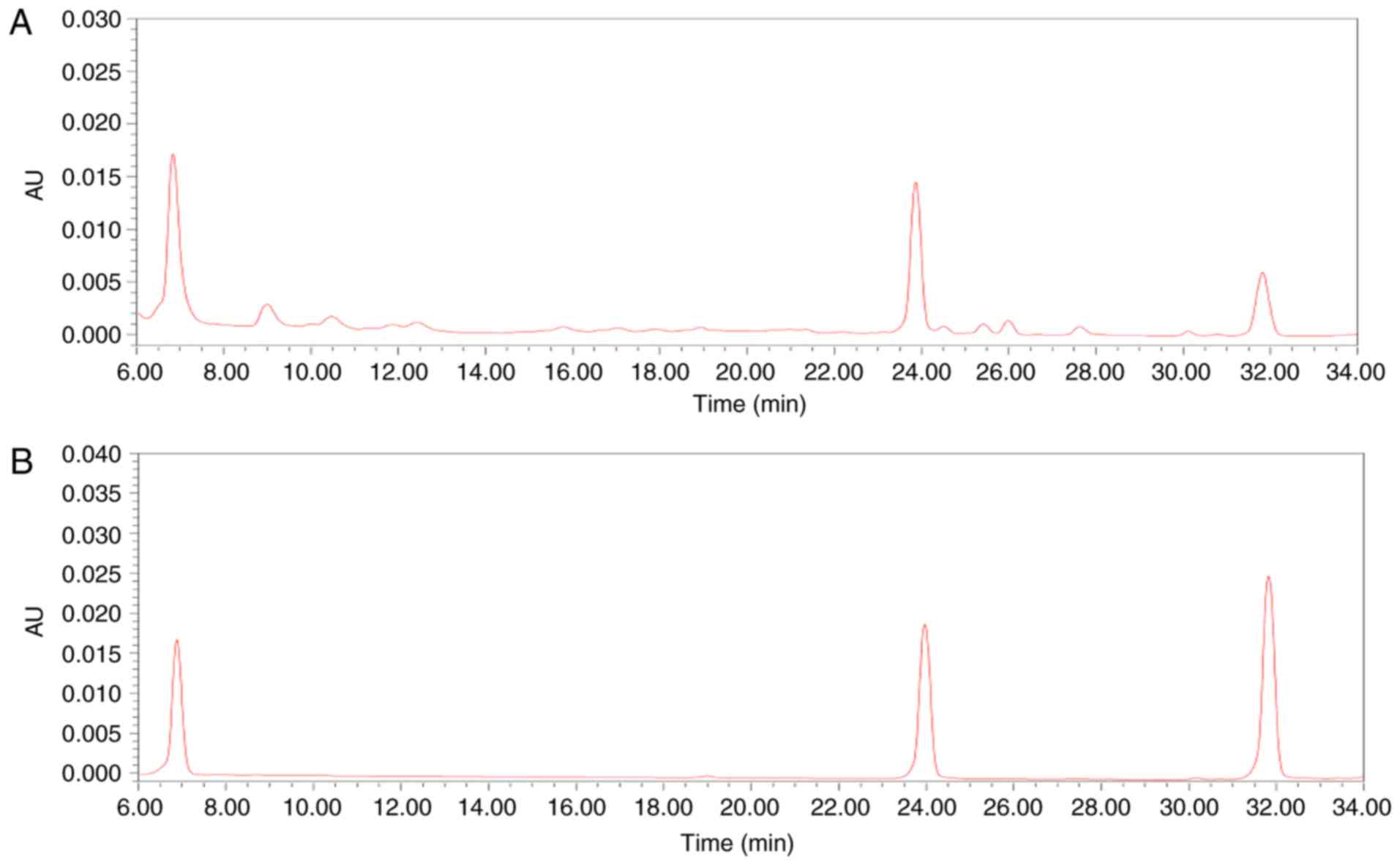
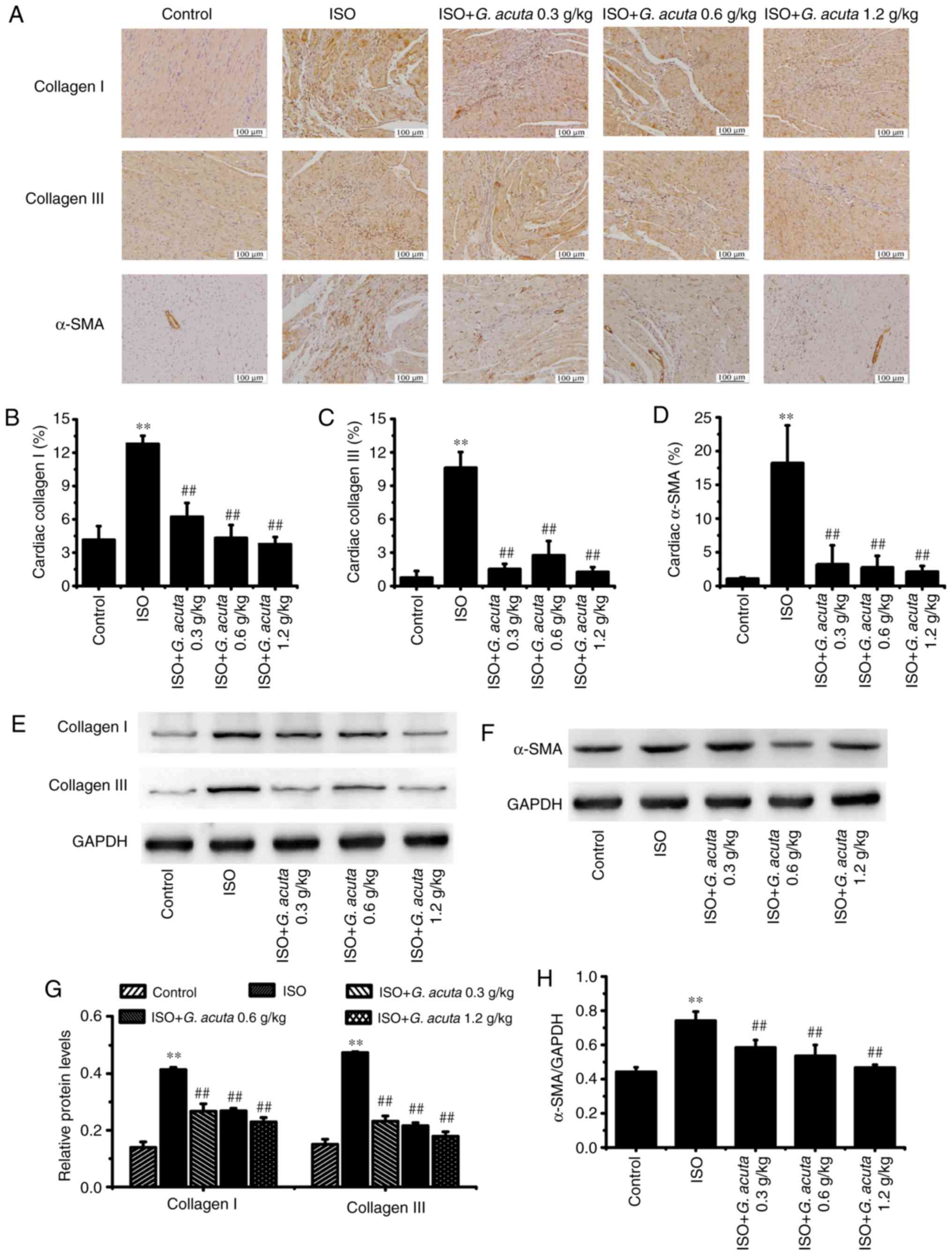
|
1
|
Masci PG, Schuurman R, Andrea B, Ripoli A,
Coceani M, Chiappino S, Todiere G, Srebot V, Passino C, Aquaro GD,
et al: Myocardial fibrosis as a key determinant of left ventricular
remodeling in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: A
contrast-enhanced cardiovascular magnetic study. Circ Cardiovasc
Imaging. 6:790–799. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dixon JA and Spinale FG: Pathophysiology
of myocardial injury and remodeling: Implications for molecular
imaging. J Nucl Med. 51(Suppl3r 1): 102S–106S. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li L, Zhao Q and Kong W: Extracellular
matrix remodeling and cardiac fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 68-69:490–506.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Frangogiannis NG: Cardiac fibrosis: Cell
biological mechanisms, molecular pathways and therapeutic
opportunities. Mol Aspects Med. 65:70–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Czubryt MP: Common threads in cardiac
fibrosis, infarct scar formation, and wound healing. Fibrogenesis
Tissue Repair. 5:192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meyers TA and Townsend D: Early right
ventricular fibrosis and reduction in biventricular cardiac reserve
in the dystrophin-deficient mdx heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 308:H303–H315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Raman B, Ariga R, Spartera M,
Sivalokanathan S, Chan K, Dass S, Petersen SE, Daniels MJ, Francis
J, Smillie R, et al: Progression of myocardial fibrosis in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and clinical implications.
Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 20:157–167. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Goumans MJ and Ten Dijke P: TGF-β
signaling in control of cardiovascular function. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 10:a0222102018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yue Y, Meng K, Pu Y and Zhang X:
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) mediates cardiac fibrosis
and induces diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
133:124–130. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G,
Vaziri ND and Zhao YY: New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in
tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 292:76–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leask A: Potential therapeutic targets for
cardiac fibrosis: TGFbeta, angiotensin, endothelin, CCN2, and PDGF,
partners in fibroblast activation. Circ Res. 106:1675–1680. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gyorfi AH, Matei AE and Distler JHW:
Targeting TGF-β signaling for the treatment of fibrosis. Matrix
Biol. 68-69:8–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wunir, Chunliang and Khasbagan: Ewenki
folk medicinal plants and its comparison with Mongolian medicine.
Chin J Ethnomed Ethnopharm. 18:156–158. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, Ni Y, Ruan J, Qu L, Yu H, Han L,
Zhang Y and Wang T: Bioactive gentixanthone and gentichromone from
the whole plants of Gentianella acuta (Michx.) Hulten. Fitoterapia.
113:164–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Wu G, Liu H, Xing N, Sun Y, Zhai
Y, Yang B, Kong AT, Kuang H and Wang Q: Cardioprotective effect of
the xanthones from Gentianella acuta against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart. Biomed
Pharmacother. 93:626–635. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Wu G, Yu Y, Liu H, Yang B, Kuang H
and Wang Q: Xanthones isolated from Gentianella acuta and their
protective effects against H2O2-induced
myocardial cell injury. Nat Prod Res. 32:2171–2177. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yu Y, Wang ZB, Zhai YD, Song PY, Wang QH,
Yang BY and Kuang H: Lignan glycosides from Gentianella acuta
(Michx.) Hulten and their protective effects against
H2O2-induced apop-tosis in H9c2
cardiomyoblast. Rec Nat Prod. 8:234–241. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Li AY, Wang JJ, Yang SC, Zhao YS, Li JR,
Liu Y, Sun JH, An LP, Guan P and Ji ES: Protective role of
Gentianella acuta on isoprenaline induced myocardial fibrosis in
rats via inhibition of NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
110:733–741. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu SY, Bian RL and Chen X: Experimental
methodology of pharmacology. People's Medical Publishing House;
Beijing: 1982
|
|
20
|
Blanchard OL and Smoliga JM: Translating
dosages from animal models to human clinical trials-revisiting body
surface area scaling. FASEB J. 29:1629–1634. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou H, Chen X, Chen L, Zhou X, Zheng G,
Zhang H, Huang W and Cai J: Anti-fibrosis effect of scutellarin via
inhibition of endothelial-mesenchymal transition on
isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in rats. Molecules.
19:15611–15623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wan Y, Xu L, Wang Y, Tuerdi N, Ye M and Qi
R: Preventive effects of astragaloside IV and its active sapogenin
cycloas-tragenol on cardiac fibrosis of mice by inhibiting the
NLRP3 inflammasome. Eur J Pharmacol. 833:545–554. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen J, Zhan Y, Wang Y, Han D, Tao B, Luo
Z, Ma S, Wang Q, Li X, Fan L, et al: Chitosan/silk fibroin modified
nanofibrous patches with mesenchymal stem cells prevent heart
remodeling post-myocardial infarction in rats. Acta Biomater.
80:154–168. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Koga M, Kuramochi M, Karim MR, Izawa T,
Kuwamura M and Yamate J: Immunohistochemical characterization of
myofibro-blasts appearing in isoproterenol-induced rat myocardial
fibrosis. J Vet Med Sci. 81:127–133. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Daley WP and Yamada KM: ECM-modulated
cellular dynamics as a driving force for tissue morphogenesis. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 23:408–414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gyöngyösi M, Winkler J, Ramos I, Do QT,
Firat H, McDonald K, González A, Thum T, Díez J, Jaisser F, et al:
Myocardial fibrosis: Biomedical research from bench to bedside. Eur
J Heart Fail. 19:177–191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Voorhees AP and Han HC: Biomechanics of
cardiac function. Compr Physiol. 5:1623–1644. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nielsen SH, Mouton AJ, DeLeon-Pennell KY,
Genovese F, Karsdal M and Lindsey ML: Understanding cardiac
extracellular matrix remodeling to develop biomarkers of myocardial
infarction outcomes. Matrix Biol. 75-76:43–57. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN and Bobryshev
YV: The role of cardiac fibroblasts in post-myocardial heart tissue
repair. Exp Mol Pathol. 101:231–240. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van Putten S, Shafieyan Y and Hinz B:
Mechanical control of cardiac myofibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
93:133–142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gabbiani G: The myofibroblast in wound
healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J Pathol. 200:500–503. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dobaczewski M, Chen W and Frangogiannis
NG: Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac
remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 51:600–606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shinde AV, Humeres C and Frangogiannis NG:
The role of α-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix
contraction and remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1863:298–309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Luo K and Lodish HF: Positive and negative
regulation of type II TGF-beta receptor signal transduction by
autophosphorylation on multiple serine residues. EMBO J.
16:1970–1981. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li PF, He RH, Shi SB, Li R, Wang QT, Rao
GT and Yang B: Modulation of miR-10a-mediated TGF-β1/Smads
signaling affects atrial fibrillation-induced cardiac fibrosis and
cardiac fibroblast proliferation. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201819312019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Khalil H, Kanisicak O, Prasad V, Correll
RN, Fu X, Schips T, Vagnozzi RJ, Liu R, Huynh T, Lee SJ, et al:
Fibroblast-specific TGF-β-Smad2/3 signaling underlies cardiac
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 127:3770–3783. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Chu J, Yi P, Dong W, Saultz J,
Wang Y, Wang H, Scoville S, Zhang J, Wu LC, et al: SMAD4 promotes
TGF-β-independent NK cell homeostasis and maturation and antitumor
immunity. J Clin Invest. 128:5123–5136. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ding Z, Liu Y, Ruan J, Yang S, Yu H, Chen
M, Zhang Y and Wang T: Bioactive constituents from the whole plants
of Gentianella acuta (Michx.) Hulten. Molecules. 22:E13092017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Feng CY, Wu Q, Yin DD, Li B, Li SS, Tang
ZQ, Xu YJ and Wang LS: Determination of xanthones and flavonoids of
methanol extracts obtained from different parts of the plants of
three Gentianaceae species. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 161:455–463. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ren K, Su H, Lv LJ, Yi LT, Gong X, Dang
LS, Zhang RF and Li MH: Effects of four compounds from Gentianella
acuta (Michx.) Hulten on hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in H9c2
cells. Biomed Res Int. 2019:26929702019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Tungmunnithum D, Thongboonyou A, Pholboon
A and Yangsabai A: Flavonoids and other phenolic compounds from
medicinal plants for pharmaceutical and medical aspects: An
overview. Medicines (Basel). 5:E932018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hammad S, Cavalcanti E, Werle J, Caruso
ML, Dropmann A, Ignazzi A, Ebert MP, Dooley S and Giannelli G:
Galunisertib modifies the liver fibrotic composition in the Abcb4Ko
mouse model. Arch Toxicol. 92:2297–2309. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luangmonkong T, Suriguga S, Adhyatmika A,
Adlia A, Oosterhuis D, Suthisisang C, de Jong KP, Mutsaers HAM and
Olinga P: In vitro and ex vivo anti-fibrotic effects of LY2109761,
a small molecule inhibitor against TGF-β. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
355:127–137. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|