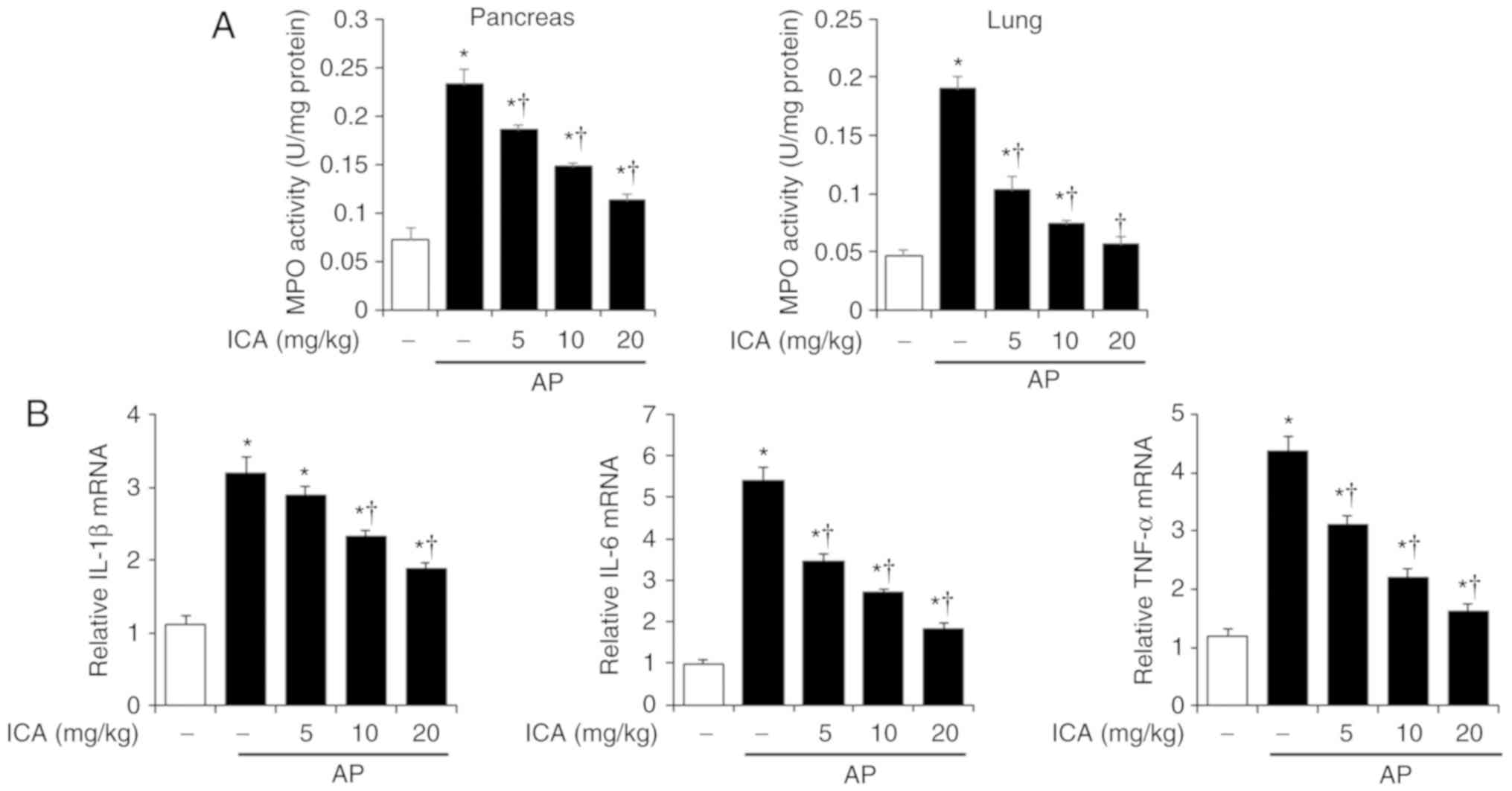
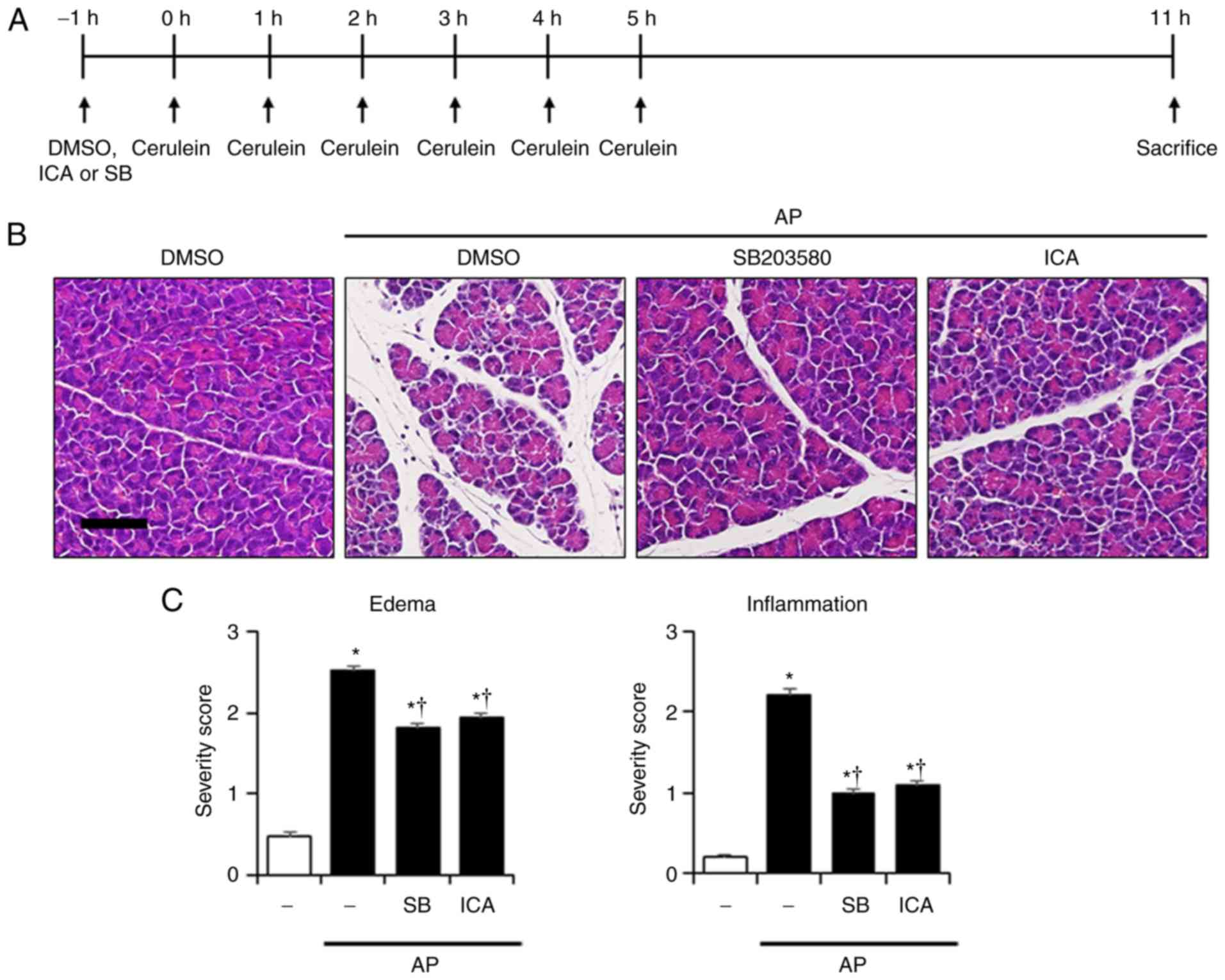
|
1
|
Peery AF, Crockett SD, Barritt AS, Dellon
ES, Eluri S, Gangarosa LM, Jensen ET, Lund JL, Pasricha S, Runge T,
et al: Burden of gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases
in the United States. Gastroenterology. 149:1731–1741. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maléth J and Hegyi P: Ca2+ toxicity and
mitochondrial damage in acute pancreatitis: Translational overview.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 371:201504252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bettaieb A, Koike S, Chahed S, Bachaalany
S, Griffey S, Sastre J and Haj FG: Pancreatic protein tyrosine
phosphatase 1B deficiency exacerbates acute pancreatitis in mice.
Am J Pathol. 186:2043–2054. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yadav D and Lowenfels AB: The epidemiology
of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology.
144:1252–1261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Minkov GA, Halacheva KS, Yovtchev YP and
Gulubova MV: Pathophysiological mechanisms of acute pancreatitis
define inflammatory markers of clinical prognosis. Pancreas.
44:713–717. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Büchler MW, Gloor B, Müller CA, Friess H,
Seiler CA and Uhl W: Acute necrotizing pancreatitis: Treatment
strategy according to the status of infection. Ann Surg.
232:619–626. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bae GS, Heo KH, Park KC, Choi SB, Jo IJ,
Seo SH, Kim DG, Shin JY, Kang DG, Lee HS, et al: Apamin attenuated
cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis by inhibition of JNK pathway in
mice. Dig Dis Sci. 58:2908–2917. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chakraborty M, Hickey AJ, Petrov MS,
Macdonald JR, Thompson N, Newby L, Sim D, Windsor JA and Phillips
AR: Mitochondrial dysfunction in peripheral blood mononuclear cells
in early experimental and clinical acute pancreatitis.
Pancreatology. 16:739–747. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li LS, Luo YM, Liu J, Zhang Y, Fu XX and
Yang DL: Icariin inhibits pulmonary hypertension induced by
monocrotaline through enhancement of NO/cGMP signaling pathway in
rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2016:79154152016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hsueh TY, Ho JK, Lin LC, Chiu AW, Lin CH
and Tsai TH: Herb-drug interaction of Epimedium extract on the
pharmaco-kinetic of dapoxetine in rats. J Chromatogr B Analyt
Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1014:64–69. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen G, Wang C, Wang J, Yin S, Gao H,
Xiang LU, Liu H, Xiong Y, Wang P, Zhu X, et al: Antiosteoporotic
effect of icariin in ovariectomized rats is mediated via the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Exp Ther Med. 12:279–287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang ZS, Xiao HJ, Qi T, Hu ZM, Li H, Chen
DL, Xu YL and Chen J: Antioxidative protective effect of icariin on
the FeSO4/H2O2-damaged human sperm
based on confocal raman micro-spectroscopy. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 34:755–760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kong L, Liu J, Wang J, Luo Q, Zhang H, Liu
B, Xu F, Pang Q, Liu Y and Dong J: Icariin inhibits TNF-α/IFN-γ
induced inflammatory response via inhibition of the substance P and
p38-MAPK signaling pathway in human keratinocytes. Int
Immunopharmacol. 29:401–407. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan HL, Chan KG, Pusparajah P, Saokaew S,
Duangjai A, Lee LH and Goh BH: Anti-cancer properties of the
naturally occurring aphrodisiacs: Icariin and its derivatives.
Front Pharmacol. 7:1912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu B, Xu C, Wu X, Liu F, Du Y, Sun J, Tao
J and Dong J: Icariin exerts an antidepressant effect in an
unpredictable chronic mild stress model of depression in rats and
is associated with the regulation of hippocampal neuroinflammation.
Neuroscience. 294:193–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen YJ, Zheng HY, Huang XX, Han SX, Zhang
DS, Ni JZ and He XY: Neuroprotective effects of icariin on brain
metabolism, mitochondrial functions, and cognition in
triple-transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice. CNS Neurosci Ther.
22:63–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Wang YS, Song SL, Liang H and Ji
AG: Icariin inhibits atherosclerosis progress in Apoe null mice by
downregulating CX3CR1 in macrophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
470:845–850. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei Y, Liu B, Sun J, Lv Y, Luo Q, Liu F
and Dong J: Regulation of Th17/Treg function contributes to the
attenuation of chronic airway inflammation by icariin in
ovalbumin-induced murine asthma model. Immunobiology. 220:789–797.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu T, Xin H, Li WR, Zhou F, Li GY, Gong
YQ, Gao ZZ, Qin XC, Cui WS, Shindel AW and Xin ZC: Effects of
icariin on improving erectile function in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. J Sex Med. 8:2761–2772. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ethridge RT, Chung DH, Slogoff M, Ehlers
RA, Hellmich MR, Rajaraman S, Saito H, Uchida T and Evers BM:
Cyclooxygenase-2 gene disruption attenuates the severity of acute
pancreatitis and pancreatitis-associated lung injury.
Gastroenterology. 123:1311–1322. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim MJ, Bae GS, Choi SB, Jo IJ, Kim DG,
Shin JY, Lee SK, Kim MJ, Shong HJ and Park SJ: Lupeol protects
against cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice. Phytother Res.
29:1634–1639. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Que RS, Cao LP, Ding GP, Hu JA, Mao KJ and
Wang GF: Correlation of nitric oxide and other free radicals with
the severity of acute pancreatitis and complicated systemic
inflammatory response syndrome. Pancreas. 39:536–540. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Andersson R, Andersson B, Haraldsen P,
Drewsen G and Eckerwall G: Incidence, management and recurrence
rate of acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 39:891–894.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Johnson CD, Besselink MG and Carter R:
Acute pancreatitis. BMJ. 349:g48592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mossad DE, Dinh BV, Markert RJ, Musleh MN
and Agrawal S: Predictors of in hospital mortality in acute
pancreatitis. JOP J Pancreas. 18:465–469. 2017.
|
|
26
|
Popa CC, Badiu DC, Rusu OC, Grigorean VT,
Neagu SI and Strugaru CR: Mortality prognostic factors in acute
pancreatitis. J Med Life. 9:413–418. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kimura W and Mössner J: Role of
hypertriglyceridemia in the pathogenesis of experimental acute
pancreatitis in rats. Int J Pancreatol. 20:177–184. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Raraty MG, Murphy JA, Mcloughlin E, Smith
D, Criddle D and Sutton R: Mechanisms of acinar cell injury in
acute pancreatitis. Scand J Surg. 94:89–96. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, Geenen JE,
Russell RC, Meyers WC, Liqoury C and Nickl N: Endoscopic
sphincterotomy complications and their management: An attempt at
consensus. Gastrointest Endosc. 37:383–393. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Winslet M, Hall C, London NJ and
Neoptolemos JP: Relation of diagnostic serum amylase levels to
aetiology and severity of acute pancreatitis. Gut. 33:982–986.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tietz NW and Shuey DF: Lipase in serum-the
elusive enzyme: An overview. Clin Chem. 39:746–756. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Montecucco F, Mach F, Lenglet S, Vonlaufen
A, Gomes Quinderé AL, Pelli G, Burger F, Galan K, Dallegri F,
Carbone F, et al: Treatment with Evasin-3 abrogates
neutrphil-mediated inflammation in mouse acute pancreatitis. Eur J
Clin Invest. 44:940–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Merza M, Hartman H, Rahman M, Hwaiz R,
Zhang E, Renström E, Luo L, Mörgelin M, Regner S and Thorlacius H:
Neutrophil extracellular traps induce trypsin activation,
inflammation, and tissue damage in mice with severe acute
pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 149:1920–1931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C
and Jaillon S: Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of
innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:519–531. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang ZW, Meng XX and Xu P: Central role of
neutrophil in the pathogenesis of severe acute pancreatitis. J Cell
Mol Med. 19:2513–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sandoval D, Gukovskaya A, Reavey P,
Gukovsky S, Sisk A, Braquet P, Pandol SJ and Poucell-Hatton S: The
role of neutrophils and platelet-activating factor in mediating
experimental pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 111:1081–1091. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
El-Menyar A, Thani E, Zakaria A, Zarour A,
Tuma M, AbdulRahman H, Parchani A, Peralta R and Latifi R: Multiple
organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS): Is it preventable or inevitable.
Int J Clin Med. 3:722–730. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Elder AS, Saccone GT and Dixon DL: Lung
injury in acute pancreatitis: Mechanisms underlying augmented
secondary injury. Pancreatology. 12:49–56. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shields CJ, Winter DC and Redmond HP: Lung
injury in acute pancreatitis: Mechanisms, prevention, and therapy.
Curr Opin Crit Care. 8:158–163. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E,
Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, Stern EJ and Hudson LD: Incidence and
outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 353:1685–1693. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
van Westerloo DJ, Schultz MJ, Bruno MJ, de
Vos AF, Florquin S and van der Poll T: Acute pancreatitis in mice
impairs bacterial clearance from the lungs, whereas concurrent
pneumonia prolongs the course of pancreatitis. Crit Care Med.
32:1997–2001. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou MT, Chen CS, Chen BC, Zhang QY and
Andersson R: Acute lung injury and ARDS in acute pancreatitis:
Mechanisms and potential intervention. World J Gastroenterology.
16:2094–2099. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Aeffner F, Bolon B and Davis IC: Mouse
models of acute respiratory distress syndrome: A review of
analytical approaches, pathologic features, and common
measurements. Toxicol Pathol. 43:1074–1092. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jaffray C, Yang J and Norman J: Elastase
mimics pancreatitis-induced hepatic injury via inflammatory
mediators. J Surg Res. 90:95–101. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee WL and Downey GP: Neutrophil
activation and acute lung injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 7:1–7. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lopez-Font I, Gea-Sorlí S, de-Madaria E,
Gutiérrez LM, Pérez-Mateo M and Closa D: Pancreatic and pulmonary
mast cells activation during experimental acute pancreatitis. World
J Gastroenterol. 16:3411–3417. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fritz S, Hackert T, Hartwig W, Rossmanith
F, Strobel O, Schneider L, Will-Schweiger K, Kommerell M, Büchler
MW and Werner J: Bacterial translocation and infected pancreatic
necrosis in acute necrotizing pancreatitis derives from small bowel
rather than from colon. Am J Surg. 200:111–117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Matull WR, Pereira SP and O'donohue JW:
Biochemical markers of acute pancreatitis. J Clin Pathol.
59:340–344. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ma P, Zhang S, Su X, Qiu G and Wu Z:
Protective effects of icariin on cisplatin-induced acute renal
injury in mice. Am J Transl Res. 7:2105–2014. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Arthur JS and Ley SC: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:679–692.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|