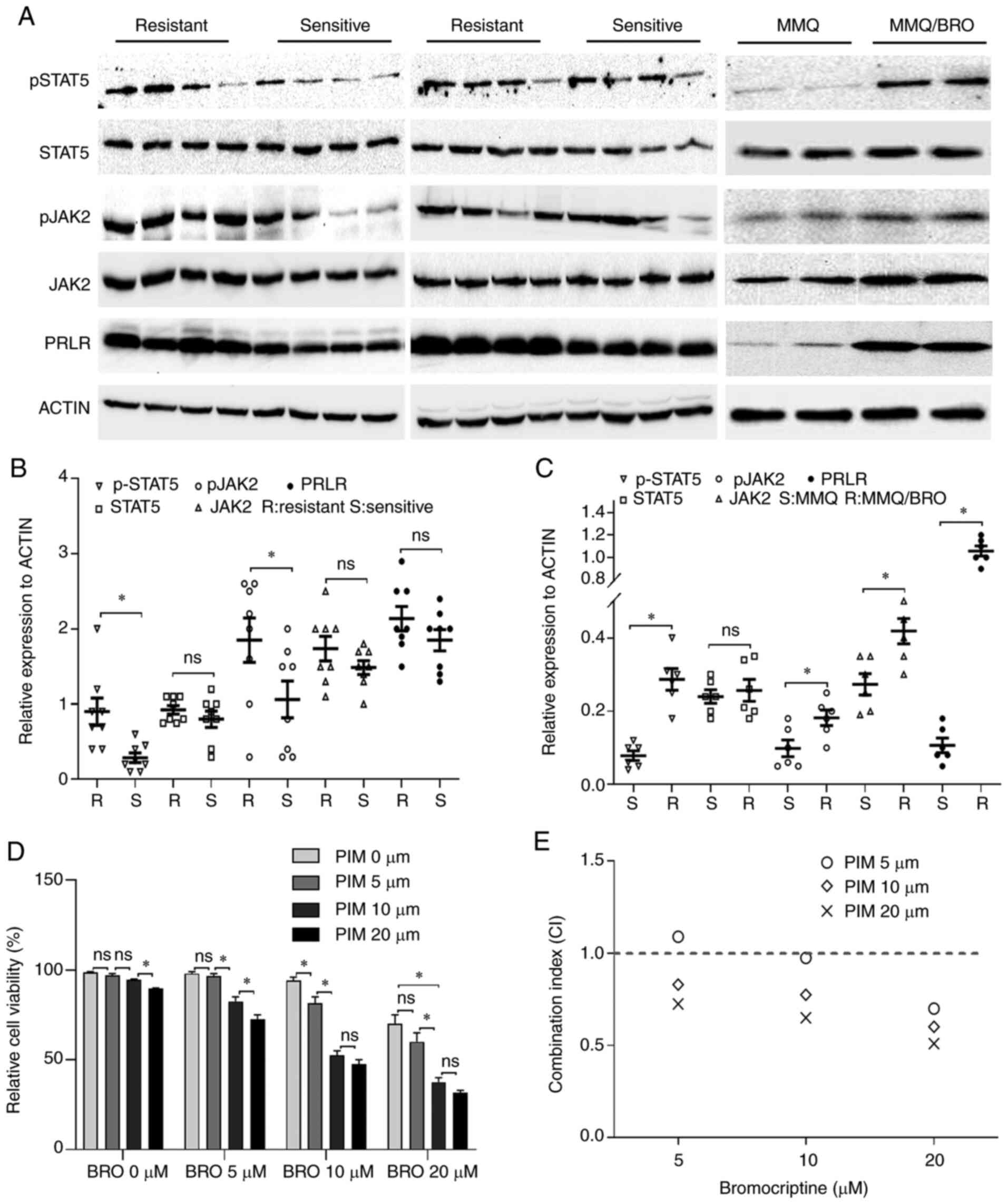
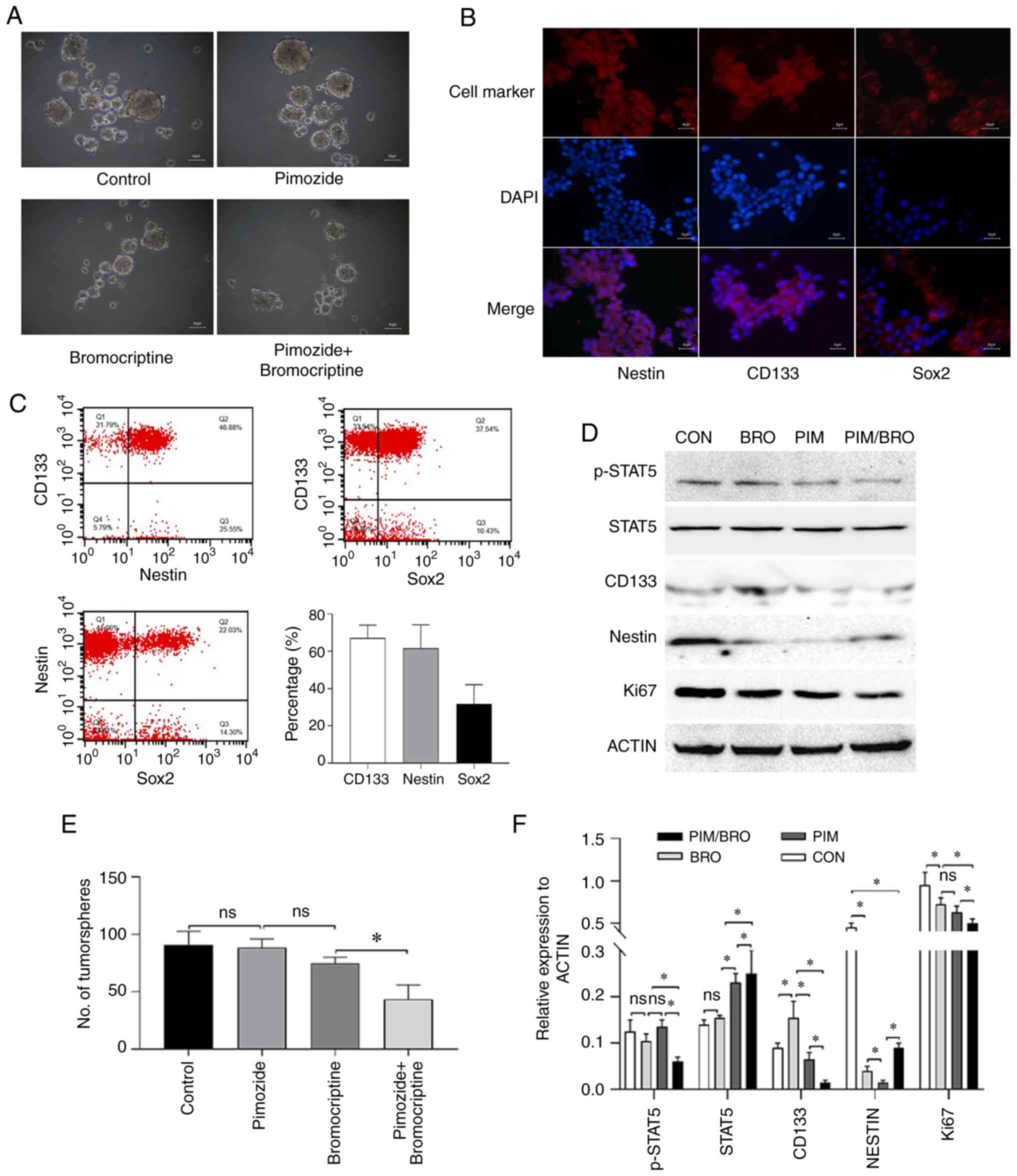
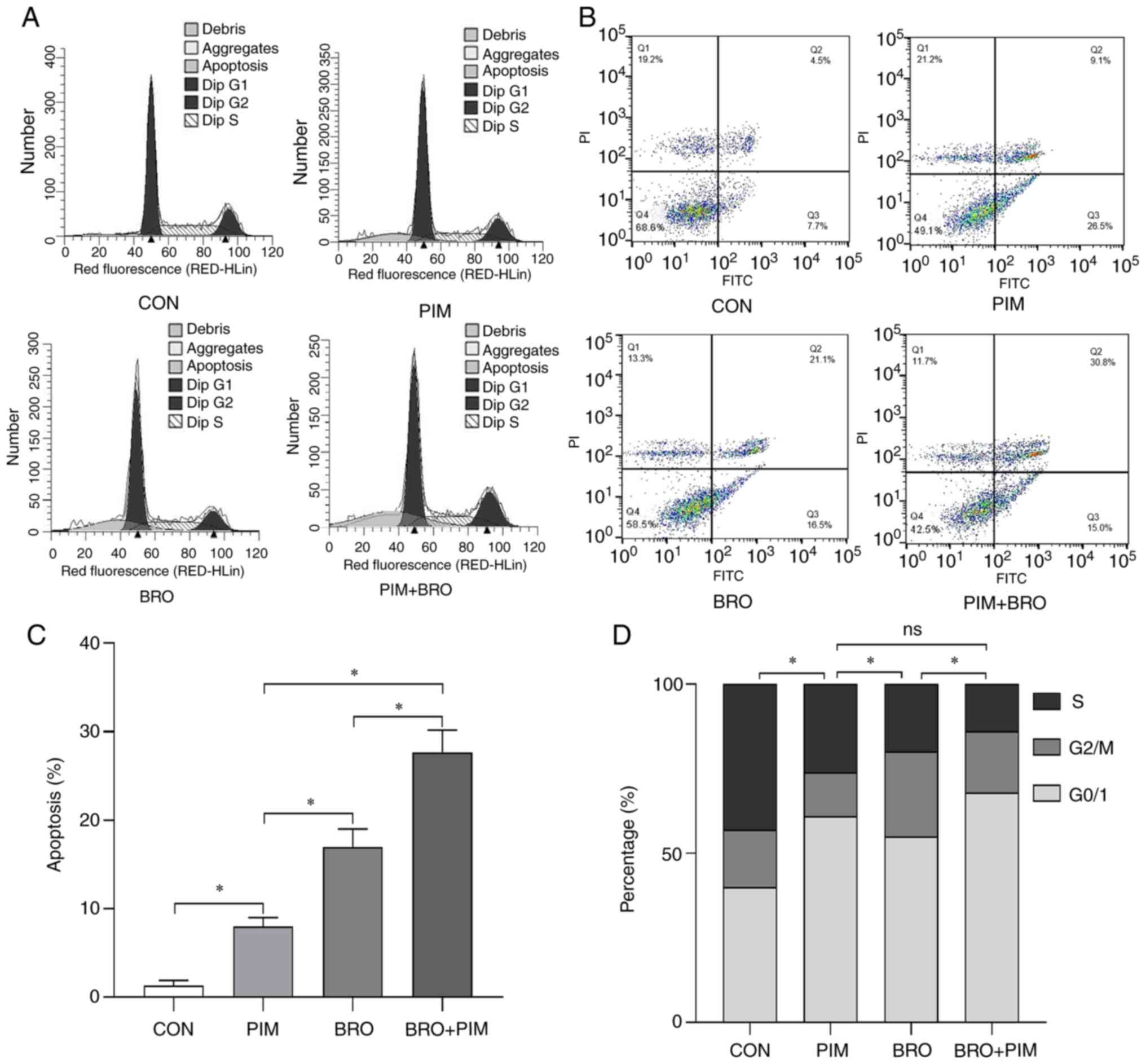
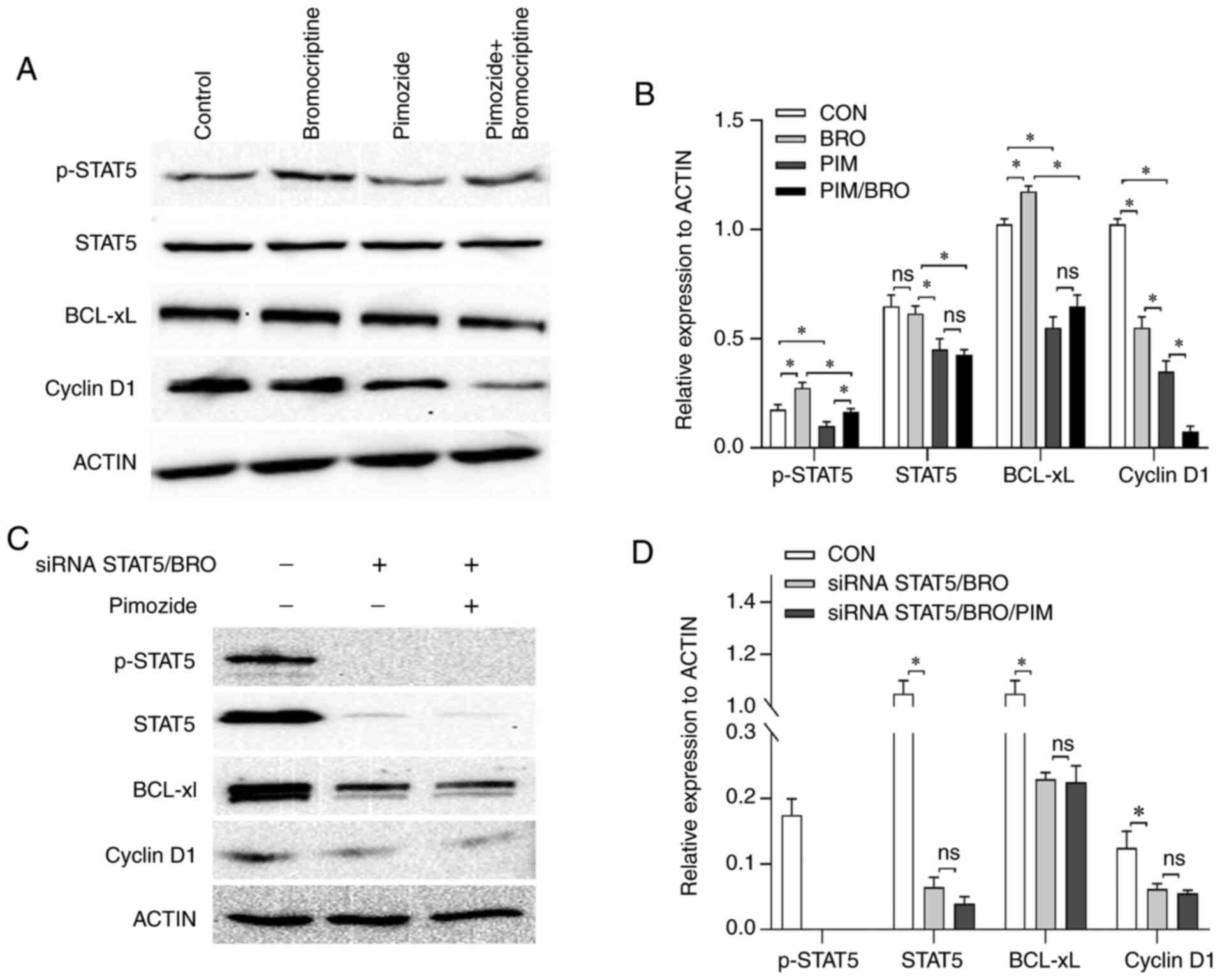
|
1
|
Mete O, Cintosun A, Pressman I and Asa SL:
Epidemiology and biomarker profile of pituitary adenohypophysial
tumors. Mod Pathol. 31:900–909. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu J, He Y, Zhang X, Yan X and Huang Y:
Clinicopathological analysis of 250 cases of pituitary adenoma
under the new WHO classification. Oncol Lett. 19:1890–1898.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lim CT and Korbonits M: Update on the
clinicopathology of pituitary adenomas. Endocr Pract. 24:473–488.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tang C, Sun R, Wen G, Zhong C, Yang J, Zhu
J, Cong Z, Luo X and Ma C: Bromocriptine and cabergoline induce
cell death in prolactinoma cells via the ERK/EGR1 and AKT/mTOR
pathway respectively. Cell Death Dis. 10:3352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Molitch ME: Pharmacologic resistance in
prolactinoma patients. Pituitary. 8:43–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kavarthapu R and Dufau ML: Essential role
of endogenous prolactin and CDK7 in estrogen-induced upregulation
of the prolactin receptor in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:27353–27363. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clevenger CV, Gadd SL and Zheng J: New
mechanisms for PRLr action in breast cancer. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 20:223–229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gorvin CM, Newey PJ, Rogers A, Stokes V,
Neville MJ, Lines KE, Ntali G, Lees P, Morrison PJ, Singhellakis
PN, et al: Association of prolactin receptor (PRLR) variants with
prolactinomas. Hum Mol Genet. 28:1023–1037. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Kwinta BM, Grzywna E, Krzyżewski RM and
Adamek D: The quantitative evaluation of the immunohistochemical
expression of the pituitary adenomas. Folia Med Cracov. 57:83–96.
2017.
|
|
10
|
Naguy A: Pimozide: An old wine in a new
bottle. Indian J Psychol Med. 39:382–383. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Preskorn SH: Changes in the product label
for pimozide illustrate both the promises and the challenges of
personalized medicine. J Clin Psychiatry. 73:1191–1193. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Friedman JI, Lindenmayer JP, Alcantara F,
Bowler S, Parak M, White L, Iskander A, Parrella M, Adler DN,
Tsopelas ND, et al: Pimozide augmentation of clozapine inpatients
with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder unresponsive to
clozapine monotherapy. Neuropsychopharmacology. 36:1289–1295. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rondanin R, Simoni D, Maccesi M, Romagnoli
R, Grimaudo S, Pipitone RM, Meli M, Cascio A and Tolomeo M: Effects
of pimo-zide derivatives on pSTAT5 in K562 cells. ChemMedChem.
12:1183–1190. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rondanin R, Simoni D, Romagnoli R,
Baruchello R, Marchetti P, Costantini C, Fochi S, Padroni G,
Grimaudo S, Pipitone RM, et al: Inhibition of activated STAT5 in
Bcr/Abl expressing leukemia cells with new pimozide derivatives.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 24:4568–4574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li H, Zheng H, Sun Y, Yu Q and Li L:
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a inhibited by
pimozide may regulate survival of goat mammary gland epithelial
cells by regulating parathyroid hormone-related protein. Gene.
551:279–289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen JJ, Cai N, Chen GZ, Jia CC, Qiu DB,
Du C, Liu W, Yang Y, Long ZJ and Zhang Q: The neuroleptic drug
pimozide inhibits stem-like cell maintenance and tumorigenicity in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:17593–17609. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Zhou W, Chen MK, Yu HT, Zhong ZH, Cai N,
Chen GZ, Zhang P and Chen JJ: The antipsychotic drug pimozide
inhibits cell growth in prostate cancer through suppression of
STAT3 activation. Int J Oncol. 48:322–328. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hadzijusufovic E, Keller A, Berger D,
Greiner G, Wingelhofer B, Witzeneder N, Ivanov D, Pecnard E,
Nivarthi H, Schur F, et al: STAT5 is expressed in
CD34+/CD38-stem cells and serves as a potential
molecular target in ph-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Cancers (Basel). 12:10212020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Subramaniam D, Angulo P, Ponnurangam S,
Dandawate P, Ramamoorthy P, Srinivasan P, Iwakuma T, Weir SJ,
Chastain K and Anant S: Suppressing STAT5 signaling affects
osteosarcoma growth and stemness. Cell Death Dis. 11:1492020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao Y, Jin D, Lian W, Xing B, Feng M, Liu
X and Wang R: Clinical characteristics and surgical outcome of
prolactinoma in patients under 14 years old. Medicine (Baltimore).
98:e143802019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhao Y, Xiao Z, Chen W, Yang J, Li T and
Fan B: Disulfiram sensitizes pituitary adenoma cells to
temozolomide by regulating O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase
expression. Mol Med Rep. 12:2313–2322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Turhan AG: STAT5 as a CML target: STATinib
therapies. Blood. 117:3252–3253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Florio T: Adult pituitary stem cells: From
pituitary plasticity to adenoma development. Neuroendocrinology.
94:265–277. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pastrana E, Silva-Vargas V and Doetsch F:
Eyes wide open: A critical review of sphere-formation as an assay
for stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 8:486–498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Würth R, Barbieri F, Pattarozzi A,
Gaudenzi G, Gatto F, Fiaschi P, Ravetti JL, Zona G, Daga A, Persani
L, et al: Phenotypical and pharmacological characterization of
stem-like cells in human pituitary adenomas. Mol Neurobiol.
54:4879–4895. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Santos-Pinheiro F, Penas-Prado M,
Kamiya-Matsuoka C, Waguespack SG, Mahajan A, Brown PD, Shah KB,
Fuller GN and McCutcheon IE: Treatment and long-term outcomes in
pituitary carcinoma: A cohort study. Eur J Endocrinol. 181:397–407.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akinduro OO, Lu VM, Izzo A, De Biase G,
Vilanilam G, Van Gompel JJ, Bernet V, Donaldson A, Olomu O, Meyer
FB, et al: Radiographic and hormonal regression in prolactinomas:
An analysis of treatment failure. World Neurosurg. 129:e686–e694.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang HY, Lin SJ, Zhao WG and Wu ZB:
Cabergoline versus bromocriptine for the treatment of giant
prolactinomas: A quantitative and systematic review. Metab Brain
Dis. 33:969–976. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hachim IY, Shams A, Lebrun JJ and Ali S: A
favorable role of prolactin in human breast cancer reveals novel
pathway-based gene signatures indicative of tumor differentiation
and favorable patient outcome. Hum Pathol. 53:142–152. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wen Y, Zand B, Ozpolat B, Szczepanski MJ,
Lu C, Yuca E, Carroll AR, Alpay N, Bartholomeusz C, Tekedereli I,
et al: Antagonism of tumoral prolactin receptor promotes
autophagy-related cell death. Cell Rep. 7:488–500. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kalita A, Gupta S, Singh P, Surolia A and
Banerjee K: IGF-1 stimulated upregulation of cyclin D1 is mediated
via STAT5 signaling pathway in neuronal cells. IUBMB Life.
65:462–471. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mao Y, Li Z, Lou C and Zhang Y: Expression
of phosphorylated Stat5 predicts expression of cyclin D1 and
correlates with poor prognosis of colonic adenocarcinoma. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 26:29–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Brockman JL and Schuler LA: Prolactin
signals via Stat5 and Oct-1 to the proximal cyclin D1 promoter. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 239:45–53. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Magné S, Caron S, Charon M, Rouyez MC and
Dusanter-Fourt I: STAT5 and Oct-1 form a stable complex that
modulates cyclin D1 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8934–8945. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qian YH, Xiao Q, Chen H and Xu J:
Dexamethasone inhibits camptothecin-induced apoptosis in C6-glioma
via activation of Stat5/Bcl-xL pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1793:764–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fujinaka Y, Takane K, Yamashita H and
Vasavada RC: Lactogens promote beta cell survival through
JAK2/STAT5 activation and Bcl-XL upregulation. J Biol Chem.
282:30707–30717. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kanie T, Abe A, Matsuda T, Kuno Y,
Towatari M, Yamamoto T, Saito H, Emi N and Naoe T: TEL-Syk fusion
constitutively activates PI3-K/Akt, MAPK and JAK2-independent STAT5
signal pathways. Leukemia. 18:548–555. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moldovan IM, Şuşman S, Pîrlog R, Jianu EM,
Leucuţa DC, Melincovici CS, Crişan D and Florian IŞ: Molecular
markers in the diagnosis of invasive pituitary adenomas-an
immunohisto-chemistry study. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 58:1357–1364.
2017.
|
|
39
|
Bălinişteanu B, Cîmpean AM, Ceauşu AR,
Corlan AS, Melnic E and Raica M: High Ki-67 expression is
associated with prolactin secreting pituitary adenomas. Bosn J
Basic Med Sci. 17:104–108. 2017.
|
|
40
|
Oshige T, Nakamura Y, Sasaki Y, Kawano S,
Ohki T, Tsuruta M, Tokubuchi I, Nakayama H, Yamada K, Ashida K, et
al: Bromocriptine as a potential glucose-lowering agent for the
treatment of prolactinoma with type 2 diabetes. Intern Med.
58:3125–3128. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gschwantler-Kaulich D, Grunt TW, Muhr D,
Wagner R, Kölbl H and Singer CF: HER Specific TKIs exert their
antineoplastic effects on breast cancer cell lines through the
involvement of STAT5 and JNK. PLoS One. 11:e01463112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hazzan T, Eberle J, Worm M and Babina M:
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin interferes with the apoptosis of human
skin mast cells by a dual strategy involving STAT5/Mcl-1 and
JNK/Bcl-xL. Cells. 8:8292019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Kim U, Kim CY, Lee JM, Ryu B, Kim J, Shin
C and Park JH: Pimozide inhibits the human prostate cancer cells
through the generation of reactive oxygen species. Front Pharmacol.
10:15172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nyga R, Pecquet C, Harir N, Gu H,
Dhennin-Duthille I, Régnier A, Gouilleux-Gruart V, Lassoued K and
Gouilleux F: Activated STAT5 proteins induce activation of the PI
3-kinase/Akt and Ras/MAPK pathways via the Gab2 scaffolding
adapter. Biochem J. 390:359–366. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gupta MA, Vujcic B, Pur DR and Gupta AK:
Use of antipsychotic drugs in dermatology. Clin Dermatol.
36:765–773. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Biller BM: Hyperprolactinemia. Int J
Fertil Womens Med. 44:74–77. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|