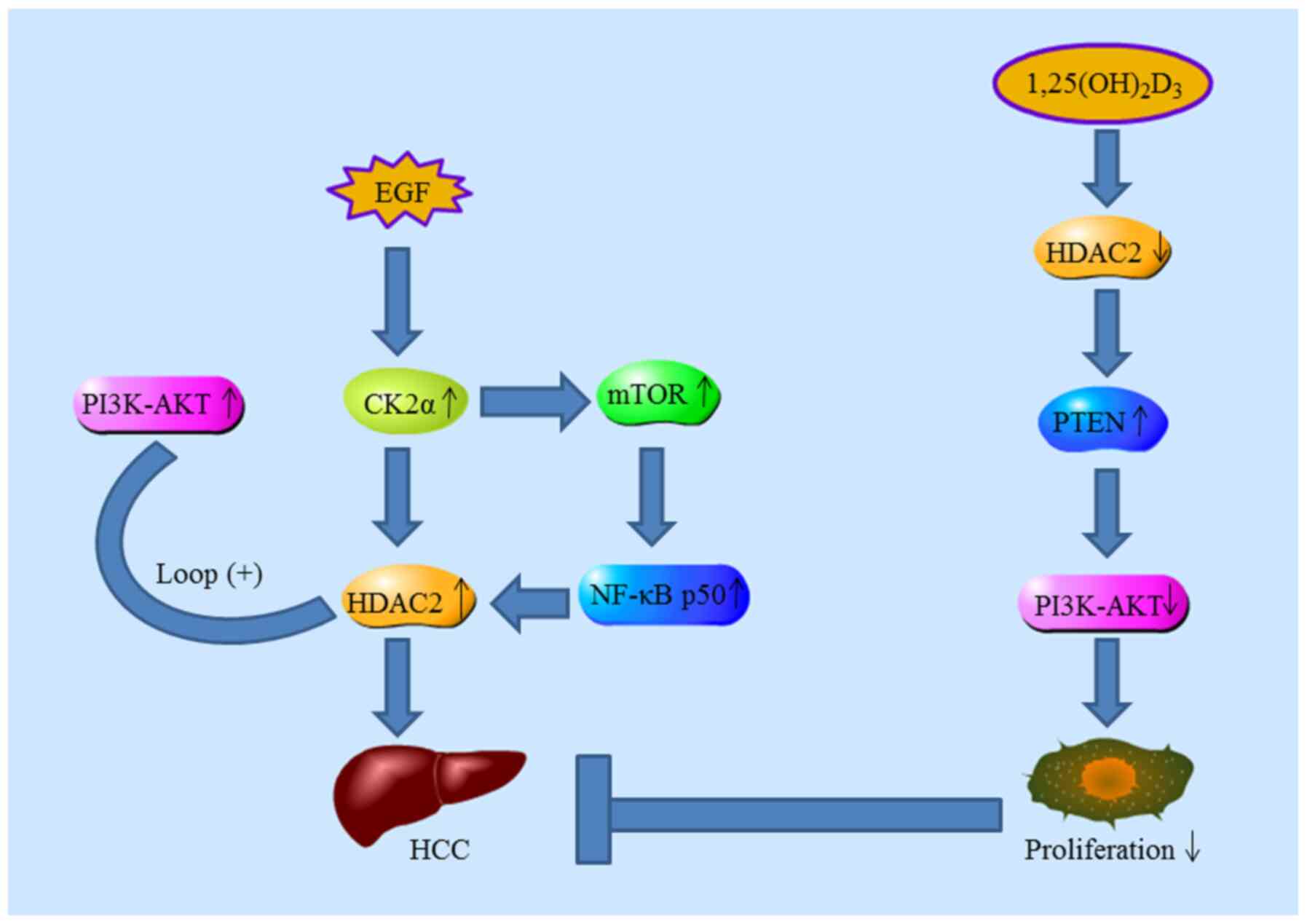
|
1
|
Cai C, Yu H, Huang G, Du X, Yu X, Zhou Y
and Shen W: Histone modifications in fatty acid synthase modulated
by carbohydrate responsive element binding protein are associated
with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Med.
42:1215–1228. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferriero R, Nusco E, De Cegli R, Carissimo
A, Manco G and Brunetti-Pierri N: Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
and lactate dehydrogenase are targets for therapy of acute liver
failure. J Hepatol. 69:325–335. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kanyal A, Rawat M, Gurung P, Choubey D,
Anamika K and Karmodiya K: Genome-wide survey and phylogenetic
analysis of histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases of
Plasmodium falciparum. FEBS J. 285:1767–1782. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Berger SL: The complex language of
chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 447:407–412.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Khangura RK, Bali A, Jaggi AS and Singh N:
Histone acetylation and histone deacetylation in neuropathic pain:
An unresolved puzzle? Eur J Pharmacol. 795:36–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kouzarides T: Chromatin modifications and
their function. Cell. 128:693–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leipe DD and Landsman D: Histone
deacetylases, acetoin utilization proteins and acetylpolyamine
amidohydrolases are members of an ancient protein superfamily.
Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3693–3697. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
West AC and Johnstone RW: New and emerging
HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J Clin Invest. 124:30–39.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ibi D and Gonzalez-Maeso J: Epigenetic
signaling in schizophrenia. Cell Signal. 27:2131–2136. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Levenson JM, O'Riordan KJ, Brown KD, Trinh
MA, Molfese DL and Sweatt JD: Regulation of histone acetylation
during memory formation in the hippocampus. J Biol Chem.
279:40545–40559. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cao YN, Xue Y, Xue L, Jiang X, Wang X,
Zhang Z, Yang J, Lu J, Zhang C, Wang W and Ning G: Hepatic menin
recruits SIRT1 to control liver steatosis through histone
deacetylation. J Hepatol. 59:1299–1306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Simões-Pires C, Zwick V, Nurisso A,
Schenker E, Carrupt PA and Cuendet M: HDAC6 as a target for
neurodegenerative diseases: What makes it different from the other
HDACs? Mol Neurodegener. 8:72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim HJ and Bae SC: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors: Molecular mechanisms of action and clinical trials as
anti-cancer drugs. Am J Transl Res. 3:166–179. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Glauben R, Batra A, Stroh T, Erben U,
Fedke I, Lehr HA, Leoni F, Mascagni P, Dinarello CA, Zeitz M and
Siegmund B: Histone deacetylases: Novel targets for prevention of
colitis-associated cancer in mice. Gut. 57:613–622. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dokmanovic M, Clarke C and Marks PA:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Overview and perspectives. Mol
Cancer Res. 5:981–989. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marchion DC, Bicaku E, Turner JG, Schmitt
ML, Morelli DR and Munster PN: HDAC2 regulates chromatin plasticity
and enhances DNA vulnerability. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:794–801. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jahan S, Sun JM, He S and Davie JR:
Transcription-dependent association of HDAC2 with active chromatin.
J Cell Physiol. 233:1650–1657. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Noh H, Oh EY, Seo JY, Yu MR, Kim YO, Ha H
and Lee HB: Histone deacetylase-2 is a key regulator of diabetes-
and transforming growth factor-beta1-induced renal injury. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 297:F729–F739. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang FQ, Liu M, Yang FP, Che J, Li W, Zhai
W, Wang GC, Zheng JH and Li X: VPA inhibits renal cancer cell
migration by targeting HDAC2 and down-regulating HIF–1α. Mol Biol
Rep. 41:1511–1518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fritzsche FR, Weichert W, Roske A, Gekeler
V, Beckers T, Stephan C, Jung K, Scholman K, Denkert C, Dietel M
and Kristiansen G: Class I histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are
highly expressed in renal cell cancer. BMC Cancer. 8:3812008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shang L, Pin L, Zhu S, Zhong X, Zhang Y,
Shun M, Liu Y and Hou M: Plantamajoside attenuates
isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy associated with the HDAC2
and AKT/GSK–3β signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 307:21–28.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Datta M, Staszewski O, Raschi E, Frosch M,
Hagemeyer N, Tay TL, Blank T, Kreutzfeldt M, Merkler D,
Ziegler-Waldkirch S, et al: Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 regulate
microglia function during development, homeostasis, and
neurodegeneration in a context-dependent manner. Immunity.
48:514–529.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bin YF, Wu LJ, Sun XJ, Liang Y, Bai J,
Zhang JQ, Li MH, Zhong XN, Liang YJ and He ZY: Expression of GR-α
and HDAC2 in steroid-Sensitive and steroid-Insensitive interstitial
lung disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 118:1093802019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mahady L, Nadeem M, Malek-Ahmadi M, Chen
K, Perez SE and Mufson EJ: HDAC2 dysregulation in the nucleus
basalis of Meynert during the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 45:380–397. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lin CL, Tsai ML, Lin CY, Hsu KW, Hsieh WS,
Chi WM, Huang LC and Lee CH: HDAC1 and HDAC2 double knockout
triggers cell apoptosis in advanced thyroid cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
20:4542019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Stojanovic N, Hassan Z, Wirth M, Wenzel P,
Beyer M, Schäfer C, Brand P, Kroemer A, Stauber RH, Schmid RM, et
al: HDAC1 and HDAC2 integrate the expression of p53 mutants in
pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 36:1804–1815. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tang W, Zhou W, Xiang L, Wu X, Zhang P,
Wang J, Liu G, Zhang W, Peng Y, Huang X, et al: The
p300/YY1/miR-500a-5p/HDAC2 signalling axis regulates cell
proliferation in human colorectal cancer. Nat Commun. 10:6632019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lai T, Wu M, Zhang C, Che L, Xu F, Wang Y,
Wu Y, Xuan N, Cao C, Du X, et al: HDAC2 attenuates airway
inflammation by suppressing IL-17A production in HDM-challenged
mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 316:L269–L279. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Barnes PJ: Corticosteroid resistance in
patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 131:636–645. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wilting RH, Yanover E, Heideman MR, Jacobs
H, Horner J, van der Torre J, DePinho RA and Dannenberg JH:
Overlapping functions of Hdac1 and Hdac2 in cell cycle regulation
and haematopoiesis. EMBO J. 29:2586–2597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Yang F, Jiao FZ, Chen Q, Zhang WB,
Wang LW and Gong ZJ: Modulations of histone deacetylase 2 offer a
protective effect through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in
acute liver failure. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019:81730162019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu J, Zhu P, Lu T, Du Y, Wang Y, He L, Ye
B, Liu B, Yang L, Wang J, et al: The long non-coding RNA LncHDAC2
drives the self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells via activation
of Hedgehog signaling. J Hepatol. 70:918–929. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Verdone L, Agricola E, Caserta M and Di
Mauro E: Histone acetylation in gene regulation. Brief Funct
Genomic Proteomic. 5:209–221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Millard CJ, Fairall L, Ragan TJ, Savva CG
and Schwabe JWR: The topology of chromatin-binding domains in the
NuRD deacetylase complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:12972–12982. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Verdone L, Caserta M and Di Mauro E: Role
of histone acetylation in the control of gene expression. Biochem
Cell Biol. 83:344–353. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brownell JE, Zhou J, Ranalli T, Kobayashi
R, Edmondson DG, Roth SY and Allis CD: Tetrahymena histone
acetyltransferase A: A homolog to yeast Gcn5p linking histone
acetylation to gene activation. Cell. 84:843–851. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kurdistani SK and Grunstein M: Histone
acetylation and deacetylation in yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
4:276–284. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang D, Kon N, Lasso G, Jiang L, Leng W,
Zhu WG, Qin J, Honig B and Gu W: Acetylation-regulated interaction
between p53 and SET reveals a widespread regulatory mode. Nature.
538:118–122. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Z, Zang C, Cui K, Schones DE, Barski
A, Peng W and Zhao K: Genome-wide mapping of HATs and HDACs reveals
distinct functions in active and inactive genes. Cell.
138:1019–1031. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Abel T and Zukin RS: Epigenetic targets of
HDAC inhibition in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders.
Curr Opin Pharmacol. 8:57–64. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN,
Kemp S and van Kuilenburg AB: Histone deacetylases (HDACs):
Characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J. 370(Pt
3): 737–749. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gregoretti IV, Lee YM and Goodson HV:
Molecular evolution of the histone deacetylase family: Functional
implications of phylogenetic analysis. J Mol Biol. 338:17–31. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kiweler N, Brill B, Wirth M, Breuksch I,
Laguna T, Dietrich C, Strand S, Schneider G, Groner B, Butter F, et
al: The histone deacetylases HDAC1 and HDAC2 are required for the
growth and survival of renal carcinoma cells. Arch Toxicol.
92:2227–2243. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bush EW and McKinsey TA: Protein
acetylation in the cardiorenal axis: The promise of histone
deacetylase inhibitors. Circ Res. 106:272–284. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang XJ and Seto E: The Rpd3/Hda1 family
of lysine deacetylases: From bacteria and yeast to mice and men.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:206–218. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang WM, Tsai SC, Wen YD, Fejer G and Seto
E: Functional domains of histone deacetylase-3. J Biol Chem.
277:9447–9454. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Martin M, Kettmann R and Dequiedt F: Class
IIa histone deacetylases: Regulating the regulators. Oncogene.
26:5450–5467. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Haberland M, Montgomery RL and Olson EN:
The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and
physiology: Implications for disease and therapy. Nat Rev Genet.
10:32–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Guardiola AR and Yao TP: Molecular cloning
and characterization of a novel histone deacetylase HDAC10. J Biol
Chem. 277:3350–3356. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Grozinger CM, Hassig CA and Schreiber SL:
Three proteins define a class of human histone deacetylases related
to yeast Hda1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:4868–4873. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Marks PA and Breslow R: Dimethyl sulfoxide
to vorinostat: Development of this histone deacetylase inhibitor as
an anti-cancer drug. Nat Biotechnol. 25:84–90. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Johnstone RW: Histone-deacetylase
inhibitors: Novel drugs for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 1:287–299. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Michan S and Sinclair D: Sirtuins in
mammals: Insights into their biological function. Biochem J.
404:1–13. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Abbas A and Gupta S: The role of histone
deacetylases in prostate cancer. Epigenetics. 3:300–309. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yamamoto H, Schoonjans K and Auwerx J:
Sirtuin functions in health and disease. Mol Endocrinol.
21:1745–1755. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB and Marks PA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors: Molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene.
26:5541–5552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gao L, Cueto MA, Asselbergs F and Atadja
P: Cloning and functional characterization of HDAC11, a novel
member of the human histone deacetylase family. J Biol Chem.
277:25748–25755. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Verdin E and Ott M: 50 years of protein
acetylation: From gene regulation to epigenetics, metabolism and
beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 16:258–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gong F and Miller KM: Mammalian DNA
repair: HATs and HDACs make their mark through histone acetylation.
Mutat Res. 750:23–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Brunmeir R, Lagger S and Seiser C: Histone
deacetylase HDAC1/HDAC2-controlled embryonic development and cell
differentiation. Int J Dev Biol. 53:275–289. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Montgomery RL, Hsieh J, Barbosa AC,
Richardson JA and Olson EN: Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 control
the progression of neural precursors to neurons during brain
development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:7876–7881. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bressi JC, Jennings AJ, Skene R, Wu Y,
Melkus R, De Jong R, O'Connell S, Grimshaw CE, Navre M and Gangloff
AR: Exploration of the HDAC2 foot pocket: Synthesis and SAR of
substituted N-(2-aminophenyl)benzamides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
20:3142–3145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hou J, Feng C, Li Z, Fang Q, Wang H, Gu G,
Shi Y, Liu P, Xu F, Yin Z, et al: Structure-based optimization of
click-based histone deacetylase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem.
46:3190–3200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhou H, Wang C, Ye J, Chen H and Tao R:
Design, virtual screening, molecular docking and molecular dynamics
studies of novel urushiol derivatives as potential HDAC2 selective
inhibitors. Gene. 637:63–71. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xie R, Yao Y, Tang P, Chen G, Liu X, Yun
F, Cheng C, Wu X and Yuan Q: Design, synthesis and biological
evaluation of novel hydroxamates and 2-aminobenzamides as potent
histone deacetylase inhibitors and antitumor agents. Eur J Med
Chem. 134:1–12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu J, Zhou J, He F, Gao L, Wen Y, Gao L,
Wang P, Kang D and Hu L: Design, synthesis and biological
evaluation of novel indazole-based derivatives as potent HDAC
inhibitors via fragment-based virtual screening. Eur J Med Chem.
192:112–189. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Fournier JF, Bhurruth-Alcor Y, Musicki B,
Aubert J, Aurelly M, Bouix-Peter C, Bouquet K, Chantalat L, Delorme
M, Drean B, et al: Squaramides as novel class I and IIB histone
deacetylase inhibitors for topical treatment of cutaneous t-cell
lymphoma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 28:2985–2992. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yun F, Cheng C, Ullah S, He J, Zahi MR and
Yuan Q: Thioether-based 2-aminobenzamide derivatives: Novel HDAC
inhibitors with potent in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity. Eur
J Med Chem. 176:195–207. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Alsawalha M, Rao Bolla S, Kandakatla N,
Srinivasadesikan V, Veeraraghavan VP and Surapaneni KM: Molecular
docking and ADMET analysis of hydroxamic acids as HDAC2 inhibitors.
Bioinformation. 15:380–387. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ford J, Ahmed S, Allison S, Jiang M and
Milner J: JNK2-dependent regulation of SIRT1 protein stability.
Cell cycle. 7:3091–3097. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sun JM, Chen HY and Davie JR: Differential
distribution of unmodified and phosphorylated histone deacetylase 2
in chromatin. J Biol Chem. 282:33227–33236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ashktorab H, Belgrave K, Hosseinkhah F,
Brim H, Nouraie M, Takkikto M, Hewitt S, Lee EL, Dashwood RH and
Smoot D: Global Histone H4 Acetylation and HDAC2 expression in
colon adenoma and carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 54:2109–2117. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
73
|
Krämer OH, Zhu P, Ostendorff HP,
Golebiewski M, Tiefenbach J, Peters MA, Brill B, Groner B, Bach I,
Heinzel T and Göttlicher M: The histone deacetylase inhibitor
valproic acid selectively induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2.
EMBO J. 22:3411–3420. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Brandl A, Wagner T, Uhlig KM, Knauer SK,
Stauber RH, Melchior F, Schneider G, Heinzel T and Krämer OH:
Dynamically regulated sumoylation of HDAC2 controls p53
deacetylation and restricts apoptosis following genotoxic stress. J
Mol Cell Biol. 4:284–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Adenuga D and Rahman I: Protein kinase
CK2-mediated phosphorylation of HDAC2 regulates co-repressor
formation, deacetylase activity and acetylation of HDAC2 by
cigarette smoke and aldehydes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 498:62–73.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tsai SC and Seto E: Regulation of histone
deacetylase 2 by protein kinase CK2. J Biol Chem. 277:31826–31833.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Chen PJ, Cai SP, Huang C, Meng XM and Li
J: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B): A key regulator and
therapeutic target in liver diseases. Toxicology. 337:10–20. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kan C, Ungelenk L, Lupp A, Dirsch O and
Dahmen U: Ischemia-Reperfusion injury in aged Livers-The energy
metabolism, inflammatory response, and autophagy. Transplantation.
102:368–377. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Guicciardi ME, Malhi H, Mott JL and Gores
GJ: Apoptosis and necrosis in the liver. Compr Physiol. 3:977–1010.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lei WW, Zhang KH, Pan XC, Wang DM, Hu Y,
Yang YN and Song JG: Histone deacetylase 1 and 2 differentially
regulate apoptosis by opposing effects on extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Cell Death Dis. 1:e442010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Romero-Gallo J, Sozmen EG, Chytil A,
Russell WE, Whitehead R, Parks WT, Holdren MS, Her MF, Gautam S,
Magnuson M, et al: Inactivation of TGF-beta signaling in
hepatocytes results in an increased proliferative response after
partial hepatectomy. Oncogene. 24:3028–3041. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Raven A, Lu WY, Man TY, Ferreira-Gonzalez
S, O'Duibhir E, Dwyer BJ, Thomson JP, Meehan RR, Bogorad R,
Koteliansky V, et al: Cholangiocytes act as facultative liver stem
cells during impaired hepatocyte regeneration. Nature. 547:350–354.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Willis-Martinez D, Richards HW, Timchenko
NA and Medrano EE: Role of HDAC1 in senescence, aging, and cancer.
Exp Gerontol. 45:279–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Harms KL and Chen X: Histone deacetylase 2
modulates p53 transcriptional activities through regulation of
p53-DNA binding activity. Cancer Res. 67:3145–3152. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Turgeon N, Blais M, Gagne JM, Tardif V,
Boudreau F, Perreault N and Asselin C: HDAC1 and HDAC2 restrain the
intestinal inflammatory response by regulating intestinal
epithelial cell differentiation. PLoS One. 8:e737852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ler SY, Leung CH, Khin LW, Lu GD,
Salto-Tellez M, Hartman M, Iau PT, Yap CT and Hooi SC: HDAC1 and
HDAC2 independently predict mortality in hepatocellular carcinoma
by a competing risk regression model in a Southeast Asian
population. Oncol Rep. 34:2238–2250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Noh JH, Chang YG, Kim MG, Jung KH, Kim JK,
Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q, Kim SJ, Kwon SH, et al: MiR–145 functions
as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting histone deacetylase 2
in liver cancer. Cancer Lett. 335:455–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Makar AB, Mcmartin KE, Palese M and Tephly
TR: Formate assay in body fluids: Application in methanol poisoning
App. Biochem Med. 13:117–126. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Noh JH, Jung KH, Kim JK, Eun JW, Bae HJ,
Xie HJ, Chang YG, Kim MG, Park WS, Lee JY and Nam SW: Aberrant
Regulation of HDAC2 Mediates proliferation of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by deregulating expression of G1/S cell cycle
proteins. PLoS One. 6:e281032011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yuan X, Yan S, Zhao J, Shi D, Yuan B, Dai
W, Jiao B, Zhang W and Miao M: Lipid metabolism and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor signaling pathways participate in
late-phase liver regeneration. J Proteome Res. 10:1179–1190. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Michalopoulos GK and Bhushan B: Liver
regeneration: Biological and pathological mechanisms and
implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:40–55. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Michalopoulos GK: Principles of liver
regeneration and growth homeostasis. Compr Physiol. 3:485–513.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li L, Guo J, Chen Y, Chang C and Xu C:
Comprehensive CircRNA expression profile and selection of key
CircRNAs during priming phase of rat liver regeneration. BMC
Genomics. 18:802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xia J, Zhou Y, Ji H, Wang Y, Wu Q, Bao J,
Ye F, Shi Y and Bu H: Loss of Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 in
hepatocytes impairs murine liver regeneration through Ki67
depletion. Hepatology. 58:2089–2098. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wang Y, Ye F, Ke Q, Wu Q, Yang R and Bu H:
Gender-dependent histone deacetylases injury may contribute to
differences in liver recovery rates of male and female mice.
Transplant Proc. 45:463–473. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Bansal R, Nagorniewicz B and Prakash J:
Clinical advancements in the targeted therapies against liver
fibrosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2016:76297242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Aydın MM and Akçalı KC: Liver fibrosis.
Turk J Gastroenterol. 29:14–21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Gounder PP, Haering C, Bruden DJ,
Townshend-Bulson L, Simons BC, Spradling PR and McMahon BJ: Does
incorporating change in APRI or FIB–4 indices over time improve the
accuracy of a single index for identifying liver fibrosis in
persons with chronic hepatitis C virus infection? J Clin
Gastroenterol. 52:60–66. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Bilal U, Lau B, Lazo M, McCaul ME, Hutton
HE, Sulkowski MS, Moore RD and Chander G: Interaction between
alcohol consumption patterns, antiretroviral therapy type, and
liver fibrosis in persons living with HIV. AIDS Patient Care STDS.
30:200–207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Lainé F, Bendavid C, Moirand R, Tessier S,
Perrin M, Guillygomarc'h A, Guyader D, Calon E, Renault A, Brissot
P, et al: Prediction of liver fibrosis in patients with features of
the metabolic syndrome regardless of alcohol consumption.
Hepatology. 39:1639–1646. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Sunami Y, Leithäuser F, Gul S, Fiedler K,
Güldiken N, Espenlaub S, Holzmann KH, Hipp N, Sindrilaru A, Luedde
T, et al: Hepatic activation of IKK/NFκB signaling induces liver
fibrosis via macrophage-mediated chronic inflammation. Hepatology.
56:1117–1128. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhang H, Wu P, Chen F, Hao Y, Lao Y, Ren
L, Sun L, Sun W, Wei H, Chan DW, et al: SILAC-based quantitative
proteomic analysis of secretome between activated and reverted
hepatic stellate cells. Proteomics. 14:1977–1986. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Mannaerts I, Eysackers N, Onyema OO, Van
Beneden K, Valente S, Mai A, Odenthal M and van Grunsven LA: Class
II HDAC inhibition hampers hepatic stellate cell activation by
induction of microRNA–29. PLoS One. 8:e557862013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Pannem RR, Dorn C, Hellerbrand C and
Massoumi R: Cylindromatosis gene CYLD regulates hepatocyte growth
factor expression in hepatic stellate cells through interaction
with histone deacetylase 7. Hepatology. 60:1066–1081. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Mannaerts I, Nuytten NR, Rogiers V,
Vanderkerken K, van Grunsven LA and Geerts A: Chronic
administration of valproic acid inhibits activation of mouse
hepatic stellate cells in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology.
51:603–614. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Qin L and Han YP: Epigenetic repression of
matrix metalloproteinases in myofibroblastic hepatic stellate cells
through histone deacetylases 4: Implication in tissue fibrosis. Am
J Pathol. 177:1915–1928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Huang SK, Scruggs AM, Donaghy J, Horowitz
JC, Zaslona Z, Przybranowski S, White ES and Peters-Golden M:
Histone modifications are responsible for decreased Fas expression
and apoptosis resistance in fibrotic lung fibroblasts. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e6212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Lee YH, Seo D, Choi KJ, Andersen JB, Won
MA, Kitade M, Gómez-Quiroz LE, Judge AD, Marquardt JU, Raggi C, et
al: Antitumor effects in hepatocarcinoma of isoform-selective
inhibition of HDAC2. Cancer Res. 74:4752–4761. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Li X, Wu XQ, Xu T, Li XF, Yang Y, Li WX,
Huang C, Meng XM and Li J: Role of histone deacetylases(HDACs) in
progression and reversal of liver fibrosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
306:58–68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Dooley S, Hamzavi J, Breitkopf K,
Wiercinska E, Said HM, Lorenzen J, Ten Dijke P and Gressner AM:
Smad7 prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver
fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology. 125:178–191. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Dooley S, Hamzavi J, Ciuclan L, Godoy P,
Ilkavets I, Ehnert S, Ueberham E, Gebhardt R, Kanzler S, Geier A,
et al: Hepatocyte-specific Smad7 expression attenuates
TGF-beta-mediated fibrogenesis and protects against liver damage.
Gastroenterology. 135:642–659. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Hamzavi J, Ehnert S, Godoy P, Ciuclan L,
Weng H, Mertens PR, Heuchel R and Dooley S: Disruption of the Smad7
gene enhances CCI4-dependent liver damage and fibrogenesis in mice.
J Cell Mol Med. 12(5B): 2130–2144. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Oseini AM and Sanyal AJ: Therapies in
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Liver Int. 37(Suppl 1):
S97–S103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Utsunomiya H, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita E,
Tokumoto Y, Tada F, Miyake T, Hirooka M, Abe M, Kumagi T, Matsuura
B, et al: Upregulated absorption of dietary palmitic acids with
changes in intestinal transporters in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
(NASH). J Gastroenterol. 52:940–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Fukushima J, Kamada Y, Matsumoto H,
Yoshida Y, Ezaki H, Takemura T, Saji Y, Igura T, Tsutsui S, Kihara
S, et al: Adiponectin prevents progression of steatohepatitis in
mice by regulating oxidative stress and Kupffer cell phenotype
polarization. Hepatol Res. 39:724–738. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Afrin R, Arumugam S, Rahman A, Wahed MI,
Karuppagounder V, Harima M, Suzuki H, Miyashita S, Suzuki K,
Yoneyama H, et al: Curcumin ameliorates liver damage and
progression of NASH in NASH-HCC mouse model possibly by modulating
HMGB1-NF-κB translocation. Int Immunopharmacol. 44:174–182. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhong S, Zhao L, Wang Y, Zhang C, Liu J,
Wang P, Zhou W, Yang P, Varghese Z, Moorhead JF, et al: CD36
deficiency aggravates macrophage infiltration and hepatic
inflammation by up-regulating MCP–1 expression of hepatocytes
through HDAC2-dependant pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal. Aug
1–2017.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Chen Z, Xie H, Hu M, Huang T, Hu Y, Sang N
and Zhao Y: Recent progress in treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 10:2993–3036. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Lee JS, Chu IS, Heo J, Calvisi DF, Sun Z,
Roskams T, Durnez A, Demetris AJ and Thorgeirsson SS:
Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular
carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology. 40:667–676.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ropero S and Esteller M: The role of
histone deacetylases (HDACs) in human cancer. Mol Oncol. 1:19–25.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Bayat S, Mansoori Derakhshan S, Mansoori
Derakhshan N, Shekari Khaniani M and Alivand MR: Downregulation of
HDAC2 and HDAC3 via oleuropein as a potent prevention and
therapeutic agent in MCF–7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
120:9172–9180. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Quint K, Agaimy A, Di Fazio P, Montalbano
R, Steindorf C, Jung R, Hellerbrand C, Hartmann A, Sitter H,
Neureiter D and Ocker M: Clinical significance of histone
deacetylases 1, 2, 3, and 7: HDAC2 is an independent predictor of
survival in HCC. Virchows Arch. 459:129–139. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Kim HS, Chang YG, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q,
Park SJ, Shin WC, Lee EK, Park S, Ahn YM, et al: Oncogenic
potential of CK2α and its regulatory role in EGF-induced HDAC2
expression in human liver cancer. FEBS J. 281:851–861. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Noh JH, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q, Park SJ,
Kim HS, Nam B, Shin WC, Lee EK, Lee K, et al: HDAC2 provides a
critical support to malignant progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma through feedback control of mTORC1 and AKT. Cancer Res.
74:1728–1738. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Huang J, Yang G, Huang Y, Kong W and Zhang
S: 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
via down-regulating HDAC2 and upregulating P21(WAFI/CIP1). Mol Med
Re. 13:1373–1380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Huang J, Yang G, Huang Y and Zhang S:
Inhibitory effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on the proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the downregulation of HDAC2.
Oncol Rep. 38:1845–1850. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Wang H, Kohashi K, Yoshizumi T, Okumura Y,
Tanaka Y, Shimokawa M, Iwasaki T, Aishima S, Maehara Y and Oda Y:
Coexpression of SALL4 with HDAC1 and/or HDAC2 is associated with
underexpression of PTEN and poor prognosis in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 64:69–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Gryder BE, Pomella S, Sayers C, Wu XS,
Song Y, Chiarella AM, Bagchi S, Chou HC, Sinniah RS, Walton A, et
al: Histone hyperacetylation disrupts core gene regulatory
architecture in rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Genet. 51:1714–1722. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Methot JL, Hamblett CL, Mampreian DM, Jung
J, Harsch A, Szewczak AA, Dahlberg WK, Middleton RE, Hughes B,
Fleming JC, et al: SAR profiles of spirocyclic nicotinamide derived
selective HDAC1/HDAC2 inhibitors (SHI–1:2). Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
18:6104–6109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Methot JL, Chakravarty PK, Chenard M,
Close J, Cruz JC, Dahlberg WK, Fleming J, Hamblett CL, Hamill JE,
Harrington P, et al: Exploration of the internal cavity of histone
deacetylase (HDAC) with selective HDAC1/HDAC2 inhibitors (SHI-1:2).
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:973–978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Qi Z, Wang C, Jiang J and Wu C: Novel C15
Triene Triazole, D-A derivatives anti-HepG2, and as HDAC2
inhibitors: A synergy study. Int J Mol Sci. 19:31842018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
133
|
Venturelli S, Niessner H, Sinnberg T,
Berger A, Burkard M, Urmann C, Donaubauer K, Böcker A, Leischner C,
Riepl H, et al: 6– and 8-Prenylnaringenin, novel natural histone
deacetylase inhibitors found in hops, exert antitumor activity on
melanoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 51:543–556. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Al-Sanea MM, Gotina L, Mohamed MF, Grace
Thomas Parambi D, Gomaa HA, Mathew B, Youssif BG, Alharbi KS,
Elsayed ZM, Abdelgawad MA and Eldehna WM: Design, synthesis and
biological evaluation of new HDAC1 and HDAC2 inhibitors endowed
with ligustrazine as a novel cap moiety. Drug Des Devel Ther.
14:497–508. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Jang YG, Hwang KA and Choi KC: Rosmarinic
acid, a component of rosemary tea, induced the cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis through modulation of HDAC2 expression in prostate
cancer cell lines. Nutrients. 10:17842018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
136
|
Deng L, Tang J, Yang H, Cheng C, Lu S,
Jiang R and Sun B: MTA1 modulated by miR–30e contributes to
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma
through an ErbB2-dependent pathway. Oncogene. 36:3976–3985. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Buurman R, Gürlevik E, Schäffer V, Eilers
M, Sandbothe M, Kreipe H, Wilkens L, Schlegelberger B, Kühnel F and
Skawran B: Histone deacetylases activate hepatocyte growth factor
signaling by repressing MicroRNA–449 in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Gastroenterology. 143:811–820.e15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
He QL, Qin SY, Tao L, Ning HJ and Jiang
HX: Prognostic value and prospective molecular mechanism of
miR–100-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive study based
on 1,258 samples. Oncol Lett. 18:6126–6142. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Kim HS, Lee KS, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q,
Park SJ, Shin WC, Yang HD, Park M, Park WS, et al: MicroRNA–31
functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell cycle and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulatory proteins in liver
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:8089–8102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Dai W, Dai JL, Tang MH, Ye MS and Fang S:
lncRNA-SNHG15 accelerates the development of hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting miR–490-3p/histone deacetylase 2 axis. World
J Gastroenterol. 25:5789–5799. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Turner BM: Cellular memory and the histone
code. Cell. 111:285–291. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Khan SN and Khan AU: Role of histone
acetylation in cell physiology and diseases: An update. Clin Chim
Acta. 411:1401–1411. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Budillon A, Di Gennaro E, Bruzzese F,
Rocco M, Manzo G and Caraglia M: Histone deacetylase inhibitors: A
new wave of molecular targeted anticancer agents. Recent Pat
Anticancer Drug Discov. 2:119–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Wade PA: Transcriptional control at
regulatory checkpoints by histone deacetylases: Molecular
connections between cancer and chromatin. Hum Mol Genet.
10:693–698. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Forsberg EC and Bresnick EH: Histone
acetylation beyond promoters: Long-range acetylation patterns in
the chromatin world. Bioessays. 23:820–830. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Zhang L, Qiu Z, Hu Y, Yang F, Yan S, Zhao
L, Li B, He S, Huang M, Li J and Li L: ABA treatment of germinating
maize seeds induces VP1 gene expression and selective
promoter-associated histone acetylation. Physiol Plant.
143:287–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Tian XL, Lu X, Feng JB, Cai TJ, Li S, Tian
M and Liu QJ: Alterations in histone acetylation following exposure
to 60Co ү-rays and their relationship with chromosome
damage in human lymphoblastoid cells. Radiat Environ Biophys.
57:215–222. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Heinz KS, Rapp A, Casas-Delucchi CS,
Lehmkuhl A, Romero-Fernández I, Sánchez A, Krämer OH, Marchal JA
and Cardoso MC: DNA replication dynamics of vole genome and its
epigenetic regulation. Epigenetics Chromatin. 12:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Ibi D, de la Fuente Revenga M, Kezunovic
N, Muguruza C, Saunders JM, Gaitonde SA, Moreno JL, Ijaz MK,
Santosh V, Kozlenkov A, et al: Antipsychotic-induced Hdac2
transcription via NF-kB leads to synaptic and cognitive side
effects. Nat Neurosci. 20:1247–1259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Bhandari DR, Seo KW, Jung JW, Kim HS, Yang
SR and Kang KS: The regulatory role of c-MYC on HDAC2 and PcG
expression in human multipotent stem cells. J Cell Mol Med.
15:1603–1614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Yang H, Salz T, Zajac-Kaye M, Liao D,
Huang S and Qiu Y: Overexpression of histone deacetylases in cancer
cells is controlled by interplay of transcription factors and
epigenetic modulators. FASEB J. 28:4265–4279. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|