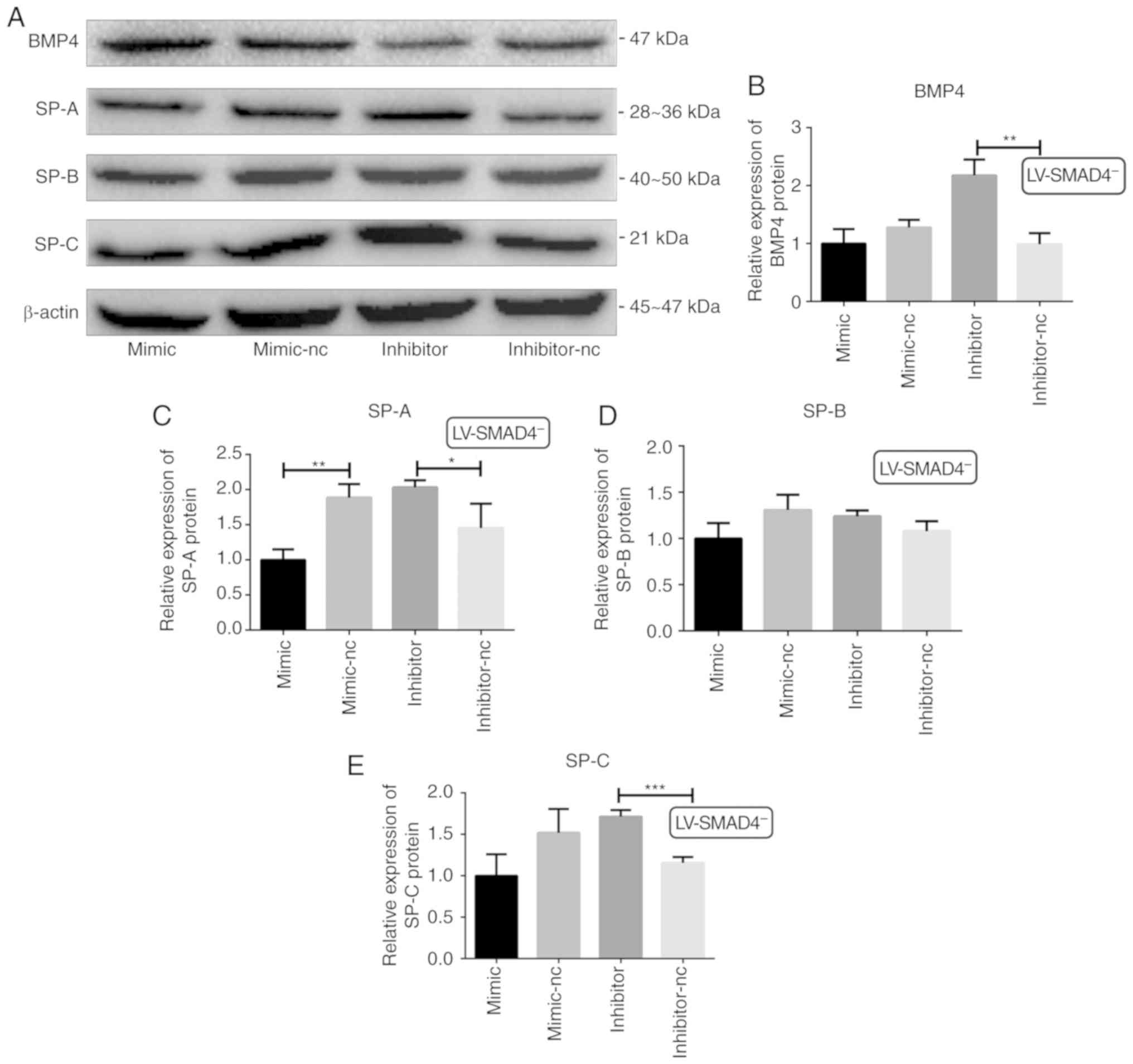
|
1
|
Condò V, Cipriani S, Colnaghi M, Bellù R,
Zanini R, Bulfoni C, Parazzini F and Mosca F: Neonatal respiratory
distress syndrome: Are risk factors the same in preterm and term
infants? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 30:1267–1272. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Volckaert T and De Langhe SP: Wnt and FGF
mediated epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk during lung development.
Dev Dyn. 244:342–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Colin AA, McEvoy C and Castile RG:
Respiratory morbidity and lung function in preterm infants of 32 to
36 weeks’ gestational age. Pediatrics. 126:115–128. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mahoney AD and Jain L: Respiratory
disorders in moderately preterm, late preterm, and early term
infants. Clin Perinatol. 40:665–678. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sweet DG, Carnielli V, Greisen G, Hallman
M, Ozek E, Plavka R, Saugstad OD, Simeoni U, Speer CP, Vento M, et
al: European consensus guidelines on the management of neonatal
respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants-2013 update.
Neonatology. 103:353–368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ameis D, Khoshgoo N, Iwasiow BM, Snarr P
and Keijzer R: MicroRNAs in lung development and disease. Paediatr
Respir Rev. 22:38–43. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Herriges M and Morrisey EE: Lung
development: Orchestrating the generation and regeneration of a
complex organ. Development. 141:502–513. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kan Q, Ding S, Yang Y and Zhou X:
Expression profile of plasma microRNAs in premature infants with
respiratory distress syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 12:2858–2864. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun ZY, Shen YQ, Chen XQ, Zhou XY, Cheng
R, Bao ZD and Yang Y: Expression and potential regulation of
miRNA-431 during lung development of Sprague-Dawley rats. Mol Med
Rep. 19:4980–4988. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu J, Wang Y, Liu G, Jia Y, Yang J, Shi J,
Dong J, Wei J and Liu X: Characterization of air-liquid interface
culture of A549 alveolar epithelial cells. Braz J Med Biol Res.
51:e69502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grek CL, Newton DA, Qiu Y, Wen X,
Spyropoulos DD and Baatz JE: Characterization of alveolar
epithelial cells cultured in semipermeable hollow fibers. Exp Lung
Res. 35:155–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ryndak MB, Singh KK, Peng Z and Laal S:
Transcriptional profile of Mycobacterium tuberculosis replicating
in type II alveolar epithelial cells. PLoS One. 10:e01237452015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li S, Sun Z, Chen T, Pan J, Shen Y, Chen
X, Zhou X, Cheng R and Yang Y: The role of miR-431-5p in regulating
pulmonary surfactant expression in vitro. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
24:252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shen YQ, Yang Y, Sun ZY, Li SJ, Shen JX
and Zhou XY: Continuous expression of miR-431 during lung
development in Sprague-Dawley rats. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi.
21:287–293. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zeng Y, Zhu J, Shen D, Qin H, Lei Z, Li W,
Huang JA and Liu Z: Repression of Smad4 by miR-205 moderates
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 cell lines.
Int J Oncol. 49:700–708. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xing Y, Li C, Hu L, Tiozzo C, Li M, Chai
Y, Bellusci S, Anderson S and Minoo P: Mechanisms of TGFbeta
inhibition of LUNG endodermal morphogenesis: The role of TbetaRII,
Smads, Nkx2.1 and Pten. Dev Biol. 320:340–350. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Geng Y, Dong Y, Yu M, Zhang L, Yan X, Sun
J, Qiao L, Geng H, Nakajima M, Furuichi T, et al: Follistatin-like
1 (Fstl1) is a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 4 signaling
antagonist in controlling mouse lung development. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:7058–7063. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mullassery D and Smith NP: Lung
development. Semin Pediatr Surg. 24:152–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Johar D, Siragam V, Mahood TH and Keijzer
R: New insights into lung development and diseases: The role of
microRNAs. Biochem Cell Biol. 93:139–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tian Y, Zhang Y, Hurd L, Hannenhalli S,
Liu F, Lu MM and Morrisey EE: Regulation of lung endoderm
progenitor cell behavior by miR302/367. Development. 138:1235–1245.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carraro G, El-Hashash A, Guidolin D,
Tiozzo C, Turcatel G, Young BM, De Langhe SP, Bellusci S, Shi W,
Parnigotto PP and Warburton D: miR-17 family of microRNAs controls
FGF10-mediated embryonic lung epithelial branching morphogenesis
through MAPK14 and STAT3 regulation of E-Cadherin distribution. Dev
Biol. 333:238–250. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin C, Yao E and Chuang PT: A conserved
MST1/2-YAP axis mediates Hippo signaling during lung growth. Dev
Biol. 403:101–113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mahoney JE, Mori M, Szymaniak AD, Varelas
X and Cardoso WV: The hippo pathway effector Yap controls
patterning and differentiation of airway epithelial progenitors.
Dev Cell. 30:137–150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Shi J, Huang Y and Lai L:
Expression of canonical WNT/β-CATENIN signaling components in the
developing human lung. BMC Dev Biol. 12:212012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li C, Xiao J, Hormi K, Borok Z and Minoo
P: Wnt5a participates in distal lung morphogenesis. Dev Biol.
248:68–81. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Woik N and Kroll J: Regulation of lung
development and regeneration by the vascular system. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 72:2709–2718. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Lin Y, Tian B, Miao J, Xi C and Liu
C: Maternal protein restriction alters VEGF signaling and decreases
pulmonary alveolar in fetal rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:3101–3111. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Y, Kai G, Pu XD, Qing K, Guo XR and
Zhou XY: Expression profile of microRNAs in fetal lung development
of Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Mol Med. 29:393–402. 2012.
|
|
31
|
Zhao J, Lee M, Smith S and Warburton D:
Abrogation of Smad3 and Smad2 or of Smad4 gene expression
positively regulates murine embryonic lung branching morphogenesis
in culture. Dev Biol. 194:182–195. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alejandre-Alcázar MA, Kwapiszewska G,
Reiss I, Amarie OV, Marsh LM, Sevilla-Pérez J, Wygrecka M, Eul B,
Köbrich S, Hesse M, et al: Hyperoxia modulates TGF-beta/BMP
signaling in a mouse model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L537–L549. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chen D, Zhao M, Harris SE and Mi Z: Signal
transduction and biological functions of bone morphogenetic
proteins. Front Biosci. 9:349–358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alejandre-Alcázar MA, Shalamanov PD,
Amarie OV, Sevilla-Pérez J, Seeger W, Eickelberg O and Morty RE:
Temporal and spatial regulation of bone morphogenetic protein
signaling in late lung development. Dev Dyn. 236:2825–2835. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Winnier G, Blessing M, Labosky PA and
Hogan BL: Bone morphogenetic protein-4 is required for mesoderm
formation and patterning in the mouse. Genes Dev. 9:2105–2116.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bragg AD, Moses HL and Serra R: Signaling
to the epithelium is not sufficient to mediate all of the effects
of transforming growth factor beta and bone morphogenetic protein 4
on murine embryonic lung development. Mech Dev. 109:13–26. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sanders RL, Hassett RJ and Vatter AE:
Isolation of lung lamellar bodies and their conversion to tubular
myelin figures in vitro. Anat Rec. 198:485–501. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Crouch E and Wright JR: Surfactant
proteins a and d and pulmonary host defense. Annu Rev Physiol.
63:521–554. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weaver TE and Conkright JJ: Function of
surfactant proteins B and C. Annu Rev Physiol. 63:555–578. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Parmigiani S, Solari E and Bevilacqua G:
Current concepts on the pulmonary surfactant in infants. J Matern
Fetal Neonatal Med. 18:369–380. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rubarth LB and Quinn J: Respiratory
development and respiratory distress syndrome. Neonatal Netw.
34:231–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Reuter S, Moser C and Baack M: Respiratory
distress in the newborn. Pediatr Rev. 35:417–429. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|