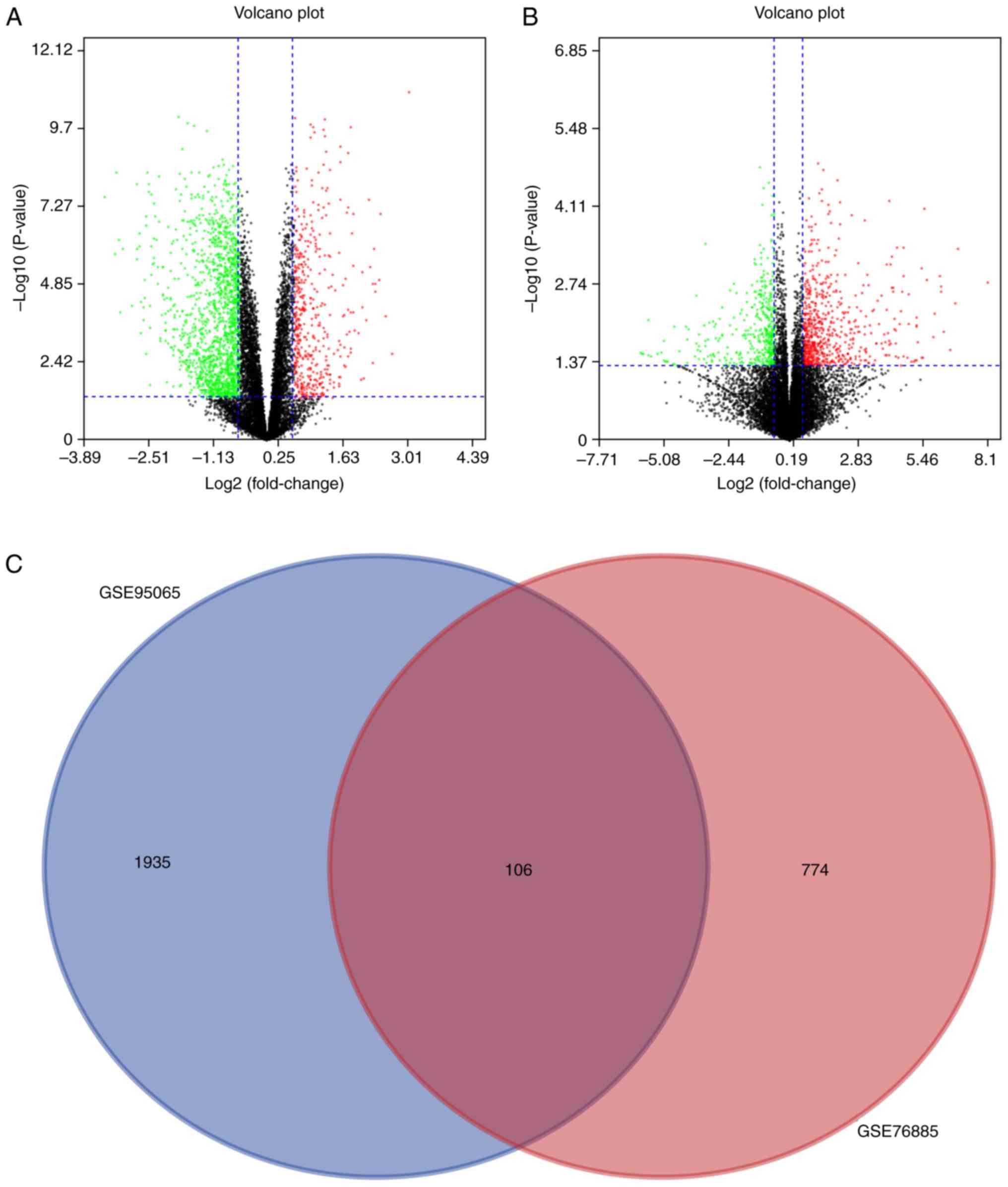
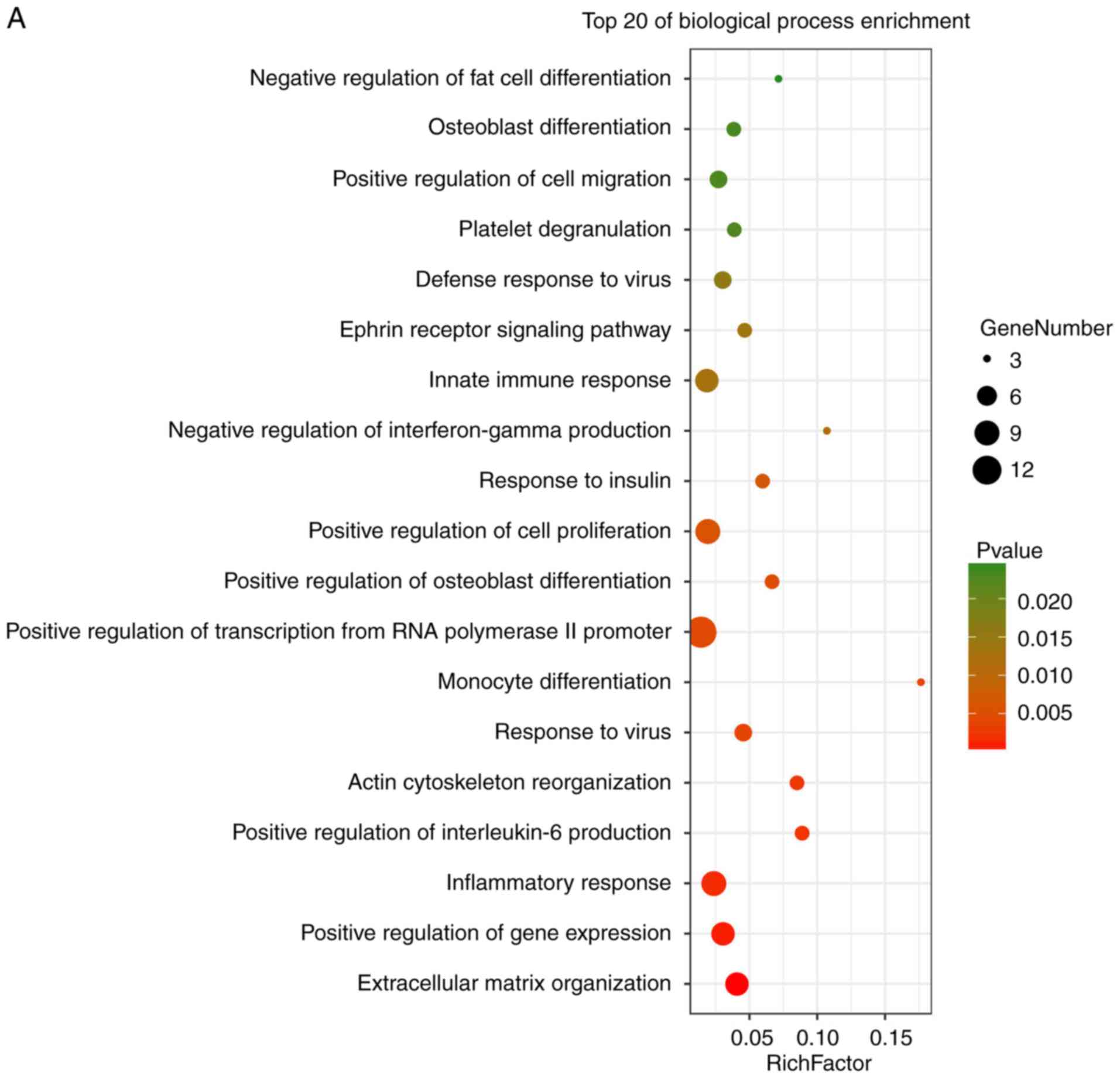
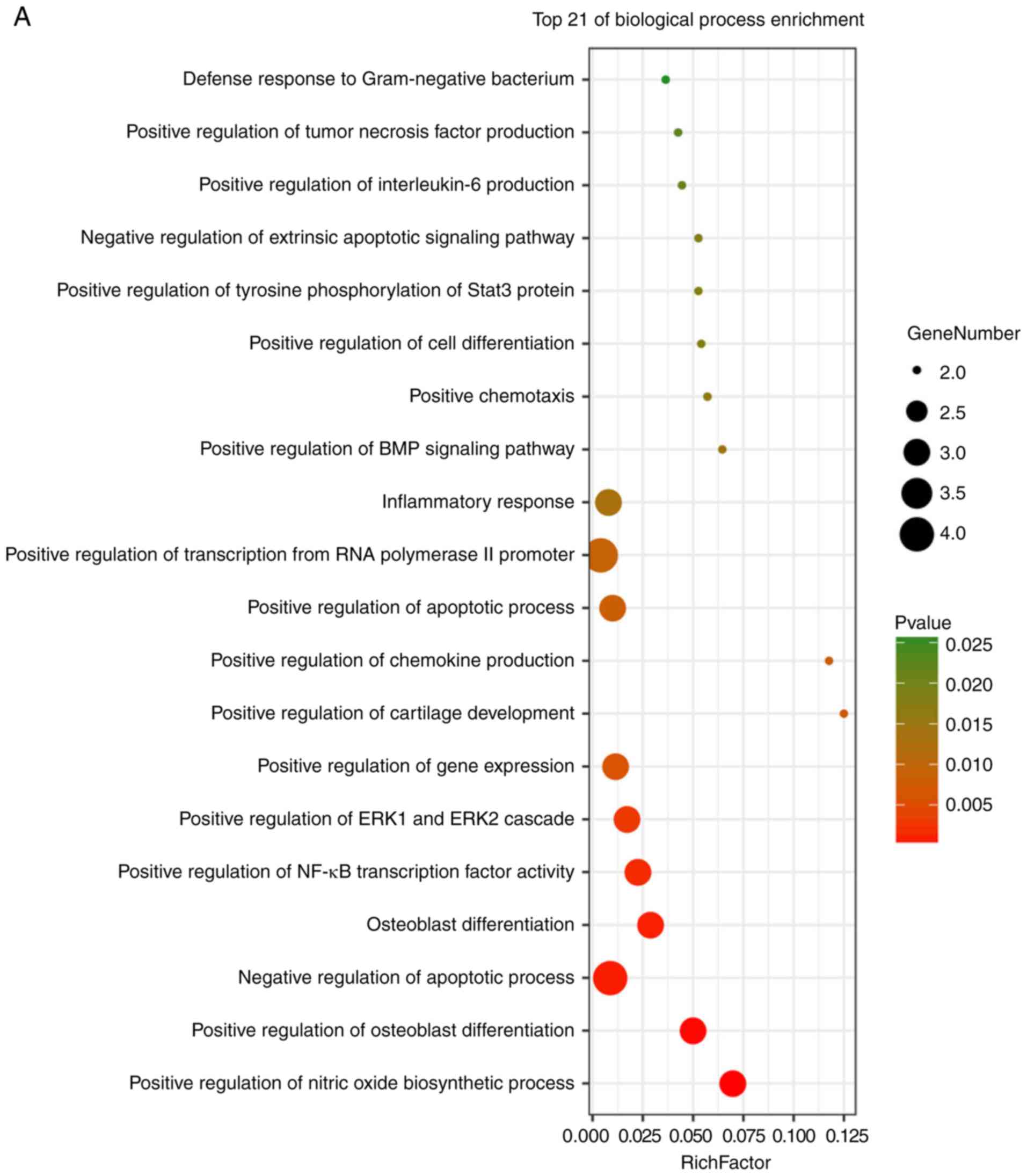
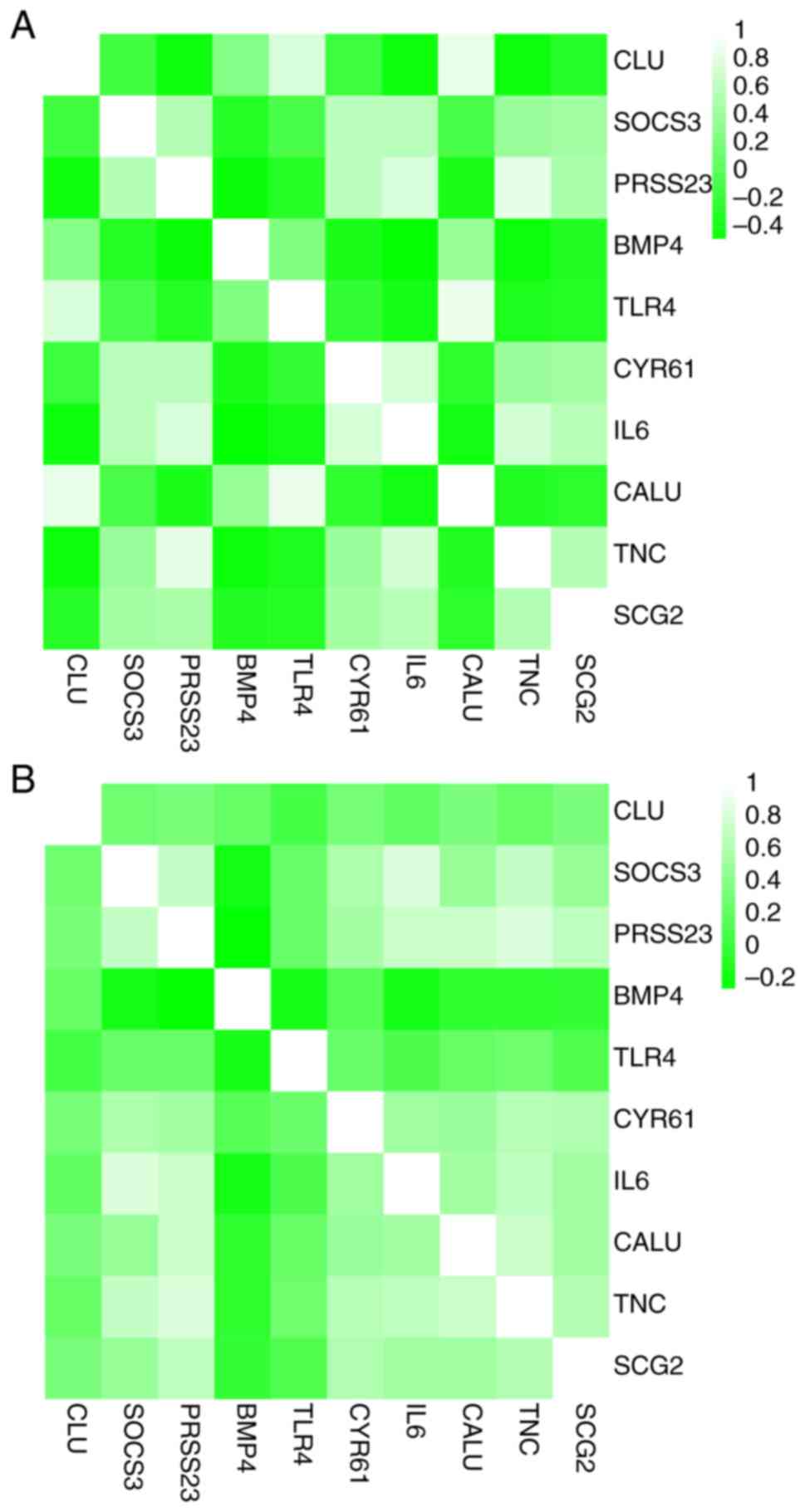
|
1
|
Denton CP and Khanna D: Systemic
sclerosis. Lancet. 390:1685–1699. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chifflot H, Fautrel B, Sordet C, Chatelus
E and Sibilia J: Incidence and prevalence of systemic sclerosis: A
systematic literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 37:223–235.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nihtyanova SI, Tang EC, Coghlan JG, Wells
AU, Black CM and Denton CP: Improved survival in systemic sclerosis
is associated with better ascertainment of internal organ disease:
A retrospective cohort study. QJM. 103:109–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, Airo P,
Cozzi F, Carreira PE, Bancel DF, Allanore Y, Muller-Ladner U,
Distler O, et al: Causes and risk factors for death in systemic
sclerosis: A study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research
(EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:1809–1815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bossini-Castillo L, Lopez-Isac E, Mayes MD
and Martin J: Genetics of systemic sclerosis. Semin Immunopathol.
37:443–451. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Salazar G and Mayes MD: Genetics,
epigenetics, and genomics of systemic sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin
North Am. 41:345–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Derrett-Smith EC, Martyanov V, Chighizola
CB, Moinzadeh P, Campochiaro C, Khan K, Wood TA, Meroni PL, Abraham
DJ, Ong VH, et al: Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis skin
demonstrates distinct molecular subsets separated by a
cardiovascular development gene expression signature. Arthritis Res
Ther. 19:1562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gardner H, Shearstone JR, Bandaru R,
Crowell T, Lynes M, Trojanowska M, Pannu J, Smith E, Jablonska S,
Blaszczyk M, et al: Gene profiling of scleroderma skin reveals
robust signatures of disease that are imperfectly reflected in the
transcript profiles of explanted fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum.
54:1961–1973. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chouri E, Servaas NH, Bekker CPJ, Affandi
AJ, Cossu M, Hillen MR, Angiolilli C, Mertens JS, van den Hoogen
LL, Silva-Cardoso S, et al: Serum microRNA screening and functional
studies reveal miR-483-5p as a potential driver of fibrosis in
systemic sclerosis. J Autoimmun. 89:162–170. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Falzone L, Scola L, Zanghi A, Biondi A, Di
Cataldo A, Libra M and Candido S: Integrated analysis of colorectal
cancer microRNA datasets: Identification of microRNAs associated
with tumor development. Aging (Albany NY). 10:1000–1014. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Falzone L, Candido S, Salemi R, Basile MS,
Scalisi A, McCubrey JA, Torino F, Signorelli SS, Montella M and
Libra M: Computational identification of microRNAs associated to
both epithelial to mesenchymal transition and NGAL/MMP-9 pathways
in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 7:72758–72766. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hafsi S, Candido S, Maestro R, Falzone L,
Soua Z, Bonavida B, Spandidos DA and Libra M: Correlation between
the overexpression of Yin Yang 1 and the expression levels of
miRNAs in Burkitt's lymphoma: A computational study. Oncol Lett.
11:1021–1025. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Falzone L, Lupo G, La Rosa GRM, Crimi S,
Anfuso CD, Salemi R, Rapisarda E, Libra M and Candido S:
Identification of novel MicroRNAs and their diagnostic and
prognostic significance in oral cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11. pp.
E6102019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:Database Issue.
pp. D991–D995. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Edgar R, Domrachev M and Lash AE: Gene
Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array
data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:207–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Sun YH, Xie M, Wu SD, Zhang J and Huang
CZ: Identification and interaction analysis of key genes and
MicroRNAs in systemic sclerosis by bioinformatics approaches. Curr
Med Sci. 39:645–652. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:pp. e472015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Young A and Khanna D: Systemic sclerosis:
A systematic review on therapeutic management from 2011 to 2014.
Curr Opin Rheumatol. 27:241–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Elhai M, Avouac J, Kahan A and Allanore Y:
Systemic sclerosis: Recent insights. Joint Bone Spine. 82:148–153.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takahashi T, Asano Y, Ichimura Y, Toyama
T, Taniguchi T, Noda S, Akamata K, Tada Y, Sugaya M, Kadono T and
Sato S: Amelioration of tissue fibrosis by toll-like receptor 4
knockout in murine models of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 67:254–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bhattacharyya S, Kelley K, Melichian DS,
Tamaki Z, Fang F, Su Y, Feng G, Pope RM, Budinger GR, Mutlu GM, et
al: Toll-like receptor 4 signaling augments transforming growth
factor-β responses: A novel mechanism for maintaining and
amplifying fibrosis in scleroderma. Am J Pathol. 182:192–205. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Fineschi S, Goffin L, Rezzonico R, Cozzi
F, Dayer JM, Meroni PL and Chizzolini C: Antifibroblast antibodies
in systemic sclerosis induce fibroblasts to produce profibrotic
chemokines, with partial exploitation of toll-like receptor 4.
Arthritis Rheum. 58:3913–3923. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Molteni M, Gemma S and Rossetti C: The
role of Toll-like receptor 4 in infectious and noninfectious
inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2016.6978936:2016.
|
|
28
|
Barton GM and Medzhitov R: Toll-like
receptor signaling pathways. Science. 300:1524–1525. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bhattacharyya S and Varga J: Endogenous
ligands of TLR4 promote unresolving tissue fibrosis: Implications
for systemic sclerosis and its targeted therapy. Immunol Lett.
195:9–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Bhattacharyya S, Midwood KS, Yin H and
Varga J: Toll-like receptor-4 signaling drives persistent
fibroblast activation and prevents fibrosis resolution in
scleroderma. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 6:356–369. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bhattacharyya S, Wang W, Morales-Nebreda
L, Feng G, Wu M, Zhou X, Lafyatis R, Lee J, Hinchcliff M,
Feghali-Bostwick C, et al: Tenascin-C drives persistence of organ
fibrosis. Nat Commun. 7:117032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stifano G, Affandi AJ, Mathes AL, Rice LM,
Nakerakanti S, Nazari B, Lee J, Christmann RB and Lafyatis R:
Chronic Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation in skin induces
inflammation, macrophage activation, transforming growth factor
beta signature gene expression, and fibrosis. Arthritis Res Ther.
16:R1362014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang HZ, Wang JP, Mi S, Liu HZ, Cui B, Yan
HM, Yan J, Li Z, Liu H, Hua F, et al: TLR4 activity is required in
the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis after acute
and chronic lung injury. Am J Pathol. 180:275–292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T,
Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL and Kuchroo VK: Reciprocal
developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector
TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 441:235–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mangan PR, Harrington LE, O'Quinn DB,
Helms WS, Bullard DC, Elson CO, Hatton RD, Wahl SM, Schoeb TR and
Weaver CT: Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of
the T(H)17 lineage. Nature. 441:231–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Koch AE, Kronfeld-Harrington LB, Szekanecz
Z, Cho MM, Haines GK, Harlow LA, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Massa MC,
Barr WG, et al: In situ expression of cytokines and cellular
adhesion molecules in the skin of patients with systemic sclerosis.
Their role in early and late disease. Pathobiology. 61:239–246.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kawaguchi Y, Hara M and Wright TM:
Endogenous IL-1alpha from systemic sclerosis fibroblasts induces
IL-6 and PDGF-A. J Clin Invest. 103:1253–1260. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kitaba S, Murota H, Terao M, Azukizawa H,
Terabe F, Shima Y, Fujimoto M, Tanaka T, Naka T, Kishimoto T and
Katayama I: Blockade of interleukin-6 receptor alleviates disease
in mouse model of scleroderma. Am J Pathol. 180:165–176. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sato S, Hasegawa M and Takehara K: Serum
levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 correlate with total
skin thickness score in patients with systemic sclerosis. J
Dermatol Sci. 27:140–146. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gudbjörnsson B, Hällgren R, Nettelbladt O,
Gustafsson R, Mattsson A, af Geijerstam E and Totterman TH:
Phenotypic and functional activation of alveolar macrophages, T
lymphocytes and NK cells in patients with systemic sclerosis and
primary Sjogren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 53:574–579. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Khanna D, Denton CP, Jahreis A, van Laar
JM, Frech TM, Anderson ME, Baron M, Chung L, Fierlbeck G,
Lakshminarayanan S, et al: Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous
tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (faSScinate): A phase
2, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 387:2630–2640. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Taniguchi T, Asano Y, Fukasawa T,
Yoshizaki A and Sato S: Critical contribution of the
interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
axis to vasculopathy associated with systemic sclerosis. J
Dermatol. 44:967–971. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Honore B and Vorum H: The CREC family, a
novel family of multiple EF-hand, low-affinity Ca(2+)-binding
proteins localised to the secretory pathway of mammalian cells.
FEBS Lett. 466:11–18. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vorum H, Liu X, Madsen P, Rasmussen HH and
Honore B: Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding human calumenin,
expression in Escherichia coli and analysis of its Ca2+-binding
activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1386:121–131. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nimmrich I, Erdmann S, Melchers U, Finke
U, Hentsch S, Moyer MP, Hoffmann I and Muller O: Seven genes that
are differentially transcribed in colorectal tumor cell lines.
Cancer Lett. 160:37–43. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nagano K, Imai S, Zhao X, Yamashita T,
Yoshioka Y, Abe Y, Mukai Y, Kamada H, Nakagawa S, Tsutsumi Y and
Tsunoda S: Identification and evaluation of metastasis-related
proteins, oxys-terol binding protein-like 5 and calumenin, in lung
tumors. Int J Oncol. 47:195–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang Q, Shen B, Chen L, Zheng P, Feng H,
Hao Q, Liu X, Liu L, Xu S, Chen J and Teng J: Extracellular
calumenin suppresses ERK1/2 signaling and cell migration by
protecting fibulin-1 from MMP-13-mediated proteolysis. Oncogene.
34:1006–1018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Vorum H, Jacobsen C and Honore B:
Calumenin interacts with serum amyloid P component. FEBS Lett.
465:129–134. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Miyakoshi K, Murphy MJ, Yeoman RR, Mitra
S, Dubay CJ and Hennebold JD: The identification of novel ovarian
proteases through the use of genomic and bioinformatic
methodologies. Biol Reprod. 75:823–835. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|