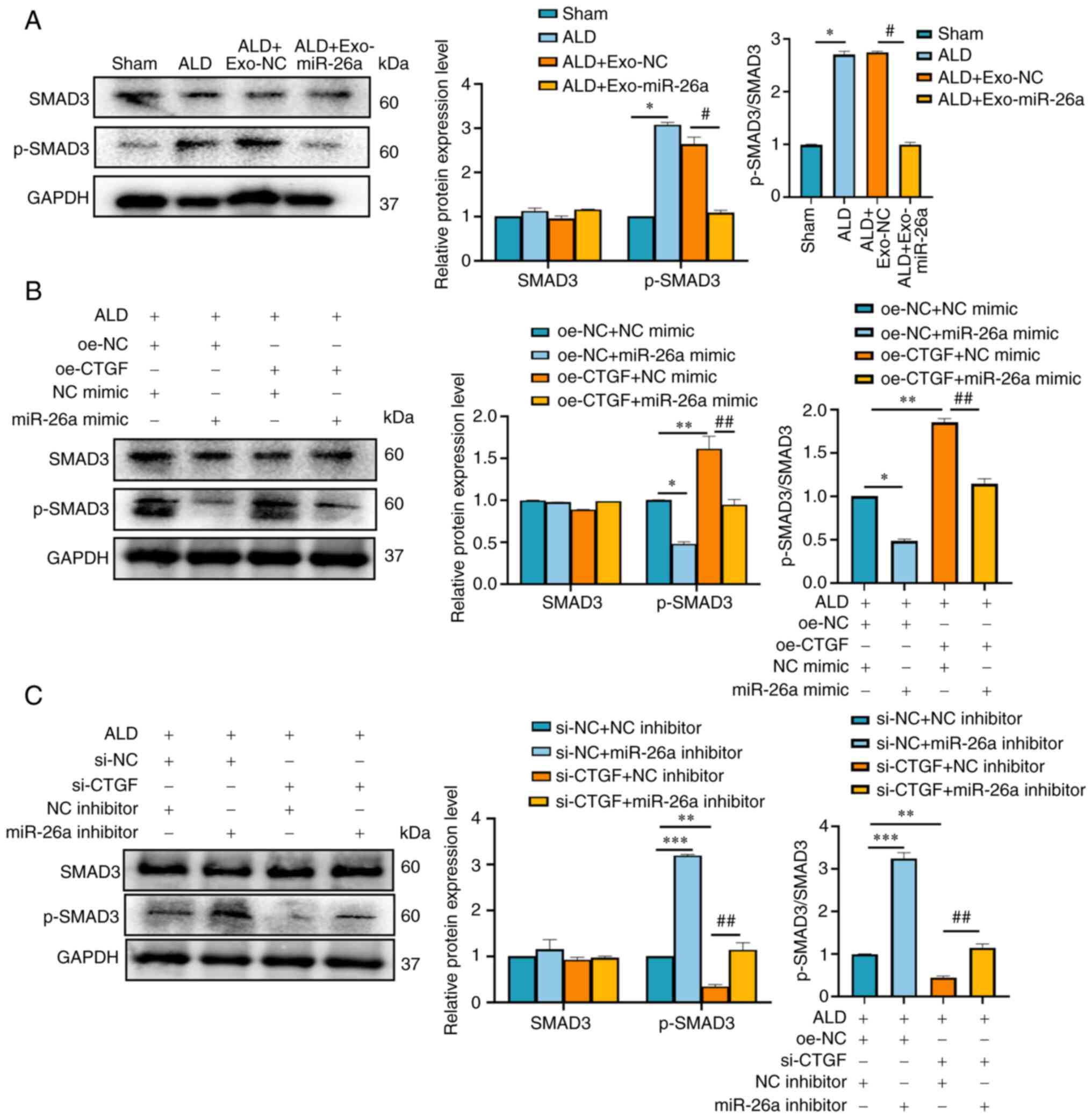
|
1
|
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration:
Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease,
1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease
study 2017. Lancet. 395:709–733. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kramer H: Diet and chronic kidney disease.
Adv Nutr. 10(Suppl 4): S367–S379. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liyanage T, Toyama T, Hockham C, Ninomiya
T, Perkovic V, Woodward M, Fukagawa M, Matsushita K,
Praditpornsilpa K, Hooi LS, et al: Prevalence of chronic kidney
disease in Asia: A systematic review and analysis. BMJ Glob Health.
7:e0075252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qi R and Yang C: Renal tubular epithelial
cells: The neglected mediator of tubulointerstitial fibrosis after
injury. Cell Death Dis. 9:11262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lerman LO: Imaging: BOLD
assessment-effects of RAAS inhibition in CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol.
10:247–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Blasi ER, Rocha R, Rudolph AE, Blomme EAG,
Polly ML and McMahon EG: Aldosterone/salt induces renal
inflammation and fibrosis in hypertensive rats. Kidney Int.
63:1791–1800. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan Y, Zhang A, Qi J, Wang H, Liu X, Zhao
M, Duan S, Huang Z, Zhang C, Wu L, et al: p53/Drp1-dependent
mitochondrial fission mediates aldosterone-induced podocyte injury
and mitochondrial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
314:F798–F808. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shi H, Zhang A, He Y, Yang M and Gan W:
Effects of p53 on aldosterone-induced mesangial cell apoptosis in
vivo and in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 13:5102–5108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qu G, Shi H, Wang B, Li S, Zhang A and Gan
W: Alterations in the long noncoding RNA transcriptome in mesangial
cells treated with aldosterone in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 16:6004–6012.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell.
173:20–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chandrasekaran K, Karolina DS, Sepramaniam
S, Armugam A, Wintour EM, Bertram JF and Jeyaseelan K: Role of
microRNAs in kidney homeostasis and disease. Kidney Int.
81:617–627. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng Z, Guan M, Jia Y, Wang D, Pang R, Lv
F, Xiao Z, Wang L, Zhang H and Xue Y: The coordinated roles of
miR-26a and miR-30c in regulating TGFbeta1-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy. Sci
Rep. 6:374922016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Wang B, Zhang A, Hassounah F, Seow
Y, Wood M, Ma F, Klein JD, Price SR and Wang XH: Exosome-mediated
miR-29 transfer reduces muscle atrophy and kidney fibrosis in mice.
Mol Ther. 27:571–583. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang A, Wang H, Wang B, Yuan Y, Klein JD
and Wang XH: Exogenous miR-26a suppresses muscle wasting and renal
fibrosis in obstructive kidney disease. FASEB J. 33:13590–13601.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei C, Kim IK, Kumar S, Jayasinghe S, Hong
N, Castoldi G, Catalucci D, Jones WK and Gupta S: NF-kappaB
mediated miR-26a regulation in cardiac fibrosis. J Cell Physiol.
228:1433–1442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kadota T, Fujita Y, Araya J, Watanabe N,
Fujimoto S, Kawamoto H, Minagawa S, Hara H, Ohtsuka T, Yamamoto Y,
et al: Human bronchial epithelial cell-derived extracellular
vesicle therapy for pulmonary fibrosis via inhibition of
TGF-beta-WNT crosstalk. J Extracell Vesicles. 10:e121242021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Xiao W, Chen W, Liu X, Wu M, Bo Q,
Luo Y, Ye S, Cao Y and Liu Y: MicroRNA-26a and -26b inhibit lens
fibrosis and cataract by negatively regulating Jagged-1/Notch
signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 24:1431–1442. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang S, Jiang W, Xu Y, Wang X, Mu Y and
Liu P: Serum miR-21 and miR-26a levels negatively correlate with
severity of cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
Microrna. 8:86–92. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Smyth T, Kullberg M, Malik N, Smith-Jones
P, Graner MW and Anchordoquy TJ: Biodistribution and delivery
efficiency of unmodified tumor-derived exosomes. J Control Release.
199:145–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Mahtal N, Lenoir O, Tinel C, Anglicheau D
and Tharaux PL: MicroRNAs in kidney injury and disease. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 18:643–662. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Srivastava SP, Koya D and Kanasaki K:
MicroRNAs in kidney fibrosis and diabetic nephropathy: Roles on EMT
and EndMT. Biomed Res Int. 2013:1254692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Trionfini P, Benigni A and Remuzzi G:
MicroRNAs in kidney physiology and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.
11:23–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Colombo M, Raposo G and Thery C:
Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes
and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
30:255–289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer
DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky
AM and Breakefield XO: Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and
proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic
biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1470–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jalabert A, Vial G, Guay C, Wiklander OPB,
Nordin JZ, Aswad H, Forterre A, Meugnier E, Pesenti S, Regazzi R,
et al: Exosome-like vesicles released from lipid-induced
insulin-resistant muscles modulate gene expression and
proliferation of beta recipient cells in mice. Diabetologia.
59:1049–1058. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vinas JL, Burger D, Zimpelmann J, Haneef
R, Knoll W, Campbell P, Gutsol A, Carter A, Allan DS and Burns KD:
Transfer of microRNA-486-5p from human endothelial colony forming
cell-derived exosomes reduces ischemic kidney injury. Kidney Int.
90:1238–1250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liang H, Xu C, Pan Z, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Chen
Y, Li T, Li X, Liu Y, Huangfu L, et al: The antifibrotic effects
and mechanisms of microRNA-26a action in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Mol Ther. 22:1122–1133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang PM, Zhang YY, Mak TSK, Tang PCT,
Huang XR and Lan HY: Transforming growth factor-beta signalling in
renal fibrosis: From smads to non-coding RNAs. J Physiol.
596:3493–3503. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li ZL and Liu BC: Hypoxia and renal
tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1165:467–485. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Epstein M: Aldosterone blockade: An
emerging strategy for abrogating progressive renal disease. Am J
Med. 119:912–919. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hostetter TH and Ibrahim HN: Aldosterone
in chronic kidney and cardiac disease. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:2395–2401. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shinde AV, Humeres C and Frangogiannis NG:
The role of alpha-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix
contraction and remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1863:298–309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rudman-Melnick V, Adam M, Potter A,
Chokshi SM, Ma Q, Drake KA, Schuh MP, Kofron JM, Devarajan P and
Potter SS: Single-cell profiling of AKI in a murine model reveals
novel transcriptional signatures, profibrotic phenotype, and
epithelial-to-stromal crosstalk. J Am Soc Nephrol. 31:2793–2814.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shen AR, Zhong X, Tang TT, Wang C, Jing J,
Liu BC and Lv LL: Integrin, exosome and kidney disease. Front
Physiol. 11:6278002020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kalluri R and LeBleu VS: The biology,
function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science.
367:eaau69772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang B, Zhang A, Wang H, Klein JD, Tan L,
Wang ZM, Du J, Naqvi N, Liu BC and Wang XH: miR-26a limits muscle
wasting and cardiac fibrosis through exosome-mediated microrna
transfer in chronic kidney disease. Theranostics. 9:1864–1877.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chiang MH, Liang CJ, Lin LC, Yang YF,
Huang CC, Chen YH, Kao HL, Chen YC, Ke SR and Lee CW: miR-26a
attenuates cardiac apoptosis and fibrosis by targeting
ataxia-telangiectasia mutated in myocardial infarction. J Cell
Physiol. 235:6085–6102. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang W, Wang Q, Feng Y, Chen X, Yang L,
Xu M, Wang X, Li W, Niu X and Gao D: MicroRNA-26a protects the
heart against hypertension-induced myocardial fibrosis. J Am Heart
Assoc. 9:e0179702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu C, Zhang H, Wei D and Sun Z: Silencing
lncRNA GAS5 alleviates apoptosis and fibrosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy by targeting miR-26a/b-5p. Acta Diabetol.
58:1491–1501. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ito Y, Aten J, Bende RJ, Oemar BS,
Rabelink TJ, Weening JJ and Goldschmeding R: Expression of
connective tissue growth factor in human renal fibrosis. Kidney
Int. 53:853–861. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Perbal B: CCN proteins: Multifunctional
signalling regulators. Lancet. 363:62–64. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang S, Denichilo M, Brubaker C and
Hirschberg R: Connective tissue growth factor in tubulointerstitial
injury of diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 60:96–105. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Okada H, Kikuta T, Kobayashi T, Inoue T,
Kanno Y, Takigawa M, Sugaya T, Kopp JB and Suzuki H: Connective
tissue growth factor expressed in tubular epithelium plays a
pivotal role in renal fibrogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:133–143.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lan HY: Transforming growth
factor-beta/Smad signalling in diabetic nephropathy. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 39:731–738. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sato M, Muragaki Y, Saika S, Roberts AB
and Ooshima A: Targeted disruption of TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling
protects against renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by
unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Clin Invest. 112:1486–1494.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|