerative changes in cellular and rat
models of diabetes-related Alzheimer’s disease by exendin-4. Age
(Dordr). 34:1211–1224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu D, Zhang H, Gu W and Zhang M: Effects
of exposure to high glucose on primary cultured hippocampal
neurons: Involvement of intracellular ROS accumulation. Neurol Sci.
35:831–837. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Allen SJ, Watson JJ, Shoemark DK, Barua NU
and Patel NK: GDNF, NGF and BDNF as therapeutic options for
neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Ther. 138:155–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noble EE, Billington CJ, Kotz CM and Wang
C: The lighter side of BDNF. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 300:R1053–R1069. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jo YH and Chua SC Jr: The brain-liver
connection between BDNF and glucose control. Diabetes.
62:1367–1368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakagawa T, Tsuchida A, Itakura Y,
Nonomura T, Ono M, Hirota F, Inoue T, Nakayama C, Taiji M and
Noguchi H: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates glucose
metabolism by modulating energy balance in diabetic mice. Diabetes.
49:436–444. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nonomura T, Tsuchida A, Ono-Kishino M,
Nakagawa T, Taiji M and Noguchi H: Brain-derived neurotrophic
factor regulates energy expenditure through the central nervous
system in obese diabetic mice. Int J Exp Diabetes Res. 2:201–209.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Meek TH, Wisse BE, Thaler JP, Guyenet SJ,
Matsen ME, Fischer JD, Taborsky GJ Jr, Schwartz MW and Morton GJ:
BDNF action in the brain attenuates diabetic hyperglycemia via
insulin-independent inhibition of hepatic glucose production.
Diabetes. 62:1512–1518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sheng M, Sabatini BL and Südhof TC:
Synapses and Alzheimer’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
4:pii: a0057772012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gaspar JM, Castilho A, Baptista FI,
Liberal J and Ambrosio AF: Long-term exposure to high glucose
induces changes in the content and distribution of some exocytotic
proteins in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience.
171:981–992. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Masliah E, Terry RD, Alford M and DeTeresa
R: Quantitative immunohistochemistry of synaptophysin in human
neocortex: An alternative method to estimate density of presynaptic
terminals in paraffin sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 38:837–844.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tarsa L and Goda Y: Synaptophysin
regulates activity-dependent synapse formation in cultured
hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:1012–1016. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao Y, Li Q, Jin A, Cui M and Liu X: E3
ubiquitin ligase Siah-1 downregulates synaptophysin expression
under high glucose and hypoxia. Am J Transl Res. 7:15–27.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Q, Zhu XL, Jin AP, Liu XY and Zhao YX:
Inhibition of synaptophysin ubiquitination may improve the
intelligent drop due to high glucose and hypoxia. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 7:5021–5030. 2014.
|
|
20
|
Lonze BE and Ginty DD: Function and
regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous
system. Neuron. 35:605–623. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Middei S, Houeland G, Cavallucci V,
Ammassari-Teule M, D’Amelio M and Marie H: CREB is necessary for
synaptic maintenance and learning-induced changes of the AMPA
receptor GluA1 subunit. Hippocampus. 23:488–499. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pugazhenthi S, Wang M, Pham S, Sze CI and
Eckman CB: Downregulation of CREB expression in Alzheimer’s brain
and in Aβ-treated rat hippocampal neurons. Mol Neurodegener.
6:602011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang N, Wen Q, Ren L, Liang W, Xia Y,
Zhang X, Zhao D, Sun D, Hu Y, Hao H, et al: Neuroprotective effect
of arctigenin via upregulation of P-CREB in mouse primary neurons
and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Int J Mol Sci.
14:18657–18669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lacor PN, Buniel MC, Chang L, Fernandez
SJ, Gong Y, Viola KL, Lambert MP, Velasco PT, Bigio EH, Finch CE,
et al: Synaptic targeting by Alzheimer’s-related amyloid beta
oligomers. J Neurosci. 24:10191–10200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wegenast-Braun BM, Fulgencio Maisch A,
Eicke D, Radde R, Herzig MC, Staufenbiel M, Jucker M and Calhoun
ME: Independent effects of intra- and extracellular Abeta on
learning-related gene expression. Am J Pathol. 175:271–282. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dickey CA, Gordon MN, Mason JE, Wilson NJ,
Diamond DM, Guzowski JF and Morgan D: Amyloid suppresses induction
of genes critical for memory consolidation in APP + PS1 transgenic
mice. J Neurochem. 88:434–442. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ennis K, Dotterman H, Stein A and Rao R:
Hyperglycemia accentuates and ketonemia attenuates
hypoglycemia-induced neuronal injury in the developing rat brain.
Pediatr Res. 77:84–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liao GY, Li Y and Xu B: Ablation of TrkB
expression in RGS92 cells leads to hyperphagic obesity. Mol Metab.
2:491–497. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Tao L, Fu X, Zhao Y and Xu X: BDNF
protects retinal neurons from hyperglycemia through the
TrkB/ERK/MAPK pathway. Mol Med Rep. 7:1773–1778. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiang Q, Zhang J, Li CY, Wang Y, Zeng MJ,
Cai ZX, Tian RB, Jia W and Li XH: Insulin resistance-induced
hyperglycemia decreased the activation of Akt/CREB in hippocampus
neurons: Molecular evidence for mechanism of diabetes-induced
cognitive dysfunction. Neuropeptides. 54:9–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen TJ, Wang DC and Chen SS: Amyloid-beta
interrupts the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway that could be
involved in brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced Arc
expression in rat cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res. 87:2297–2307.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kaech S and Banker G: Culturing
hippocampal neurons. Nat Protoc. 1:2406–2415. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chen Y, Cao CP, Li CR, Wang W, Zhang D,
Han LL, Zhang XQ, Kim A, Kim S and Liu GL: Ghrelin modulates
insulin sensitivity and tau phosphorylation in high glucose-induced
hippocampal neurons. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1165–1169. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fath T, Ke YD, Gunning P, Götz J and
Ittner LM: Primary support cultures of hippocampal and substantia
nigra neurons. Nat Protoc. 4:78–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen YJ, Huang XB, Li ZX, Yin LL, Chen WQ
and Li L: Tenuigenin protects cultured hippocampal neurons against
methylglyoxal-induced neurotoxicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 645:1–8.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shao JL, Wan XH, Chen Y, Bi C, Chen HM,
Zhong Y, Heng XH and Qian JQ: H2S protects hippocampal neurons from
anoxia-reoxygenation through cAMP-mediated PI3K/Akt/p70S6K
cell-survival signaling pathways. J Mol Neurosci. 43:453–460. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chen WS, Yueh CY, Huang YA and Hwang E: An
inverted method for culturing dissociated mouse hippocampal
neurons. Neurosci Res. 70:118–123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Boldrini M, Santiago AN, Hen R, Dwork AJ,
Rosoklija GB, Tamir H, Arango V and John Mann J: Hippocampal
granule neuron number and dentate gyrus volume in
antidepressant-treated and untreated major depression.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 38:1068–1077. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luo XL, Mao M, Zhou H, Sun XM and Li SF:
Neuroprotective effect of BDNF on hypoxia for embryonic rat
cortical neurons in vitro. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
37:373–377. 2006.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rankin SL, Guy CS, Rahimtula M and Mearow
KM: Neurotrophin-induced upregulation of p75NTR via a protein
kinase C-delta-dependent mechanism. Brain Res. 1217:10–24. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Smith ED, Prieto GA, Tong L,
Sears-Kraxberger I, Rice JD, Steward O and Cotman CW: Rapamycin and
interleukin-1β impair brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent
neuron survival by modulating autophagy. J Biol Chem.
289:20615–20629. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bathina S, Srinivas N and Das UN:
Streptozotocin produces oxidative stress, inflammation and
decreases BDNF concentrations to induce apoptosis of RIN5F cells
and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Wistar rats. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 486:406–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Leal G, Afonso PM, Salazar IL and Duarte
CB: Regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity by BDNF. Brain
Res. 1621:82–101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Stranahan AM, Norman ED, Lee K, Cutler RG,
Telljohann RS, Egan JM and Mattson MP: Diet-induced insulin
resistance impairs hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cognition in
middle-aged rats. Hippocampus. 18:1085–1088. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cohan CH, Stradecki-Cohan HM,
Morris-Blanco KC, Khoury N, Koronowski KB, Youbi M, Wright CB and
Perez-Pinzon MA: Protein kinase C epsilon delays latency until
anoxic depolarization through arc expression and GluR2
internalization. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 37:3774–3788. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bathina S and Das UN: Brain-derived
neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch Med Sci.
11:1164–1178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Garelick MG and Kennedy BK: TOR on the
brain. Exp Gerontol. 46:155–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kennedy MB, Beale HC, Carlisle HJ and
Washburn LR: Integration of biochemical signalling in spines. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 6:423–434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yin Z, Yu H, Chen S, Ma C, Ma X, Xu L, Ma
Z, Qu R and Ma S: Asiaticoside attenuates diabetes-induced
cognition deficits by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway. Behav
Brain Res. 292:288–299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Deogracias R, Espliguero G, Iglesias T and
Rodriguez-Peña A: Expression of the neurotrophin receptor trkB is
regulated by the cAMP/CREB pathway in neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci.
26:470–480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nikolaienko O, Eriksen MS, Patil S, Bito H
and Bramham CR: Stimulus-evoked ERK-dependent phosphorylation of
activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (Arc) regulates
its neuronal subcellular localization. Neuroscience. 360:68–80.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|