|
1
|
Vocke K, Dauner K, Hahn A, Ulbrich A,
Broecker J, Keller S, Frings S and Möhrlen F: Calmodulin-dependent
activation and inactivation of anoctamin calcium-gated chloride
channels. J Gen Physiol. 142:381–404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Whitlock JM and Hartzell HC:
Anoctamins/TMEM16 proteins: Chloride channels flirting with lipids
and extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Physiol. 79:119–143. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Kunzelmann K, Ousingsawat J, Benedetto R,
Cabrita I and Schreiber R: Contribution of Anoctamins to cell
survival and cell death. Cancers. 11:3822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scudieri P, Sondo E, Ferrera L and
Galietta LJV: The anoctamin family: TMEM16A and TMEM16B as
calcium-activated chloride channels. Exp Physiol. 97:177–183. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim H, Kim H, Lee J, Lee B, Kim HR, Jung
J, Lee MO and Oh U: Anoctamin 9/TMEM16J is a cation channel
activated by cAMP/PKA signal. Cell Calcium. 71:75–85. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
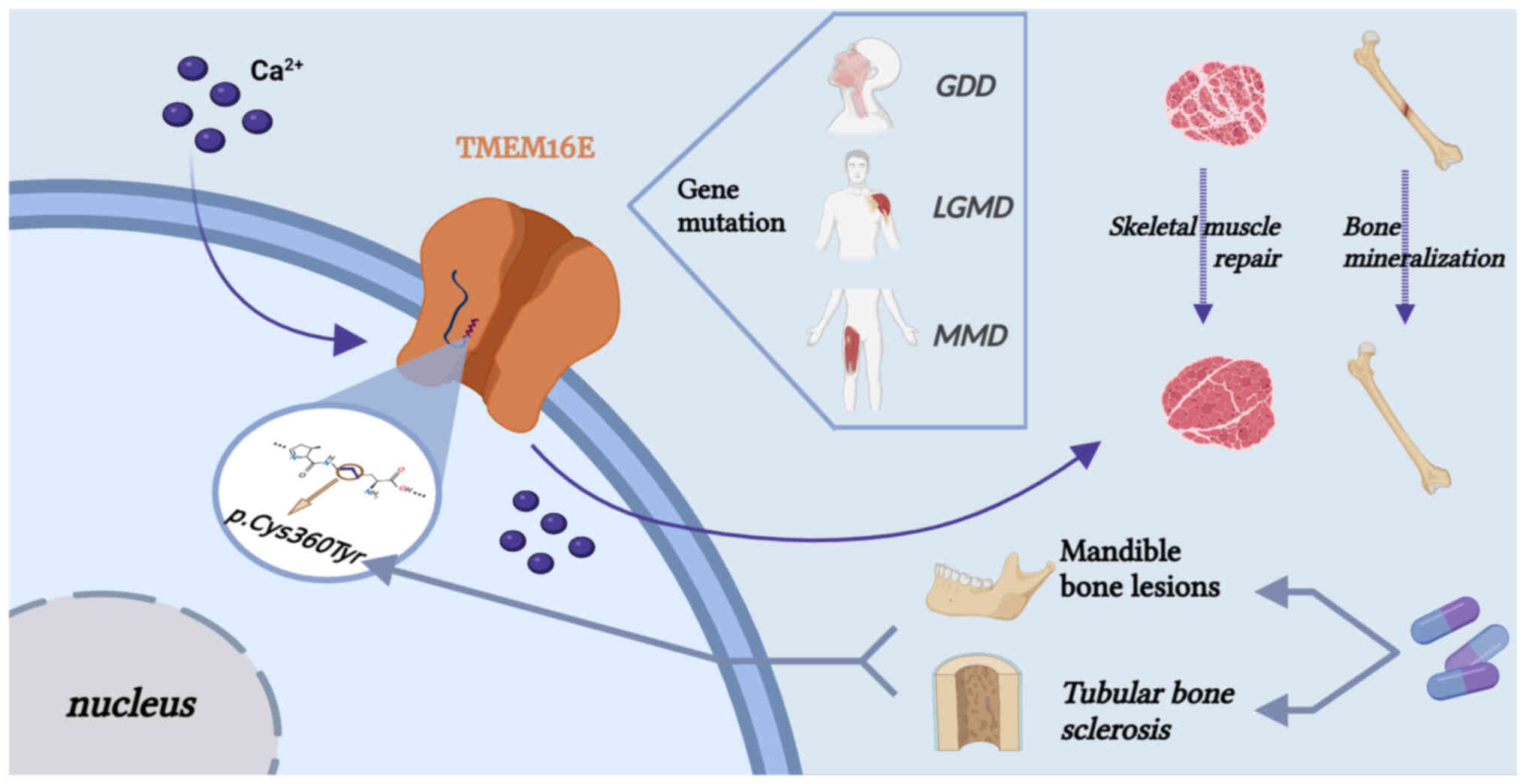
|
Khelashvili G, Falzone ME, Cheng X, Lee
B-C, Accardi A and Weinstein H: Dynamic modulation of the lipid
translocation groove generates a conductive ion channel in
Ca2+-bound nhTMEM16. Nat Commun. 10:49722019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Agostinelli E and Tammaro P: Polymodal
control of TMEM16x channels and Scramblases. Int J Mol Sci.
23:15802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baethge C, Goldbeck-Wood S and Mertens S:
SANRA-a scale for the quality assessment of narrative review
articles. Res Integr Peer Rev. 4:52019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Falzone ME, Malvezzi M, Lee BC and Accardi
A: Known structures and unknown mechanisms of TMEM16 scramblases
and channels. J Gen Physiol. 150:933–947. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Falzone ME, Rheinberger J, Lee BC, Peyear
T, Sasset L, Raczkowski AM, Eng ET, Di Lorenzo A, Andersen OS,
Nimigean CM and Accardi A: Structural basis of Ca2+-dependent
activation and lipid transport by a TMEM16 scramblase. ELife.
8:e432292019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Cheng Y, Feng S, Puchades C, Ko J,
Figueroa E, Chen Y, Wu H, Gu S, Han T, Li J, et al: Identification
of a conserved drug binding pocket in TMEM16 proteins. Res Sq.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pedemonte N and Galietta LJV: Structure
and function of TMEM16 proteins (Anoctamins). Physiol Rev.
94:419–459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
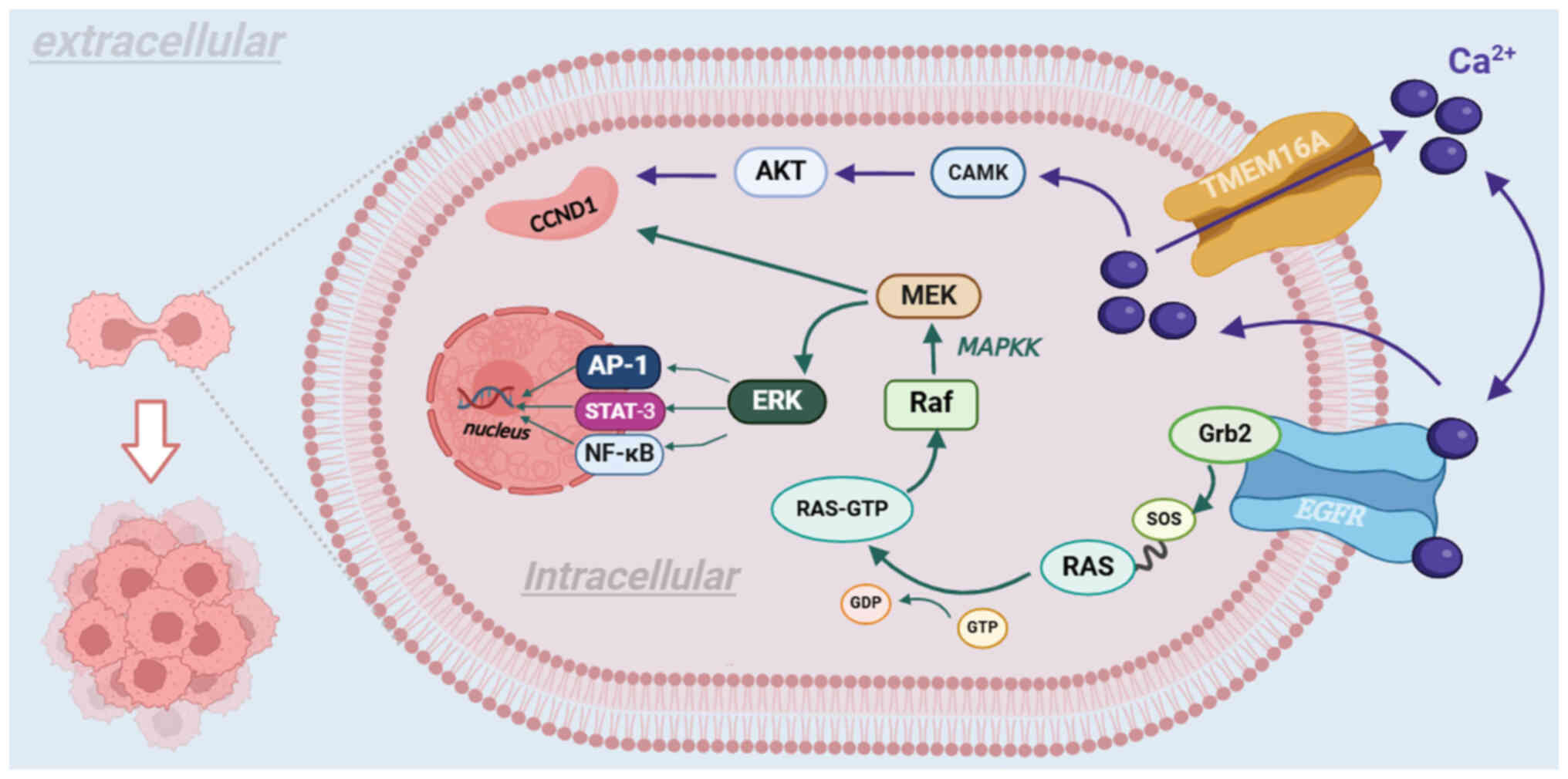
Yu K, Duran C, Qu Z, Cui YY and Hartzell
HC: Explaining calcium-dependent gating of Anoctamin-1 chloride
channels requires a revised topology. Circ Res. 110:990–999. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jung J, Nam JH, Park HW, Oh U, Yoon JH and
Lee MG: Dynamic modulation of ANO1/TMEM16A HCO3−
permeability by Ca2+/calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:360–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tian Y, Kongsuphol P, Hug M, Ousingsawat
J, Witzgall R, Schreiber R and Kunzelmann K: Calmodulin-dependent
activation of the epithelial calcium-dependent chloride channel
TMEM16A. FASEB J. 25:1058–1068. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hahn A, Salomon JJ, Leitz D, Feigenbutz D,
Korsch L, Lisewski I, Schrimpf K, Millar-Büchner P, Mall MA, Frings
S and Möhrlen F: Expression and function of Anoctamin 1/TMEM16A
calcium-activated chloride channels in airways of in vivo mouse
models for cystic fibrosis research. Pflugers Arch. 470:1335–1348.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Falzone ME, Feng Z, Alvarenga OE, Pan Y,
Lee B, Cheng X, Fortea E, Scheuring S and Accardi A: TMEM16
scramblases thin the membrane to enable lipid scrambling. Nat
Commun. 13:26042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jansen K and Steurer S: DOG1 expression is
in common human tumors: A tissue microarray study on more than
15,000 tissue samples. Am J Clin Pathol. 156(Suppl): S108–S109.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lam AK and Dutzler R: Calcium-dependent
electrostatic control of anion access to the pore of the
calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A. ELife. 7:e391222018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
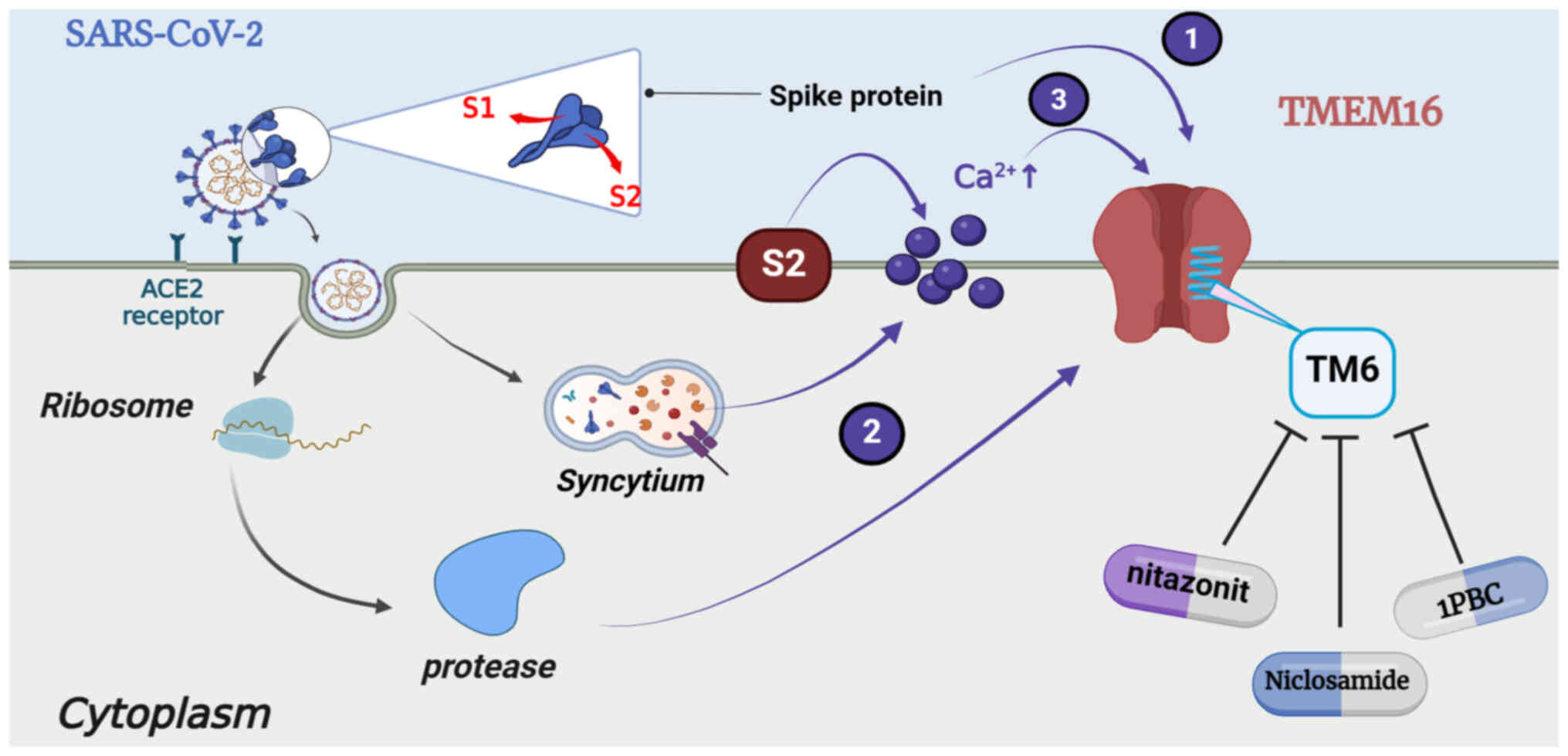
|
20
|
Huang WC, Xiao S, Huang F, Harfe BD, Jan
YN and Jan L: Calcium-Activated chloride channels (CaCCs) regulate
action potential and synaptic response in hippocampal neurons.
Neuron. 74:179–192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Davis AJ, Forrest AS, Jepps TA, Valencik
ML, Wiwchar M, Singer CA, Sones WR, Greenwood IA and Leblanc N:
Expression profile and protein translation of TMEM16A in murine
smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 299:C948–C959. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thomas-Gatewood C, Neeb ZP, Bulley S,
Adebiyi A, Bannister JP, Leo MD and Jaggar JH: TMEM16A channels
generate Ca2+-activated Cl-currents in cerebral artery
smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Circ Physiol. 301:H1819–H1827.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li RS, Wang Y, Chen HS, Jiang FY, Tu Q, Li
WJ and Yin RX: TMEM16A contributes to angiotensin II-induced
cerebral vasoconstriction via the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Mol
Med Report. 13:3691–3699. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lian H, Cheng Y and Wu X: TMEM16A
exacerbates renal injury by activating P38/JNK signaling pathway to
promote podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy mice. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 487:201–208. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dutta AK, Khimji AK, Liu S, Karamysheva Z,
Fujita A, Kresge C, Rockey DC and Feranchak AP: PKCα regulates
TMEM16A-mediated Cl-secretion in human biliary cells. Am J Physiol
Liver Physiol. 310:G34–G42. 2016.
|
|
26
|
Arreola J, López-Romero AE, Pérez-Cornejo
P and Rodríguez-Menchaca AA: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
and cholesterol regulators of the calcium-activated chloride
channels TMEM16A and TMEM16B. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1422:279–304. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee D, Lim H, Lee J, Ha GE, No KT and
Cheong E: Intracellular loop in the brain isoforms of anoctamin 2
channels regulates calcium-dependent activation. Exp Neurobiol.
32:133–146. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pietra G, Dibattista M, Menini A, Reisert
J and Boccaccio A: The Ca2+-activated Cl-channel TMEM16B
regulates action potential firing and axonal targeting in olfactory
sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 148:293–311. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ayoglu B, Mitsios N, Kockum I, Khademi M,
Zandian A, Sjöberg R, Forsström B, Bredenberg J, Lima Bomfim I,
Holmgren E, et al: Anoctamin 2 identified as an autoimmune target
in multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:2188–2193. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ha GE, Lee J, Kwak H, Song K, Kwon J, Jung
SY, Hong J, Chang GE, Hwang EM, Shin HS, et al: The
Ca2+-activated chloride channel anoctamin-2 mediates
spike-frequency adaptation and regulates sensory transmission in
thalamocortical neurons. Nat Commun. 7:137912016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Xiao S, Tien J, Le S, Le
T, Jan LY and Yang H: Inferior Olivary TMEM16B mediates cerebellar
motor learning. Neuron. 95:1103–1111.e4. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim H, Kim E and Lee BC: Investigation of
phosphatidylserine-transporting activity of human TMEM16C isoforms.
Membranes (Basel). 12:10052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang TA, Chen C, Huang F, Feng S, Tien J,
Braz JM, Basbaum AI, Jan YN and Jan LY: TMEM16C is involved in
thermoregulation and protects rodent pups from febrile seizures.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e20233421182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang F, Wang X, Ostertag EM, Nuwal T,
Huang B, Jan YN, Basbaum AI and Jan LY: TMEM16C facilitates
Na(+)-activated K+ currents in rat sensory neurons and regulates
pain processing. Nat Neurosci. 16:1284–1290. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Carvalho V, Martins J, Correia F, Costa M,
Massano J and Temudo T: Another twist in the tale: Intrafamilial
phenotypic heterogeneity in ANO3-related dystonia. Mov Disord Clin
Pract. 8:758–762. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stamelou M, Charlesworth G, Cordivari C,
Schneider SA, Kägi G, Sheerin UM, Rubio-Agusti I, Batla A, Houlden
H, Wood NW and Bhatia KP: The phenotypic spectrum of DYT24 due to
ANO3 mutations. Mov Disord. 29:928–934. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Esposito M, Trinchillo A, Piceci-Sparascio
F, D'Asdia MC, Consoli F and De Luca A: A novel ANO3 variant in two
siblings with different phenotypes. Parkinsonism Relat Disord.
111:1054132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Reichhart N, Milenkovic VM, Wetzel CH and
Strauß O: Prediction of functional consequences of missense
mutations in ANO4 Gene. Int J Mol Sci. 22:27322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maniero C, Scudieri P, Haris Shaikh L,
Zhao W, Gurnell M, Galietta LJV and Brown MJ: ANO4 (Anoctamin 4) Is
a novel marker of zona glomerulosa that regulates stimulated
aldosterone secretion. Hypertension. 74:1152–1159. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sherva R, Tripodis Y, Bennett DA, Chibnik
LB, Crane PK, de Jager PL, Farrer LA, Saykin AJ, Shulman JM, Naj A,
et al: Genome-wide association study of the rate of cognitive
decline in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 10:45–52. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Di Zanni E, Gradogna A, Scholz-Starke J
and Boccaccio A: Gain of function of TMEM16E/ANO5 scrambling
activity caused by a mutation associated with gnathodiaphyseal
dysplasia. Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:1657–1670. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Di Zanni E, Gradogna A, Picco C,
Scholz-Starke J and Boccaccio A: TMEM16E/ANO5 mutations related to
bone dysplasia or muscular dystrophy cause opposite effects on
lipid scrambling. Hum Mutat. 41:1157–1170. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Whitlock JM, Yu K, Cui YY and Hartzell HC:
Anoctamin 5/TMEM16E facilitates muscle precursor cell fusion. J Gen
Physiol. 150:1498–1509. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Foltz SJ, Cui YY, Choo HJ and Hartzell HC:
ANO5 ensures trafficking of annexins in wounded myofibers. J Cell
Biol. 220:e2020070592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
van Kruchten R, Mattheij NJ, Saunders C,
Feijge MA, Swieringa F, Wolfs JL, Collins PW, Heemskerk JW and
Bevers EM: Both TMEM16F-dependent and TMEM16F-independent pathways
contribute to phosphatidylserine exposure in platelet apoptosis and
platelet activation. Blood. 121:1850–1857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Arndt M, Alvadia C, Straub MS, Clerico
Mosina V, Paulino C and Dutzler R: Structural basis for the
activation of the lipid scramblase TMEM16F. Nat Commun.
13:66922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fujii T, Sakata A, Nishimura S, Eto K and
Nagata S: TMEM16F is required for phosphatidylserine exposure and
microparticle release in activated mouse platelets. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 112:12800–12805. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Millington-Burgess SL and Harper MT: Gene
of the issue: ANO6 and Scott syndrome. Platelets. 31:964–967. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li H, Xu L, Gao Y, Zuo Y, Yang Z, Zhao L,
Chen Z, Guo S and Han R: BVES is a novel interactor of ANO5 and
regulates myoblast differentiation. Cell Biosci. 11:2222021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Guo J, Wang D, Dong Y, Gao X, Tong H, Liu
W, Zhang L and Sun M: ANO7: Insights into topology, function, and
potential applications as a biomarker and immunotherapy target.
Tissue Cell. 72:1015462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kaikkonen E, Rantapero T, Zhang Q, Taimen
P, Laitinen V, Kallajoki M, Jambulingam D, Ettala O, Knaapila J,
Boström PJ, et al: ANO7 is associated with aggressive prostate
cancer. Int J Cancer. 143:2479–2487. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jha A, Chung WY, Vachel L, Maleth J, Lake
S, Zhang G, Ahuja M and Muallem S: Anoctamin 8 tethers endoplasmic
reticulum and plasma membrane for assembly of Ca2+
signaling complexes at the ER/PM compartment. EMBO J.
38:e1014522019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Liu X, Lai H, Zeng X, Xin S, Nie L, Liang
Z, Wu M, Chen Y, Zheng J and Zou Y: Whole-exome sequencing reveals
ANO8 as a genetic risk factor for intrahepatic cholestasis of
pregnancy. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 20:5442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Schreiber R, Ousingsawat J and Kunzelmann
K: Targeting of intracellular TMEM16 proteins to the plasma
membrane and activation by purinergic signaling. Int J Mol Sci.
21:40652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Katsurahara K, Shiozaki A, Kosuga T, Kudou
M, Shoda K, Arita T, Konishi H, Komatsu S, Kubota T, Fujiwara H, et
al: ANO9 regulated cell cycle in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 27:3218–3230. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Katsurahara K, Shiozaki A, Kosuga T,
Shimizu H, Kudou M, Arita T, Konishi H, Komatsu S, Kubota T,
Fujiwara H, et al: ANO9 regulates PD-L2 expression and binding
ability to PD-1 in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 112:1026–1037. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jun I, Park HS, Piao H, Han JW, An MJ, Yun
BG, Zhang X, Cha YH, Shin YK, Yook JI, et al: ANO9/TMEM16J promotes
tumourigenesis via EGFR and is a novel therapeutic target for
pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 117:1798–1809. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Schreiber R, Talbi K, Ousingsawat J and
Kunzelmann K: A TMEM16J variant leads to dysregulated cytosolic
calcium which may lead to renal disease. FASEB J. 37:e226832023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Chrysanthou A, Ververis A and
Christodoulou K: ANO10 function in health and disease. Cerebellum.
22:447–467. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wanitchakool P, Ousingsawat J, Sirianant
L, Cabrita I, Faria D, Schreiber R and Kunzelmann K: Cellular
defects by deletion of ANO10 are due to deregulated local calcium
signaling. Cell Signal. 30:41–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Hammer C, Wanitchakool P, Sirianant L,
Papiol S, Monnheimer M, Faria D, Ousingsawat J, Schramek N, Schmitt
C, Margos G, et al: A coding variant of ANO10, affecting volume
regulation of macrophages, is associated with borrelia
seropositivity. Mol Med. 21:26–37. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gentzsch M and Mall MA: Ion channel
modulators in cystic fibrosis. Chest. 154:383–393. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shteinberg M, Haq IJ, Polineni D and
Davies JC: Cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 397:2195–2211. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lopes-Pacheco M, Pedemonte N and Veit G:
Discovery of CFTR modulators for the treatment of cystic fibrosis.
Expert Opin Drug Discov. 16:897–913. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Villamizar O, Waters SA, Scott T, Grepo N,
Jaffe A and Morris KV: Mesenchymal Stem Cell exosome delivered Zinc
Finger Protein activation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane
conductance regulator. J Extracell Vesicles. 10:e120532021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Simon MA and Csanady L: Understanding
impact of δF508 and G551D CFTR mutations on CFTR/PKA-c interaction.
Biophys J. 122:112a2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Harrison MJ, Murphy DM and Plant BJ:
Ivacaftor in a G551D homozygote with cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med.
369:1280–1282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ramsey BW, Davies J, McElvaney NG, Tullis
E, Bell SC, Dřevínek P, Griese M, McKone EF, Wainwright CE, Konstan
MW, et al: A CFTR potentiator in patients with cystic fibrosis and
theG551Dmutation. N Engl J Med. 365:1663–1672. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Fiedorczuk K and Chen J: Mechanism of CFTR
correction by type I folding correctors. Cell. 185:158–168.e11.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Veit G, Roldan A, Hancock MA, Da Fonte DF,
Xu H, Hussein M, Frenkiel S, Matouk E, Velkov T and Lukacs GL:
Allosteric folding correction of F508del and rare CFTR mutants by
Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor (Trikafta) combination. JCI
Insight. 5:e1399832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Rowe SM, McColley SA, Rietschel E, Li X,
Bell SC, Konstan MW, Marigowda G, Waltz D and Boyle MP;
VX09-809-102 Study Group: Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor treatment of
patients with cystic fibrosis heterozygous for F508del-CFTR. Ann Am
Thorac Soc. 14:213–219. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
72
|
Wainwright CE, Elborn JS, Ramsey BW,
Marigowda G, Huang X, Cipolli M, Colombo C, Davies JC, De Boeck K,
Flume PA, et al: Lumacaftor-Ivacaftor in patients with cystic
fibrosis homozygous for Phe508delCFTR. N Engl J Med. 373:220–231.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Clancy JP, Rowe SM, Accurso FJ, Aitken ML,
Amin RS, Ashlock MA, Ballmann M, Boyle MP, Bronsveld I, Campbell
PW, et al: Results of a phase IIa study of VX-809, an
investigational CFTR corrector compound, in subjects with cystic
fibrosis homozygous for theF508del-CFTRmutation. Thorax. 67:12–18.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Flume PA, Harris RS, Paz-Diaz H, Ahluwalia
N, Higgins M, Campbell D, Berhane I, Shih JL and Sawicki G:
Long-term tezacaftor/ivacaftor safety and efficacy in people with
cystic fibrosis and an F508del-CFTR mutation: 96-week, open-label
extension of the EXTEND trial. J Cyst Fibros. 22:464–470. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Bruscia EM: The effects of
Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor beyond the epithelium: Spurring
macrophages to fight infections. Eur Respir J. 61:23002162023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Sawicki GS, Van Brunt K, Booth J, Bailey
E, Millar SJ, Konstan MW and Flume PA: Disease burden in people
with cystic fibrosis heterozygous for F508del and a minimal
function mutation. J Cyst Fibros. 21:96–103. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
77
|
Galietta LJV: TMEM16A (ANO1) as a
therapeutic target in cystic fibrosis. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
64:1022062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Simões FB, Quaresma MC, Clarke LA, Silva
IA, Pankonien I, Railean V, Kmit A and Amaral MD: TMEM16A chloride
channel does not drive mucus production. Life Sci Alliance.
2:e2019004622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ruffin M, Voland M, Marie S, Bonora M,
Blanchard E, Blouquit-Laye S, Naline E, Puyo P, Le Rouzic P,
Guillot L, et al: Anoctamin 1 dysregulation alters bronchial
epithelial repair in cystic fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1832:2340–2351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kirk KL and Wang W: A unified view of
cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gating:
Combining the allosterism of a ligand-gated channel with the
enzymatic activity of an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter. J
Biol Chem. 286:12813–12819. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Deng Z, Chen X, Lin Z, Alahdal M, Wang D,
Liu J and Li W: The homeostasis of cartilage matrix remodeling and
the regulation of volume-sensitive ion channel. Aging Dis.
13:787–800. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Talbi K, Ousingsawat J, Centeio R,
Schreiber R and Kunzelmann K: Calmodulin-dependent regulation of
overexpressed but not endogenous TMEM16A expressed in airway
epithelial cells. Membranes (Basel). 11:7232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Cabrita I, Benedetto R, Schreiber R and
Kunzelmann K: Niclosamide repurposed for the treatment of
inflammatory airway disease. JCI Insight. 4:e1284142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Danahay H, Fox R, Lilley S, Charlton H,
Adley K, Christie L, Ansari E, Ehre C, Flen A, Tuvim MJ, et al:
Potentiating TMEM16A does not stimulate airway mucus secretion or
bronchial and pulmonary arterial smooth muscle contraction. FASEB
Bioadv. 2:464–477. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Danahay HL, Lilley S, Fox R, Charlton H,
Sabater J, Button B, McCarthy C, Collingwood SP and Gosling M:
TMEM16A potentiation: A novel therapeutic approach for the
treatment of cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
201:946–954. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ousingsawat J, Centeio R, Cabrita I, Talbi
K, Zimmer O, Graf M, Göpferich A, Schreiber R and Kunzelmann K:
Airway delivery of hydrogel-encapsulated niclosamide for the
treatment of inflammatory airway disease. Int J Mol Sci.
23:10852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Centeio R, Ousingsawat J, Cabrita I,
Schreiber R, Talbi K, Benedetto R, Doušová T, Verbeken EK, De Boeck
K, Cohen I and Kunzelmann K: Mucus release and airway constriction
by TMEM16A may worsen pathology in inflammatory lung disease. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:78522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Sonneville F, Ruffin M, Coraux C,
Rousselet N, Le Rouzic P, Blouquit-Laye S, Corvol H and Tabary O:
MicroRNA-9 downregulates the ANO1 chloride channel and contributes
to cystic fibrosis lung pathology. Nat Commun. 8:7102017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Kamaleddin MA: Molecular, biophysical, and
pharmacological properties of calcium-activated chloride channels.
J Cell Physiol. 233:787–798. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sah SP and McCluggage WG: DOG1
immunoreactivity in uterine leiomyosarcomas. J Clin Pathol.
66:40–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Filippou A, Pehkonen H, Karhemo PR,
Väänänen J, Nieminen AI, Klefström J, Grénman R, Mäkitie AA,
Joensuu H and Monni O: ANO1 expression orchestrates
p27Kip1/MCL1-Mediated signaling in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 13:11702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ishaque N, Abba ML, Hauser C, Patil N,
Paramasivam N, Huebschmann D, Leupold JH, Balasubramanian GP,
Kleinheinz K, Toprak UH, et al: Whole genome sequencing puts
forward hypotheses on metastasis evolution and therapy in
colorectal cancer. Nat Commun. 9:47822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Sauter DRP, Novak I, Pedersen SF, Larsen
EH and Hoffmann EK: ANO1 (TMEM16A) in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Pflugers Arch. 467:1495–1508. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
94
|
Song Y, Gao J, Guan L, Chen X, Gao J and
Wang K: Inhibition of ANO1/TMEM16A induces apoptosis in human
prostate carcinoma cells by activating TNF-α signaling. Cell Death
Dis. 9:7032018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Britschgi A, Bill A, Brinkhaus H, Rothwell
C, Clay I, Duss S, Rebhan M, Raman P, Guy CT, Wetzel K, et al:
Calcium-activated chloride channel ANO1 promotes breast cancer
progression by activating EGFR and CAMK signaling. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:E1026–E1034. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Sui Y, Sun M, Wu F, Yang L, Di W, Zhang G,
Zhong L, Ma Z, Zheng J, Fang X and Ma T: Inhibition of TMEM16A
expression suppresses growth and invasion in human colorectal
cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e1154432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Cao Q, Liu F, Ji K, Liu N, He Y, Zhang W
and Wang L: MicroRNA-381 inhibits the metastasis of gastric cancer
by targeting TMEM16A expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:292017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lee YS, Lee JK, Bae Y, Lee BS, Kim E, Cho
CH, Ryoo K, Yoo J, Kim CH, Yi GS, et al: Suppression of
14-3-3γ-mediated surface expression of ANO1 inhibits cancer
progression of glioblastoma cells. Sci Rep. 6:264132016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Shang L, Hao JJ, Zhao XK, He JZ, Shi ZZ,
Liu HJ, Wu LF, Jiang YY, Shi F, Yang H, et al: ANO1 protein as a
potential biomarker for esophageal cancer prognosis and
precancerous lesion development prediction. Oncotarget.
7:24374–24382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Akpalo H, Lange C and Zustin J: Discovered
on gastrointestinal stromal tumour 1 (DOG1): A useful
immunohistochemical marker for diagnosing chondroblastoma.
Histopathology. 60:1099–1106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Chang Z, Cai C, Han D, Gao Y, Li Q, Feng
L, Zhang W, Zheng J, Jin J, Zhang H and Wei Q: Anoctamin5 regulates
cell migration and invasion in thyroid cancer. Int J Oncol.
51:1311–1319. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Li Y, Wang X, Vural S, Mishra NK, Cowan KH
and Guda C: Exome analysis reveals differentially mutated gene
signatures of stage, grade and subtype in breast cancers. PLoS One.
10:e01193832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Chen W, Gu M, Gao C, Chen B, Yang J, Xie
X, Wang X, Sun J and Wang J: The prognostic value and mechanisms of
TMEM16A in human cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 8:5421562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Liu F, Yang X, Geng M and Huang M:
Targeting ERK, an Achilles' heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer
therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 8:552–562. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Wang H, Yao F, Luo S, Ma K, Liu M, Bai L,
Chen S, Song C, Wang T, Du Q, et al: A mutual activation loop
between the Ca2+-activated chloride channel TMEM16A and
EGFR/STAT3 signaling promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis. Cancer
Lett. 455:48–59. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Bai W, Liu M and Xiao Q: The diverse roles
of TMEM16A Ca2+-activated Cl-channels in inflammation. J
Adv Res. 33:53–68. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Lin Z, Deng Z, Liu J, Lin Z, Chen S, Deng
Z and Li W: Chloride channel and inflammation-mediated pathogenesis
of osteoarthritis. J Inflamm Res. 15:953–964. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Liu J, Liu Y, Ren Y, Kang L and Zhang L:
Transmembrane protein with unknown function 16A overexpression
promotes glioma formation through the nuclear factor-κB signaling
pathway. Mol Med Report. 9:1068–1074. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Zhou L, Deng ZZ, Li HY, Jiang N, Wei ZS,
Hong MF, Chen XD, Wang JH, Zhang MX, Shi YH, et al: TRIM31 promotes
glioma proliferation and invasion through activating NF-κB pathway.
Onco Targets Ther. 12:2289–2297. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
110
|
Duvvuri U, Shiwarski DJ, Xiao D, Bertrand
C, Huang X, Edinger RS, Rock JR, Harfe BD, Henson BJ, Kunzelmann K,
et al: TMEM 16 A induces MAPK and contributes directly to
tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Res. 72:3270–3281.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Deng L, Yang J, Chen H, Ma B, Pan K, Su C,
Xu F and Zhang J: Knockdown of TMEM16A suppressed MAPK and
inhibited cell proliferation and migration in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 9:325–333. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ruiz C, Martins JR, Rudin F, Schneider S,
Dietsche T, Fischer CA, Tornillo L, Terracciano LM, Schreiber R,
Bubendorf L and Kunzelmann K: Enhanced expression of ANO1 in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma causes cell migration and
correlates with poor prognosis. PLoS One. 7:e432652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Dixit R, Kemp C, Kulich S, Seethala R,
Chiosea S, Ling S, Ha PK and Duvvuri U: TMEM16A/ANO1 is
differentially expressed in HPV-negative versus HPV-positive head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma through promoter methylation. Sci
Rep. 5:166572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Mokutani Y, Uemura M, Munakata K, Okuzaki
D, Haraguchi N, Takahashi H, Nishimura J, Hata T, Murata K,
Takemasa I, et al: Down-regulation of microRNA-132 is associated
with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
23:599–608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Lin S and Gregory RI: MicroRNA biogenesis
pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:321–333. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wang H, Zou L, Ma K, Yu J, Wu H, Wei M and
Xiao Q: Cell-specific mechanisms of TMEM16A
Ca2+-activated chloride channel in cancer. Mol Cancer.
16:1522017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Wanitchakool P, Wolf L, Koehl GE,
Sirianant L, Schreiber R, Kulkarni S, Duvvuri U and Kunzelmann K:
Role of anoctamins in cancer and apoptosis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond
B Biol Sci. 369:201300962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Ahn SY, Yang JH, Kim NH, Lee K, Cha YH,
Yun JS, Kang HE, Lee Y, Choi J, Kim HS and Yook J: Anti-helminthic
niclosamide inhibits Ras-driven oncogenic transformation via
activation of GSK-3. Oncotarget. 8:31856–31863. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Miner K, Labitzke K, Liu B, Wang P,
Henckels K, Gaida K, Elliott R, Chen JJ, Liu L, Leith A, et al:
Drug repurposing: The anthelmintics niclosamide and nitazoxanide
are potent TMEM16A antagonists that fully bronchodilate airways.
Front Pharmacol. 10:512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Jin Y, Lu Z, Ding K, Li J, Du X, Chen C,
Sun X, Wu Y, Zhou J and Pan J: Antineoplastic mechanisms of
niclosamide in acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells: Inactivation
of the NF-κB pathway and generation of reactive oxygen species.
Cancer Res. 70:2516–2527. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Han Z, Li Q, Wang Y, Wang L, Li X, Ge N,
Wang Y and Guo C: Niclosamide induces cell cycle arrest in G1 phase
in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through Let-7d/CDC34 Axis.
Front Pharmacol. 9:15442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Li Y, Li PK, Roberts MJ, Arend RC, Samant
RS and Buchsbaum DJ: Multi-targeted therapy of cancer by
niclosamide: A new application for an old drug. Cancer Lett.
349:8–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Gangrade A,
Katre AA, Kurpad C, Li Y, Samant RS, Li PK, Landen CN, Yang ES, et
al: Correction: Niclosamide and its analogs are potent inhibitors
of Wnt/β-catenin, mTOR and STAT3 signaling in ovarian cancer.
Oncotarget. 9:19459. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Lafkas D, Shelton A, Chiu C, de Leon
Boenig G, Chen Y, Stawicki SS, Siltanen C, Reichelt M, Zhou M, Wu
X, et al: Therapeutic antibodies reveal Notch control of
transdifferentiation in the adult lung. Nature. 528:127–131. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Danahay H, Pessotti AD, Coote J,
Montgomery BE, Xia D, Wilson A, Yang H, Wang Z, Bevan L, Thomas C,
et al: Notch2 is required for inflammatory cytokine-driven goblet
cell metaplasia in the lung. Cell Rep. 10:239–252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Seo Y, Kim J, Chang J, Kim SS, Namkung W
and Kim I: Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel Ani9
derivatives as potent and selective ANO1 inhibitors. Eur J
Medicinal Chem. 160:245–255. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Burock S, Daum S, Keilholz U, Neumann K,
Walther W and Stein U: Phase II trial to investigate the safety and
efficacy of orally applied niclosamide in patients with
metachronous or sychronous metastases of a colorectal cancer
progressing after therapy: The NIKOLO trial. BMC Cancer.
18:2972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Schweizer MT, Haugk K, McKiernan JS,
Gulati R, Cheng HH, Maes JL, Dumpit RF, Nelson PS, Montgomery B,
McCune JS, et al: Correction: A phase I study of niclosamide in
combination with enzalutamide in men with castration-resistant
prostate cancer. PLoS One. 13:e02027092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Yan Y, Ding X, Han C, Gao J, Liu Z, Liu Y
and Wang K: Involvement of TMEM16A/ANO1 upregulation in the
oncogenesis of colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1868:1663702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Khalil A, Elesawy BH, Ali TM and Ahmed OM:
Bee venom: From venom to drug. Molecules. 26:49412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Badawi JK: Bee venom components as
therapeutic tools against prostate cancer. Toxins (Basel).
13:3372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Schreiber R, Ousingsawat J, Wanitchakool
P, Sirianant L, Benedetto R, Reiss K and Kunzelmann K: Regulation
of TMEM16A/ANO1 and TMEM16F/ANO6 ion currents and phospholipid
scrambling by Ca2+ and plasma membrane lipid. J Physiol.
596:217–229. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Simões F, Ousingsawat J, Wanitchakool P,
Fonseca A, Cabrita I, Benedetto R, Schreiber R and Kunzelmann K:
CFTR supports cell death through ROS-dependent activation of
TMEM16F (anoctamin 6). Pflugers Arch. 470:305–314. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Xue Q, Yan D, Chen X, Li X, Kang R,
Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, Chen X, Tang D and Liu J: Copper-dependent
autophagic degradation of GPX4 drives ferroptosis. Autophagy.
19:1982–1996. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
El-Didamony SE, Amer RI and El-Osaily GH:
Formulation, characterization and cellular toxicity assessment of a
novel bee-venom microsphere in prostate cancer treatment. Sci Rep.
12:132132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Schreiber R, Buchholz B, Kraus A, Schley
G, Scholz J, Ousingsawat J and Kunzelmann K: Lipid peroxidation
drives renal cyst growth in vitro through activation of TMEM16A. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 30:228–242. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Schmaier AA, Anderson PF, Chen SM,
El-Darzi E, Aivasovsky I, Kaushik MP, Sack KD, Hartzell HC, Parikh
SM, Flaumenhaft R and Schulman S: TMEM16E regulates endothelial
cell procoagulant activity and thrombosis. J Clin Invest.
133:e1638082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Fujii Y, Taniguchi M, Nagaya S, Ueda Y,
Hashizume C, Watanabe K, Takeya H, Kosaka T and Okazaki T: A novel
mechanism of thrombocytopenia by PS exposure through TMEM16F in
sphingomyelin synthase 1 deficiency. Blood Adv. 5:4265–4277. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Filep JG: Two to tango: Endothelial cell
TMEM16 scramblases drive coagulation and thrombosis. J Clin Invest.
133:e1706432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Wu N, Cernysiov V, Davidson D, Song H,
Tang J, Luo S, Lu Y, Qian J, Gyurova IE, Waggoner SN, et al:
Critical role of lipid scramblase TMEM16F in phosphatidylserine
exposure and repair of plasma membrane after pore formation. Cell
Rep. 30:1129–1140.e5. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Taylor KA and Mahaut-Smith MP: A major
interspecies difference in the ionic selectivity of megakaryocyte
Ca2+-activated channels sensitive to the TMEM16F
inhibitor CaCCinh-A01. Platelets. 30:962–966. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
143
|
Yang H, Kim A, David T, Palmer D, Jin T,
Tien J, Huang F, Cheng T, Coughlin SR, Jan YN and Jan LY: TMEM16F
Forms a Ca2+-activated cation channel required for lipid
scrambling in platelets during blood coagulation. Cell.
151:111–122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Yu H, Wang Z, Li Z, An Y, Yan M, Ji S, Xu
M, Wang L, Dong W, Shi J and Gao C: Hyperuricemia enhances
procoagulant activity of vascular endothelial cells through TMEM16F
regulated phosphatidylserine exposure and microparticle release.
FASEB J. 35:e218082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Goyal P, Choi JJ, Pinheiro LC, Schenck EJ,
Chen R, Jabri A, Satlin MJ, Campion TR Jr, Nahid M, Ringel JB, et
al: Clinical characteristics of Covid-19 in new york city. N Engl J
Med. 382:2372–2374. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Levi M, Thachil J, Iba T and Levy JH:
Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19.
Lancet Haematol. 7:e438–e440. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Edler C, Schröder AS, Aepfelbacher M,
Fitzek A, Heinemann A, Heinrich F, Klein A, Langenwalder F,
Lütgehetmann M, Meißner K, et al: Correction to: Dying with
SARS-CoV-2 infection-an autopsy study of the first consecutive 80
cases in Hamburg, Germany. Int J Legal Med. 134:19772020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S,
Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH,
Nitsche A, et al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell.
181:271–280.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Hoffmann M, Hofmann-Winkler H and Pöhlmann
S: Priming time: How Cellular Proteases Arm Coronavirus Spike
Proteins. Springer International Publishing; Cham: pp. 71–98.
2018
|
|
150
|
Braga L, Ali H, Secco I, Chiavacci E,
Neves G, Goldhill D, Penn R, Jimenez-Guardeño JM, Ortega-Prieto AM,
Bussani R, et al: Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block
SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia. Nature. 594:88–93. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Cappelletto A, Allan HE, Crescente M,
Schneider E, Bussani R, Ali H, Secco I, Vodret S, Simeone R,
Mascaretti L, et al: SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein activates
TMEM16F-mediated platelet procoagulant activity. Front Cardiovasc
Med. 9:10132622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Abdulamir AS, Gorial FI, Saadi SJ, Maulood
MF, Hashim HA, Alnuaimi AS and Abdulrrazaq MK: A randomised
controlled trial of effectiveness and safety of Niclosamide as add
on therapy to the standard of care measures in COVID-19 management.
Ann Med Surg (Lond). 69:1027792021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Chen W, Mook RA Jr, Premont RT and Wang J:
Niclosamide: Beyond an antihelminthic drug. Cell Signal. 41:89–96.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Kalienkova V, Clerico Mosina V and Paulino
C: The Groovy TMEM16 family: Molecular mechanisms of lipid
scrambling and ion conduction. J Mol Biol. 433:1669412021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Lam AKM, Rutz S and Dutzler R: Inhibition
mechanism of the chloride channel TMEM16A by the pore blocker 1PBC.
Nat Commun. 13:27982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Bill A, Gutierrez A, Kulkarni S, Kemp C,
Bonenfant D, Voshol H, Duvvuri U and Gaither LA: ANO1/TMEM16A
interacts with EGFR and correlates with sensitivity to
EGFR-targeting therapy in head and neck cancer. Oncotarget.
6:9173–9188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Zhang X, Zhang G, Zhai W, Zhao Z, Wang S
and Yi J: Inhibition of TMEM16A Ca2+-activated
Cl-channels by avermectins is essential for their anticancer
effects. Pharmacol Res. 156:1047632020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Fang H, Deng Z, Liu J, Chen S, Deng Z and
Li W: The mechanism of bone remodeling after bone aging. Clin
Interv Aging. 17:405–415. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Genovese M, Buccirossi M, Guidone D, De
Cegli R, Sarnataro S, di Bernardo D and Galietta LJV: Analysis of
inhibitors of the anoctamin-1 chloride channel (transmembrane
member 16A, TMEM16A) reveals indirect mechanisms involving
alterations in calcium signalling. Br J Pharmacol. 180:775–785.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Shaibani A, Khan S and Shinawi M:
Autosomal dominant ANO5-Related disorder associated with myopathy
and gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia. Neurol Genet. 7:e6122021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Liu X, Wang X, Ma X, Li H, Miao C, Tian Z
and Hu Y: Genetic disruption of Ano5 leads to impaired
osteoclastogenesis for gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia. Oral Dis.
30:1403–1415. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Chandra G, Defour A, Mamchoui K, Pandey K,
Mishra S, Mouly V, Sreetama S, Mahad Ahmad M, Mahjneh I, Morizono
H, et al: Dysregulated calcium homeostasis prevents plasma membrane
repair in Anoctamin 5/TMEM16E-deficient patient muscle cells. Cell
Death Discov. 5:1182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Thiruvengadam G, Sreetama SC, Charton K,
Hogarth M, Novak JS, Suel-Petat L, Chandra G, Allard B, Richard I
and Jaiswal JK: Anoctamin 5 Knockout mouse model recapitulates
LGMD2L muscle pathology and offers insight into in vivo functional
deficits. J Neuromuscul Dis. 8(Suppl): S243–S255. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Li H, Wang X, Chen E, Liu X, Ma X, Miao C,
Tian Z, Dong R and Hu Y: Introduction of a Cys360Tyr Mutation in
ANO5 creates a mouse model for gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia. J Bone
Miner Res. 37:515–530. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Jiang LT, Li LX, Liu Y, Zhang XL, Pan YG,
Wang L, Wan XH and Jin LJ: The expanding clinical and genetic
spectrum of ANO3 dystonia. Neurosci Lett. 746:1355902021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|