|
1
|
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman
M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C,
et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A report
from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 135:e146–e603.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators: Global, regional, and national life expectancy,
all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of
death, 1980-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of
Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 388:1459–1544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bailey EL, Smith C, Sudlow CL and Wardlaw
JM: Pathology of lacunar ischemic stroke in humans-a systematic
review. Brain Pathol. 22:583–591. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Warlow C, Sudlow C, Dennis M, Wardlaw J
and Sandercock P: Stroke. Lancet. 362:1211–1224. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Balch MHH, Nimjee SM, Rink C and Hannawi
Y: Beyond the brain: The systemic pathophysiological response to
acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke. 22:159–172. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Boyle PA, Yang J, Yu L, Leurgans SE,
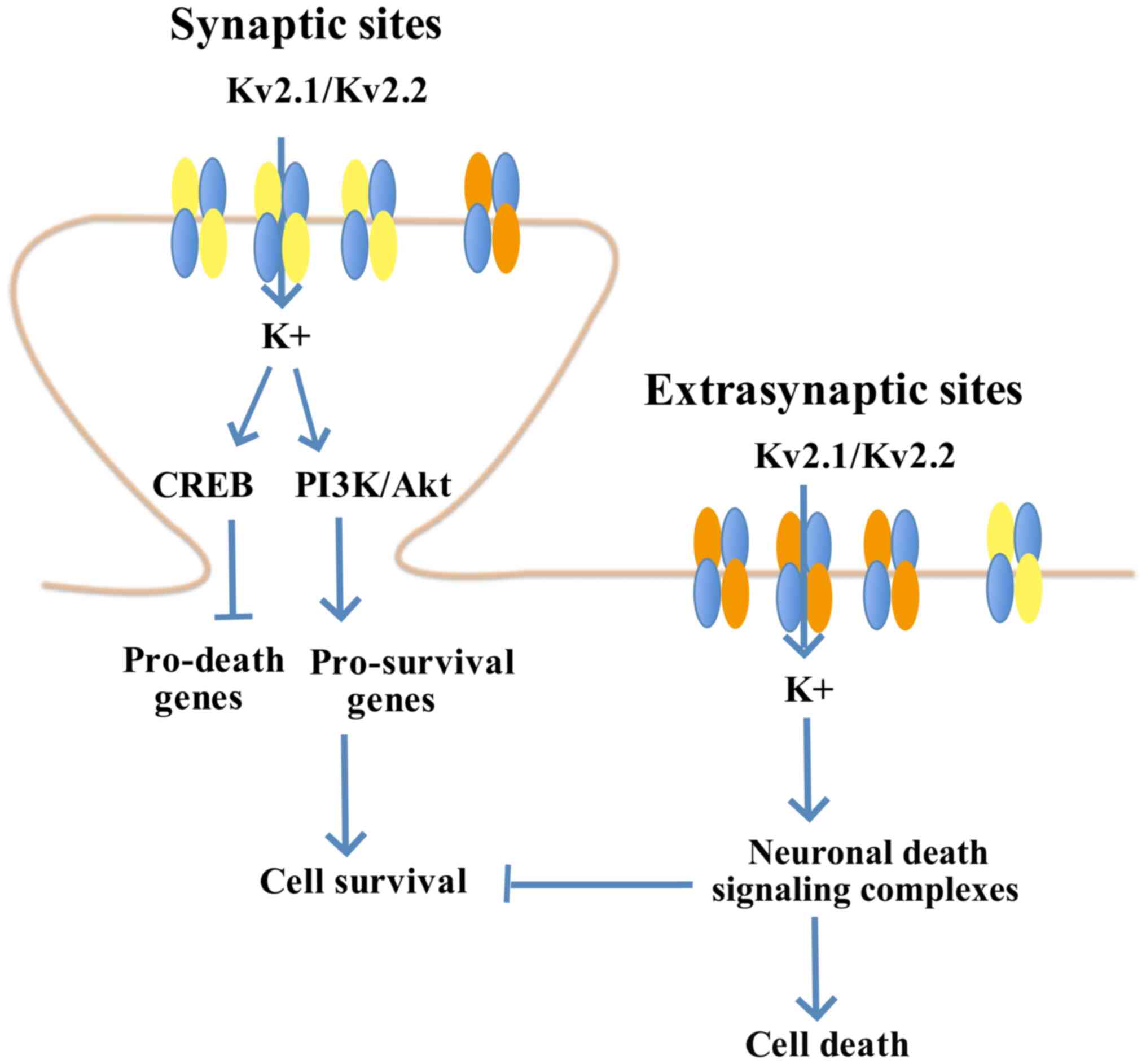
Capuano AW, Schneider JA, Wilson RS and Bennett DA: Varied effects
of age-related neuropathologies on the trajectory of late life
cognitive decline. Brain. 140:804–812. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boyle PA, Yu L, Wilson RS, Schneider JA
and Bennett DA: Relation of neuropathology with cognitive decline
among older persons without dementia. Front Aging Neurosci.
5:502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Corrada MM, Sonnen JA, Kim RC and Kawas
CH: Microinfarcts are common and strongly related to dementia in
the oldest-old: The 90+ study. Alzheimers Dement. 12:900–908. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
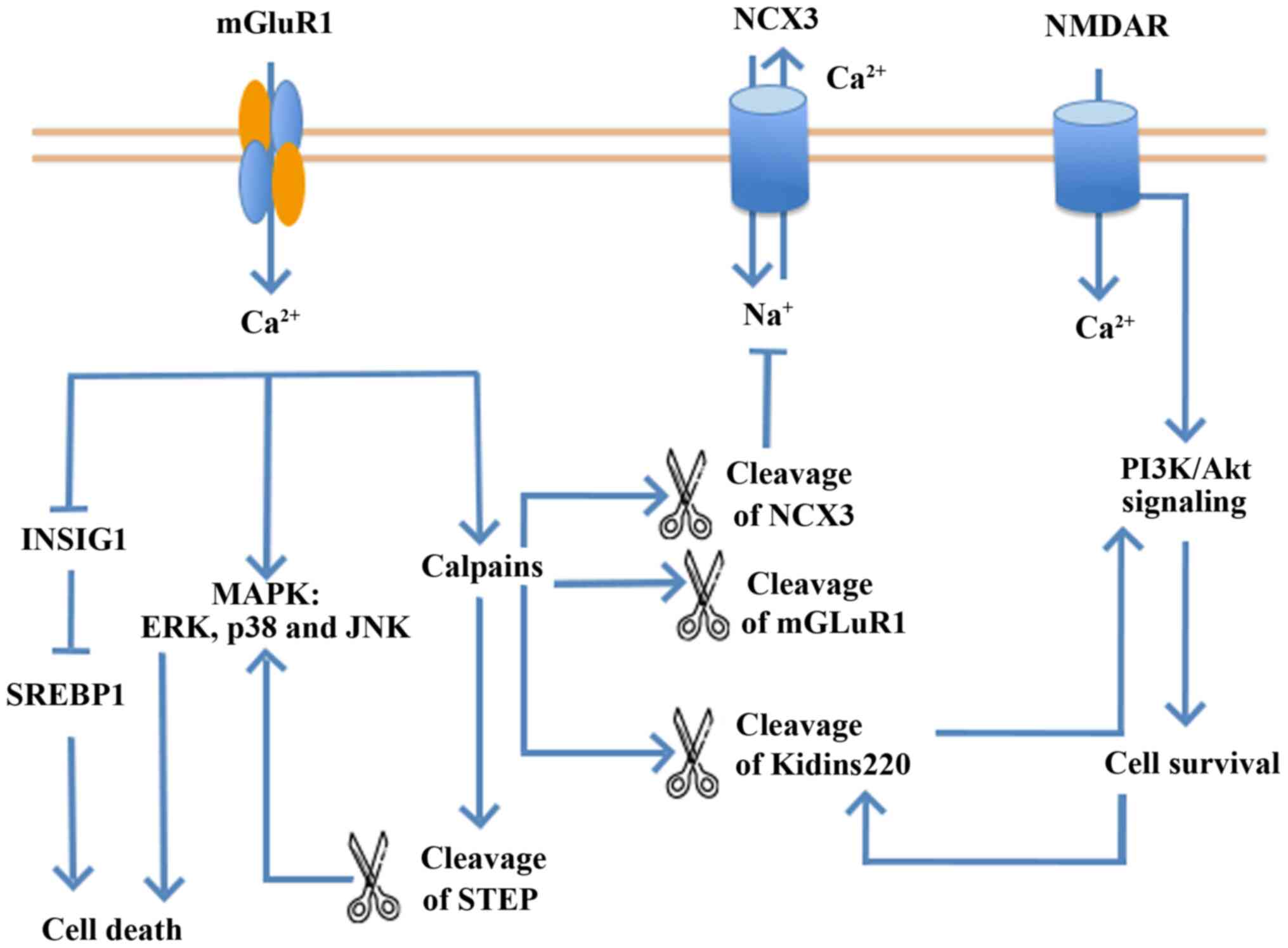
9
|
Ince PG, Minett T, Forster G, Brayne C and
Wharton SB: Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing
Neuropathology Study: Microinfarcts in an older
population-representative brain donor cohort (MRC CFAS):
Prevalence, relation to dementia and mobility, and implications for
the evaluation of cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Neuropathol Appl
Neurobiol. 43:409–418. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kawas CH, Kim RC, Sonnen JA, Bullain SS,
Trieu T and Corrada MM: Multiple pathologies are common and related
to dementia in the oldest-old: The 90+ study. Neurology.
85:535–542. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
White LR, Edland SD, Hemmy LS, Montine KS,
Zarow C, Sonnen JA, Uyehara-Lock JH, Gelber RP, Ross GW, Petrovitch
H, et al: Neuropathologic comorbidity and cognitive impairment in
the Nun and Honolulu-Asia aging studies. Neurology. 86:1000–1008.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Buchman AS, Yu L, Boyle PA, Levine SR, Nag
S, Schneider JA and Bennett DA: Microvascular brain pathology and
late-life motor impairment. Neurology. 80:712–718. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hogan AM, Kirkham FJ, Prengler M, Telfer
P, Lane R, Vargha-Khadem F and Haan M: An exploratory study of
physiological correlates of neurodevelopmental delay in infants
with sickle cell anaemia. Br J Haematol. 132:99–107. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bernaudin F, Verlhac S, Freard F,
Roudot-Thoraval F, Benkerrou M, Thuret I, Mardini R, Vannier JP,
Ploix E, Romero M, et al: Multicenter prospective study of children
with sickle cell disease: Radiographic and psychometric
correlation. J Child Neurol. 15:333–343. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brown RT, Davis PC, Lambert R, Hsu L,
Hopkins K and Eckman J: Neurocognitive functioning and magnetic
resonance imaging in children with sickle cell disease. J Pediatr
Psychol. 25:503–513. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
DeBaun MR, Schatz J, Siegel MJ, Koby M,
Craft S, Resar L, Chu JY, Launius G, Dadash-Zadeh M, Lee RB and
Noetzel M: Cognitive screening examinations for silent cerebral
infarcts in sickle cell disease. Neurology. 50:1678–1682. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hogan AM, Pit-ten Cate IM, Vargha-Khadem
F, Prengler M and Kirkham FJ: Physiological correlates of
intellectual function in children with sickle cell disease:
Hypoxaemia, hyperaemia and brain infarction. Dev Sci. 9:379–387.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Steen RG, Miles MA, Helton KJ, Strawn S,
Wang W, Xiong X and Mulhern RK: Cognitive impairment in children
with hemoglobin SS sickle cell disease: Relationship to MR imaging
findings and hematocrit. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 24:382–389.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Watkins KE, Hewes DK, Connelly A, Kendall
BE, Kingsley DP, Evans JE, Gadian DG, Vargha-Khadem F and Kirkham
FJ: Cognitive deficits associated with frontal-lobe infarction in
children with sickle cell disease. Dev Med Child Neurol.
40:536–543. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen YC, Ma NX, Pei ZF, Wu Z, Do-Monte FH,
Keefe S, Yellin E, Chen MS, Yin JC, Lee G, et al: A neuroD1
AAV-based gene therapy for functional brain repair after ischemic
injury through in vivo astrocyte-to-neuron conversion. Mol Ther.
28:217–234. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hu X, Wu D, He X, Zhao H, He Z, Lin J,
Wang K, Wang W, Pan Z, Lin H and Wang M: circGSK3β promotes
metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by augmenting
β-catenin signaling. Mol Cancer. 18:1602019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ren X, Hu H, Farooqi I and Simpkins JW:
Blood substitution therapy rescues the brain of mice from ischemic
damage. Nat Commun. 11:40782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sommer CJ: Ischemic stroke: Experimental
models and reality. Acta Neuropathol. 133:245–261. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang L, Zhang RL, Jiang Q, Ding G, Chopp
M and Zhang ZG: Focal embolic cerebral ischemia in the rat. Nat
Protoc. 10:539–547. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McBride DW and Zhang JH: Precision stroke
animal models: The permanent MCAO model should be the primary
model, not transient MCAO. Transl Stroke Res. Jul 17–2017.Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lunardi Baccetto S and Lehmann C:
Microcirculatory changes in experimental models of stroke and
CNS-injury induced immunodepression. Int J Mol Sci. 20:51842019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Fujie W, Kirino T, Tomukai N, Iwasawa T
and Tamura A: Progressive shrinkage of the thalamus following
middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke. 21:1485–1488.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Prabhakaran S, Ruff I and Bernstein RA:
Acute stroke intervention: A systematic review. JAMA.
313:1451–1462. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao Y, Yuan B, Chen J, Feng D, Zhao B,
Qin C and Chen YF: Endothelial progenitor cells: Therapeutic
perspective for ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 19:67–75. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kidwell CS, Alger JR and Saver JL: Beyond
mismatch: Evolving paradigms in imaging the ischemic penumbra with
multimodal magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke. 34:2729–2735. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farzaneh M, Farbood
Y and Moghaddam HF: Pathogenic mechanisms following ischemic
stroke. Neurol Sci. 38:1167–1186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo JD, Zhao X, Li Y, Li GR and Liu XL:
Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson's
disease (Review). Int J Mol Med. 41:1817–1825. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kierdorf K, Wang Y and Neumann H:
Immune-mediated CNS damage. Results Probl Cell Differ. 51:173–196.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lazarov O and Hollands C: Hippocampal
neurogenesis: Learning to remember. Prog Neurobiol. 138-140:1–18.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun L, Zhang Y, Liu E, Ma Q, Anatol M, Han
H and Yan J: The roles of astrocyte in the brain pathologies
following ischemic stroke. Brain Inj. 33:712–716. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Liu Z and Chopp M: Astrocytes, therapeutic
targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic
stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 144:103–120. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
L'Episcopo F, Serapide MF, Tirolo C, Testa
N, Caniglia S, Morale MC, Pluchino S and Marchetti B: A Wnt1
regulated Frizzled-1/β-Catenin signaling pathway as a candidate
regulatory circuit controlling mesencephalic dopaminergic
neuron-astrocyte crosstalk: Therapeutical relevance for neuron
survival and neuroprotection. Mol Neurodegener. 6:492011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Salinas PC: Wnt signaling in the
vertebrate central nervous system: From axon guidance to synaptic
function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:a0080032012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Grainger S and Willert K: Mechanisms of
Wnt signaling and control. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. Mar
30–2018, Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kalani MY, Cheshier SH, Cord BJ, Bababeygy
SR, Vogel H, Weissman IL, Palmer TD and Nusse R: Wnt-mediated
self-renewal of neural stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:16970–16975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Clevers H, Loh KM and Nusse R: Stem cell
signaling. An integral program for tissue renewal and regeneration:
Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Science. 346:12480122014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pal S, Hartnett KA, Nerbonne JM, Levitan
ES and Aizenman E: Mediation of neuronal apoptosis by Kv2.1-encoded
potassium channels. J Neurosci. 23:4798–4802. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Baver SB and O'Connell KM: The C-terminus
of neuronal Kv2.1 channels is required for channel localization and
targeting but not for NMDA-receptor-mediated regulation of channel
function. Neuroscience. 217:56–66. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Justice JA, Schulien AJ, He K, Hartnett
KA, Aizenman E and Shah NH: Disruption of KV2.1 somato-dendritic
clusters prevents the apoptogenic increase of potassium currents.
Neuroscience. 354:158–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schulien AJ, Yeh CY, Orange BN, Pav OJ,
Hopkins MP, Moutal A, Khanna R, Sun D, Justice JA and Aizenman E:
Targeted disruption of Kv2.1-VAPA association provides
neuroprotection against ischemic stroke in mice by declustering
Kv2.1 channels. Sci Adv. 6:eaaz81102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sánchez-Morán I, Rodríguez C, Lapresa R,
Agulla J, Sobrino T, Castillo J, Bolaños JP and Almeida A: Nuclear
WRAP53 promotes neuronal survival and functional recovery after
stroke. Sci Adv. 6:eabc57022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ji HJ, Wang DM, Hu JF, Sun MN, Li G, Li
ZP, Wu DH, Liu G and Chen NH: IMM-H004, a novel courmarin
derivative, protects against oxygen-and
glucose-deprivation/restoration-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 723:259–266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Canudas S, Hernández-Alonso P, Galié S,
Muralidharan J, Morell-Azanza L, Zalba G, García-Gavilán J, Martí
A, Salas-Salvadó J and Bulló M: Pistachio consumption modulates DNA
oxidation and genes related to telomere maintenance: A crossover
randomized clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 109:1738–1745. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
van Rooden S, Goos JD, van Opstal AM,
Versluis MJ, Webb AG, Blauw GJ, van der Flier WM, Scheltens P,
Barkhof F, van Buchem MA and van der Grond J: Increased number of
microinfarcts in Alzheimer disease at 7-T MR imaging. Radiology.
270:205–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Bernaudin F, Verlhac S, Arnaud C, Kamdem
A, Chevret S, Hau I, Coïc L, Leveillé E, Lemarchand E, Lesprit E,
et al: Impact of early transcranial Doppler screening and intensive
therapy on cerebral vasculopathy outcome in a newborn sickle cell
anemia cohort. Blood. 117:1130–1140. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hindmarsh PC, Brozovic M, Brook CG and
Davies SC: Incidence of overt and covert neurological damage in
children with sickle cell disease. Postgrad Med J. 63:751–753.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kwiatkowski JL, Zimmerman RA, Pollock AN,
Seto W, Smith-Whitley K, Shults J, Blackwood-Chirchir A and
Ohene-Frempong K: Silent infarcts in young children with sickle
cell disease. Br J Haematol. 146:300–305. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Moser FG, Miller ST, Bello JA, Pegelow CH,
Zimmerman RA, Wang WC, Ohene-Frempong K, Schwartz A, Vichinsky EP,
Gallagher D and Kinney TR: The spectrum of brain MR abnormalities
in sickle-cell disease: A report from the cooperative study of
sickle cell disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 17:965–972.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Westover MB, Bianchi MT, Yang C, Schneider
JA and Greenberg SM: Estimating cerebral microinfarct burden from
autopsy samples. Neurology. 80:1365–1369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hilal S, Sikking E, Shaik MA, Chan QL, van
Veluw SJ, Vrooman H, Cheng CY, Sabanayagam C, Cheung CY, Wong TY,
et al: Cortical cerebral microinfarcts on 3T MRI: A novel marker of
cerebrovascular disease. Neurology. 87:1583–1590. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
van Veluw SJ, Hilal S, Kuijf HJ, Ikram MK,
Xin X, Yeow TB, Venketasubramanian N, Biessels GJ and Chen C:
Cortical microinfarcts on 3T MRI: Clinical correlates in
memory-clinic patients. Alzheimers Dement. 11:1500–1509. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Anenberg E, Arstikaitis P, Niitsu Y,
Harrison TC, Boyd JD, Hilton BJ, Tetzlaff W and Murphy TH:
Ministrokes in channel-rhodopsin-2 transgenic mice reveal
widespread deficits in motor output despite maintenance of cortical
neuronal excitability. J Neurosci. 34:1094–1104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Summers PM, Hartmann DA, Hui ES, Nie X,
Deardorff RL, McKinnon ET, Helpern JA, Jensen JH and Shih AY:
Functional deficits induced by cortical microinfarcts. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 37:3599–3614. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang M, Iliff JJ, Liao Y, Chen MJ,
Shinseki MS, Venkataraman A, Cheung J, Wang W and Nedergaard M:
Cognitive deficits and delayed neuronal loss in a mouse model of
multiple microinfarcts. J Neurosci. 32:17948–17960. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Armstrong FD, Thompson RJ Jr, Wang W,
Zimmerman R, Pegelow CH, Miller S, Moser F, Bello J, Hurtig A and
Vass K: Cognitive functioning and brain magnetic resonance imaging
in children with sickle cell disease. Neuropsychology committee of
the cooperative study of sickle cell disease. Pediatrics.
97:864–870. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Steen RG, Reddick WE, Mulhern RK, Langston
JW, Ogg RJ, Bieberich AA, Kingsley PB and Wang WC: Quantitative MRI
of the brain in children with sickle cell disease reveals
abnormalities unseen by conventional MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging.
8:535–543. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang W, Enos L, Gallagher D, Thompson R,
Guarini L, Vichinsky E, Wright E, Zimmerman R and Armstrong FD:
Cooperative Study of Sickle Cell Disease: Neuropsychologic
performance in school-aged children with sickle cell disease: A
report from the cooperative study of sickle cell disease. J
Pediatr. 139:391–397. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hardingham GE and Bading H: Synaptic
versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: Implications for
neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 11:682–696. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lai TW, Shyu WC and Wang YT: Stroke
intervention pathways: NMDA receptors and beyond. Trends Mol Med.
17:266–275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wu QJ and Tymianski M: Targeting NMDA
receptors in stroke: New hope in neuroprotection. Mol Brain.
11:152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen M, Lu TJ, Chen XJ, Zhou Y, Chen Q,
Feng XY, Xu L, Duan WH and Xiong ZQ: Differential roles of NMDA
receptor subtypes in ischemic neuronal cell death and ischemic
tolerance. Stroke. 39:3042–3048. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Choo AM, Geddes-Klein DM, Hockenberry A,
Scarsella D, Mesfin MN, Singh P, Patel TP and Meaney DF: NR2A and
NR2B subunits differentially mediate MAP kinase signaling and
mitochondrial morphology following excitotoxic insult. Neurochem
Int. 60:506–516. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu Y, Wong TP, Aarts M, Rooyakkers A, Liu
L, Lai TW, Wu DC, Lu J, Tymianski M, Craig AM and Wang YT: NMDA
receptor subunits have differential roles in mediating excitotoxic
neuronal death both in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci. 27:2846–2857.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
DeRidder MN, Simon MJ, Siman R, Auberson
YP, Raghupathi R and Meaney DF: Traumatic mechanical injury to the
hippocampus in vitro causes regional caspase-3 and calpain
activation that is influenced by NMDA receptor subunit composition.
Neurobiol Dis. 22:165–176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Eyo UB, Bispo A, Liu J, Sabu S, Wu R,
DiBona VL, Zheng J, Murugan M, Zhang H, Tang Y and Wu LJ: The
GluN2A subunit regulates neuronal NMDA receptor-induced
microglia-neuron physical interactions. Sci Rep. 8:8282018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Manzerra P, Behrens MM, Canzoniero LM,
Wang XQ, Heidinger V, Ichinose T, Yu SP and Choi DW: Zinc induces a
Src family kinase-mediated up-regulation of NMDA receptor activity
and excitotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:11055–11061. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Terasaki Y, Sasaki T, Yagita Y, Okazaki S,
Sugiyama Y, Oyama N, Omura-Matsuoka E, Sakoda S and Kitagawa K:
Activation of NR2A receptors induces ischemic tolerance through
CREB signaling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:1441–1449. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang X, Zhang Q, Tu J, Zhu Y, Yang F, Liu
B, Brann D and Wang R: Prosurvival NMDA 2A receptor signaling
mediates postconditioning neuroprotection in the hippocampus.
Hippocampus. 25:286–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zhou M and Baudry M: Developmental changes
in NMDA neurotoxicity reflect developmental changes in subunit
composition of NMDA receptors. J Neurosci. 26:2956–2963. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hardingham GE, Fukunaga Y and Bading H:
Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB
shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat Neurosci. 5:405–414. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Lu W, Man H, Ju W, Trimble WS, MacDonald
JF and Wang YT: Activation of synaptic NMDA receptors induces
membrane insertion of new AMPA receptors and LTP in cultured
hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 29:243–254. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Karpova A, Mikhaylova M, Bera S, Bar J,
Reddy PP, Behnisch T, Rankovic V, Spilker C, Bethge P, Sahin J, et
al: Encoding and transducing the synaptic or extrasynaptic origin
of NMDA receptor signals to the nucleus. Cell. 152:1119–1133. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kaufman AM, Milnerwood AJ, Sepers MD,
Coquinco A, She K, Wang L, Lee H, Craig AM, Cynader M and Raymond
LA: Opposing roles of synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptor
signaling in cocultured striatal and cortical neurons. J Neurosci.
32:3992–4003. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lau D, Bengtson CP, Buchthal B and Bading
H: BDNF reduces toxic extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signaling via
synaptic NMDA receptors and nuclear-calcium-induced transcription
of inhba/activin A. Cell Rep. 12:1353–1366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wang WY, Jia LJ, Luo Y, Zhang HH, Cai F,
Mao H, Xu WC, Fang JB, Peng ZY, Ma ZW, et al: Location- and
subunit-specific NMDA receptors determine the developmental
sevoflurane neurotoxicity through ERK1/2 signaling. Mol Neurobiol.
53:216–230. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Wang Y, Briz V, Chishti A, Bi X and Baudry
M: Distinct roles for µ-calpain and m-calpain in synaptic
NMDAR-mediated neuroprotection and extrasynaptic NMDAR-mediated
neurodegeneration. J Neurosci. 33:18880–18892. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ivanov A, Pellegrino C, Rama S, Dumalska
I, Salyha Y, Ben-Ari Y and Medina I: Opposing role of synaptic and
extra-synaptic NMDA receptors in regulation of the extracellular
signal-regulated kinases (ERK) activity in cultured rat hippocampal
neurons. J Physiol. 572:789–798. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wu GY, Deisseroth K and Tsien RW:
Activity-dependent CREB phosphorylation: Convergence of a fast,
sensitive calmodulin kinase pathway and a slow, less sensitive
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:2808–2813. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Aarts M, Liu Y, Liu L, Besshoh S, Arundine
M, Gurd JW, Wang YT, Salter MW and Tymianski M: Treatment of
ischemic brain damage by perturbing NMDA receptor-PSD-95 protein
interactions. Science. 298:846–850. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sattler R, Xiong Z, Lu WY, Hafner M,
MacDonald JF and Tymianski M: Specific coupling of NMDA receptor
activation to nitric oxide neurotoxicity by PSD-95 protein.
Science. 284:1845–1848. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Pei L, Shang Y, Jin H, Wang S, Wei N, Yan
H, Wu Y, Yao C, Wang X, Zhu LQ and Lu Y: DAPK1-p53 interaction
converges necrotic and apoptotic pathways of ischemic neuronal
death. J Neurosci. 34:6546–6556. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Tu W, Xu X, Peng L, Zhong X, Zhang W,
Soundarapandian MM, Balel C, Wang M, Jia N, Zhang W, et al: DAPK1
interaction with NMDA receptor NR2B subunits mediates brain damage
in stroke. Cell. 140:222–234. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ning K, Pei L, Liao M, Liu B, Zhang Y,
Jiang W, Mielke JG, Li L, Chen Y, El-Hayek YH, et al: Dual
neuroprotective signaling mediated by downregulating two distinct
phosphatase activities of PTEN. J Neurosci. 24:4052–4060. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Beschorner R, Adjodah D, Schwab JM,
Mittelbronn M, Pedal I, Mattern R, Schluesener HJ and Meyermann R:
Long-term expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1, HSP-32) following
focal cerebral infarctions and traumatic brain injury in humans.
Acta Neuropathol. 100:377–384. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Komkova MA, Karyakina EE and Karyakin AA:
Catalytically synthesized prussian blue nanoparticles defeating
natural enzyme peroxidase. J Am Chem Soc. 140:11302–11307. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang W, Hu S, Yin JJ, He W, Lu W, Ma M,
Gu N and Zhang Y: Prussian blue nanoparticles as multienzyme
mimetics and reactive oxygen species scavengers. J Am Chem Soc.
138:5860–5865. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang K, Tu M, Gao W, Cai X, Song F, Chen
Z, Zhang Q, Wang J, Jin C, Shi J, et al: Hollow prussian blue
nanozymes drive neuroprotection against ischemic stroke via
attenuating oxidative stress, counteracting inflammation, and
suppressing cell apoptosis. Nano Lett. 19:2812–2823. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Dirnagl U, Klehmet J, Braun JS, Harms H,
Meisel C, Ziemssen T, Prass K and Meisel A: Stroke-induced
immunodepression: Experimental evidence and clinical relevance.
Stroke. 38(Suppl 2): S770–S773. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Sarvari S, Moakedi F, Hone E, Simpkins JW
and Ren X: Mechanisms in blood-brain barrier opening and
metabolism-challenged cerebrovascular ischemia with emphasis on
ischemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis. 35:851–868. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Simpkins AN, Dias C and Leigh R: National
Institutes of Health Natural History of Stroke Investigators:
Identification of reversible disruption of the human blood-brain
barrier following acute ischemia. Stroke. 47:2405–2408. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A and Hofer M:
Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Therapeutic approaches.
J Transl Med. 7:972009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wang Q, Wei J and Shi Y: Platelet
microvesicles promote the recovery of neurological function in
mouse model of cerebral infarction by inducing angiogenesis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 513:997–1004. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Rosińska J, Maciejewska J, Narożny R,
Kozubski W and Łukasik M: Association of platelet-derived
microvesicles with high on-treatment platelet reactivity in
convalescent ischemic stroke patients treated with acetylsalicylic
acid. Wiad Lek. 72:1426–1436. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Ghoreishy A, Khosravi A and Ghaemmaghami
A: Exosomal microRNA and stroke: A review. J Cell Biochem.
120:16352–16361. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Loffreda A, Nizzardo M, Arosio A, Ruepp
MD, Calogero RA, Volinia S, Galasso M, Bendotti C, Ferrarese C,
Lunetta C, et al: miR-129-5p: A key factor and therapeutic target
in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Prog Neurobiol. 190:1018032020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Krützfeldt J, Kuwajima S, Braich R, Rajeev
KG, Pena J, Tuschl T, Manoharan M and Stoffel M: Specificity,
duplex degradation and subcellular localization of antagomirs.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35:2885–2892. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Jickling GC, Ander BP, Zhan X, Noblett D,
Stamova B and Liu D: microRNA expression in peripheral blood cells
following acute ischemic stroke and their predicted gene targets.
PLoS One. 9:e992832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Shi Y, Li K, Xu K and Liu QH: MiR-155-5p
accelerates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via targeting
DUSP14 by regulating NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:1408–1419. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Sun H, Zhong D, Wang C, Sun Y, Zhao J and
Li G: MiR-298 exacerbates ischemia/reperfusion injury following
ischemic stroke by targeting act1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
48:528–539. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Liu W, Wang X, Zheng Y, Shang G, Huang J,
Tao J and Chen L: Electroacupuncture inhibits inflammatory injury
by targeting the miR-9-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway following
ischemic stroke. Mol Med Rep. 13:1618–1626. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Guo D, Ma J, Li T and Yan L: Up-regulation
of miR-122 protects against neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke
through the heat shock protein 70-dependent NF-κB pathway by
targeting FOXO3. Exp Cell Res. 369:34–42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Block HS and Biller J: Commonly asked
questions: Thrombolytic therapy in the management of acute stroke.
Expert Rev Neurother. 13:157–165. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Murray V, Norrving B, Sandercock PA,
Terént A, Wardlaw JM and Wester P: The molecular basis of
thrombolysis and its clinical application in stroke. J Intern Med.
267:191–208. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Röther J, Ford GA and Thijs VN:
Thrombolytics in acute ischaemic stroke: Historical perspective and
future opportunities. Cerebrovasc Dis. 35:313–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Saver JL: Number needed to treat estimates
incorporating effects over the entire range of clinical outcomes:
Novel derivation method and application to thrombolytic therapy for
acute stroke. Arch Neurol. 61:1066–1070. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Saver JL, Gornbein J, Grotta J, Liebeskind
D, Lutsep H, Schwamm L, Scott P and Starkman S: Number needed to
treat to benefit and to harm for intravenous tissue plasminogen
activator therapy in the 3- to 4.5-h window: Joint outcome table
analysis of the ECASS 3 trial. Stroke. 40:2433–2437. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ahmed N, Wahlgren N, Grond M, Hennerici M,
Lees KR, Mikulik R, Parsons M, Roine RO and Toni D: Implementation
and outcome of thrombolysis with alteplase 3-4.5 h after an acute
stroke: An updated analysis from SITS-ISTR. Lancet Neurol.
9:866–874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Schwamm LH, Ali SF, Reeves MJ, Smith EE,
Saver JL, Messe S, Bhatt DL, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Peterson ED and
Fonarow GC: Temporal trends in patient characteristics and
treatment with intravenous thrombolysis among acute ischemic stroke
patients at Get With The Guidelines-Stroke hospitals. Circ
Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 6:543–549. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Davalos A, Ford GA,
Grond M, Hacke W, Hennerici MG, Kaste M, Kuelkens S, Larrue V, et
al: Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in the
safe implementation of thrombolysis in stroke-monitoring study
(SITS-MOST): An observational study. Lancet. 369:275–282. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Ingall TJ, O'Fallon WM, Asplund K,
Goldfrank LR, Hertzberg VS, Louis TA and Christianson TJH: Findings
from the reanalysis of the NINDS tissue plasminogen activator for
acute ischemic stroke treatment trial. Stroke. 35:2418–2424. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Jansen O, von Kummer R, Forsting M, Hacke
W and Sartor K: Thrombolytic therapy in acute occlusion of the
intracranial internal carotid artery bifurcation. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 16:1977–1986. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wolpert SM, Bruckmann H, Greenlee R,
Wechsler L, Pessin MS and del Zoppo GJ: Neuroradiologic evaluation
of patients with acute stroke treated with recombinant tissue
plasminogen activator. The rt-PA acute stroke study group. AJNR Am
J Neuroradiol. 14:3–13. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Mandavia R, Qureshi MI, Dharmarajah B,
Head K and Davies AH: Safety of carotid intervention following
thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg.
48:505–512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Furlan AJ and Abou-Chebl A: The role of
recombinant pro-urokinase (r-pro-UK) and intra-arterial
thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke: The PROACT trials. Prolyse
in acute cerebral thromboembolism. Curr Med Res Opin. 18(Suppl 2):
S44–S47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Hao C, Ding W, Xu X, Sun Q, Li X, Wang W,
Zhao Z and Tang L: Effect of recombinant human prourokinase on
thrombolysis in a rabbit model of thromboembolic stroke. Biomed
Rep. 8:77–84. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Agrawal A, Golovoy D, Nimjee S, Ferrell A,
Smith T and Britz G: Mechanical thrombectomy devices for
endovascular management of acute ischemic stroke: Duke stroke
center experience. Asian J Neurosurg. 7:166–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Deng L, Qiu S, Wang L, Li Y, Wang D and
Liu M: Comparison of four food and drug administration-approved
mechanical thrombectomy devices for acute ischemic stroke: A
network meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 127:e49–e57. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Nogueira RG, Lutsep HL, Gupta R, Jovin TG,
Albers GW, Walker GA, Liebeskind DS and Smith WS: TREVO 2
Trialists: Trevo versus Merci retrievers for thrombectomy
revascularisation of large vessel occlusions in acute ischaemic
stroke (TREVO 2): A randomised trial. Lancet. 380:1231–1240. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Saver JL, Jahan R, Levy EI, Jovin TG,
Baxter B, Nogueira RG, Clark W, Budzik R and Zaidat OO: SWIFT
Trialists: Solitaire flow restoration device versus the merci
retriever in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (SWIFT): A
randomised, parallel-group, non-inferiority trial. Lancet.
380:1241–1249. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Suzuki K, Matsumaru Y, Takeuchi M,
Morimoto M, Kanazawa R, Takayama Y, Kamiya Y, Shigeta K, Okubo S,
Hayakawa M, et al: Effect of mechanical thrombectomy without vs
with intravenous thrombolysis on functional outcome among patients
with acute ischemic stroke: The SKIP randomized clinical trial.
JAMA. 325:244–253. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Machado M, Alves M, Fior A, Fragata I,
Papoila AL, Reis J and Nunes AP: Functional outcome after
mechanical thrombectomy with or without previous thrombolysis. J
Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 30:1054952021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Cirillo C, Le Friec A, Frisach I, Darmana
R, Robert L, Desmoulin F and Loubinoux I: Focal malonate injection
into the internal capsule of rats as a model of lacunar stroke.
Front Neurol. 9:10722018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Fries W, Danek A, Scheidtmann K and
Hamburger C: Motor recovery following capsular stroke. Role of
descending pathways from multiple motor areas. Brain. 116:369–382.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Haga KK, Gregory LJ, Hicks CA, Ward MA,
Beech JS, Bath PW, Williams SC and O'Neill MJ: The neuronal nitric
oxide synthase inhibitor, TRIM, as a neuroprotective agent: Effects
in models of cerebral ischaemia using histological and magnetic
resonance imaging techniques. Brain Res. 993:42–53. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|