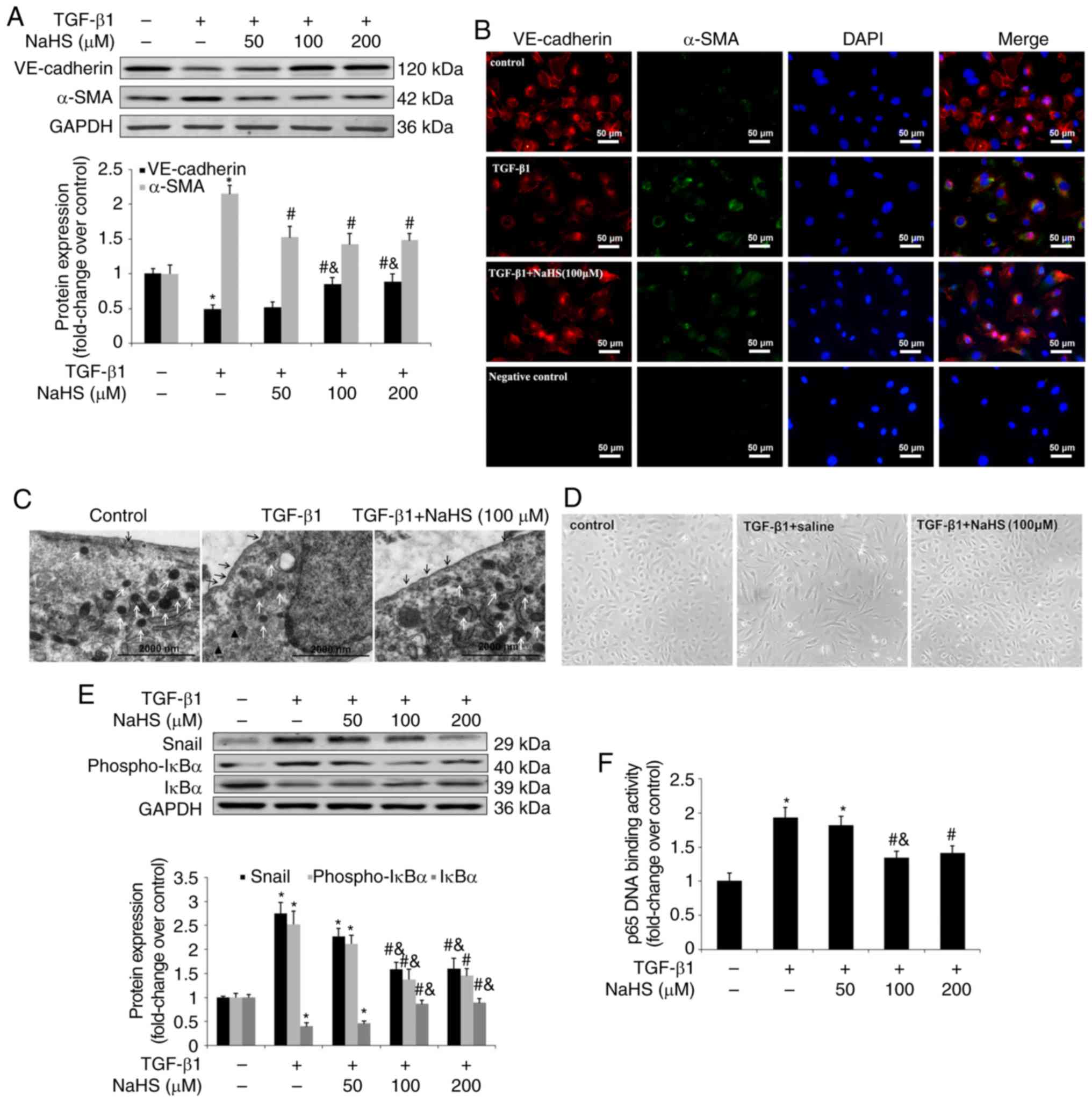
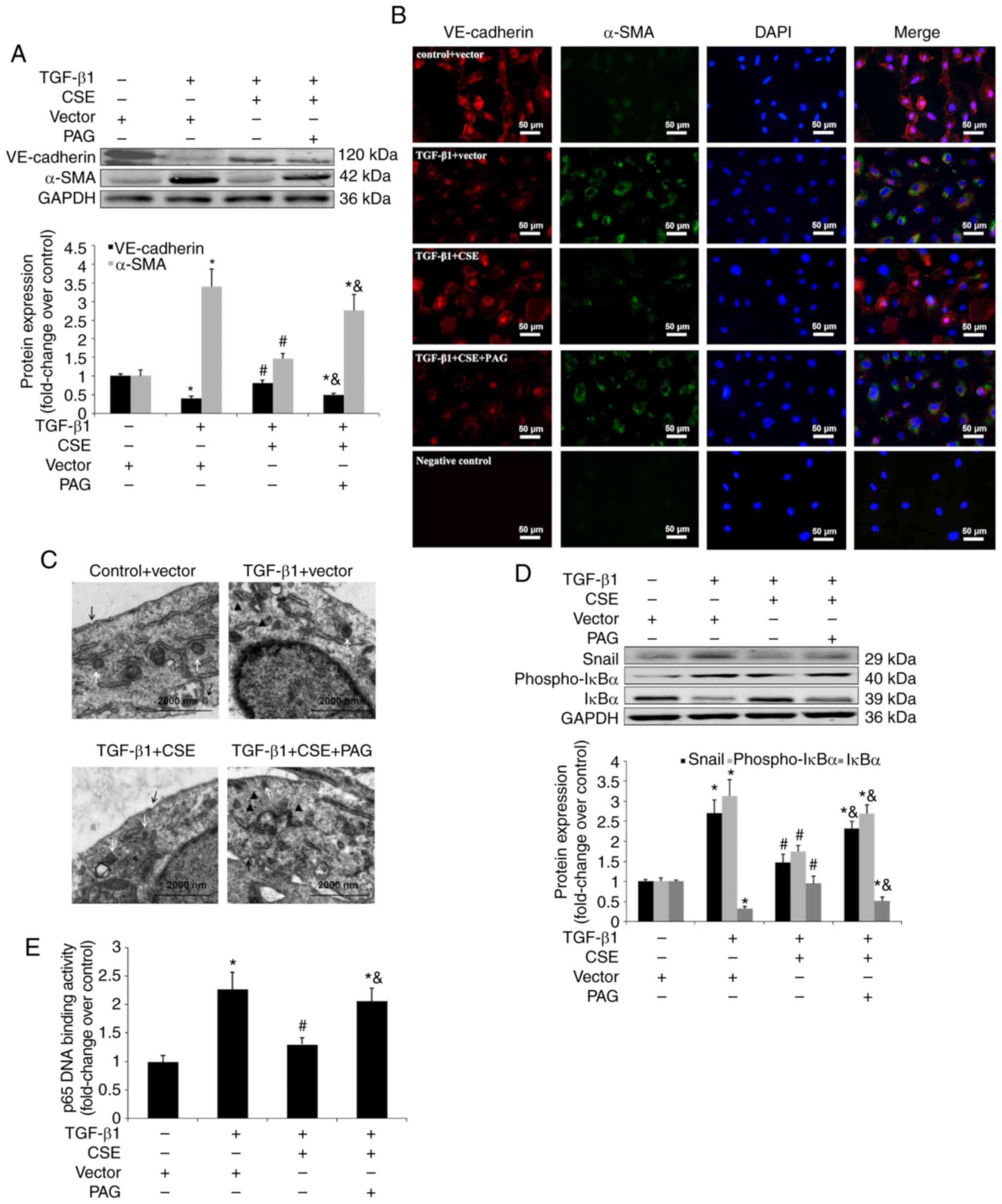
|
1
|
Goumans MJ, van Zonneveld AJ and ten Dijke
P: Transforming growth factor beta-induced
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: A switch to cardiacfibrosis?
Trends Cardiovasc Med. 18:293–298. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Willis BC and Borok Z: TGF-beta-induced
EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L525–L534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeisberg EM, Potenta SE, Sugimoto H,
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: Fibroblasts in kidney fibrosis emerge via
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:2282–2287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M,
Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E, Chandraker A, Yuan X, Pu WT,
Roberts AB, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:952–961. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Arciniegas E, Frid MG, Douglas IS and
Stenmark KR: Perspectives onendothelial-to-mesenchymal transition:
Potential contribution to vascular remodeling in chronic pulmonary
hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L1–L8. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hopper RK, Moonen JR, Diebold I, Cao A,
Rhodes CJ, Tojais NF, Hennigs JK, Gu M, Wang L and Rabinovitch M:
In pulmonary arterial hypertension, reduced BMPR2 promotes
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition via HMGA1 and its target
slug. Circulation. 133:1783–1794. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ranchoux B, Antigny F, Rucker-Martin C,
Hautefort A, Péchoux C, Bogaard HJ, Dorfmüller P, Remy S, Lecerf F,
Planté S, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary
hypertension. Circulation. 131:1006–1018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lefer DJ: A new gaseous signaling molecule
emerges: Cardioprotective role of hydrogen sulfide. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 104:17907–17908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Elsey DJ, Fowkes RC and Baxter GF:
Regulation of cardiovascular cell function by hydrogen sulfide
(H2S). Cell Biochem Funct. 28:95–106. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tang C, Li X and Du J: Hydrogen sulfide as
a new endogenous gaseous transmitter in the cardiovascular system.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 4:17–22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hongfang J, Cong Bailin, Bin Zhao, Zhang
Chunyu, Xinmin Liu, Weijin Zhou, Ying Shi, Tang Chaoshu and Junbao
D: Effects of hydrogen sulfide on hypoxic pulmonary vascular
structural remodeling. Life Sci. 78:1299–1309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li X, Du J, Jin H, Tang X, Bu D and Tang
C: The regulatory effect of endogenous hydrogen sulfide on
pulmonary vascular structure and gasotransmitters in rats with high
pulmonary blood flow. Life Sci. 81:841–849. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li X, Du J, Jin H, Geng B and Tang C:
Sodium hydrosul-fide alleviates pulmonary artery collagen
remodeling in rats with high pulmonary blood flow. Heart Vessels.
23:409–419. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo L, Liu D, Tang C, Du J, Liu AD,
Holmberg L and Jin H: Sulfur dioxide upregulates the inhibited
endogenous hydrogen sulfide pathway in rats with pulmonary
hypertension induced by high pulmonary blood flow. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 433:519–525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stenmark KR, Meyrick B, Galie N, Mooi WJ
and McMurtry IF: Animal models of pulmonary arterial hypertension:
The hope for etiological discovery and pharmacological cure. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L1013–L1032. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang H, Guo C, Wu D, Zhang A, Gu T, Wang
L and Wang C: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits the development of
atherosclerosis with suppressing CX3CR1 and CX3CL1 expression. PLoS
One. 7:e411472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin Y, Zeng H, Gao L, Gu T, Wang C and
Zhang H: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates atherosclerosis in a partially
ligated carotid artery mouse model via regulating angiotensin
converting enzyme 2 expression. Front Physiol. 8:7822017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barberà MJ, Puig I, Domínguez D,
Julien-Grille S, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Peiró S, Baulida J, Francí C,
Dedhar S, Larue L and García de Herreros A: Regulation of Snail
transcription during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor
cells. Oncogene. 23:7345–7354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J, García De and Herreros A: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumor cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Julien S, Puig I, Caretti E, Bonaventure
J, Nelles L, van Roy F, Dargemont C, de Herreros AG, Bellacosa A
and Larue L: Activation of NF-kappaB by Akt upregulates Snail
expression and induces epithelium mesenchyme transition. Oncogene.
26:7445–7456. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nikitopoulou I, Orfanos SE, Kotanidou A,
Maltabe V, Manitsopoulos N, Karras P, Kouklis P, Armaganidis A and
Maniatis NA: Vascular endothelial-cadherin downregulation as a
feature of endothelial transdifferentiation in
monocrota-line-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 311:L352–L363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Long L, Crosby A, Yang X, Southwood M,
Upton PD, Kim DK and Morrell NW: Altered bone morphogenetic protein
and transforming growth factor-beta signaling in rat models of
pulmonary hypertension: Potential for activin receptor-like
kinase-5 inhibition in prevention and progression of disease.
Circulation. 119:566–576. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zakrzewicz A, Kouri FM, Nejman B,
Kwapiszewska G, Hecker M, Sandu R, Dony E, Seeger W, Schermuly RT,
Eickelberg O and Morty RE: The transforming growth
factor-beta/Smad2,3 signaling axis is impaired in experimental
pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 29:1094–1104. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reynolds AM, Holmes MD, Danilov SM and
Reynolds PN: Targeted gene delivery of BMPR2 attenuates pulmonary
hypertension. Eur Respir J. 39:329–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Frid MG, Kale VA and Stenmark KR: Mature
vascular endothelium can give rise to smooth muscle cells via
endothe-lial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation: In vitro analysis.
Circ Res. 90:1189–1196. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fan HN, Wang HJ, Ren L, Ren B, Dan CR, Li
YF, Hou LZ and Deng Y: Decreased expression of p38 MAPK mediates
protective effects of hydrogen sulfide on hepatic fibrosis. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:644–652. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fang L, Li H, Tang C, Geng B, Qi Y and Liu
X: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates the pathogenesis of pulmonary
fibrosis induced by bleomycin in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
87:531–538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jung KJ, Jang HS, Kim JI, Han SJ, Park JW
and Park KM: Involvement of hydrogen sulfide and homocysteine
transsulfuration pathway in the progression of kidney fibrosis
after ureteral obstruction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:1989–1997.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang Y, Zhang Z, Huang Y, Mao Z, Yang X,
Nakamura Y, Sawada N, Mitsui T, Takeda M and Yao J: Induction of
inactive TGF-β1 monomer formation by hydrogen sulfide contributes
to its suppressive effects on Ang II- and TGF-β1-induced EMT in
renal tubular epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
501:534–540. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo L, Peng W, Tao J, Lan Z, Hei H, Tian
L, Pan W, Wang L and Zhang X: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits
transforming growth factor-β1-induced EMT via Wnt/Catenin pathway.
PLoS One. 11:e01470182016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lv M, Li Y, Ji MH, Zhuang M and Tang JH:
Inhibition of invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
human breast cancer cells by hydrogen sulfide through decreased
phospho-p38 expression. Mol Med Rep. 10:341–346. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pan Y, Zhou C, Yuan D, Zhang J and Shao C:
Radiation exposure promotes hepatocarcinoma cell invasion through
epithelial mesenchymal transition mediated by H2S/CSE
pathway. Radiat Res. 185:96–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ying R, Wang XQ, Yang Y, Gu ZJ, Mai JT,
Qiu Q, Chen YX and Wang JF: Hydrogen sulfide suppresses endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
through Src pathway. Life Sci. 144:208–217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang D, Du J, Tang C, Huang Y and Jin H:
H2S-induced sulf-hydration: Biological function and
detection methodology. Front Pharmacol. 8:6082017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cheng S, Lu Y, Li Y, Gao L, Shen H and
Song K: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in peritoneal mesothelial cells. Sci Rep. 8:58632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fang LP, Lin Q, Tang CS and Liu XM:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
human alveolar epithelial cells. Pharmacol Res. 61:298–305. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|