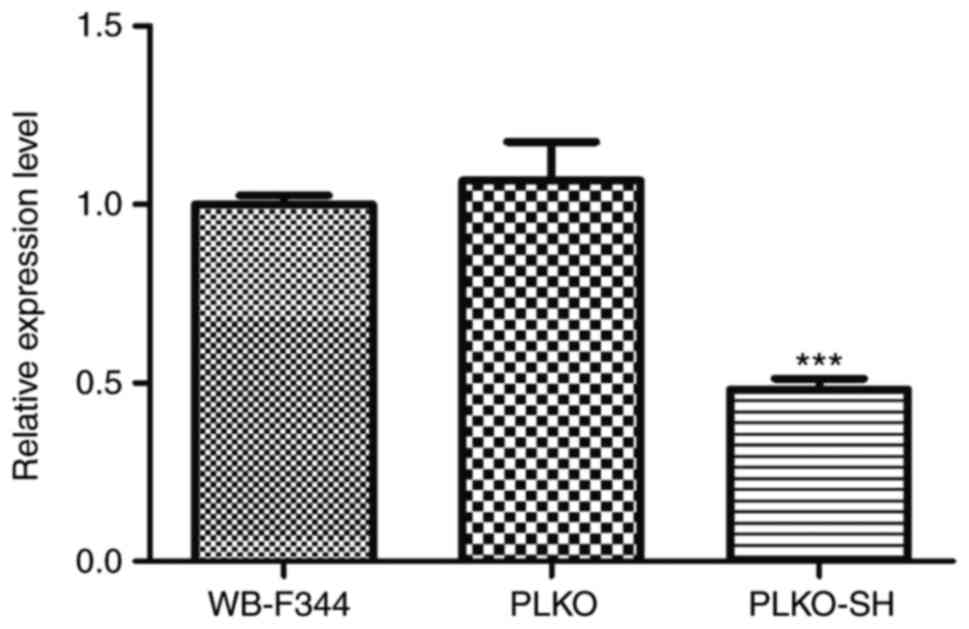
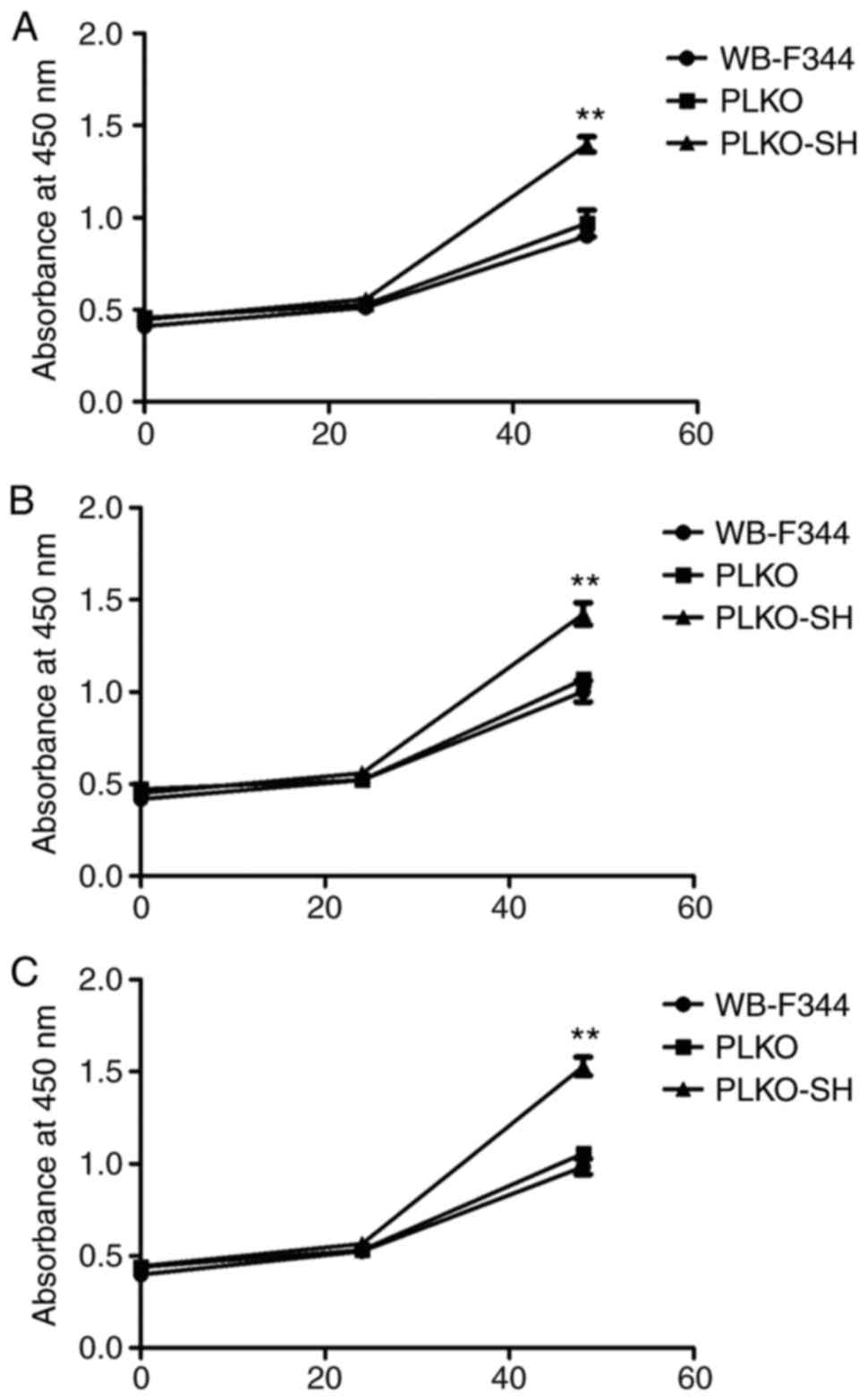
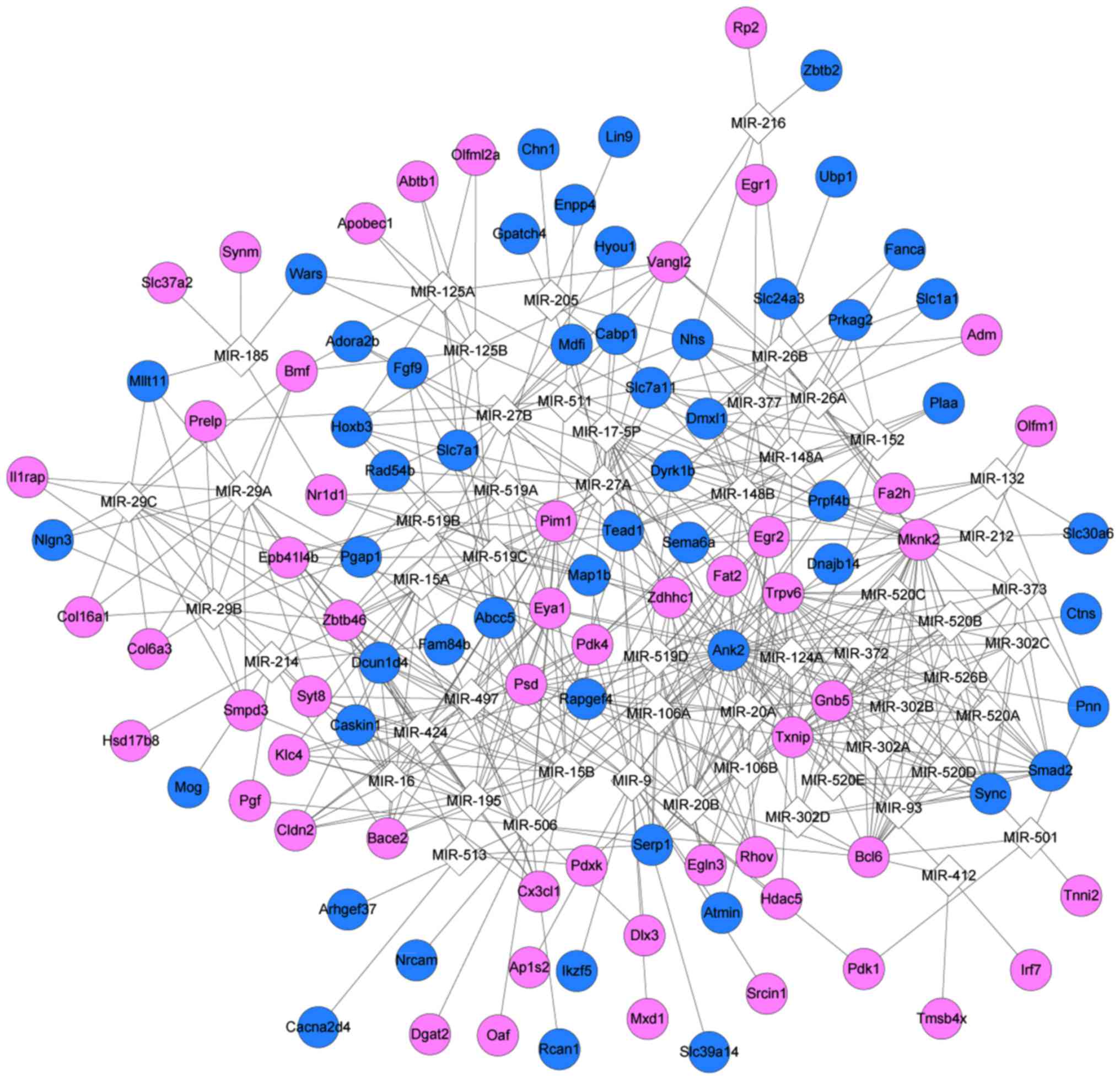
|
1
|
Chandra V, Huang P, Potluri N, Wu D, Kim Y
and Rastinejad F: Multidomain integration in the structure of the
HNF-4α nuclear receptor complex. Nature. 495:394–398. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saha SK, Parachoniak CA, Ghanta KS,
Fitamant J, Ross KN, Najem MS, Gurumurthy S, Akbay EA, Sia D,
Cornella H, et al: Mutant IDH inhibits HNF-4α to block hepatocyte
differentiation and promote biliary cancer. Nature. 513:110–114.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li J, Ning G and Duncan SA: Mammalian
hepatocyte differentiation requires the transcription factor
HNF-4α. Genes Dev. 14:464–474. 2000.
|
|
4
|
Takayama K, Inamura M, Kawabata K,
Katayama K, Higuchi M, Tashiro K, Nonaka A, Sakurai F, Hayakawa T,
Furue MK and Mizuguchi H: Efficient generation of functional
hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent
stem cells by HNF4α transduction. Mol Ther. 20:127–137. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen KT, Pernelle K, Tsai YH, Wu YH, Hsieh
JY, Liao KH, Guguen-Guillouzo C and Wang HW: Liver X receptor α
(LXRα/NR1H3) regulates differentiation of hepatocyte-like cells via
reciprocal regulation of HNF4α. J Hepatol. 61:1276–1286. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simó R, Barbosa-Desongles A, Hernandez C
and Selva DM: IL1β down-regulation of sex hormone-binding globulin
production by decreasing HNF-4α via MEK-1/2 and JNK MAPK pathways.
Mol Endocrinol. 26:1917–1927. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Simó R, Barbosadesongles A, Sáezlopez C,
Lecube A, Hernandez C and Selva DM: Molecular mechanism of
TNFα-induced down-regulation of SHBG expression. Mol Endocrinol.
26:438–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li WQ, Li YM, Guo J, Liu YM, Yang XQ, Ge
HJ, Xu Y, Liu HM, He J and Yu HY: Hepatocytic precursor (stem-like)
WB-F344 cells reduce tumorigenicity of hepatoma CBRH-7919 cells via
TGF-beta/Smad pathway. Oncol Rep. 23:1601–1607. 2010.
|
|
9
|
Liu J, Liu Y, Wang H, Hao H, Han Q, Shen
J, Shi J, Li C, Mu Y and Han W: Direct differentiation of hepatic
stem-like WB cells into insulin-producing cells using small
molecules. Sci Rep. 3:11852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Couchie D, Holic N, Chobert MN, Corlu A
and Laperche Y: In vitro differentiation of WB-F344 rat liver
epithelial cells into the biliary lineage. Differentiation.
69:209–215. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang Z, Wang L and Wang X: Matrine induces
the hepatic differentiation of WB-F344 rat hepatic progenitor cells
and inhibits Jagged 1/HES1 signaling. Mol Med Rep. 14:3841–3847.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vasilescu C, Rossi S, Shimizu M, Tudor S,
Veronese A, Ferracin M, Nicoloso MS, Barbarotto E, Popa M,
Stanciulea O, et al: MicroRNA fingerprints identify miR-150 as a
plasma prognostic marker in patients with sepsis. PLoS One.
4:e74052009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yao H, Jia Y, Zhou J, Wang J, Li Y, Wang
Y, Yue W and Pei X: RhoA promotes differentiation of WB-F344 cells
into the biliary lineage. Differentiation. 77:154–161. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Li XM, Zhang FK and Wang BE:
Activation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway promotes
proliferation and self-renewal of rat hepatic oval cell line
WB-F344 in vitro. World J Gastroenterol. 14:6673–6680. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arocho A, Chen B, Ladanyi M and Pan Q:
Validation of the 2-DeltaDeltaCt calculation as an alternate method
of data analysis for quantitative PCR of BCR-ABL P210 transcripts.
Diagn Mol Pathol. 15:56–61. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim D, Pertea G, Trapnell C, Pimentel H,
Kelley R and Salzberg SL: TopHat2: Accurate alignment of
transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene
fusions. Genome Biol. 14:R362014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Strozzi F and Aerts J: A Ruby API to query
the Ensembl database for genomic features. Bioinformatics.
27:1013–1014. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Anders S, Pyl PT and Huber W: HTSeq-a
Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data.
Bioinformatics. 31:166–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nikolayeva O and Robinson MD: edgeR for
differential RNA-seq and ChIP-seq analysis: An application to stem
cell biology. Methods Mol Biol. 1150:45–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Robinson MD, Mccarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Law CW, Chen Y, Shi W and Smyth GK: voom:
Precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq
read counts. Genome Biol. 15:R292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu L, Gulati P, Fernandez S, Pennell M,
Kirschner L and Jarjoura D: Fully moderated T-statistic for small
sample size gene expression arrays. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol.
10:1–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gene Ontology Consortium: Gene Ontology
Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(Database Issue):
D1049–D1056. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi
M and Tanabe M: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D457–D462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41(Database Issue): D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Saito R, Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J,
Wang PL, Lotia S, Pico AR, Bader GD and Ideker T: A travel guide to
Cytoscape plugins. Nat Methods. 9:1069–1076. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y and Wu FX:
CytoNCA: A cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation
of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 127:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rito T, Deane CM and Reinert G: The
importance of age and high degree, in protein-protein interaction
networks. J Comput Biol. 19:785–795. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goh KI, Oh E, Kahng B and Kim D:
Betweenness centrality correlation in social networks. Phys Rev E
Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 67:0171012003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Okamoto K, Chen W and Li XY: Ranking of
closeness centrality for large-scale social networks. International
Workshop on Frontiers in Algorithmics. Front Algorithmics. 186–195.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z and Zhang B:
WEB-based GEne SeT analysis toolkit (WebGestalt): Update 2013.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:W77–W83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Khurana S, Jaiswal AK and Mukhopadhyay A:
Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α induces transdifferentiation of
hematopoietic cells into hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 285:4725–4731.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Walesky C and Apte U: Role of hepatocyte
nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) in cell proliferation and cancer. Gene
Expr. 16:101–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kimata T, Nagaki M, Tsukada Y, Ogiso T and
Moriwaki H: Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha and -1 small
interfering RNA inhibits hepatocyte differentiation induced by
extracellular matrix. Hepatol Res. 35:3–9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Garibaldi F, Cicchini C, Conigliaro A,
Santangelo L, Cozzolino AM, Grassi G, Marchetti A, Tripodi M and
Amicone L: An epistatic mini-circuitry between the transcription
factors Snail and HNF4α controls liver stem cell and hepatocyte
features exhorting opposite regulation on stemness-inhibiting
microRNAs. Cell Death Differ. 19:937–946. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Walesky C, Gunewardena S, Terwilliger EF,
Edwards G, Borude P and Apte U: Hepatocyte-specific deletion of
hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α in adult mice results in increased
hepatocyte proliferation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
304:G26–G37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kim TH, Mars WM, Stolz DB and
Michalopoulos GK: Expression and activation of pro-MMP-2 and
pro-MMP-9 during rat liver regeneration. Hepatology. 31:75–82.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pham Van T, Couchie D, Martin-Garcia N,
Laperche Y, Zafrani ES and Mavier P: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and of tissue inhibitor of matrix
metalloproteinase-1 in liver regeneration from oval cells in rat.
Matrix Biol. 27:674–681. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Han YP, Yan C, Zhou L, Qin L and Tsukamoto
H: A matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation cascade by hepatic
stellate cells in trans-differentiation in the three-dimensional
extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 282:12928–12939. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kollet O, Shivtiel S, Chen YQ, Suriawinata
J, Thung SN, Dabeva MD, Kahn J, Spiegel A, Dar A, Samira S, et al:
HGF, SDF-1, and MMP-9 are involved in stress-induced human
CD34+ stem cell recruitment to the liver. J Clin Invest.
112:160–169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim HL, Cha JH, Park NR, Bae SH, Choi JY
and Yoon SK: 304 EGR1 promotes the differentiation of bm-derived
mesenchymal stem cells into functional hepatocyte with
mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition. J Hepatol. 58:S1282013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhang Y, Bonzo JA, Gonzalez FJ and Wang L:
Diurnal regulation of the early growth response 1 (Egr-1) protein
expression by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF4alpha) and
small heterodimer partner (SHP) cross-talk in liver fibrosis. J
Biol Chem. 286:29635–29643. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ju W, Ogawa A, Heyer J, Nierhof D, Yu L,
Kucherlapati R, Shafritz DA and Böttinger EP: Deletion of Smad2 in
mouse liver reveals novel functions in hepatocyte growth and
differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 26:654–667. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jiang F, Mu J, Wang X, Ye X, Si L, Ning S,
Li Z and Li Y: The repressive effect of miR-148a on TGF beta-SMADs
signal pathway is involved in the glabridin-induced inhibition of
the cancer stem cells-like properties in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. PLoS One. 9:e966982014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Teng NY, Liu YS, Wu HH, Liu YA, Ho JH and
Lee OK: Promotion of mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition by Rac1
inhibition with small molecules accelerates hepatic differentiation
of mesenchymal stromal cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 21:1444–1454.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|