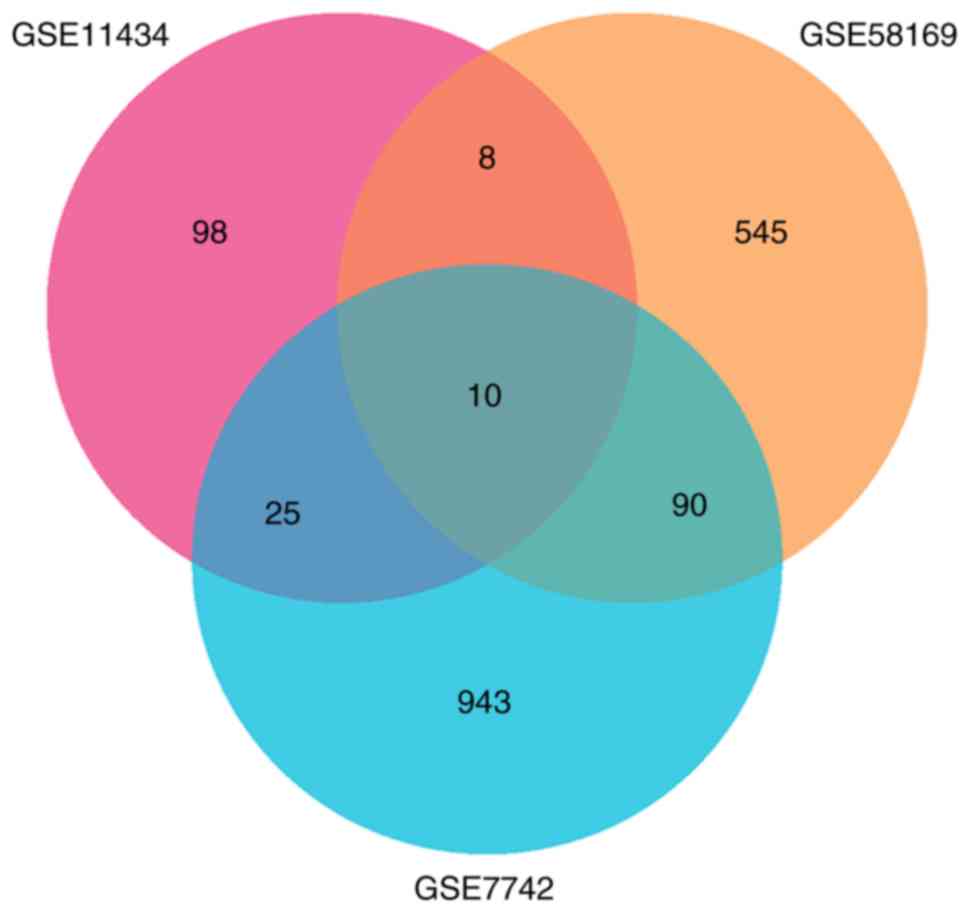
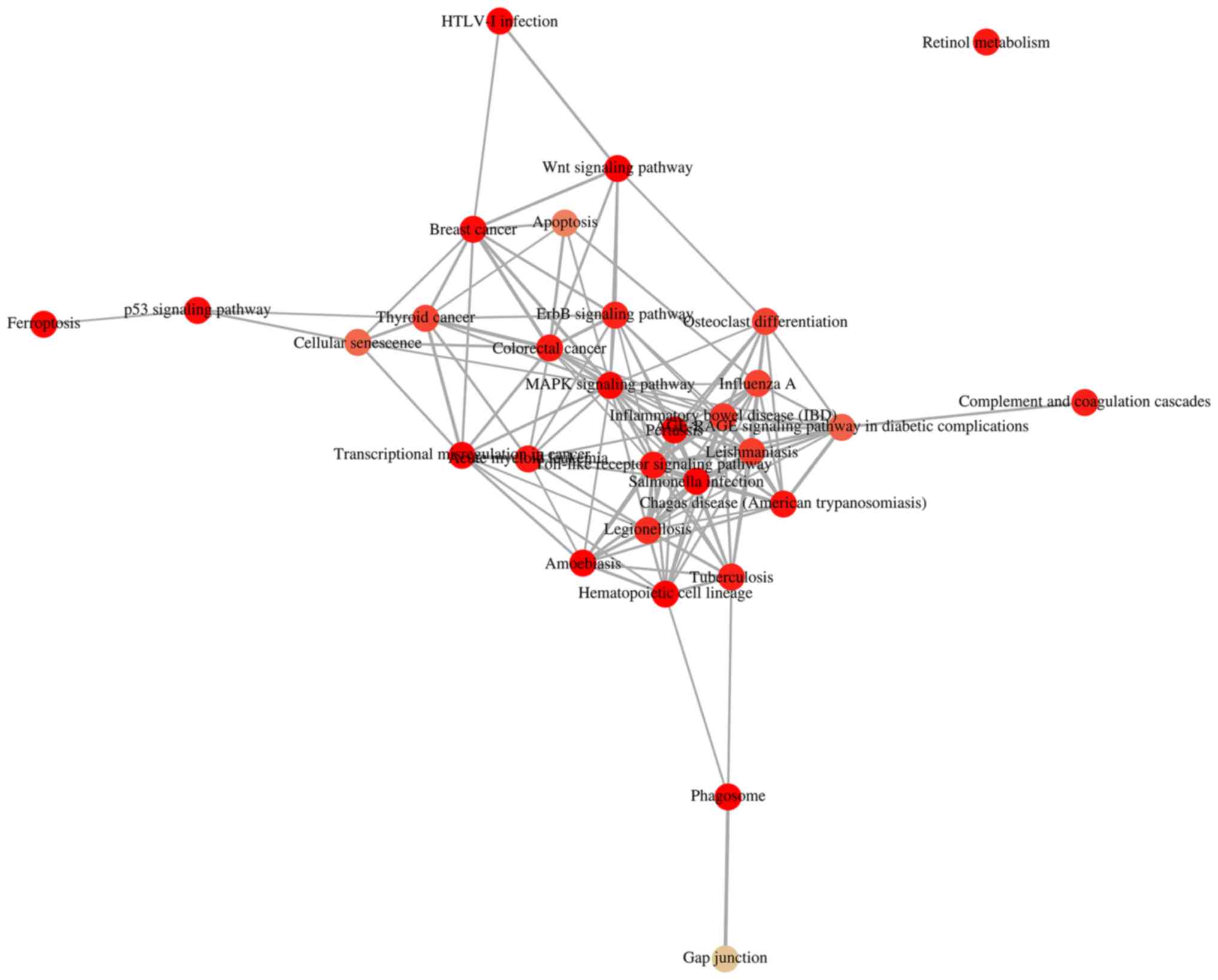
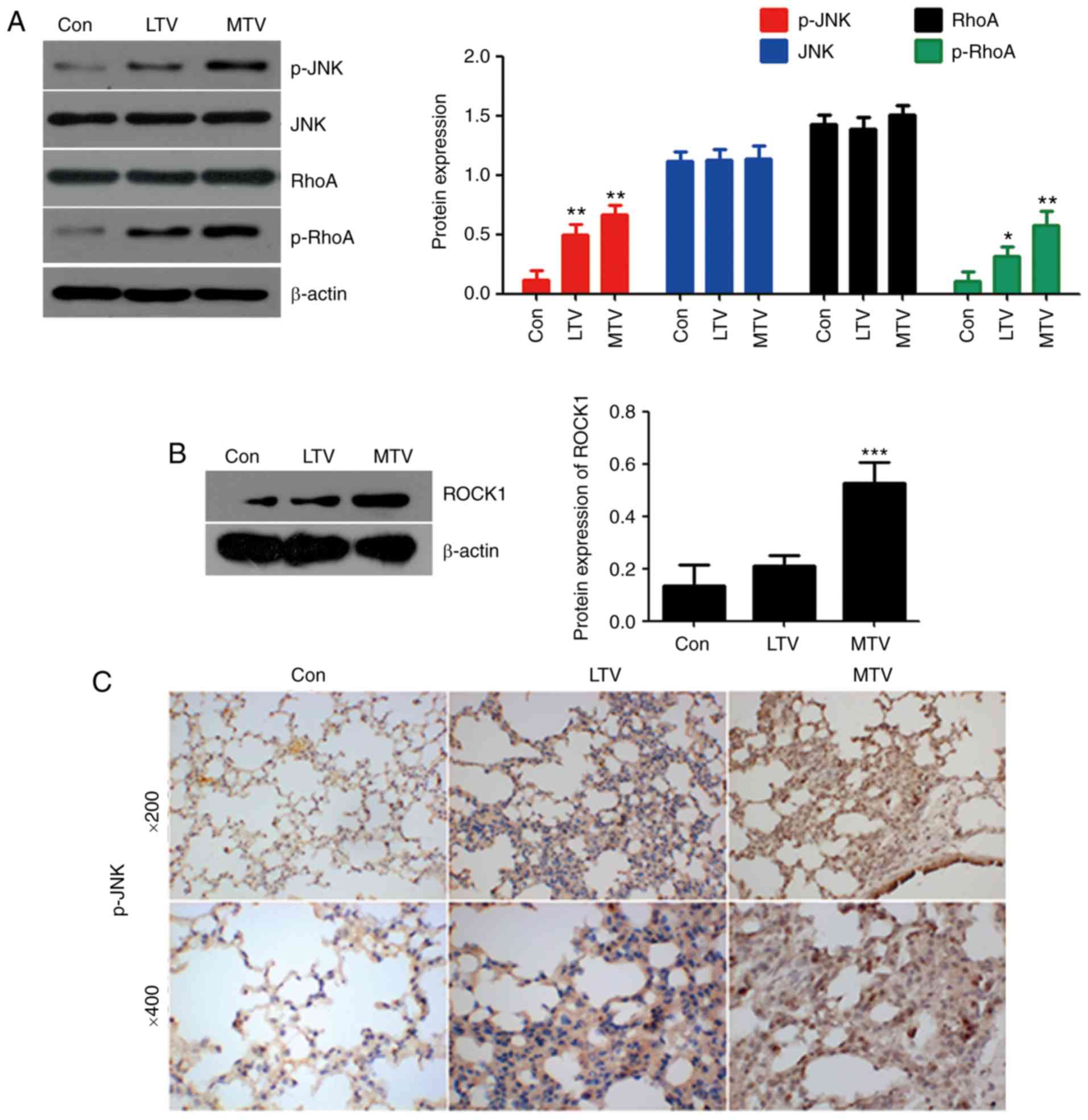
|
1
|
Hashemian SM, Mohajerani SA and Jamaati
HR: Ventilator-induced lung injury. N Engl J Med. 370:979–980.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rahaman U: Mathematics of
ventilator-induced lung injury. Indian J Crit Care Med. 21:521–524.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beitler JR, Malhotra A and Thompson BT:
Ventilator-induced lung injury. Clin Chest Med. 37:633–646. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Plötz FB: Ventilator-induced lung injury.
Intensive Care Med. 27:4522001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Amato MB, Barbas CS, Medeiros DM, Magaldi
RB, Schettino GP, Lorenzi-Filho G, Kairalla RA, Deheinzelin D,
Munoz C, Oliveira R, et al: Effect of a protective-ventilation
strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N
Engl J Med. 338:347–354. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu H, He J, Liu J, Zhang X, Yang F, Liu P
and Wang S: Alpha 1-antitrypsin ameliorates ventilator-induced lung
injury in rats by inhibiting inflammatory responses and apoptosis.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 243:87–95. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Park BH, Shin MH, Douglas IS, Chung KS,
Song JH, Kim SY, Kim EY, Jung JY, Kang YA, Chang J, et al:
Erythropoietin-producing hepatoma receptor tyrosine kinase A2
modulation associates with protective effect of prone position in
ventilator-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
58:519–529. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Suryadevara V, Fu P, Ebenezer DL,
Berdyshev E, Bronova IA, Huang LS, Harijith A and Natarajan V:
Sphingolipids in ventilator induced lung injury: Role of
sphingosine-1-phosphate. lyase Int J Mol Sci. 19:E1142018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Huang X, Zhou W and Ding S: Downregulated
Smad4 affects extracellular matrix remodeling in ventilator-induced
lung injury. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 46:451–456. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao T, Zhao H, Li G, Zheng S, Liu M, Gu C
and Wang Y: Role of the PKCα-c-Src tyrosine kinase pathway in the
mediation of p120-catenin degradation in ventilator-induced lung
injury. Respirology. 21:1404–1410. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chian CF, Chiang CH, Chuang CH, Liu SL and
Tsai CL: SN50, a cell-permeable-inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB,
attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in an isolated and
perfused rat lung model. Shock. 46:194–201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jun JI and Lau LF: Taking aim at the
extracellular matrix: CCN proteins as emerging therapeutic targets.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:945–963. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li HH, Li Q, Liu P, Liu Y, Li J,
Wasserloos K, Chao W, You M, Oury TD, Chhinder S, et al:
WNT1-inducible signaling pathway protein 1 contributes to
ventilator-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
47:528–535. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Z, Ding X, Jin S, Pitt B, Zhang L,
Billiar T and Li Q: WISP1-αvβ3 integrin signaling positively
regulates TLR-triggered inflammation response in sepsis induced
lung injury. Sci Rep. 6:288412016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ding X, Wang X, Zhao X, Jin S, Tong Y, Ren
H, Chen Z and Li Q: RGD peptides protects against acute lung injury
in septic mice through Wisp1-integrin β6 pathway inhibition. Shock.
43:352–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jin S, Chen Z, Ding X, Zhao X, Jiang X,
Tong Y, Billiar TR and Li Q: Mechanical ventilation augments
poly(I:C)induced lung injury via a WISP1-integrin β3 dependent
pathway in mice. Mol Med. 22:54–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Borcherding N, Kusner D, Kolb R, Xie Q, Li
W, Yuan F, Velez G, Askeland R, Weigel RJ and Zhang W: Paracrine
WNT5A signaling inhibits expansion of tumor-initiating cells.
Cancer Res. 75:1972–1982. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, Ueno
N, Yasuda J, Waterman M, Shibuya H, Moon RT, Ninomiya-Tsuji J and
Matsumoto K: The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade
functions in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 23:131–139. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Li C, Xiao J, Hormi K, Borok Z and Minoo
P: Wnt5a participates in distal lung morphogenesis. Dev Biol.
248:68–81. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li C, Hu L, Xiao J, Chen H, Li JT,
Bellusci S, Delanghe S and Minoo P: Wnt5a regulates Shh and Fgf10
signaling during lung development. Dev Biol. 287:86–97. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vuga LJ, Ben-Yehudah A,
Kovkarova-Naumovski E, Oriss T, Gibson KF, Feghali-Bostwick C and
Kaminski N: WNT5A is a regulator of fibroblast proliferation and
resistance to apoptosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 41:583–589.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Spassov S, Pfeifer D, Strosing K, Ryter S,
Hummel M, Faller S and Hoetzel A: Genetic targets of hydrogen
sulfide in ventilator-induced lung injury-a microarray study. PLoS
One. 9:e1024012014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dolinay T, Wu W, Kaminski N, Ifedigbo E,
Kaynar AM, Szilasi M, Watkins SC, Ryter SW, Hoetzel A and Choi AM:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate susceptibility to
ventilator-induced lung injury. PLoS One. 3:e16012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wray C, Mao Y, Pan J, Chandrasena A,
Piasta F and Frank JA: Claudin-4 augments alveolar epithelial
barrier function and is induced in acute lung injury. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L219–L227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie C, Mao X, Huang J, Ding Y, Wu J, Dong
S, Kong L, Gao G, Li CY and Wei L: KOBAS 2.0: A web server for
annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39(Web Server issue): W316–W322. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi
M and Tanabe M: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D457–D462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol.
8:e10004122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen T, Chen C, Zhang Z, Zou Y, Peng M and
Wang Y: Toll-like receptor 4 knockout ameliorates neuroinflammation
due to lung-brain interaction in mechanically ventilated mice.
Brain Behav Immun. 56:42–55. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li H, Su X, Yan X, Wasserloos K, Chao W,
Kaynar AM, Liu ZQ, Leikauf GD, Pitt BR and Zhang LM: Toll-like
receptor 4-myeloid differentiation factor 88 signaling contributes
to ventilator-induced lung injury in mice. Anesthesiology.
113:619–629. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Achouiti A, van der Meer AJ, Florquin S,
Yang H, Tracey KJ, van't Veer C, de Vos AF and van der Poll T:
High-mobility group box 1 and the receptor for advanced glycation
end products contribute to lung injury during Staphylococcus aureus
pneumonia. Crit Care. 17:R2962013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Villar J, Cabrera NE, Valladares F, Casula
M, Flores C, Blanch L, Quilez ME, Santana-Rodríguez N, Kacmarek RM
and Slutsky AS: Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
by mechanical ventilation is associated with ventilator-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in healthy lungs. PLoS One. 6:e239142011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tao G, Pan L, Jing R, Lin F, Dai H and Ge
W: Study on Rac1/MAPK/ERK pathway mediated mechanism and role in
rats with ventilator induced lung injury. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing
Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 29:249–254. 2017.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Villar J, Cabrera NE, Casula M, Valladares
F, Flores C, López-Aguilar J, Blanch L, Zhang H, Kacmarek RM and
Slutsky AS: WNT/β-catenin signaling is modulated by mechanical
ventilation in an experimental model of acute lung injury.
Intensive Care Med. 37:1201–1209. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiao J, Zhou H, Wu N and Wu L: The
non-canonical Wnt pathway negatively regulates dendritic cell
differentiation by inhibiting the expansion of Flt3+
lymphocyte-primed multipotent precursors. Cell Mol Immunol.
13:593–604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ouyang W, Zhou H, Liu C, Wang S, Han Y,
Xia J and Xu F: 25-Hydroxycholesterol protects against acute lung
injury via targeting MD-2. J Cell Mol Med. 22:5494–5503. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu F, Diao R, Liu J, Kang Y, Wang X and
Shi L: Curcumin attenuates staphylococcus aureus-induced acute lung
injury. Clin Respir J. 9:87–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Cheng L, Zhao Y, Qi D, Li W and Wang D:
Wnt/β-catenin pathway promotes acute lung injury induced by LPS
through driving the Th17 response in mice. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 495:1890–1895. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chen X, Shi C, Meng X, Zhang K, Li X, Wang
C, Xiang Z, Hu K and Han X: Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
suppresses bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by attenuating the
expression of TGF-β1 and FGF-2. Exp Mol Pathol. 101:22–30. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ying H, Kang Y, Zhang H, Zhao D, Xia J, Lu
Z, Wang H, Xu F and Shi L: MiR-127 modulates macrophage
polarization and promotes lung inflammation and injury by
activating the JNK pathway. J Immunol. 194:1239–1251. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kim J, Chang W, Jung Y, Song K and Lee I:
Wnt5a activates THP-1 monocytic cells via a β-catenin-independent
pathway involving JNK and NF-κB activation. Cytokine. 60:242–248.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Koval A, Purvanov V, Egger-Adam D and
Katanaev VL: Yellow submarine of the Wnt/Frizzled signaling:
Submerging from the G protein harbor to the targets. Biochem
Pharmacol. 82:1311–1319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsieh JC, Kodjabachian L, Rebbert ML,
Rattner A, Smallwood PM, Samos CH, Nusse R, Dawid IB and Nathans J:
A new secreted protein that binds to Wnt proteins and inhibits
their activities. Nature. 398:431–436. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Saito S, Tampe B, Müller GA and Zeisberg
M: Primary cilia modulate balance of canonical and non-canonical
Wnt signaling responses in the injured kidney. Fibrogenesis Tissue
Repair. 8:62015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nakamura K, Sano S, Fuster JJ, Kikuchi R,
Shimizu I, Ohshima K, Katanasaka Y, Ouchi N and Walsh K: Secreted
Frizzled-related protein 5 diminishes cardiac inflammation and
protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Biol Chem.
291:2566–2575. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Meyer IS, Jungmann A, Dieterich C, Zhang
M, Lasitschka F, Werkmeister S, Haas J, Müller OJ, Boutros M,
Nahrendorf M, et al: The cardiac microenvironment uses
non-canonical WNT signaling to activate monocytes after myocardial
infarction. EMBO Mol Med. 9:1279–1293. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Guan S and Zhou J: Frizzled-7 mediates
TGF-β-induced pulmonary fibrosis by transmitting non-canonical Wnt
signaling. Exp Cell Res. 359:226–234. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|