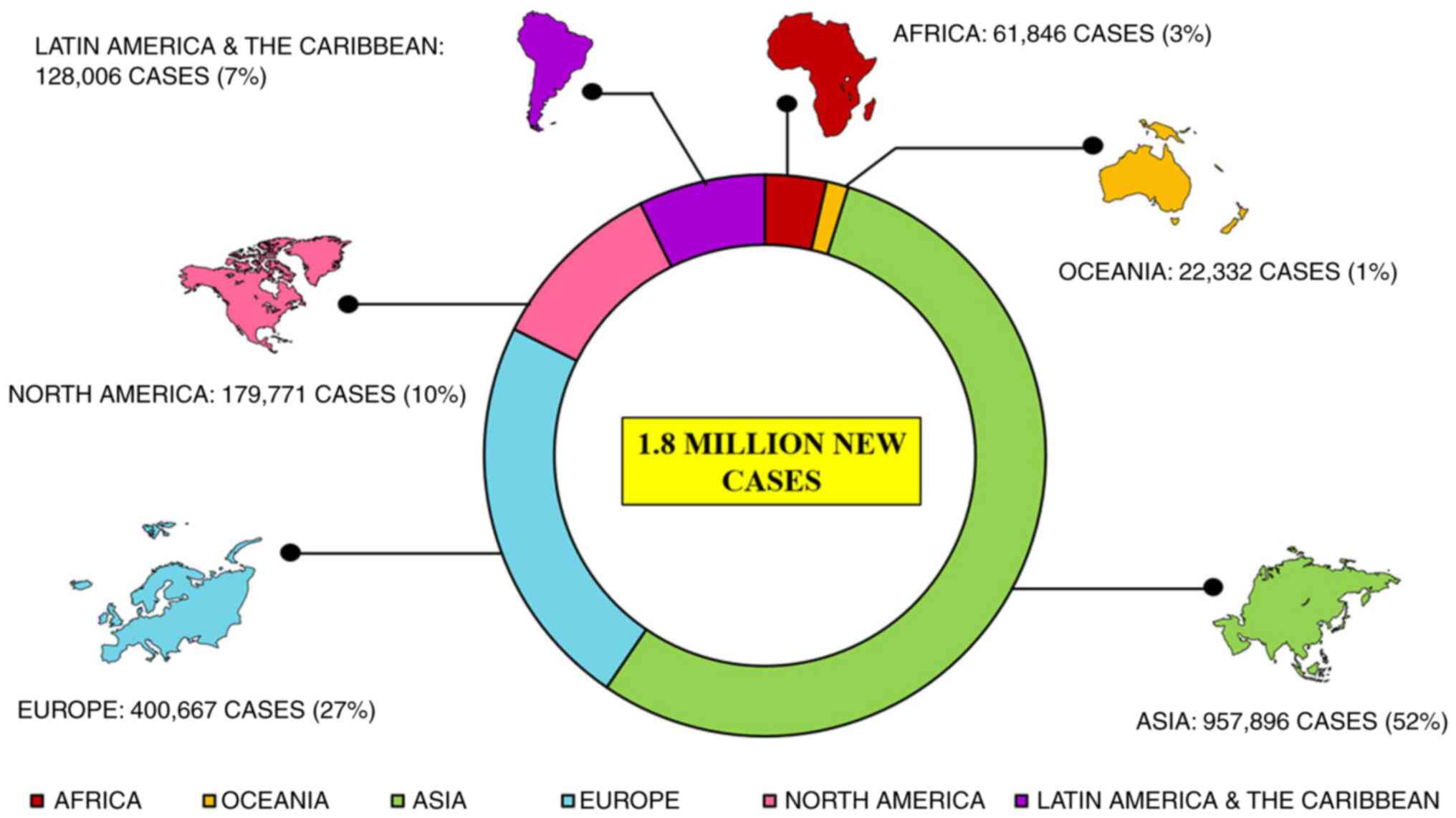
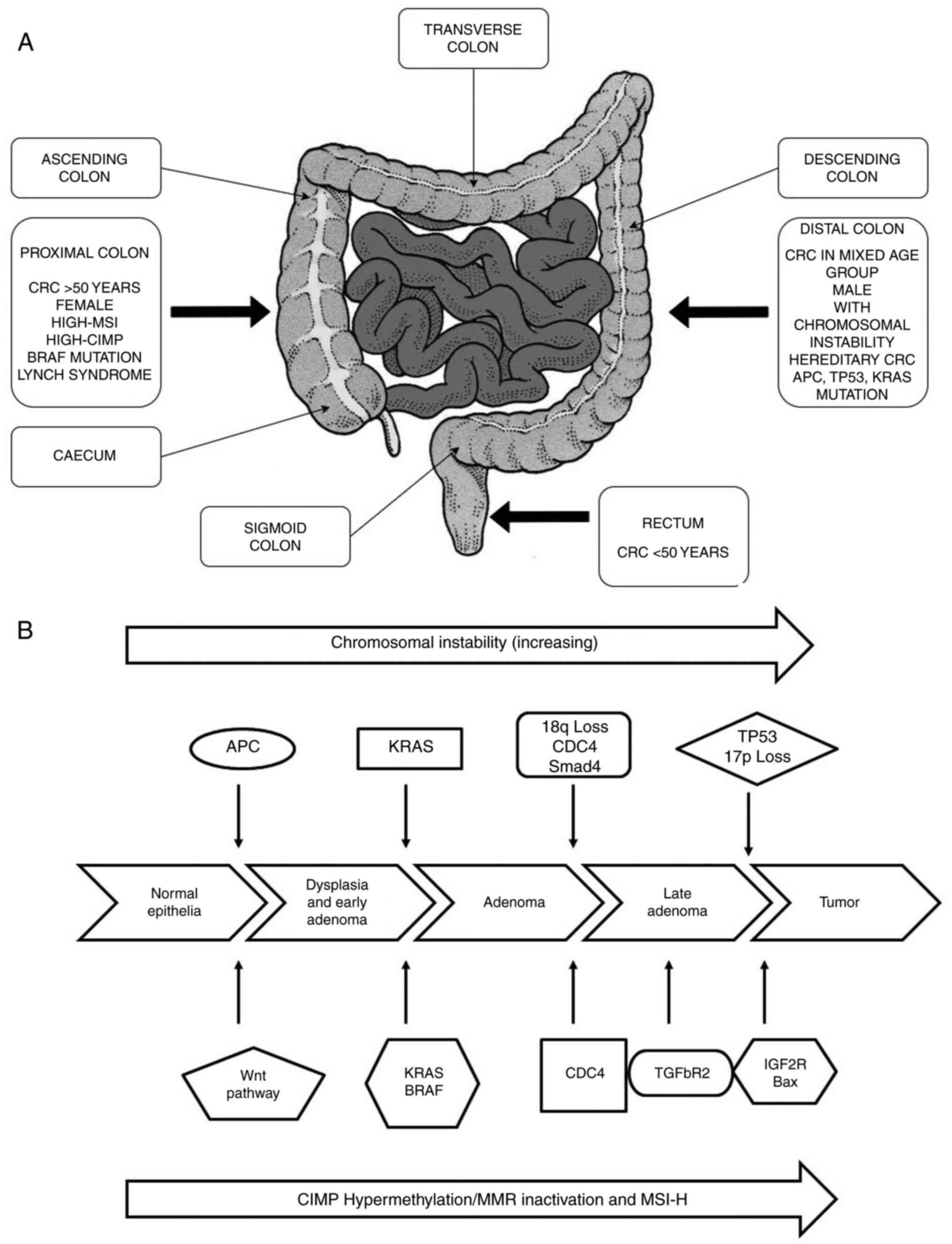
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A,
Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC, Cercek A, Smith RA and Jemal
A: Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin.
70:145–164. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 66:683–691. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fleming M, Ravula S, Tatishchev SF and
Wang HL: Colorectal carcinoma: Pathologic aspects. J Gastrointest
Oncol. 3:153–173. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jasperson KW, Tuohy TM, Neklason DW and
Burt RW: Hereditary and familial colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2044–2058. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Graff RE, Möller S, Passarelli MN, Witte
JS, Skytthe A, Christensen K, Tan Q, Adami HO, Czene K, Harris JR,
et al: Familial risk and heritability of colorectal cancer in the
nordic twin study of cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
15:1256–1264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK,
Iliadou A, Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M, Pukkala E, Skytthe A and Hemminki
K: Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of
cancer-analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and
Finland. N Engl J Med. 343:78–85. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Keum N and Giovannucci E: Global burden of
colorectal cancer: Emerging trends, risk factors and prevention
strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:713–732. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ogino S and Goel A: Molecular
classification and correlates in colorectal cancer. J Mol Diagn.
10:13–27. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grady WM and Carethers JM: Genomic and
epigenetic instability in colorectal cancer pathogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 135:1079–1099. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bakhoum SF, Silkworth WT, Nardi IK,
Nicholson JM, Compton DA and Cimini D: The mitotic origin of
chromosomal instability. Curr Biol. 24:R148–R149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nazemalhosseini Mojarad E, Kuppen PJK,
Aghdaei HA and Zali MR: The CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP)
in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 6:120–128.
2013.
|
|
12
|
Markowitz SD and Bertagnolli MM: Molecular
origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J
Med. 361:2449–2460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pawlik TM, Raut CP and Rodriguez-Bigas MA:
Colorectal carcinogenesis: MSI-H versus MSI-L. Dis Markers.
20:199–206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pitot HC: The molecular biology of
carcinogenesis. Cancer. 72(3 Suppl): S962–S970. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
O'Connell JB, Maggard MA and Ko CY: Colon
cancer survival rates with the new American joint committee on
cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1420–1425.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu W, He Y, Wang Y, Li X, Young J,
Ioannidis JPA, Dunlop MG and Theodoratou E: Risk factors and risk
prediction models for colorectal cancer metastasis and recurrence:
An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of
observational studies. BMC Med. 18:1722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jensen KH, Izarzugaza JMG, Juncker AS,
Hansen RB, Hansen TF, Timshel P, Blondal T, Jensen TS,
Rygaard-Hjalsted E, Mouritzen P, et al: Analysis of a gene panel
for targeted sequencing of colorectal cancer samples. Oncotarget.
9:9043–9060. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fearon ER and Vogelstein B: A genetic
model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 61:759–767. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fearon ER: Molecular genetics of
colorectal cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:479–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Kern
SE, Preisinger AC, Leppert M, Nakamura Y, White R, Smits AM and Bos
JL: Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl
J Med. 319:525–532. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jass JR and Smith M: Sialic acid and
epithelial differentiation in colorectal polyps and cancer-a
morphological, mucin and lectin histochemical study. Pathology.
24:233–242. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dekker E: IJspeert JEG: Serrated pathway:
A paradigm shift in CRC prevention. Gut. 67:1751–1752. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
East JE, Vieth M and Rex DK: Serrated
lesions in colorectal cancer screening: Detection, resection,
pathology and surveillance. Gut. 64:991–1000. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Longacre TA and Fenoglio-Preiser CM: Mixed
hyperplastic adenomatous polyps/serrated adenomas. A distinct form
of colorectal neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol. 14:524–537. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Snover DC, Ahnen D, Burt R and Odze R:
Serrated polyps of the colon and rectum and serrated
('hyperplastic') polyposis WHO classification of tumours of the
digestive system. International Agency for Research on Cancer;
Lyon: pp. 160–165. 2010
|
|
26
|
Groff RJ, Nash R and Ahnen DJ:
Significance of serrated polyps of the colon. Curr Gastroenterol
Rep. 10:490–498. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aust DE and Baretton GB; Members of the
Working Group GI-Pathology of the German Society of Pathology:
Serrated polyps of the colon and rectum (hyperplastic polyps,
sessile serrated adenomas, traditional serrated adenomas, and mixed
polyps)-proposal for diagnostic criteria. Virchows Arch.
457:291–297. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Torlakovic E, Skovlund E, Snover DC,
Torlakovic G and Nesland JM: Morphologic reappraisal of serrated
colorectal polyps. Am J Surg Pathol. 27:65–81. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Goldstein NS, Bhanot P, Odish E and Hunter
S: Hyperplastic-like colon polyps that preceded
microsatellite-unstable adenocarcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol.
119:778–796. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim KM, Lee EJ, Kim YH, Chang DK and Odze
RD: KRAS mutations in traditional serrated adenomas from Korea
herald an aggressive phenotype. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:667–675. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC): Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN). IARC; Lyon:
2018
|
|
32
|
Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery
L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I and Bray F: Global Cancer
Observatory: Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on
Cancer; Lyon: 2018
|
|
33
|
Li FY and Lai MD: Colorectal cancer, one
entity or three. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 10:219–229. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Murphy N, Ward HA, Jenab M, Rothwell JA,
Boutron-Ruault MC, Carbonnel F, Kvaskoff M, Kaaks R, Kühn T, Boeing
H, et al: Heterogeneity of colorectal cancer risk factors by
anatomical subsite in 10 european countries: A multinational cohort
study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:1323–1331.e6. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yang L, Xiong Z, He W, Xie K, Liu S, Kong
P, Jiang C, Guo G and Xia L: Proximal shift of colorectal cancer
with increasing age in different ethnicities. Cancer Manag Res.
10:2663–2673. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Murphy G, Devesa SS, Cross AJ, Inskip PD,
McGlynn KA and Cook MB: Sex disparities in colorectal cancer
incidence by anatomic subsite, race and age. Int J Cancer.
128:1668–1675. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Shin A, Kim KZ, Jung KW, Park S, Won YJ,
Kim J, Kim DY and Oh JH: Increasing trend of colorectal cancer
incidence in Korea,. 1999–2009. Cancer Res Treat. 44:219–226. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Rawla P, Sunkara T and Barsouk A:
Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival,
and risk factors. Prz Gastroenterol. 14:89–103. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Win AK, Jenkins MA, Dowty JG, Antoniou AC,
Lee A, Giles GG, Buchanan DD, Clendenning M, Rosty C, Ahnen DJ, et
al: Prevalence and penetrance of major genes and polygenes for
colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 26:404–412.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Aaltonen LA, Peltomäki P, Leach FS,
Sistonen P, Pylkkänen L, Mecklin JP, Järvinen H, Powell SM, Jen J,
Hamilton SR, et al: Clues to the pathogenesis of familial
colorectal cancer. Science. 260:812–416. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ionov Y, Peinado MA, Malkhosyan S, Shibata
D and Perucho M: Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated
sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis.
Nature. 363:558–561. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Thibodeau SN, Bren G and Schaid D:
Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon.
Science. 260:816–819. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hampel H, Frankel WL, Martin E, Arnold M,
Khanduja K, Kuebler P, Nakagawa H, Sotamaa K, Prior TW, Westman J,
et al: Screening for the Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis
colorectal cancer). N Engl J Med. 352:1851–1860. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Patel SG and Ahnen DJ: Familial colon
cancer syndromes: An update of a rapidly evolving field. Curr
Gastroenterol Rep. 14:428–438. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Half E, Bercovich D and Rozen P: Familial
adenomatous polyposis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 4:222009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vasen HF, Tomlinson I and Castells A:
Clinical management of hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:88–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sir Michael M, Tola A, Tim B and Junshi C:
World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research.
Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: A
Global Perspective. AICR; Washington, DC: 2007
|
|
48
|
Hofseth LJ, Hebert JR, Chanda A, Chen H,
Love BL, Pena MM, Murphy EA, Sajish M, Sheth A, Buckhaults PJ and
Berger FG: Early-onset colorectal cancer: Initial clues and current
views. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:352–364. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mauri G, Sartore-Bianchi A, Russo AG,
Marsoni S, Bardelli A and Siena S: Early-onset colorectal cancer in
young individuals. Mol Oncol. 13:109–131. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Bailey CE, Hu CY, You YN, Bednarski BK,
Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Skibber JM, Cantor SB and Chang GJ: Increasing
disparities in the age-related incidences of colon and rectal
cancers in the United States, 1975-2010. JAMA Surg. 150:17–22.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Pearlman R, Frankel WL, Swanson B, Zhao W,
Yilmaz A, Miller K, Bacher J, Bigley C, Nelsen L, Goodfellow PJ, et
al: Ohio colorectal cancer prevention initiative study group:
Prevalence and spectrum of germline cancer susceptibility gene
mutations among patients with early-onset colorectal cancer. JAMA
Oncol. 3:464–471. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Schellerer VS, Merkel S, Schumann SC,
Schlabrakowski A, Förtsch T, Schildberg C, Hohenberger W and Croner
RS: Despite aggressive histopathology survival is not impaired in
young patients with colorectal cancer: CRC in patients under 50
years of age. Int J Colorectal Dis. 27:71–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wang MJ, Ping J, Li Y, Adell G, Arbman G,
Nodin B, Meng WJ, Zhang H, Yu YY, Wang C, et al: The prognostic
factors and multiple biomarkers in young patients with colorectal
cancer. Sci Rep. 5:106452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Crosbie AB, Roche LM, Johnson LM, Pawlish
KS, Paddock LE and Stroup AM: Trends in colorectal cancer incidence
among younger adults-Disparities by age, sex, race, ethnicity, and
subsite. Cancer Med. 7:4077–4086. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ballester V, Rashtak S and Boardman L:
Clinical and molecular features of young-onset colorectal cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 22:1736–1744. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dozois EJ, Boardman LA, Suwanthanma W,
Limburg PJ, Cima RR, Bakken JL, Vierkant RA, Aakre JA and Larson
DW: Young-onset colorectal cancer in patients with no known genetic
predisposition: Can we increase early recognition and improve
outcome? Medicine (Baltimore). 87:259–263. 2008.
|
|
57
|
O'Connell JB, Maggard MA, Liu JH, Etzioni
DA, Livingston EH and Ko CY: Do young colon cancer patients have
worse outcomes? World J Surg. 28:558–562. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Taggarshe D, Rehil N, Sharma S, Flynn JC
and Damadi A: Colorectal cancer: Are the 'young' being overlooked?
Am J Surg. 205:312–316. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Low EE, Demb J, Liu L, Earles A,
Bustamante R, Williams CD, Provenzale D, Kaltenbach T, Gawron AJ,
Martinez ME and Gupta S: Risk factors for early-onset colorectal
cancer. Gastroenterology. 159:492–501.e7. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu PH, Wu K, Ng K, Zauber AG, Nguyen LH,
Song M, He X, Fuchs CS, Ogino S, Willett WC, et al: Association of
obesity with risk of early-onset colorectal cancer among women.
JAMA Oncol. 5:37–44. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF
and Zwahlen M: Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational
studies. Lancet. 371:569–578. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dong Y, Zhou J, Zhu Y, Luo L, He T, Hu H,
Liu H, Zhang Y, Luo D, Xu S, et al: Abdominal obesity and
colorectal cancer risk: Systematic review and meta-analysis of
prospective studies. Biosci Rep. 37:BSR201709452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tejpar S and Van Cutsem E: Molecular and
genetic defects in colorectal tumorigenesis. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 16:171–185. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B:
Genetic instability in colorectal cancers. Nature. 386:623–627.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Nojadeh JN, Behrouz Sharif S and Sakhinia
E: Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. EXCLI J.
17:159–168. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Vilar E and Gruber SB: Microsatellite
instability in colorectal cancer-the stable evidence. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 7:153–162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Geiersbach KB and Samowitz WS:
Microsatellite instability and colorectal cancer. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 135:1269–1277. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lao VV and Grady WM: Epigenetics and
colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:686–700. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kambara T, Simms LA, Whitehall VL, Spring
KJ, Wynter CV, Walsh MD, Barker MA, Arnold S, McGivern A, Matsubara
N, et al: BRAF mutation is associated with DNA methylation in
serrated polyps and cancers of the colorectum. Gut. 53:1137–1144.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Loeb LA, Loeb KR and Anderson JP: Multiple
mutations and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:776–781. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Loeb LA: A mutator phenotype in cancer.
Cancer Res. 61:3230–3239. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Prindle MJ, Fox EJ and Loeb LA: The
mutator phenotype in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and targeting
strategies. Curr Drug Targets. 11:1296–1303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B:
Genetic instabilities in human cancers. Nature. 396:643–649. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Le Scouarnec S and Gribble SM:
Characterising chromosome rearrangements: Recent technical advances
in molecular cytogenetics. Heredity (Edinb). 108:75–85. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Pino MS and Chung DC: The chromosomal
instability pathway in colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2059–2072. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Rowan A, Halford S, Gaasenbeek M, Kemp Z,
Sieber O, Volikos E, Douglas E, Fiegler H, Carter N, Talbot I, et
al: Refining molecular analysis in the pathways of colorectal
carcinogenesis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:1115–1123. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Weber JC, Meyer N, Pencreach E, Schneider
A, Guérin E, Neuville A, Stemmer C, Brigand C, Bachellier P, Rohr
S, et al: Allelotyping analyses of synchronous primary and
metastasis CIN colon cancers identified different subtypes. Int J
Cancer. 120:524–532. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Cheng YW, Pincas H, Bacolod MD, Schemmann
G, Giardina SF, Huang J, Barral S, Idrees K, Khan SA, Zeng Z, et
al: CpG island methylator phenotype associates with low-degree
chromosomal abnormalities in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
14:6005–6013. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Grady WM: Epigenetic events in the
colorectum and in colon cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 33:684–688.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shih IM, Zhou W, Goodman SN, Lengauer C,
Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B: Evidence that genetic instability
occurs at an early stage of colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
61:818–822. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sieber OM, Heinimann K and Tomlinson IP:
Genomic instability-the engine of tumorigenesis? Nat Rev Cancer.
3:701–708. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Thiagalingam S, Lengauer C, Leach FS,
Schutte M, Hahn SA, Overhauser J, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Hamilton
SR, Kern SE, et al: Evaluation of candidate tumor suppressor genes
on chromosome 18 in colorectal cancers. Nat Genet. 13:343–346.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Powell SM, Zilz N, Beazer-Barclay Y, Bryan
TM, Hamilton SR, Thibodeau SN, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: APC
mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis. Nature.
359:235–237. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B: Lessons from
hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 87:159–170. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Su LK, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Association of the APC tumor suppressor protein with catenins.
Science. 262:1734–1737. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Bokoch GM and Der CJ: Emerging concepts in
the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins. FASEB J. 7:750–759.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Arber N, Shapira I, Ratan J, Stern B,
Hibshoosh H, Moshkowitz M, Gammon M, Fabian I and Halpern Z:
Activation of c-K-ras mutations in human gastrointestinal tumors.
Gastroenterology. 118:1045–1050. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Bos JL, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Verlaan-de
Vries M, van Boom JH, van der Eb AJ and Vogelstein B: Prevalence of
ras gene mutations in human colorectal cancers. Nature.
327:293–297. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Nguyen HT and Duong HQ: The molecular
characteristics of colorectal cancer: Implications for diagnosis
and therapy. Oncol Lett. 16:9–18. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Tanaka T, Watanabe T, Kazama Y, Tanaka J,
Kanazawa T, Kazama S and Nagawa H: Chromosome 18q deletion and
Smad4 protein inactivation correlate with liver metastasis: A study
matched for T- and N-classification. Br J Cancer. 95:1562–1567.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zauber P, Sabbath-Solitare M, Marotta SP
and Bishop T: Loss of heterozygosity for chromosome 18q and
microsatellite instability are highly consistent across the region
of the DCC and SMAD4 genes in colorectal carcinomas and adenomas. J
Appl Res. 8:142008.
|
|
92
|
Kirley SD, D'Apuzzo M, Lauwers GY,
Graeme-Cook F, Chung DC and Zukerberg LR: The Cables gene on
chromosome 18Q regulates colon cancer progression in vivo. Cancer
Biol Ther. 4:861–863. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jung B, Staudacher JJ and Beauchamp D:
Transforming growth factor β superfamily signaling in development
of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 152:36–52. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Muzny DM, Bainbridge M, Chang K, Dinh HH,
Drummond JA, Fowler G, Kovar CL, Lewis LR, Morgan MB, Morgan I, et
al: Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and
rectal cancer. Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Mehlen P and Fearon ER: Role of the
dependence receptor DCC in colorectal cancer pathogenesis. J Clin
Oncol. 22:3420–3428. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hedrick L, Cho KR and Vogelstein B: Cell
adhesion molecules as tumor suppressors. Trends Cell Biol. 3:36–39.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Martínez-López E, Abad A, Font A, Monzó M,
Ojanguren I, Pifarré A, Sánchez JJ, Martín C and Rosell R: Allelic
loss on chromosome 18q as a prognostic marker in stage II
colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 114:1180–1187. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Saha MN, Qiu L and Chang H: Targeting p53
by small molecules in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol.
6:232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Li H, Zhang J, Tong JHM, Chan AWH, Yu J,
Kang W and To KF: Targeting the oncogenic p53 mutants in colorectal
cancer and other solid tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 20:59992019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
100
|
López I, P Oliveira L, Tucci P,
Alvarez-Valín F, A Coudry R and Marín M: Different mutation
profiles associated to P53 accumulation in colorectal cancer. Gene.
499:81–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Russo A, Bazan V, Iacopetta B, Kerr D,
Soussi T and Gebbia N; TP53-CRC Collaborative Study Group: The TP53
colorectal cancer international collaborative study on the
prognostic and predictive significance of p53 mutation: Influence
of tumor site, type of mutation, and adjuvant treatment. J Clin
Oncol. 23:7518–7528. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Sigal A and Rotter V: Oncogenic mutations
of the p53 tumor suppressor: The demons of the guardian of the
genome. Cancer Res. 60:6788–6793. 2000.
|
|
103
|
Teodoro JG, Evans SK and Green MR:
Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by p53: A new role for the
guardian of the genome. J Mol Med (Berl). 85:1175–1186. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Levine AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper
for growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Howe JR and Guillem JG: The genetics of
colorectal cancer. Surg Clin North Am. 77:175–195. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Boland CR and Goel A: Microsatellite
instability in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2073–2087.e3. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Boland CR: The molecular biology of
gastrointestinal cancer: Implications for diagnosis and therapy.
Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 18:401–413. vii2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR,
Sidransky D, Eshleman JR, Burt RW, Meltzer SJ, Rodriguez-Bigas MA,
Fodde R, Ranzani GN and Srivastava S: A national cancer institute
workshop on microsatellite instability for cancer detection and
familial predisposition: Development of international criteria for
the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 58:5248–5257. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Findeisen P, Kloor M, Merx S, Sutter C,
Woerner SM, Dostmann N, Benner A, Dondog B, Pawlita M, Dippold W,
et al: T25 repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the CASP2 gene:
a sensitive and specific marker for microsatellite instability in
colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 65:8072–8078. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Lynch HT, Lynch PM, Lanspa SJ, Snyder CL,
Lynch JF and Boland CR: Review of the Lynch syndrome: History,
molecular genetics, screening, differential diagnosis, and
medicolegal ramifications. Clin Genet. 76:1–18. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
van Rijnsoever M, Grieu F, Elsaleh H,
Joseph D and Iacopetta B: Characterisation of colorectal cancers
showing hypermethylation at multiple CpG islands. Gut. 51:797–802.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Toyota M, Ahuja N, Ohe-Toyota M, Herman
JG, Baylin SB and Issa JPJ: CpG island methylator phenotype in
colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:8681–8686.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Jass JR: Serrated adenoma of the
colorectum and the DNA-methylator phenotype. Nat Clin Pract Oncol.
2:398–405. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Samowitz WS, Albertsen H, Herrick J, Levin
TR, Sweeney C, Murtaugh MA, Wolff RK and Slattery ML: Evaluation of
a large, population-based sample supports a CpG island methylator
phenotype in colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 129:837–845.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Hawkins N, Norrie M, Cheong K, Mokany E,
Ku SL, Meagher A, O'Connor T and Ward R: CpG island methylation in
sporadic colorectal cancers and its relationship to microsatellite
instability. Gastroenterology. 122:1376–1387. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Chan AOO, Issa JPJ, Morris JS, Hamilton SR
and Rashid A: Concordant CpG island methylation in hyperplastic
polyposis. Am J Pathol. 160:529–536. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wynter CVA, Walsh MD, Higuchi T, Leggett
BA, Young J and Jass JR: Methylation patterns define two types of
hyperplastic polyp associated with colorectal cancer. Gut.
53:573–580. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Minoo P, Baker K, Goswami R, Chong G,
Foulkes WD, Ruszkiewicz AR, Barker M, Buchanan D, Young J and Jass
JR: Extensive DNA methylation in normal colorectal mucosa in
hyperplastic polyposis. Gut. 55:1467–1474. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Shima K, Morikawa T, Yamauchi M, Kuchiba
A, Imamura Y, Liao X, Meyerhardt JA, Fuchs CS and Ogino S: TGFBR2
and BAX mononucleotide tract mutations, microsatellite instability,
and prognosis in 1072 colorectal cancers. PLoS One.
6:e250622011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Edelstein DL, Axilbund JE, Hylind LM,
Romans K, Griffin CA, Cruz-Correa M and Giardiello FM: Serrated
polyposis: Rapid and relentless development of colorectal
neoplasia. Gut. 62:404–408. 2013.
|
|
121
|
Bettington M, Walker N, Rosty C, Brown I,
Clouston A, McKeone D, Pearson SA, Leggett B and Whitehall V:
Clinicopathological and molecular features of sessile serrated
adenomas with dysplasia or carcinoma. Gut. 66:97–106. 2017.
|
|
122
|
Johnson CM, Wei C, Ensor JE, Smolenski DJ,
Amos CI, Levin B and Berry DA: Meta-analyses of colorectal cancer
risk factors. Cancer Causes Control. 24:1207–1222. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zisman AL, Nickolov A, Brand RE, Gorchow A
and Roy HK: Associations between the age at diagnosis and location
of colorectal cancer and the use of alcohol and tobacco:
Implications for screening. Arch Intern Med. 166:629–634.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Botteri E, Iodice S, Bagnardi V, Raimondi
S, Lowenfels AB and Maisonneuve P: Smoking and colorectal cancer: A
meta-analysis. JAMA. 300:2765–2778. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Pande M, Lynch PM, Hopper JL, Jenkins MA,
Gallinger S, Haile RW, LeMarchand L, Lindor NM, Campbell PT,
Newcomb PA, et al: Smoking and colorectal cancer in Lynch syndrome:
Results from the colon cancer family registry and the University of
Texas M.D. Anderson cancer center. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1331–1339.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Figueiredo JC, Crockett SD, Snover DC,
Morris CB, McKeown-Eyssen G, Sandler RS, Ahnen DJ, Robertson DJ,
Burke CA, Bresalier RS, et al: Smoking-associated risks of
conventional adenomas and serrated polyps in the colorectum. Cancer
Causes Control. 26:377–386. 2015.
|
|
127
|
Limsui D, Vierkant RA, Tillmans LS, Wang
AH, Weisenberger DJ, Laird PW, Lynch CF, Anderson KE, French AJ,
Haile RW, et al: Cigarette smoking and colorectal cancer risk by
molecularly defined subtypes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:1012–1022.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Hannan LM, Jacobs EJ and Thun MJ: The
association between cigarette smoking and risk of colorectal cancer
in a large prospective cohort from the United States. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:3362–3367. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Ordóñez-Mena JM, Walter V, Schöttker B,
Jenab M, O'Doherty MG, Kee F, Bueno-de-Mesquita B, Peeters PHM,
Stricker BH, Ruiter R, et al: Impact of prediagnostic smoking and
smoking cessation on colorectal cancer prognosis: A meta-analysis
of individual patient data from cohorts within the CHANCES
consortium. Ann Oncol. 29:472–483. 2018.
|
|
130
|
Pöschl G and Seitz HK: Alcohol and cancer.
Alcohol Alcohol. 39:155–165. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Fedirko V, Tramacere I, Bagnardi V, Rota
M, Scotti L, Islami F, Negri E, Straif K, Romieu I, La Vecchia C,
et al: Alcohol drinking and colorectal cancer risk: An overall and
dose-response meta-analysis of published studies. Ann Oncol.
22:1958–1972. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Choi YJ, Myung SK and Lee JH: Light
alcohol drinking and risk of cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort
studies. Cancer Res Treat. 50:474–487. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
133
|
Cho E, Smith-Warner SA, Ritz J, van den
Brandt PA, Colditz GA, Folsom AR, Freudenheim JL, Giovannucci E,
Goldbohm RA, Graham S, et al: Alcohol intake and colorectal cancer:
A pooled analysis of 8 cohort studies. Ann Intern Med. 140:603–613.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Praud D, Rota M, Rehm J, Shield K,
Zatoński W, Hashibe M, La Vecchia C and Boffetta P: Cancer
incidence and mortality attributable to alcohol consumption. Int J
Cancer. 138:1380–1387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Nelson DE, Jarman DW, Rehm J, Greenfield
TK, Rey G, Kerr WC, Miller P, Shield KD, Ye Y and Naimi TS:
Alcohol-attributable cancer deaths and years of potential life lost
in the United States. Am J Public Health. 103:641–648. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Butler LM, Sinha R, Millikan RC, Martin
CF, Newman B, Gammon MD, Ammerman AS and Sandler RS: Heterocyclic
amines, meat intake, and association with colon cancer in a
population-based study. Am J Epidemiol. 157:434–445. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Kampman E, Slattery ML, Bigler J, Leppert
M, Samowitz W, Caan BJ and Potter JD: Meat consumption, genetic
susceptibility, and colon cancer risk: A United States multicenter
case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 8:15–24.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Santarelli RL, Pierre F and Corpet DE:
Processed meat and colorectal cancer: A review of epidemiologic and
experimental evidence. Nutr Cancer. 60:131–144. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Kabat GC, Miller AB, Jain M and Rohan TE:
A cohort study of dietary iron and heme iron intake and risk of
colorectal cancer in women. Br J Cancer. 97:118–122. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Sinha R: An epidemiologic approach to
studying heterocyclic amines. Mutat Res. 506-507:197–204. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Pietinen P, Malila N, Virtanen M, Hartman
TJ, Tangrea JA, Albanes D and Virtamo J: Diet and risk of
colorectal cancer in a cohort of Finnish men. Cancer Causes
Control. 10:387–396. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Terry P, Giovannucci E, Michels KB,
Bergkvist L, Hansen H, Holmberg L and Wolk A: Fruit, vegetables,
dietary fiber, and risk of colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
93:525–533. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Bardou M, Barkun AN and Martel M: Obesity
and colorectal cancer. Gut. 62:933–947. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Kelly DM and Jones TH: Testosterone and
obesity. Obes Rev. 16:581–606. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Matsuo K, Mizoue T, Tanaka K, Tsuji I,
Sugawara Y, Sasazuki S, Nagata C, Tamakoshi A, Wakai K, Inoue M, et
al: Association between body mass index and the colorectal cancer
risk in Japan: Pooled analysis of population-based cohort studies
in Japan. Ann Oncol. 23:479–490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Goh LY and Goh KL: Obesity: An
epidemiological perspective from Asia and its relationship to
gastrointestinal and liver cancers. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
28(Suppl 4): S54–S58. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
World Cancer Research Fund: Continuous
update project report. Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the
prevention of colorectal cancer. In: WCRF/AICR; 2011
|
|
148
|
Song M, Hu FB, Spiegelman D, Chan AT, Wu
K, Ogino S, Fuchs CS, Willett WC and Giovannucci EL: Long-term
status and change of body fat distribution, and risk of colorectal
cancer: A prospective cohort study. Int J Epidemiol. 45:871–883.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
149
|
Moore LL, Bradlee ML, Singer MR, Splansky
GL, Proctor MH, Ellison RC and Kreger BE: BMI and waist
circumference as predictors of lifetime colon cancer risk in
Framingham study adults. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 28:559–567.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Samaras K, Botelho NK, Chisholm DJ and
Lord RV: Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue gene expression
of serum adipokines that predict type 2 diabetes. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 18:884–889. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Lim U, Ernst T, Buchthal SD, Latch M,
Albright CL, Wilkens LR, Kolonel LN, Murphy SP, Chang L, Novotny R
and Le Marchand L: Asian women have greater abdominal and visceral
adiposity than Caucasian women with similar body mass index. Nutr
Diabetes. 1:e62011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Ma Y, Yang Y, Wang F, Zhang P, Shi C, Zou
Y and Qin H: Obesity and risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic
review of prospective studies. PLoS One. 8:e539162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Lee YJ, Myung SK, Cho B, Park BJ, Park JH,
Ju W, Park MS and Choi JH: Adiposity and the risk of colorectal
adenomatous polyps: A meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control.
22:1021–1035. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Guraya SY: Association of type 2 diabetes
mellitus and the risk of colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis and
systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 21:6026–6031. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Kahn SE, Hull RL and Utzschneider KM:
Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2
diabetes. Nature. 444:840–846. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Moller DE and Flier JS: Insulin
resistance-mechanisms, syndromes, and implications. N Engl J Med.
325:938–948. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Pollak M: Insulin and insulin-like growth
factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:915–928. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Calle EE and Kaaks R: Overweight, obesity
and cancer: Epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat
Rev Cancer. 4:579–591. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Murphy N, Strickler HD, Stanczyk FZ, Xue
X, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Rohan TE, Ho GY, Anderson GL, Potter JD
and Gunter MJ: A prospective evaluation of endogenous sex hormone
levels and colorectal cancer risk in postmenopausal women. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 107. pp. djv2102015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Hetemäki N, Savolainen-Peltonen H,
Tikkanen MJ, Wang F, Paatela H, Hämäläinen E, Turpeinen U, Haanpää
M, Vihma V and Mikkola TS: Estrogen metabolism in abdominal
subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in postmenopausal women. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 102:4588–4595. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Burkitt DP: Epidemiology of cancer of the
colon and rectum. Cancer. 28:3–13. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Aune D, Chan DS, Lau R, Vieira R,
Greenwood DC, Kampman E and Norat T: Dietary fibre, whole grains,
and risk of colorectal cancer: Systematic review and dose-response
meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ. 343. pp. d66172011,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
World Cancer Research Fund: Diet,
nutrition, physical activity and cancer: A global perspective: A
summary of the third expert report. World Cancer Research Fund
International. 2018.
|
|
164
|
Rezende LFM, Sá TH, Markozannes G,
Rey-López JP, Lee IM, Tsilidis KK, Ioannidis JPA and Eluf-Neto J:
Physical activity and cancer: An umbrella review of the literature
including 22 major anatomical sites and 770 000 cancer cases. Br J
Sports Med. 52:826–833. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Morris JS, Bradbury KE, Cross AJ, Gunter
MJ and Murphy N: Physical activity, sedentary behaviour and
colorectal cancer risk in the UK Biobank. Br J Cancer. 118:920–929.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Keum N, Bao Y, Smith-Warner SA, Orav J, Wu
K, Fuchs CS and Giovannucci EL: Association of physical activity by
type and intensity with digestive system cancer risk. JAMA Oncol.
2:1146–1153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Ma P, Yao Y, Sun W, Dai S and Zhou C:
Daily sedentary time and its association with risk for colorectal
cancer in adults: A dose-response meta-analysis of prospective
cohort studies. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e70492017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Lynch BM: Sedentary behavior and cancer: A
systematic review of the literature and proposed biological
mechanisms. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:2691–2709. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Howard RA, Freedman DM, Park Y, Hollenbeck
A, Schatzkin A and Leitzmann MF: Physical activity, sedentary
behavior, and the risk of colon and rectal cancer in the NIH-AARP
diet and health study. Cancer Causes Control. 19:939–953. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Jeong WJ, Ro EJ and Choi KY: Interaction
between Wnt/β-catenin and RAS-ERK pathways and an anti-cancer
strategy via degradations of β-catenin and RAS by targeting the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2:52018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Novellasdemunt L, Antas P and Li VS:
Targeting Wnt signalling in colorectal cancer. A review in the
theme: Cell Signalling: Proteins, pathways and mechanisms. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 309:C511–C521. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Farooqi AA, de la Roche M, Djamgoz MBA and
Siddik ZH: Overview of the oncogenic signalling pathways in
colorectal cancer: Mechanistic insights. Semin Cancer Biol.
58:65–79. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Koveitypour Z, Panahi F, Vakilian M,
Peymani M, Seyed Forootan F, Nasr Esfahani MH and Ghaedi K:
Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer progression. Cell
Biosci. 9:972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Pandurangan AK, Divya T, Kumar K,
Dineshbabu V, Velavan B and Sudhandiran G: Colorectal
carcinogenesis: Insights into the cell death and signal
transduction pathways: A review. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
10:244–259. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Tiwari A, Saraf S, Verma A, Panda PK and
Jain SK: Novel targeting approaches and signaling pathways of
colorectal cancer: An insight. World J Gastroenterol. 24:4428–4435.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Saharinen P, Eklund L, Pulkki K, Bono P
and Alitalo K: VEGF and angiopoietin signaling in tumor
angiogenesis and metastasis. Trends Mol Med. 17:347–362. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Goel HL and Mercurio AM: VEGF targets the
tumor cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:871–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Lee YJ, Karl DL, Maduekwe UN, Rothrock C,
Ryeom S, D'Amore PA and Yoon SS: Differential effects of VEGFR-1
and VEGFR-2 inhibition on tumor metastases based on host organ
environment. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Cancer Res.
70:8357–8367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Vaahtomeri K, Karaman S, Mäkinen T and
Alitalo K: Lymphangiogenesis guidance by paracrine and pericellular
factors. Genes Dev. 31:1615–1634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J and
Claesson-Welsh L: VEGF receptor signalling-in control of vascular
function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:359–371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Takahashi H and Shibuya M: The vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor system and its role
under physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond).
109:227–241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Koch S and Claesson-Welsh L: Signal
transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0065022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Garnier L, Gkountidi AO and Hugues S:
Tumor-associated lymphatic vessel features and immunomodulatory
functions. Front Immunol. 10:7202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Secker GA and Harvey NL: VEGFR signaling
during lymphatic vascular development: From progenitor cells to
functional vessels. Dev Dyn. 244:323–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Cébe-Suarez S, Zehnder-Fjällman A and
Ballmer-Hofer K: The role of VEGF receptors in angiogenesis;
complex partnerships. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:601–615. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Lopez A, Harada K, Vasilakopoulou M,
Shanbhag N and Ajani JA: Targeting angiogenesis in colorectal
carcinoma. Drugs. 79:63–74. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Seeber A, Gunsilius E, Gastl G and Pircher
A: Anti-angiogenics: Their value in colorectal cancer therapy.
Oncol Res Treat. 41:188–193. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Guba M, Seeliger H, Kleespies A, Jauch KW
and Bruns C: Vascular endothelial growth factor in colorectal
cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 19:510–517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Jain RK: Antiangiogenesis strategies
revisited: From starving tumors to alleviating hypoxia. Cancer
Cell. 26:605–622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Amelio I and Melino G: The p53 family and
the hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs): Determinants of cancer
progression. Trends Biochem Sci. 40:425–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A and Jones MK:
Angiogenesis in gastric mucosa: An important component of gastric
erosion and ulcer healing and its impairment in aging. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29(Suppl 4): S112–S23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
194
|
Wang Q, Yang S, Wang K and Sun SY: MET
inhibitors for targeted therapy of EGFR TKI-resistant lung cancer.
J Hematol Oncol. 12:632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Cheng F and Guo D: MET in glioma:
Signaling pathways and targeted therapies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:2702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Demkova L and Kucerova L: Role of the
HGF/c-MET tyrosine kinase inhibitors in metastasic melanoma. Mol
Cancer. 17:262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Lam BQ, Dai L and Qin Z: The role of
HGF/c-MET signaling pathway in lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol.
9:1352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Bradley CA, Salto-Tellez M, Laurent-Puig
P, Bardelli A, Rolfo C, Tabernero J, Khawaja HA, Lawler M, Johnston
PG and Van Schaeybroeck S; MErCuRIC consortium: Targeting c-MET in
gastrointestinal tumors: Rationale, opportunities and challenges.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:562–576. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Xing F, Liu Y, Sharma S, Wu K, Chan MD, Lo
HW, Carpenter RL, Metheny-Barlow LJ, Zhou X, Qasem SA, et al:
Activation of the c-Met pathway mobilizes an inflammatory network
in the brain microenvironment to promote brain metastasis of breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 76:4970–4980. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Ozawa Y, Nakamura Y, Fujishima F, Felizola
SJ, Takeda K, Okamoto H, Ito K, Ishida H, Konno T, Kamei T, et al:
c-Met in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: An independent
prognostic factor and potential therapeutic target. BMC Cancer.
15:4512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Anestis A, Zoi I and Karamouzis MV:
Current advances of targeting HGF/c-Met pathway in gastric cancer.
Ann Transl Med. 6:2472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Safaie Qamsari E, Safaei Ghaderi S, Zarei
B, Dorostkar R, Bagheri S, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Somi MH and Yousefi M:
The c-Met receptor: Implication for targeted therapies in
colorectal cancer. Tumor Biol. 39:10104283176991182017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Otte JM, Schmitz F, Kiehne K, Stechele HU,
Banasiewicz T, Krokowicz P, Nakamura T, Fölsch UR and Herzig K:
Functional expression of HGF and its receptor in human colorectal
cancer. Digestion. 61:237–246. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Matsumoto K, Umitsu M, De Silva DM, Roy A
and Bottaro DP: Hepatocyte growth factor/MET in cancer progression
and biomarker discovery. Cancer Sci. 108:296–307. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Bahrami A, Shahidsales S, Khazaei M,
Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Maftouh M, Hassanian SM and Avan A: C-Met as a
potential target for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancer:
Current status and future perspectives. J Cell Physiol.
232:2657–2673. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Mo HN and Liu P: Targeting MET in cancer
therapy. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 3:148–153. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Bouattour M, Raymond E, Qin S, Cheng AL,
Stammberger U, Locatelli G and Faivre S: Recent developments of
c-Met as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 67:1132–1149. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
208
|
Drilon A, Cappuzzo F, Ou SI and Camidge
DR: Targeting MET in lung cancer: Will expectations finally be MET?
J Thorac Oncol. 12:15–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
209
|
Blumenschein GR Jr, Mills GB and
Gonzalez-Angulo AM: Targeting the hepatocyte growth factor-cMET
axis in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 30:3287–3296. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Cabanillas ME, de Souza JA, Geyer S, Wirth
LJ, Menefee ME, Liu SV, Shah K, Wright J and Shah MH: Cabozantinib
as salvage therapy for patients with tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: Results of a
multicenter phase II international thyroid oncology group trial. J
Clin Oncol. 35:3315–3321. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network;
Linehan WM, Spellman PT, Ricketts CJ, Creighton CJ, Fei SS, Davis
C, Wheeler DA, Murray BA, Schmidt L, et al: Comprehensive molecular
characterization of papillary renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
374:135–145. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
212
|
Catenacci DVT, Tebbutt NC, Davidenko I,
Murad AM, Al-Batran SE, Ilson DH, Tjulandin S, Gotovkin E,
Karaszewska B, Bondarenko I, et al: Rilotumumab plus epirubicin,
cisplatin, and capecitabine as first-line therapy in advanced
MET-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer
(RILOMET-1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase
3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:1467–1482. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Sartore-Bianchi A, Loupakis F, Argilés G
and Prager GW: Challenging chemoresistant metastatic colorectal
cancer: Therapeutic strategies from the clinic and from the
laboratory. Ann Oncol. 27:1456–1466. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Gao H, Guan M, Sun Z and Bai C: High c-Met
expression is a negative prognostic marker for colorectal cancer: A
meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 36:515–520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
Luo HY and Xu RH: Predictive and
prognostic biomarkers with therapeutic targets in advanced
colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 20:3858–3874. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Baldus SE, Kort EJ, Schirmacher P, Dienes
HP and Resau JH: Quantification of MET and hepatocyte growth
factor/scatter factor expression in colorectal adenomas, carcinomas
and non-neoplastic epithelia by quantitative laser scanning
microscopy. Int J Oncol. 31:199–204. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Kentsis A, Reed C, Rice KL, Sanda T, Rodig
SJ, Tholouli E, Christie A, Valk PJ, Delwel R, Ngo V, et al:
Autocrine activation of the MET receptor tyrosine kinase in acute
myeloid leukemia. Nat Med. 18:1118–1122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Stein U, Walther W, Arlt F, Schwabe H,
Smith J, Fichtner I, Birchmeier W and Schlag PM: MACC1, a newly
identified key regulator of HGF-MET signaling, predicts colon
cancer metastasis. Nat Med. 15:59–67. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
219
|
Parseghian CM, Napolitano S, Loree JM and
Kopetz S: Mechanisms of innate and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR
therapy: A review of current knowledge with a focus on rechallenge
therapies. Clin Cancer Res. 25:6899–6908. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Boccaccio C, Luraghi P and Comoglio PM:
MET-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors: An old liaison rooted
in colorectal cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 74:3647–3651. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Van Emburgh BO, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di
Nicolantonio F, Siena S and Bardelli A: Acquired resistance to
EGFR-targeted therapies in colorectal cancer. Mol Oncol.
8:1084–1094. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Viticchiè G and Muller PAJ: c-Met and
other cell surface molecules: Interaction, activation and
functional consequences. Biomedicines. 3:46–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Sharpe AH and Freeman GJ: The B7-CD28
superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:116–126. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Jelinek T, Mihalyova J, Kascak M, Duras J
and Hajek R: PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in haematological malignancies:
Update 2017. Immunology. 152:357–371. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Chen L and Han X: Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy
of human cancer: Past, present, and future. J Clin Invest.
125:3384–3391. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Markman JL and Shiao SL: Impact of the
immune system and immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. J
Gastrointest Oncol. 6:208–223. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Xie YH, Chen YX and Fang JY: Comprehensive
review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 5:222020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Pauken KE and Wherry EJ: Overcoming T cell
exhaustion in infection and cancer. Trends Immunol. 36:265–276.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Wang HB, Yao H, Li CS, Liang LX, Zhang Y,
Chen YX, Fang JY and Xu J: Rise of PD-L1 expression during
metastasis of colorectal cancer: Implications for immunotherapy. J
Dig Dis. 18:574–581. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Fujimoto H, Saito Y, Ohuchida K, Kawakami
E, Fujiki S, Watanabe T, Ono R, Kaneko A, Takagi S, Najima Y, et
al: Deregulated mucosal immune surveillance through gut-associated
regulatory T cells and PD-1+ T cells in human colorectal
cancer. J Immunol. 200:3291–3303. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Vinson KE, George DC, Fender AW, Bertrand
FE and Sigounas G: The Notch pathway in colorectal cancer. Int J
Cancer. 138:1835–1842. 2016.
|
|
232
|
Zhi X, Tao J, Zhang L, Tao R, Ma L and Qin
J: Silencing speckle-type POZ protein by promoter hypermethylation
decreases cell apoptosis through upregulating hedgehog signaling
pathway in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis.
7:e25692016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Wu C, Zhu X, Liu W, Ruan T and Tao K:
Hedgehog signalling pathway in colorectal cancer: Function,
mechanism, and therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 10:3249–3259. 2017.
|
|
234
|
Han Y: Analysis of the role of the Hippo
pathway in cancer. J Transl Med. 17:1162019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Zhang YE: Non-Smad pathways in TGF-β
signaling. Cell Res. 19:128–139. 2009.
|
|
236
|
Cheruku HR, Mohamedali A, Cantor DI, Tan
SH, Nice EC and Baker MS: Transforming growth factor-β, MAPK and
Wnt signaling interaction in colorectal cancer. EuPA Open
Proteomics. 8:104–115. 2015.
|
|
237
|
Luo K: Signaling cross talk between
TGF-β/Smad and other signaling pathways. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 9:a0221372017.
|
|
238
|
Lee Y, Kim NH, Cho ES, Yang JH, Cha YH,
Kang HE, Yun JS, Cho SB, Lee SH, Paclikova P, et al: Dishevelled
has a YAP nuclear export function in a tumor suppressor
context-dependent manner. Nat Commun. 9:23012018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Jing L, Li J, Zhang C, Shang Y and Lin J:
YAP-mediated crosstalk between the Wnt and Hippo signaling pathways
(Review). Mol Med Rep. 22:4101–4106. 2020.
|
|
240
|
Pietrobono S, Gagliardi S and Stecca B:
Non-canonical hedgehog signalling pathway in cancer: Activation of
GLI transcription factors beyond smoothened. Front Genet.
10:5562019.
|
|
241
|
Regan JL, Schumacher D, Staudte S, Steffen
A, Haybaeck J, Keilholz U, Schweiger C, Golob-Schwarzl N, Mumberg
D, Henderson D, et al: Non-canonical hedgehog signaling is a
positive regulator of the WNT pathway and is required for the
survival of colon cancer stem cells. Cell Rep. 21:2813–2828.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Heidelberger C, Chaudhuri NK, Danneberg P,
Mooren D, Griesbach L, Duschinsky R, Schnitzer RJ, Pleven E and
Scheiner J: Fluorinated pyrimidines, a new class of
tumor-inhibitory compounds. Nature. 179:663–666. 1957.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Piawah S and Venook AP: Targeted therapy
for colorectal cancer metastases: A review of current methods of
molecularly targeted therapy and the use of tumor biomarkers in the
treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer. 125:4139–4147.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Piedbois P, Buyse M, Rustum Y, Machover D,
Erlichman C, Carlson RW, Valone F, Labianca R, Doroshow JH and
Petrelli N: Modulation of fluorouracil by leucovorin in patients
with advanced colorectal cancer: Evidence in terms of response rate
by the advanced colorectal cancer meta-analysis project. J Clin
Oncol. 10:896–903. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
245
|
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin
M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer
G, et al: Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin
as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 18:2938–2947. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD,
Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, Jandik P, Iveson T, Carmichael J,
Alakl M, et al: Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with
fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic
colorectal cancer: A multicentre randomised trial. Lancet.
355:1041–1047. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Tournigand C, André T, Achille E, Lledo G,
Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G, et
al: FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced
colorectal cancer: A randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol.
22:229–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
248
|
Colucci G, Gebbia V, Paoletti G, Giuliani
F, Caruso M, Gebbia N, Cartenì G, Agostara B, Pezzella G, Manzione
L, et al: Phase III randomized trial of FOLFIRI versus FOLFOX4 in
the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: A multicenter study of
the gruppo oncologico Dell'Italia meridionale. J Clin Oncol.
23:4866–4875. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Cassidy J, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E,
Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS,
Rivera F, et al: Randomized phase III study of capecitabine plus
oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil/folinic acid plus
oxaliplatin as first-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 26:2006–2012. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Skof E, Rebersek M, Hlebanja Z and Ocvirk
J: Capecitabine plus irinotecan (XELIRI regimen) compared to
5-FU/LV plus Irinotecan (FOLFIRI regimen) as neoadjuvant treatment
for patients with unresectable liver-only metastases of metastatic
colorectal cancer: A randomised prospective phase II trial. BMC
Cancer. 9:1202009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Obrand DI and Gordon PH: Incidence and
patterns of recurrence following curative resection for colorectal
carcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum. 40:15–24. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Brodsky FM: Monoclonal antibodies as magic
bullets. Pharm Res. 5:1–9. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Lee YT, Tan YJ and Oon CE: Molecular
targeted therapy: Treating cancer with specificity. Eur J
Pharmacol. 834:188–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Martinelli E, Ciardiello D, Martini G,
Troiani T, Cardone C, Vitiello PP, Normanno N, Rachiglio AM,
Maiello E, Latiano T, et al: Implementing anti-epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer:
Challenges and future perspectives. Ann Oncol. 31:30–40. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Oh DY and Bang YJ: HER2-targeted
therapies-a role beyond breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
17:33–48. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
256
|
Ferguson FM and Gray NS: Kinase
inhibitors: The road ahead. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 17:353–377. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Tariman JD: Changes in cancer treatment:
Mabs, Mibs, Mids, Nabs, and Nibs. Nurs Clin North Am. 52:65–81.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
André T, Blons H, Mabro M, Chibaudel B,
Bachet JB, Tournigand C, Bennamoun M, Artru P, Nguyen S, Ebenezer
C, et al: Panitumumab combined with irinotecan for patients with
KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to standard
chemotherapy: A GERCOR efficacy, tolerance, and translational
molecular study. Ann Oncol. 24:412–419. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
259
|
Papadatos-Pastos D, Rabbie R, Ross P and
Sarker D: The role of the PI3K pathway in colorectal cancer. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 94:18–30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Katz LH, Li Y, Chen JS, Muñoz NM, Majumdar
A, Chen J and Mishra L: Targeting TGF-β signaling in cancer. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 17:743–760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
261
|
Jin D, Fang Y, Li Z, Chen Z and Xiang J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated microRNAs in
colorectal cancer and drug-targeted therapies (Review). Oncol Rep.
33:515–525. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
262
|
Qiao L and Wong BC: Role of Notch
signaling in colorectal cancer. Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition-associated microRNAs in colorectal cancer and
drug-targeted therapies (Review). Carcinogenesis. 30:1979–1986.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Precision medicine
for human cancers with Notch signaling dysregulation (Review). Int
J Mol Med. 45:279–297. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Fragoulis GE, Mclnnes IB and Siebert S:
JAK-inhibitors New players in the field of immune-mediated diseases
beyond rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 58(Suppl 1):
pp. i42–i54. 2019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
265
|
Wang SW, Hu J, Guo QH, Zhao Y, Cheng JJ,
Zhang DS, Fei Q, Li J and Sun YM: AZD1480, a JAK inhibitor,
inhibits cell growth and survival of colorectal cancer via
modulating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
32:1991–1998. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Gulino A, Ferretti E and De Smaele E:
Hedgehog signalling in colon cancer and stem cells. EMBO Mol Med.
1:300–302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
267
|
Wu JY, Xu XF, Xu L, Niu PQ, Wang F, Hu GY,
Wang XP and Guo CY: Cyclopamine blocked the growth of colorectal
cancer SW116 cells by modulating some target genes of Gli1 in
vitro. Hepatogastroenterology. 58:1511–1518. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Varnat F, Duquet A, Malerba M, Zbinden M,
Mas C, Gervaz P and Ruiz i Altaba A: Human colon cancer epithelial
cells harbour active HEDGEHOG-GLI signalling that is essential for
tumour growth, recurrence, metastasis and stem cell survival and
expansion. EMBO Mol Med. 1:338–351. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
269
|
Gonzalez-Donquiles C, Alonso-Molero J,
Fernandez-Villa T, Vilorio-Marqués L, Molina AJ and Martín V: The
NRF2 transcription factor plays a dual role in colorectal cancer: A
systematic review. PLoS One. 12:e01775492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Wu WK, Wang XJ, Cheng AS, Luo MX, Ng SS,
To KF, Chan FK, Cho CH, Sung JJ and Yu J: Dysregulation and
crosstalk of cellular signaling pathways in colon carcinogenesis.
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 86:251–277. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W,
Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S,
Holmgren E, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2335–2342. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
272
|
Passardi A, Nanni O, Tassinari D, Turci D,
Cavanna L, Fontana A, Ruscelli S, Mucciarini C, Lorusso V,
Ragazzini A, et al: Effectiveness of bevacizumab added to standard
chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: Final results for
first-line treatment from the ITACa randomized clinical trial. Ann
Oncol. 26:1201–1207. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Tang PA, Cohen SJ, Kollmannsberger C,
Bjarnason G, Virik K, MacKenzie MJ, Lourenco L, Wang L, Chen A and
Moore MJ: Phase II clinical and pharmacokinetic study of
aflibercept in patients with previously treated metastatic
colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:6023–6031. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
Van Cutsem E, Sobrero AF, Siena S, Falcone
A, Ychou M, Humblet Y, Bouche O, Mineur L, Barone C, Adenis A, et
al: Phase III CORRECT trial of regorafenib in metastatic colorectal
cancer (mCRC). J Clin Oncol. 30(15 Suppl): S35022012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
275
|
Tabernero J, Yoshino T, Cohn AL,
Obermannova R, Bodoky G, Garcia-Carbonero R, Ciuleanu TE, Portnoy
DC, Van Cutsem E, Grothey A, et al: Ramucirumab versus placebo in
combination with second-line FOLFIRI in patients with metastatic
colorectal carcinoma that progressed during or after first-line
therapy with bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, and a fluoropyrimidine
(RAISE): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 study.
Lancet Oncol. 16:499–508. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
276
|
Bendell JC, Ervin TJ, Gallinson D, Singh
J, Wallace JA, Saleh MN, Vallone M, Phan SC and Hack SP: Treatment
rationale and study design for a randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled phase II study evaluating onartuzumab (MetMAb)
in combination with bevacizumab plus mFOLFOX-6 in patients with
previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal
Cancer. 12:218–222. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
277
|
Shao Z, Pan H, Tu S, Zhang J, Yan S and
Shao A: HGF/c-Met axis: The advanced development in digestive
system cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:8012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Ganesh K, Stadler ZK, Cercek A, Mendelsohn
RB, Shia J, Segal NH and Diaz LA Jr: Immunotherapy in colorectal
cancer: Rationale, challenges and potential. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 16:361–375. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Passardi A, Canale M, Valgiusti M and
Ulivi P: Immune checkpoints as a target for colorectal cancer
treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 18:13242017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
280
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
281
|
Giannakis M, Mu XJ, Shukla SA, Qian ZR,
Cohen O, Nishihara R, Bahl S, Cao Y, Amin-Mansour A, Yamauchi M, et
al: Genomic correlates of immune-cell infiltrates in colorectal
carcinoma. Cell Rep. 15:857–865. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
282
|
Llosa NJ, Cruise M, Tam A, Wicks EC,
Hechenbleikner EM, Taube JM, Blosser RL, Fan H, Wang H, Luber BS,
et al: The vigorous immune microenvironment of microsatellite
instable colon cancer is balanced by multiple counter-inhibitory
checkpoints. Cancer Discov. 5:43–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
283
|
Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR,
Kemberling H, Eyring AD, Skora AD, Luber BS, Azad NS, Laheru D, et
al: PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl
J Med. 372:2509–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
284
|
Marcus L, Lemery SJ, Keegan P and Pazdur
R: FDA approval summary: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of
microsatellite instability-high solid tumors. Clin Can Res.
25:3753–3758. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
285
|
Andre T, Shiu KK, Kim TW, Jensen BV,
Jensen LH, Punt CJA, Smith DM, Garcia-Carbonero R, Benavides M,
Gibbs P, et al: Pembrolizumab vs chemotherapy for microsatellite
instability-high/mismatch repair deficient metastatic colorectal
cancer: The phase 3 KEYNOTE-177 study. J Clin Oncol. 38(18 Suppl):
LBA42020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
286
|
U.S. Food and Drug (FDA): FDA grants
nivolumab accelerated approval for MSI-H or dMMR colorectal cancer
FDA. Silver Spring, MD: 2017, https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-nivolumab-accel-erated-approval-msi-h-or-dmmr-colorectal-cancer.
Accessed January 8, 2017.
|
|
287
|
Sun J, Zheng Y, Mamun M, Li X, Chen X and
Gao Y: Research progress of PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy in
gastrointestinal tumors. Biomed Pharmacother. 129:1105042020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|