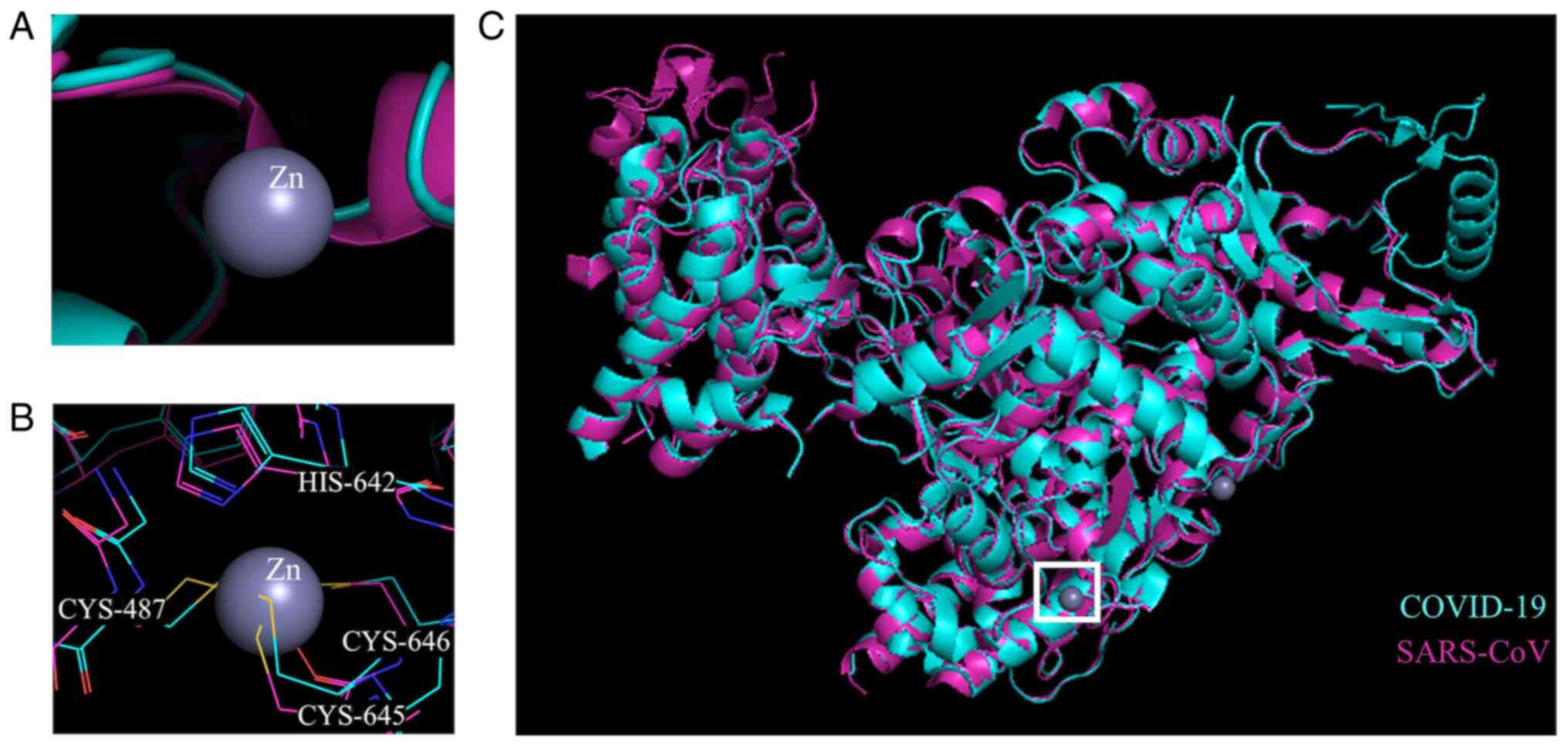
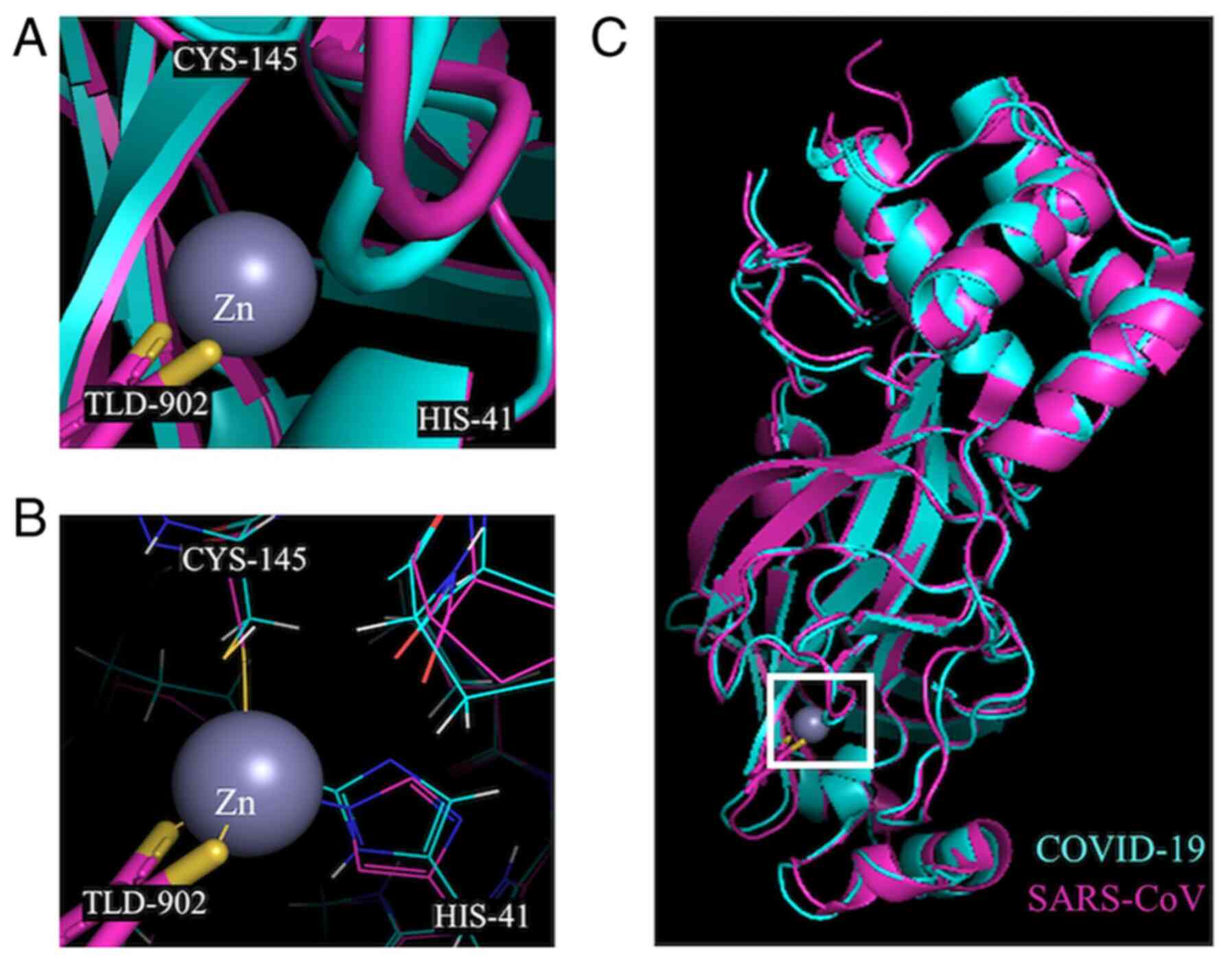
|
1
|
Beyersmann D and Haase H: Functions of
zinc in signaling, proliferation and differentiation of mammalian
cells. Biometals. 14:331–341. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Marreiro D do N, Cruz KJ, Morais JB,
Beserra JB, Severo JS and Soares de Oliveira AR: Zinc and oxidative
stress: Current mechanisms. Antioxidants (Basel). 6:242017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Maywald M, Wessels I and Rink L: Zinc
signals and immunity. Int J Mol Sci. 18:22222017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Miller BD and Welch RM: Food system
strategies for preventing micronutrient malnutrition. Food Policy.
Wolters Kluwer-Medknow Publications; pp. 115–128. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kochańczyk T, Drozd A and Krężel A:
Relationship between the architecture of zinc coordination and zinc
binding affinity in proteins-Insights into zinc regulation.
Metallomics. 7:244–257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Prasad AS: Impact of the discovery of
human zinc deficiency on health. J Am Coll Nutr. 28:257–265. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Read SA, Obeid S, Ahlenstiel C and
Ahlenstiel G: The role of zinc in antiviral immunity. Adv Nutr.
10:696–710. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Korant BD and Butterworth BE: Inhibition
by zinc of rhinovirus protein cleavage: Interaction of zinc with
capsid polypeptides. J Virol. 18:298–306. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaushik N, Subramani C, Anang S,
Muthumohan R, Shalimar, Nayak B, Ranjith-Kumar CT and Surjit M:
Zinc salts block hepatitis E virus replication by inhibiting the
activity of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol.
91:e00754–e00717. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Korant BD, Kauer JC and Butterworth BE:
Zinc ions inhibit replication of rhinoviruses. Nature. 248:588–590.
1974. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
te Velthuis AJ, van den Worml SH, Sims AC,
Baric RS, Snijder EJ and van Hemert MJ: Zn2+ inhibits
coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and
zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell
culture. PLoS Pathog. 6:e10011762010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hsu JTA, Kuo CJ, Hsieh HP, Wang YC, Huang
KK, Lin CPC, Huang PF, Chen X and Liang PH: Evaluation of
metal-conjugated compounds as inhibitors of 3CL protease of
SARS-CoV. FEBS Lett. 574:116–120. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee CC, Kuo CJ, Hsu MF, Liang PH, Fang JM,
Shie JJ and Wang AH: Structural basis of mercury- and
zinc-conjugated complexes as SARS-CoV 3C-like protease inhibitors.
FEBS Lett. 581:5454–5458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krenn BM, Gaudernak E, Holzer B, Lanke K,
Van Kuppeveld FJ and Seipelt J: Antiviral activity of the zinc
ionophores pyrithione and hinokitiol against picornavirus
infections. J Virol. 83:58–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Lanke K, Krenn BM, Melchers WJ, Seipelt J
and van Kuppeveld FJ: PDTC inhibits picornavirus polyprotein
processing and RNA replication by transporting zinc ions into
cells. J Gen Virol. 88:1206–1217. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geist FC, Bateman JA and Hayden FG: In
vitro activity of zinc salts against human rhinoviruses. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 31:622–624. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hung M, Gibbs CS and Tsiang M: Biochemical
characterization of rhinovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
Antiviral Res. 56:99–114. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Krenn BM, Holzer B, Gaudernak E, Triendl
A, van Kuppeveld FJ and Seipelt J: Inhibition of polyprotein
processing and RNA replication of human rhinovirus by pyrrolidine
dithiocarbamate involves metal ions. J Virol. 79:13892–13899. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suara RO and Crowe JE: Effect of zinc
salts on respiratory syncytial virus replication. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 48:783–790. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Srivastava V, Rawall S, Vijayan VK and
Khanna M: Influenza a virus induced apoptosis: Inhibition of DNA
laddering & caspase-3 activity by zinc supplementation in
cultured HeLa cells. Indian J Med Res. 129:579–586. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ghaffari H, Tavakoli A, Moradi A,
Tabarraei A, Bokharaei-Salim F, Zahmatkeshan M, Farahmand M,
Javanmard D, Kiani SJ, Esghaei M, et al: Inhibition of H1N1
influenza virus infection by zinc oxide nanoparticles: Another
emerging application of nanomedicine. J Biomed Sci. 26:702019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shankar AH and Prasad AS: Zinc and immune
function: The biological basis of altered resistance to infection.
Am J Clin Nutr. 68(Suppl 2): 447S–463S. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hulisz D: Efficacy of zinc against common
cold viruses: An overview. J Am Pharm Assoc 2003. 44:594–603. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hemilä H, Fitzgerald JT, Petrus EJ and
Prasad A: Zinc acetate lozenges may improve the recovery rate of
common cold patients: An individual patient data meta-analysis.
Open Forum Infect Dis. 4:ofx0592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Science M, Johnstone J, Roth DE, Guyatt G
and Loeb M: Zinc for the treatment of the common cold: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. CMAJ.
184:E551–E561. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
D'Cruze H, Arroll B and Kenealy T: Is
intranasal zinc effective and safe for the common cold? A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prim Health Care. 1:134–139.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Caruso TJ, Prober CG and Gwaltney JM Jr:
Treatment of naturally acquired common colds with zinc: A
structured review. Clin Infect Dis. 45:569–574. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou Y, Hou Y, Shen J, Huang Y, Martin W
and Cheng F: Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus
2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov. 6:142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lung J, Lin YS, Yang YH, Chou YL, Shu LH,
Cheng YC, Liu HT and Wu CY: The potential chemical structure of
anti-SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Med Virol.
92:693–697. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Prentice E, McAuliffe J, Lu X, Subbarao K
and Denison MR: Identification and characterization of severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus replicase proteins. J Virol.
78:9977–9986. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fan K, Wei P, Feng Q, Chen S, Huang C, Ma
L, Lai B, Pei J, Liu Y, Chen J and Lai L: Biosynthesis,
purification, and substrate specificity of severe acute respiratory
syndrome coronavirus 3C-like proteinase. J Biol Chem.
279:1637–1642. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Subissi L, Imbert I, Ferron F, Collet A,
Coutard B, Decroly E and Canard B: SARS-CoV ORF1b-encoded
nonstructural proteins 12-16: Replicative enzymes as antiviral
targets. Antiviral Res. 101:122–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wu YS, Lin WH, Hsu JT and Hsieh HP:
Antiviral drug discovery against SARS-CoV. Curr Med Chem.
13:2003–2020. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kirchdoerfer RN and Ward AB: Structure of
the SARS-CoV nsp12 polymerase bound to nsp7 and nsp8 co-factors.
Nat Commun. 10:23422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gao Y, Yan L, Huang Y, Liu F, Zhao Y, Cao
L, Wang T, Sun Q, Ming Z, Zhang L, et al: Structure of the
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science.
368:779–782. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mesecar AD; Center for Structural Genomics
of Infectious Diseases (CSGID): RCSB PDB-6W63: Structure of
COVID-19 main protease bound to potent broad-spectrum non-covalent
inhibitor X77. National Institutes of Health/National Institute of
Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH/NIAID); 2020
|
|
37
|
Nitulescu GM, Paunescu H, Moschos SA,
Petrakis D, Nitulescu G, Ion GND, Spandidos DA, Nikolouzakis TK,
Drakoulis N and Tsatsakis A: Comprehensive analysis of drugs to
treat SARS-CoV-2 infection: Mechanistic insights into current
COVID-19 therapies (Review). Int J Mol Med. 46:467–488. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee CC, Kuo CJ, Ko TP, Hsu MF, Tsui YC,
Chang SC, Yang S, Chen SJ, Chen HC, Hsu MC, et al: Structural basis
of inhibition specificities of 3C and 3C-like proteases by
zinc-coordinating and peptidomimetic compounds. J Biol Chem.
284:7646–7655. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pormohammad A, Ghorbani S, Khatami A,
Farzi R, Baradaran B, Turner DL, Turner RJ, Bahr NC and Idrovo JP:
Comparison of confirmed COVID-19 with SARS and MERS cases-clinical
characteristics, laboratory findings, radiographic signs and
outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Med Virol.
30:e21122020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pormohammad A, Ghorbani S, Khatami A,
Razizadeh MH, Alborzi E, Zarei M, Idrovo JP and Turner RJ:
Comparison of influenza type A and B with COVID-19: A global
systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical, laboratory and
radio-graphic findings. Rev Med Virol. Oct 9–2020.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhou Y, Fu B, Zheng X, Wang D, Zhao C, Qi
Y, Sun R, Tian Z, Xu X and Wei H: Pathogenic T cells and
inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storm in severe COVID-19
patients. Natl Sci Rev. Mar 13–2020.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Conti P, Ronconi G, Caraffa A, Gallenga C,
Ross R, Frydas I and Kritas S: Induction of pro-inflammatory
cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by coronavirus-19
(COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies. J Biol Regul
Homeost Agents. 34:327–331. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shi Y, Wang Y, Shao C, Huang J, Gan J,
Huang X, Bucci E, Piacentini M, Ippolito G and Melino G: COVID-19
infection: The perspectives on immune responses. Cell Death Differ.
27:14512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E,
Tattersall RS and Manson JJ; HLH Across Speciality Collaboration,
UK: COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and
immuno-suppression. Lancet. 395:1033–1034. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Skalny AV, Rink L, Ajsuvakova OP, Aschner
M, Gritsenko VA, Alekseenko SI, Svistunov AA, Petrakis D, Spandidos
DA, Aaseth J, et al: Zinc and respiratory tract infections:
Perspectives for CoviD'19 (Review). Int J Mol Med. 46:17–26.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wessels I, Rolles B and Rink L: The
potential impact of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis.
Front Immunol. 11:17122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Stebbing J, Phelan A, Griffin I, Tucker C,
Oechsle O, Smith D and Richardson P: COVID-19: Combining antiviral
and anti-inflammatory treatments. Lancet Infect Dis. 20:400–402.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Favalli EG, Ingegnoli F, De Lucia O,
Cincinelli G, Cimaz R and Caporali R: COVID-19 infection and
rheumatoid arthritis: Faraway, so close! Autoimmun Rev.
19:1025232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang W, Zhao Y, Zhang F, Wang Q, Li T,
Liu Z, Wang J, Qin Y, Zhang X, Yan X, et al: The use of
anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe
coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): The experience of clinical
immunologists from China. Clin Immunol. 214:1083932020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Gammoh NZ and Rink L: Zinc in infection
and inflammation. Nutrients. 9:6242017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Jarosz M, Olbert M, Wyszogrodzka G,
Młyniec K and Librowski T: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory
effects of zinc. Zinc-dependent NF-κB signaling.
Inflammopharmacology. 25:11–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Knoell DL, Smith DA, Sapkota M, Heires AJ,
Hanson CK, Smith LM, Poole JA, Wyatt TA and Romberger DJ:
Insufficient zinc intake enhances lung inflammation in response to
agricultural organic dust exposure. J Nutr Biochem. 70:56–64. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fischer KJ, Yajjala VK, Bansal S, Bauer C,
Chen R and Sun K: Monocytes represent one source of bacterial
shielding from antibiotics following influenza virus infection. J
Immunol. 202:2027–2034. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang L, Forst CV, Gordon A, Gussin G,
Geber AB, Fernandez PJ, Ding T, Lashua L, Wang M, Balmaseda A, et
al: Characterization of antibiotic resistance and host-microbiome
interactions in the human upper respiratory tract during influenza
infection. Microbiome. 8:392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Llor C and Bjerrum L: Antimicrobial
resistance: Risk associated with antibiotic overuse and initiatives
to reduce the problem. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 5:229–241. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kostoff RN, Briggs MB, Porter AL,
Hernández AF, Abdollahi M, Aschner M and Tsatsakis A: The
under-reported role of toxic substance exposures in the COVID-19
pandemic. Food Chem Toxicol. 145:1116872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Çaǧlayan Serin D, Pullukçu H, Çiçek C,
Sipahi OR, Taşbakan S, Atalay S and Pneumonia Study Group:
Bacterial and viral etiology in hospitalized community acquired
pneumonia with molecular methods and clinical evaluation. J Infect
Dev Ctries. 8:510–518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Matson MJ, Stock F, Shupert WL, Bushmaker
T, Feldmann F, Bishop WB, Frank KM, Dekker JP, Chertow DS and
Munster VJ: Compatibility of maximum-containment virus-inactivation
protocols with identification of bacterial coinfections by
matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass
spectrometry. J Infect Dis. 218(Suppl 5): S297–S300. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Stevens MP, Patel PK and Nori P: Involving
antimicrobial stewardship programs in COVID-19 response efforts:
All hands on deck. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 41:744–745. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Essack S, Bell J, Burgoyne DS, Duerden M
and Shephard A: Topical (local) antibiotics for respiratory
infections with sore throat: An antibiotic stewardship perspective.
J Clin Pharm Ther. 44:829–837. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sohrabi C, Alsafi Z, O'Neill N, Khan M,
Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A, Iosifidis C and Agha R: World Health
Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel
coronavirus (COVID-19). Int J Surg. 76:71–76. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Denny KJ, De Wale J, Laupland KB, Harris
PNA and Lipman J: When not to start antibiotics: Avoiding
antibiotic overuse in the intensive care unit. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 26:35–40. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Song Z, Hu Y, Zheng S, Yang L and Zhao R:
Hospital pharmacists' pharmaceutical care for hospitalized patients
with COVID-19: Recommendations and guidance from clinical
experience. Res Social Adm Pharm. Apr 3–2020.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gupta S, Sakhuja A, Kumar G, McGrath E,
Nanchal RS and Kashani KB: Culture-negative severe sepsis:
Nationwide trends and outcomes. Chest. 150:1251–1259. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lemire JA, Harrison JJ and Turner RJ:
Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and
applications. Nat Rev Microbiol. 11:371–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Turner RJ, Gugala N and Lemire J: Can
metals replace traditional antibiotics? Adjac Gov. November;46–47.
2016.
|
|
67
|
Lemire JA and Turner RJ: Mechanisms
underlying the anti-microbial capacity of metals. Stress and
Environmental Regulation of Gene Expression and Adaptation in
Bacteria. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; Hoboken, NJ: pp. 215–224.
2016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Turner RJ: Metal-based antimicrobial
strategies. Microb Biotechnol. 10:1062–1065. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Monych NK, Gugala N and Turner RJ: Chapter
9. Metal-based Antimicrobials. Antimicrobial Materials for
Biomedical Applications. Thomas Graham House; Cambridge: pp.
252–276. 2019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Gugala N, Lemire JA and Turner RJ: The
efficacy of different anti-microbial metals at preventing the
formation of, and eradicating bacterial biofilms of pathogenic
indicator strains. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 70:775–780. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Jesline A, John NP, Narayanan PM, Vani C
and Murugan S: Antimicrobial activity of zinc and titanium dioxide
nanoparticles against biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Nanosci. 5:157–162. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Wang X, Du Y and Liu H: Preparation,
characterization and anti-microbial activity of chitosan-Zn
complex. Carbohydr Polym. 56:21–26. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Gugala N, Vu D, Parkins MD and Turner RJ:
Specificity in the susceptibilities of escherichia coli,
pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates
to six metal antimicrobials. Antibiotics (Basel). 8:512019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
National Institutes of Health: Vitamin K -
Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/vita-minK-HealthProfessional/urisimplehttps://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/vita-minK-HealthProfessional/
Accessed June 3, 2020.
|
|
75
|
Plum LM, Rink L and Hajo H: The essential
toxin: Impact of zinc on human health. Int J Environ Res Public
Health. 7:1342–1365. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|