|
1
|
Hofbauer L, Kuhne C and Viereck V: The
OPG/RANKL/RANK system in metabolic bone diseases. J Musculoskel
Neuro Inter. 4:268–275. 2004.
|
|
2
|
Wang L, You X, Zhang L, Zhang C and Zou W:
Mechanical regulation of bone remodeling. Bone Res. 10:162022.
|
|
3
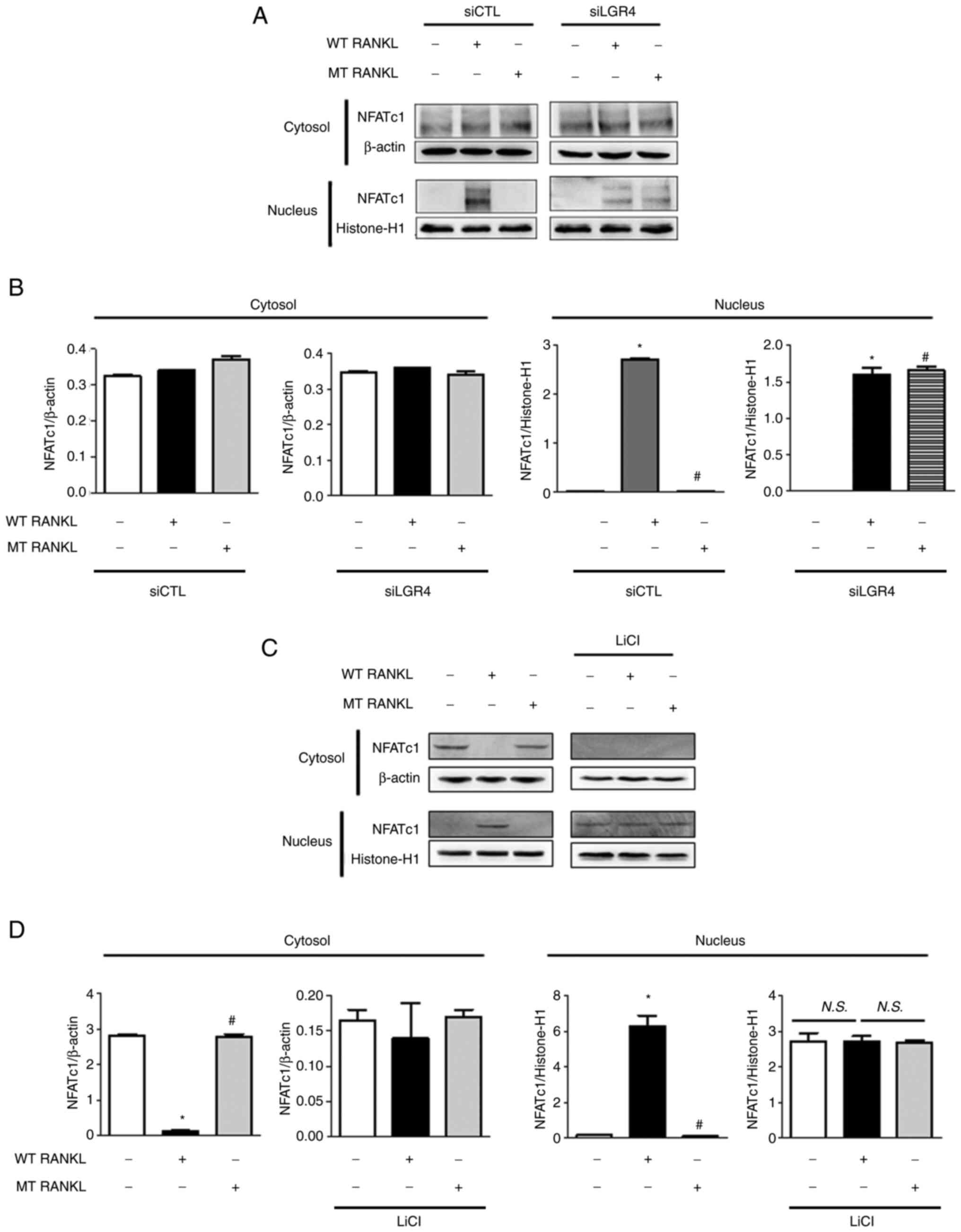
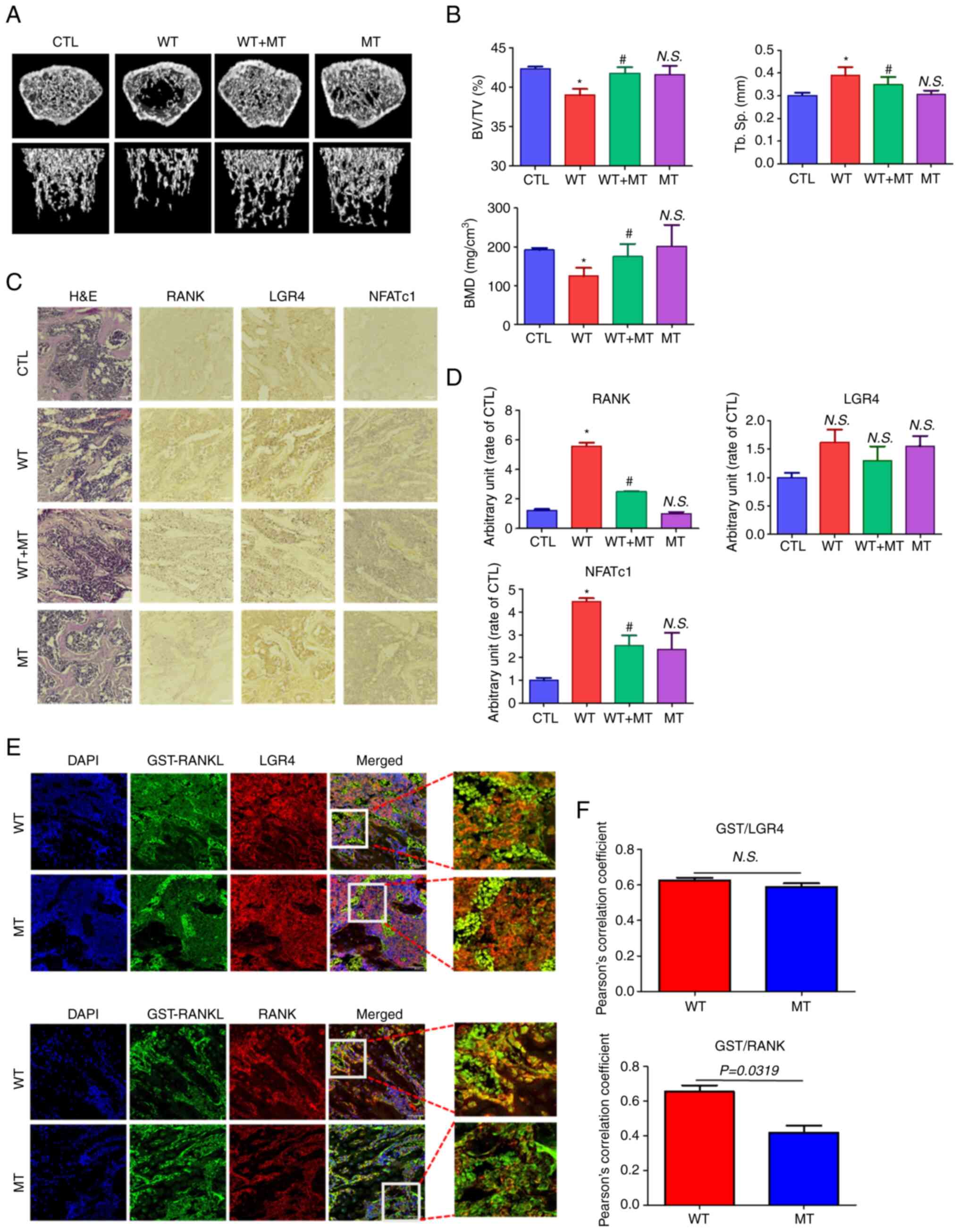
|
Hanley DA, Adachi JD, Bell A and Brown V:
Denosumab: Mechanism of action and clinical outcomes. Int J Clin
Pract. 66:1139–1146. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Gowen M, Stroup GB, Dodds RA, James IE,
Votta BJ, Smith BR, Bhatnagar PK, Lago AM, Callahan JF, DelMar EG,
et al: Antagonizing the parathyroid calcium receptor stimulates
parathyroid hormone secretion and bone formation in osteopenic
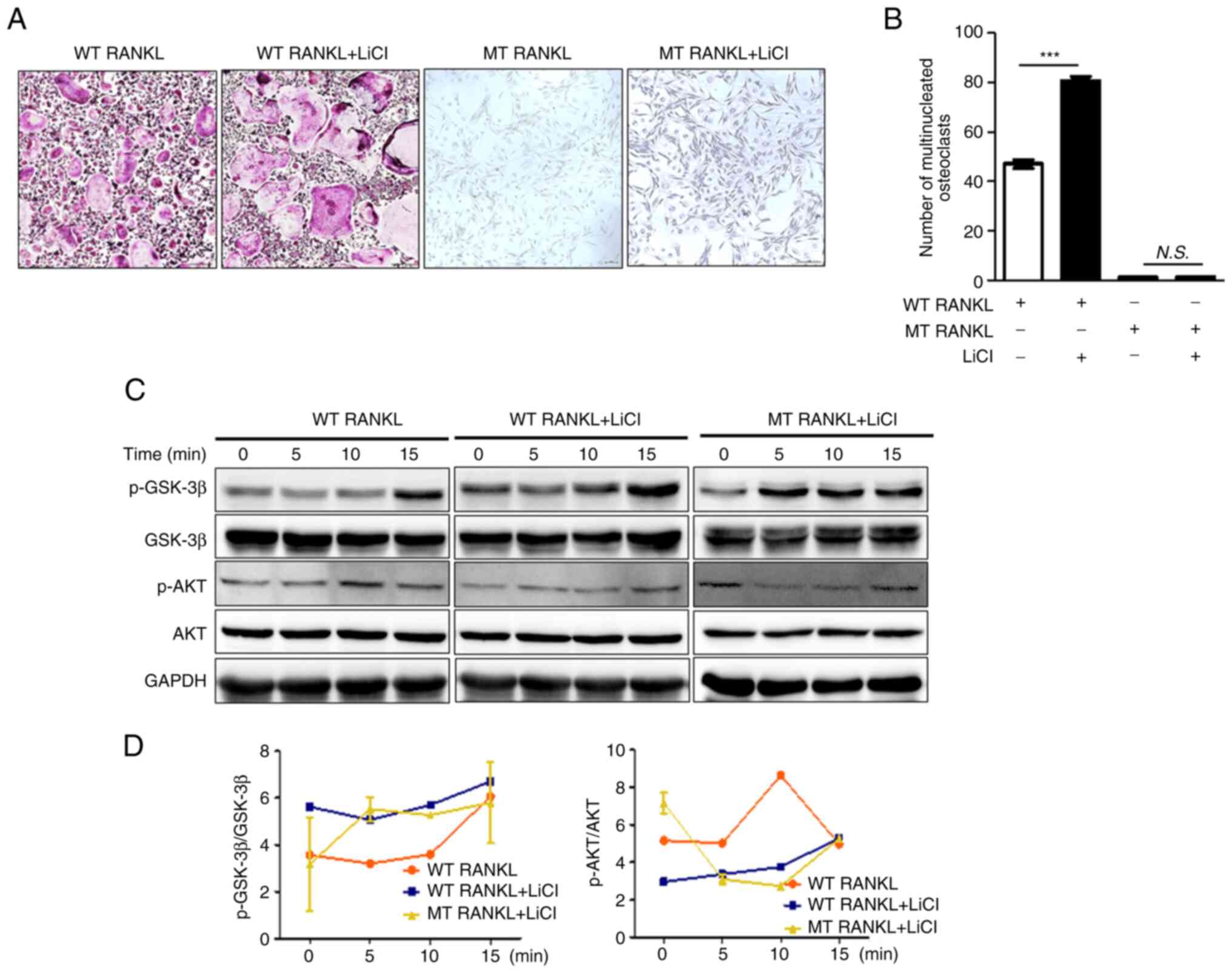
rats. J Clin Invest. 105:1595–1604. 2000.
|
|
5
|
Martin TJ: Bone biology and anabolic
therapies for bone: Current status and future prospects. J Bone
Metab. 21:8–20. 2014.
|
|
6
|
Sozen T, Ozisik L and Basaran NC: An
overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol. 4:46–56.
2017.
|
|
7
|
Miller PD: Denosumab: Anti-RANKL antibody.
Curr Osteoporos Rep. 7:18–22. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Cadieux B, Coleman R, Jafarinasabian P,
Lipton A, Orlowski RZ, Saad F, Scagliotti GV, Shimizu K and Stopeck
A: Experience with denosumab (XGEVA(R)) for prevention of
skeletal-related events in the 10 years after approval. J Bone
Oncol. 33:1004162022.
|
|
9
|
Lei MM, Tavares E, Buzgo E, Lou U, Raje N
and Yee AJ: Denosumab versus intravenous bisphosphonate use for
hypercalcemia in multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 63:1–4. 2022.
|
|
10
|
Terpos E, Jamotte A, Christodoulopoulou A,
Campioni M, Bhowmik D, Kennedy L and Willenbacher W: A
cost-effectiveness analysis of denosumab for the prevention of
skeletal-related events in patients with multiple myeloma in four
European countries: Austria, Belgium, Greece, and Italy. J Med
Econ. 22:766–776. 2019.
|
|
11
|
Benlidayi IC: Denosumab in the treatment
of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Rheumatol Int.
38:1975–1984. 2018.
|
|
12
|
Pittman K, Antill YC, Goldrick A, Goh J
and de Boer RH: Denosumab: Prevention and management of
hypocalcemia, osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical fractures. Asia
Pac J Clin Oncol. 13:266–276. 2017.
|
|
13
|
Gkoufa A, Angelousi A, Neonaki A,
Athanasouli F and Cholongitas E: Severe symptomatic hypocalcemia
associated with denosumab administration in a patient with
decompensated cirrhosis and renal dysfunction. Ann Pharmacother.
56:853–855. 2022.
|
|
14
|
Anastasilakis AD, Makras P, Yavropoulou
MP, Tabacco G, Naciu AM and Palermo A: Denosumab discontinuation
and the rebound phenomenon: A narrative review. J Clin Med.
10:1522021.
|
|
15
|
Luo J, Yang Z, Ma Y, Yue Z, Lin H, Qu G,
Huang J, Dai W, Li C, Zheng C, et al: LGR4 is a receptor for RANKL
and negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone
resorption. Nat Med. 22:539–546. 2016.
|
|
16
|
Takegahara N, Kim H and Choi Y: RANKL
biology. Bone. 159:1163532022.
|
|
17
|
Yue Z, Niu X, Yuan Z, Qin Q, Jiang W, He
L, Gao J, Ding Y, Liu Y, Xu Z, et al: RSPO2 and RANKL signal
through LGR4 to regulate osteoclastic premetastatic niche formation
and bone metastasis. J Clin Invest. 132:e1445792022.
|
|
18
|
Jin Y and Yang Y: LGR4: A new receptor for
a stronger bone. Sci China Life Sci. 59:735–736. 2016.
|
|
19
|
Luo W, Tan P, Rodriguez M, He L, Tan K,
Zeng L, Siwko S and Liu M: Leucine-rich repeat-containing G
protein-coupled receptor 4 (Lgr4) is necessary for prostate cancer
metastasis via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
292:15525–15537. 2017.
|
|
20
|
Elango J, Bao B and Wu W: The hidden
secrets of soluble RANKL in bone biology. Cytokine.
144:1555592021.
|
|
21
|
Ko Y, Lee G, Kim B, Park M, Jang Y and Lim
W: Modification of the RANKL-RANK-binding site for the
immunotherapeutic treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.
31:983–993. 2020.
|
|
22
|
Ko YJ, Sohn HM, Jang Y, Park M, Kim B, Kim
B, Park JI, Hyun H, Jeong B, Hong C and Lim W: A novel modified
RANKL variant can prevent osteoporosis by acting as a vaccine and
an inhibitor. Clin Transl Med. 11:e3682021.
|
|
23
|
Jang Y, Sohn HM, Ko YJ, Hyun H and Lim W:
Inhibition of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by novel mutant
RANKL. Int J Mol Sci. 22:4342021.
|
|
24
|
Romain M, Thiroux B, Tardy M, Quesnel B
and Thuru X: Measurement of protein-protein interactions through
microscale thermophoresis (MST). Bio Protoc. 10:e35742020.
|
|
25
|
Bartell SM, Kim HN, Ambrogini E, Han L,
Iyer S, Ucer SS, Rabinovitch P, Jilka RL, Weinstein RS, Zhao H, et
al: FoxO proteins restrain osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption
by attenuating H2O2 accumulation. Nat Commun. 5:37732014.
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
27
|
Law SM and Zheng KK: Premise and peril of
Wnt signaling activation through GSK-3β inhibition. iScience.
25:1041592022.
|
|
28
|
Fan X, Xiong H, Wei J, Gao X, Feng Y, Liu
X, Zhang G, He QY, Xu J and Liu L: Cytoplasmic hnRNPK interacts
with GSK3β and is essential for the osteoclast differentiation. Sci
Rep. 5:177322015.
|
|
29
|
Cao X: RANKL-RANK signaling regulates
osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Bone Res.
6:352018.
|
|
30
|
Tokuyama N and Tanaka S: Updates of
denosumab, anti-RANKL antibody for osteoporosis. Clin Calcium.
24:85–91. 2014.In Japanese.
|
|
31
|
Cipriani C, Piemonte S, Colangelo L, De
Martino V, Diacinti D, Ferrone F, Piazzolla V, Fassino V, Nieddu L,
Minisola S and Pepe J: Inhibition of the RANKL with denosumab has
no effect on circulating markers of atherosclerosis in women with
postmenopausal osteoporosis: A pilot study. Endocrine. 71:199–207.
2021.
|
|
32
|
Lasco A, Morabito N, Basile G, Atteritano
M, Gaudio A, Giorgianni GM, Morini E, Faraci B, Bellone F and
Catalano A: Denosumab inhibition of RANKL and insulin resistance in
postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int.
98:123–128. 2016.
|
|
33
|
Kim AS, Girgis CM and McDonald MM:
Osteoclast recycling and the rebound phenomenon following denosumab
discontinuation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 20:505–515. 2022.
|
|
34
|
Anastasilakis AD, Evangelatos G, Makras P
and Iliopoulos A: Rebound-associated vertebral fractures may occur
in sequential time points following denosumab discontinuation: Need
for prompt treatment re-initiation. Bone Rep. 12:1002672020.
|
|
35
|
Anastasilakis AD, Trovas G, Balanika A,
Polyzos SA, Makras P and Tournis S: Progression of
rebound-associated vertebral fractures following denosumab
discontinuation despite reinstitution of treatment: Suppressing
increased bone turnover may not be enough. J Clin Densitom.
24:338–340. 2021.
|
|
36
|
Luo J, Zhou W, Zhou X, Li D, Weng J, Yi Z,
Cho SG, Li C, Yi T, Wu X, et al: Regulation of bone formation and
remodeling by G-protein-coupled receptor 48. Development.
136:2747–2756. 2009.
|
|
37
|
Shi GX, Zheng XF, Zhu C, Li B, Wang YR,
Jiang SD and Jiang LS: Evidence of the role of R-spondin 1 and its
receptor lgr4 in the transmission of mechanical stimuli to
biological signals for bone formation. Int J Mol Sci.
18:5642017.
|
|
38
|
Lee Y, Kim HJ, Park CK, Kim YG, Lee HJ,
Kim JY and Kim HH: MicroRNA-124 regulates osteoclast
differentiation. Bone. 56:383–389. 2013.
|
|
39
|
Cong F, Wu N, Tian X, Fan J, Liu J, Song T
and Fu H: MicroRNA-34c promotes osteoclast differentiation through
targeting LGR4. Gene. 610:1–8. 2017.
|
|
40
|
Moon JB, Kim JH, Kim K, Youn BU, Ko A, Lee
SY and Kim N: Akt induces osteoclast differentiation through
regulating the GSK3beta/NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Immunol.
188:163–169. 2012.
|
|
41
|
Wang M, Liu J, Zhu G and Chen X: Low
levels of cadmium exposure affect bone by inhibiting Lgr4
expression in osteoblasts and osteoclasts. J Trace Elem Med Biol.
73:1270252022.
|
|
42
|
Manolagas SC and Parfitt AM: What old
means to bone. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:369–374. 2010.
|