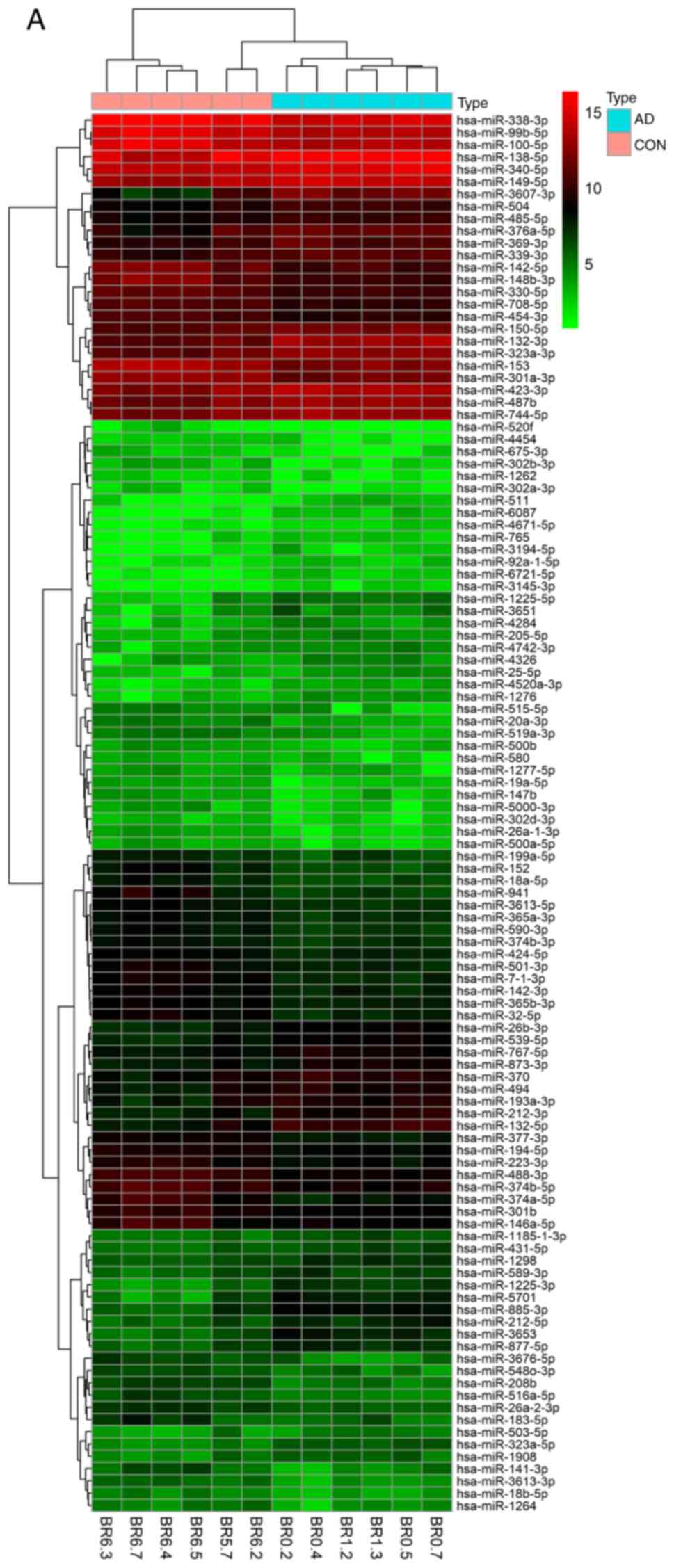
|
1
|
Nedivi E, Hevroni D, Naot D, Israeli D and
Citri Y: Numerous candidate plasticity-related genes revealed by
differential cDNA cloning. Nature. 363:718–722. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nedivi E, Wu GY and Cline HT: Promotion of
dendritic growth by CPG15, an activity-induced signaling molecule.
Science. 281:1863–1866. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Naeve GS, Ramakrishnan M, Kramer R,
Hevroni D, Citri Y and Theill LE: Neuritin: A gene induced by
neural activity and neurotrophins that promotes neuritogenesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:2648–2653. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cantallops I, Haas K and Cline HT:
Postsynaptic CPG15 promotes synaptic maturation and presynaptic
axon arbor elaboration in vivo. Nat Neurosci. 3:1004–1011. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Javaherian A and Cline HT: Coordinated
motor neuron axon growth and neuromuscular synaptogenesis are
promoted by CPG15 in vivo. Neuron. 45:505–512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karamoysoyli E, Burnand RC, Tomlinson DR
and Gardiner NJ: Neuritin mediates nerve growth factor-induced
axonal regeneration and is deficient in experimental diabetic
neuropathy. Diabetes. 57:181–189. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fargo KN, Alexander TD, Tanzer L, Poletti
A and Jones KJ: Androgen regulates neuritin mRNA levels in an in
vivo model of steroid-enhanced peripheral nerve regeneration. J
Neurotrauma. 25:561–566. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao QR, Lu JM, Yao JJ, Zhang ZY, Ling C
and Mei YA: Neuritin reverses deficits in murine novel object
associative recognition memory caused by exposure to extremely
low-frequency (50 Hz) electromagnetic fields. Sci Rep. 5:117682015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Xian L, Tang J, Zhu J,
Cui L, Li S, Yang L and Huang J: Expression and purification of
recombinant human neuritin from Pichia pastoris and a partial
analysis of its neurobiological activity in vitro. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 99:8035–8043. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao R, Li X, Xi S, Wang H, Zhang H, Zhu J,
Shan L, Song X, Luo X, Yang L and Huang J: Exogenous Neuritin
promotes nerve regeneration after acute spinal cord injury in rats.
Hum Gene Ther. 27:544–554. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang H, Li X, Shan L, Zhu J, Chen R, Li Y,
Yuan W, Yang L and Huang J: Recombinant hNeuritin promotes
structural and functional recovery of sciatic nerve injury in rats.
Front Neurosci. 10:5892016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MM, de
Strooper B, Frisoni GB, Salloway S and Van der Flier WM:
Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 388:505–517. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi Y, Lee K, Ryu J, Kim HG, Jeong AY,
Woo RS, Lee JH, Hyun JW, Hahn S, Kim JH and Kim HS: Neuritin
attenuates cognitive function impairments in tg2576 mouse model of
Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 9:e1041212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
An K, Jung JH, Jeong AY, Kim HG, Jung SY,
Lee K, Kim HJ, Kim SJ, Jeong TY, Son Y, et al: Neuritin can
normalize neural deficits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell Death Dis.
5:e15232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang TC and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in
vertebrate physiology and human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum
Genet. 8:215–239. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li F, Wei G, Bai Y, Li Y, Huang F, Lin J,
Hou Q, Deng R, Zhou JH, Zhang SX and Chen DF: MicroRNA-574 is
involved in cognitive impairment in 5-month-old APP/PS1 mice
through regulation of neuritin. Brain Res. 1627:177–188. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao R, Wang L, Sun J, Nie K, Jian H, Gao
L, Liao X, Zhang H, Huang J and Gan S: MiR-204 promotes apoptosis
in oxidative stress-induced rat Schwann cells by suppressing
neuritin expression. FEBS Lett. 588:3225–3232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shen NN, Zhang ZL, Li Z, Zhang C, Li H,
Wang JL, Wang J and Gu ZC: Identification of microRNA biomarkers in
atrial fibrillation: A protocol for systematic review and
bioinformatics analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e165382019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Kim JH, Huh JY,
Yoon H, Park DK, Lim JY, Kim JM, Jeon D, et al: MiR-206 regulates
brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer disease model. Ann
Neurol. 72:269–277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Morris R: Developments of a water-maze
procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci
Methods. 11:47–60. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Putz U, Harwell C and Nedivi E: Soluble
CPG15 expressed during early development rescues cortical
progenitors from apoptosis. Nat Neurosci. 8:322–331. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fujino T, Leslie JH, Eavri R, Chen JL, Lin
WC, Flanders GH, Borok E, Horvath TL and Nedivi E: CPG15 regulates
synapse stability in the developing and adult brain. Genes Dev.
25:2674–2685. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Corriveau RA, Shatz CJ and Nedivi E:
Dynamic regulation of cpg15 during activity-dependent synaptic
development in the mammalian visual system. J Neurosci.
19:7999–8008. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fujino T, Wu Z, Lin WC, Phillips MA and
Nedivi E: cpg15 and cpg15-2 constitute a family of
activity-regulated ligands expressed differentially in the nervous
system to promote neurite growth and neuronal survival. J Comp
Neurol. 507:1831–1845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hansra GK, Popov G, Banaczek PO, Vogiatzis
M, Jegathees T, Goldbury CS and Cullen KM: The neuritic plaque in
Alzheimer's disease: Perivascular degeneration of neuronal
processes. Neurobiol Aging. 82:88–101. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gouras GK, Olsson TT and Hansson O:
β-Amyloid peptides and amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease.
Neurotherapeutics. 12:3–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Theofilas P, Ehrenberg AJ, Nguy A,
Thackrey JM, Dunlop S, Mejia MB, Alho AT, Paraizo Leite RE,
Rodriguez RD, Suemoto CK, et al: Probing the correlation of
neuronal loss, neurofibrillary tangles, and cell death markers
across the Alzheimer's disease Braak stages: A quantitative study
in humans. Neurobiol Aging. 61:1–12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lacosta AM, Insua D, Badi H, Pesini P and
Sarasa M: Neurofibrillary tangles of Aβx-40 in Alzheimer's disease
brains. J Alzheimers Dis. 58:661–667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fainstein N, Dan-Goor N and Ben-Hur T:
Resident brain neural precursor cells develop age-dependent loss of
therapeutic functions in Alzheimer's mice. Neurobiol Aging.
72:40–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Friedman E, Lerer B and Kuster J: Loss of
cholinergic neurons in the rat neocortex produces deficits in
passive avoidance learning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 19:309–312.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lau P, Bossers K, Janky R, Salta E,
Frigerio CS, Barbash S, Rothman R, Sierksma AS, Thathiah A,
Greenberg D, et al: Alteration of the microRNA network during the
progression of Alzheimer's disease. EMBO Mol Med. 5:1613–1634.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leidinger P, Backes C, Deutscher S,
Schmitt K, Mueller SC, Frese K, Haas J, Ruprecht K, Paul F, Stähler
C, et al: A blood based 12-miRNA signature of Alzheimer disease
patients. Genome Biol. 14:R782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hébert SS, Wang WX, Zhu Q and Nelson PT: A
study of small RNAs from cerebral neocortex of pathology-verified
Alzheimer's disease, dementia with lewy bodies, hippocampal
sclerosis, frontotemporal lobar dementia, and non-demented human
controls. J Alzheimers Dis. 35:335–348. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nunez-Iglesias J, Liu CC, Morgan TE, Finch
CE and Zhou XJ: Joint genome-wide profiling of miRNA and mRNA
expression in Alzheimer's disease cortex reveals altered miRNA
regulation. PLoS One. 5:e88982010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|