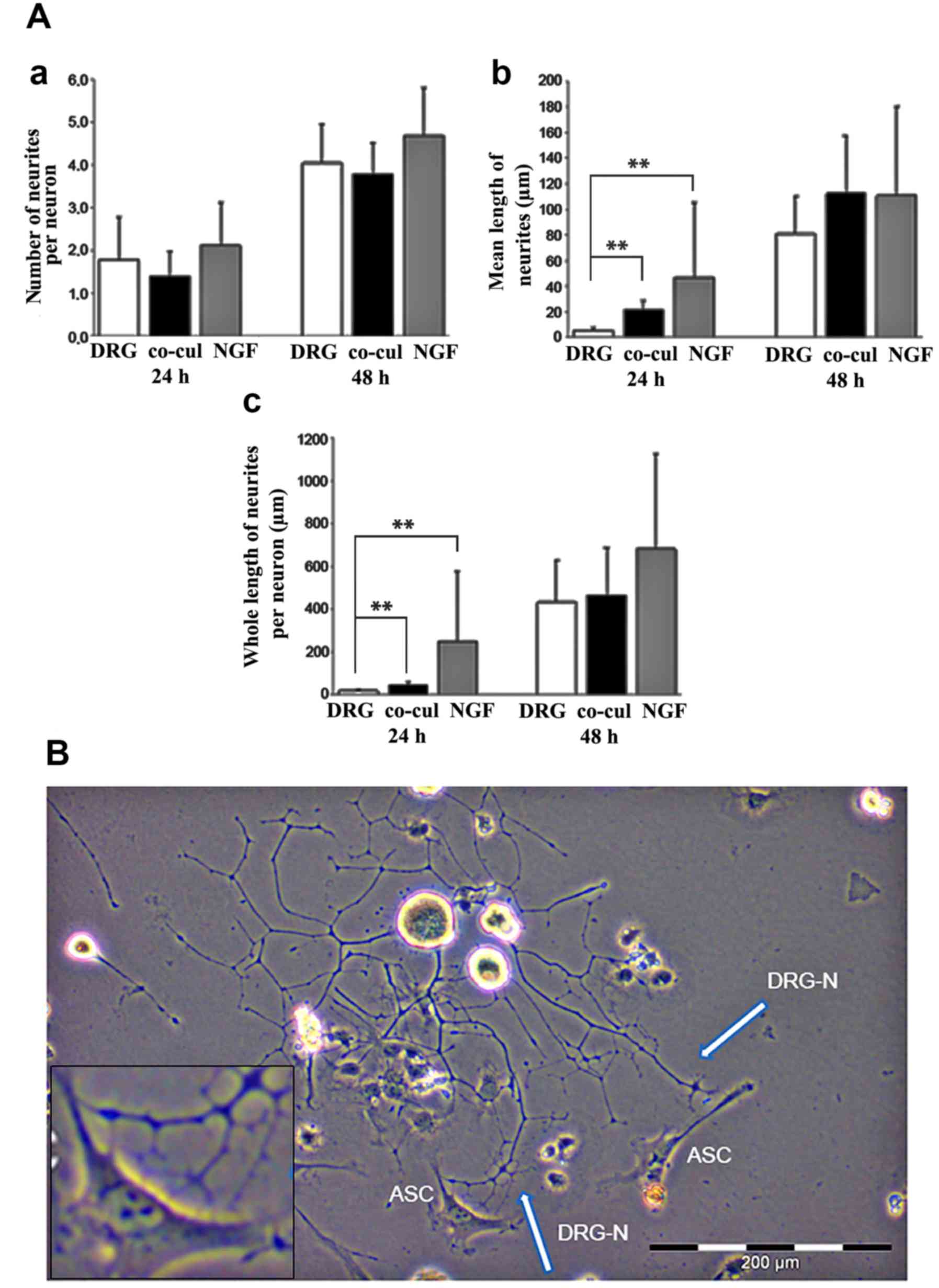
|
1
|
Madduri S and Gander B: Schwann cell
delivery of neurotrophic factors for peripheral nerve regeneration.
J Peripher Nerv Syst. 15:93–103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chimutengwende-Gordon M and Khan W: Recent
advances and developments in neural repair and regeneration for
hand surgery. Open Orthop J. 6:103–107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reid AJ, Sun M, Wiberg M, Downes S,
Terenghi G and Kingham PJ: Nerve repair with adipose-derived stem
cells protects dorsal root ganglia neurons from apoptosis.
Neuroscience. 199:515–522. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wong FS, Chan BP and Lo AC: Carriers in
cell-based therapies for neurological disorders. Int J Mol Sci.
15:10669–10723. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ide C: Peripheral nerve regeneration.
Neurosci Res. 25:101–121. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Radtke C, Wewetzer K, Reimers K and Vogt
PM: Transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells as adjunct cell
therapy for peripheral nerve injury. Cell Transplant. 20:145–152.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tohill M and Terenghi G: Stem-cell
plasticity and therapy for injuries of the peripheral nervous
system. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 40:17–24. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Muschler GF, Nitto H, Boehm CA and Easley
KA: Age- and gender-related changes in the cellularity of human
bone marrow and the prevalence of osteoblastic progenitors. J
Orthop Res. 19:117–125. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Strem BM, Hicok KC, Zhu M, Wulur I,
Alfonso Z, Schreiber RE, Fraser JK and Hedrick MH: Multipotential
differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Keio J Med.
54:132–141. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Robinton DA and Daley GQ: The promise of
induced pluripotent stem cells in research and therapy. Nature.
481:295–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Walsh S and Midha R: Use of stem cells to
augment nerve injury repair. Neurosurgery. 65(Suppl): A80–A86.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weinstein DE: The role of Schwann cells in
neural regeneration. Neuroscientist. 5:208–216. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ikeda M, Uemura T, Takamatsu K, Okada M,
Kazuki K, Tabata Y, Ikada Y and Nakamura H: Acceleration of
peripheral nerve regeneration using nerve conduits in combination
with induced pluripotent stem cell technology and a basic
fibroblast growth factor drug delivery system. J Biomed Mater Res
A. 102:1370–1378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Satarian L, Javan M, Kiani S, Hajikaram M,
Mirnajafi-Zadeh J and Baharvand H: Engrafted human induced
pluripotent stem cell-derived anterior specified neural progenitors
protect the rat crushed optic nerve. PLoS One. 8:e718552013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uemura T, Takamatsu K, Ikeda M, Okada M,
Kazuki K, Ikada Y and Nakamura H: Transplantation of induced
pluripotent stem cell-derived neurospheres for peripheral nerve
repair. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 419:130–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang A, Tang Z, Park IH, Zhu Y, Patel S,
Daley GQ and Li S: Induced pluripotent stem cells for neural tissue
engineering. Biomaterials. 32:5023–5032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rodriguez AM, Elabd C, Amri EZ, Ailhaud G
and Dani C: The human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent
stem cells. Biochimie. 87:125–128. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gimble JM, Katz AJ and Bunnell BA:
Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Circ Res.
100:1249–1260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Carvalho PP, Wu X, Yu G, Dias IR, Gomes
ME, Reis RL and Gimble JM: The effect of storage time on
adipose-derived stem cell recovery from human lipoaspirates. Cells
Tissues Organs. 194:494–500. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Radtke C, Schmitz B, Spies M, Kocsis JD
and Vogt PM: Peripheral glial cell differentiation from
neurospheres derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Dev
Neurosci. 27:817–823. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ren Z, Wang Y, Peng J, Zhao Q and Lu S:
Role of stem cells in the regeneration and repair of peripheral
nerves. Rev Neurosci. 23:135–143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Papalia I, Raimondo S, Ronchi G, Magaudda
L, Giacobini-Robecchi MG and Geuna S: Repairing nerve gaps by vein
conduits filled with lipoaspirate-derived entire adipose tissue
hinders nerve regeneration. Ann Anat. 195:225–230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Georgiou M, Golding JP, Loughlin AJ,
Kingham PJ and Phillips JB: Engineered neural tissue with aligned,
differentiated adipose-derived stem cells promotes peripheral nerve
regeneration across a critical sized defect in rat sciatic nerve.
Biomaterials. 37:242–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hsueh YY, Chang YJ, Huang TC, Fan SC, Wang
DH, Chen JJ, Wu CC and Lin SC: Functional recoveries of sciatic
nerve regeneration by combining chitosan-coated conduit and
neurosphere cells induced from adipose-derived stem cells.
Biomaterials. 35:2234–2244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Orbay H, Uysal AC, Hyakusoku H and Mizuno
H: Differentiated and undifferentiated adipose-derived stem cells
improve function in rats with peripheral nerve gaps. J Plast
Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 65:657–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sun F, Zhou K, Mi WJ and Qiu JH: Combined
use of decellularized allogeneic artery conduits with autologous
transdifferentiated adipose-derived stem cells for facial nerve
regeneration in rats. Biomaterials. 32:8118–8128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ravasi M, Scuteri A, Pasini S, Bossi M,
Menendez VR, Maggioni D and Tredici G: Undifferentiated MSCs are
able to myelinate DRG neuron processes through p75. Exp Cell Res.
319:2989–2999. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Razavi S, Mardani M, Kazemi M, Esfandiari
E, Narimani M, Esmaeili A and Ahmadi N: Effect of leukemia
inhibitory factor on the myelinogenic ability of Schwann-like cells
induced from human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
33:283–289. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Erba P, Mantovani C, Kalbermatten DF,
Pierer G, Terenghi G and Kingham PJ: Regeneration potential and
survival of transplanted undifferentiated adipose tissue-derived
stem cells in peripheral nerve conduits. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet
Surg. 63:e811–e817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Faroni A, Smith RJ and Reid AJ: Adipose
derived stem cells and nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res.
9:1341–1346. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kolar MK and Kingham PJ: Regenerative
effects of adipose-tissue-derived stem cells for treatment of
peripheral nerve injuries. Biochem Soc Trans. 42:697–701. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kingham PJ, Kalbermatten DF, Mahay D,
Armstrong SJ, Wiberg M and Terenghi G: Adipose-derived stem cells
differentiate into a Schwann cell phenotype and promote neurite
outgrowth in vitro. Exp Neurol. 207:267–274. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
di Summa PG, Kalbermatten DF, Raffoul W,
Terenghi G and Kingham PJ: Extracellular matrix molecules enhance
the neuro-trophic effect of Schwann cell-like differentiated
adipose-derived stem cells and increase cell survival under stress
conditions. Tissue Eng Part A. 19:368–379. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xu Y, Liu L, Li Y, Zhou C, Xiong F, Liu Z,
Gu R, Hou X and Zhang C: Myelin-forming ability of Schwann
cell-like cells induced from rat adipose-derived stem cells in
vitro. Brain Res. 1239:49–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kapur SK and Katz AJ: Review of the
adipose derived stem cell secretome. Biochimie 9. 5:2222–2228.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Salgado AJ, Reis RL, Sousa NJ and Gimble
JM: Adipose tissue derived stem cells secretome: Soluble factors
and their roles in regenerative medicine. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.
5:103–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chung JY, Kim W, Im W, Yoo DY, Choi JH,
Hwang IK, Won MH, Chang IB, Cho BM, Hwang HS, et al:
Neuroprotective effects of adipose-derived stem cells against
ischemic neuronal damage in the rabbit spinal cord. J Neurol Sci.
317:40–46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kalbermatten DF, Schaakxs D, Kingham PJ
and Wiberg M: Neurotrophic activity of human adipose stem cells
isolated from deep and superficial layers of abdominal fat. Cell
Tissue Res. 344:251–260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lattanzi W, Geloso MC, Saulnier N,
Giannetti S, Puglisi MA, Corvino V, Gasbarrini A and Michetti F:
Neurotrophic features of human adipose tissue-derived stromal
cells: In vitro and in vivo studies. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:4687052011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wei X, Zhao L, Zhong J, Gu H, Feng D,
Johnstone BH, March KL, Farlow MR and Du Y: Adipose stromal
cells-secreted neuroprotective media against neuronal apoptosis.
Neurosci Lett. 462:76–79. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sowa Y, Imura T, Numajiri T, Nishino K and
Fushiki S: Adipose-derived stem cells produce factors enhancing
peripheral nerve regeneration: Influence of age and anatomic site
of origin. Stem Cells Dev. 21:1852–1862. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Skouras E, Ozsoy U, Sarikcioglu L and
Angelov DN: Intrinsic and therapeutic factors determining the
recovery of motor function after peripheral nerve transection. Ann
Anat. 193:286–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mantovani C, Raimondo S, Haneef MS, Geuna
S, Terenghi G, Shawcross SG and Wiberg M: Morphological, molecular
and functional differences of adult bone marrow- and
adipose-derived stem cells isolated from rats of different ages.
Exp Cell Res. 318:2034–2048. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Simons JW: The use of frequency
distributions of cell diameters to characterize cell populations in
tissue culture. Exp Cell Res. 45:336–350. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Maleki M, Ghanbarvand F, Reza Behvarz M,
Ejtemaei M and Ghadirkhomi E: Comparison of mesenchymal stem cell
markers in multiple human adult stem cells. Int J Stem Cells.
7:118–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wan Safwani WK, Makpol S, Sathapan S and
Chua KH: The changes of stemness biomarkers expression in human
adipose-derived stem cells during long-term manipulation.
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 58:261–270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop DJ and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular
Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
di Summa PG, Kalbermatten DF, Pralong E,
Raffoul W, Kingham PJ and Terenghi G: Long-term in vivo
regeneration of peripheral nerves through bioengineered nerve
grafts. Neuroscience. 181:278–291. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
di Summa PG, Kingham PJ, Raffoul W, Wiberg
M, Terenghi G and Kalbermatten DF: Adipose-derived stem cells
enhance peripheral nerve regeneration. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet
Surg. 63:1544–1552. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zuck P: Adipose-derived stem cells in
tissue regeneration. ISRN Stem Cells. 2013:e7139592013.
|