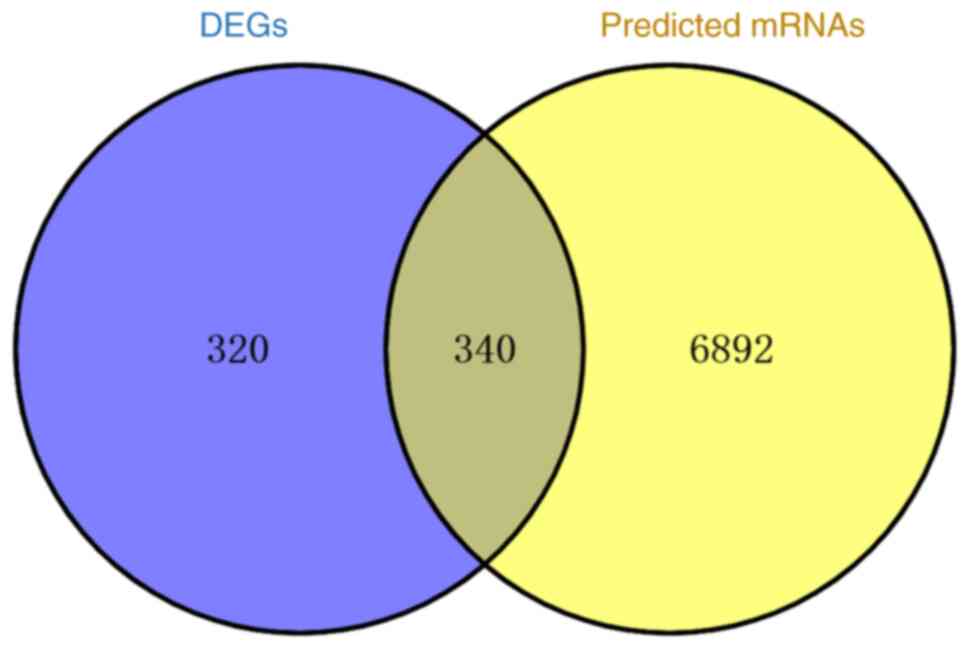
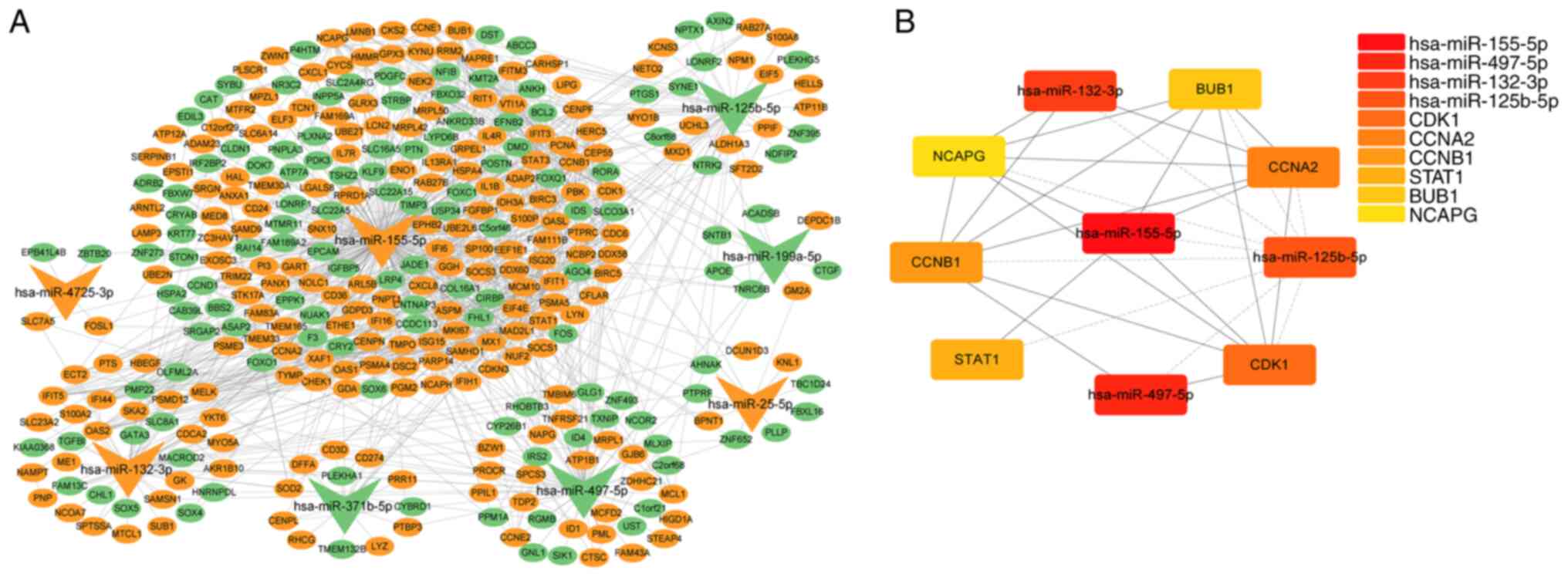
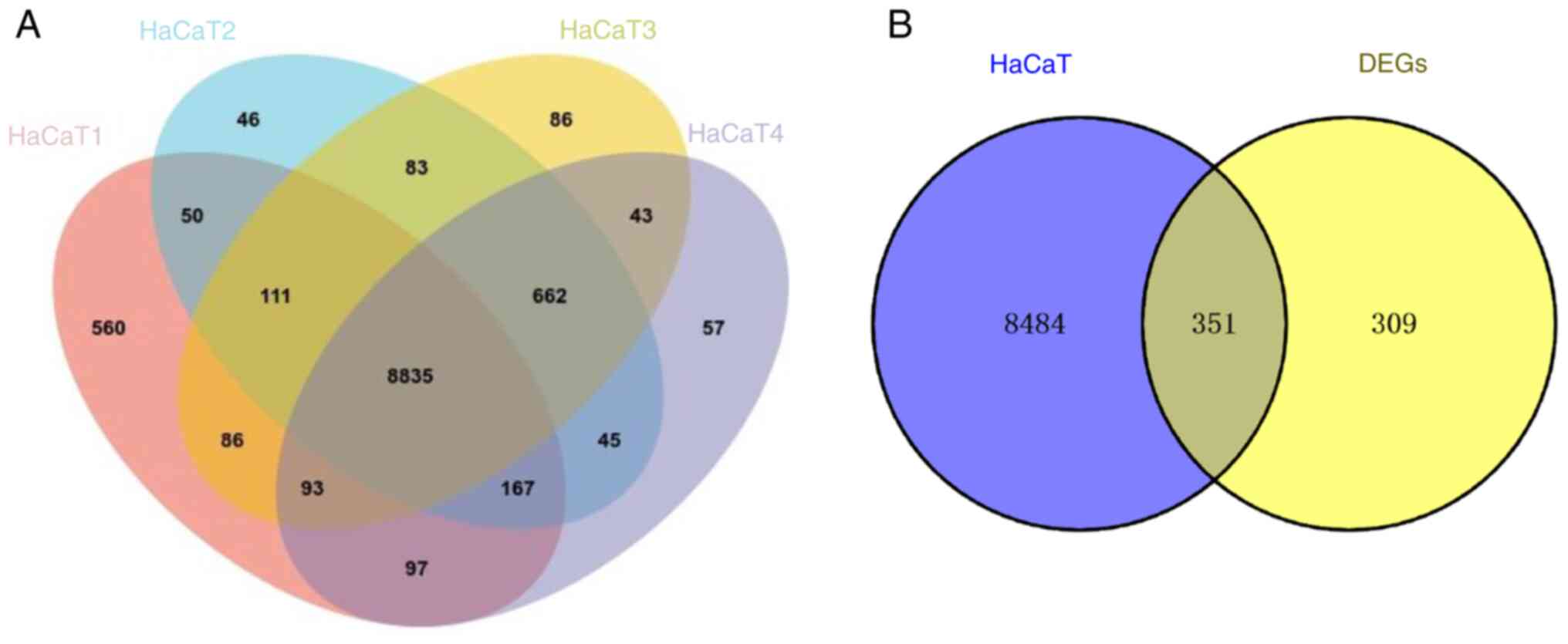
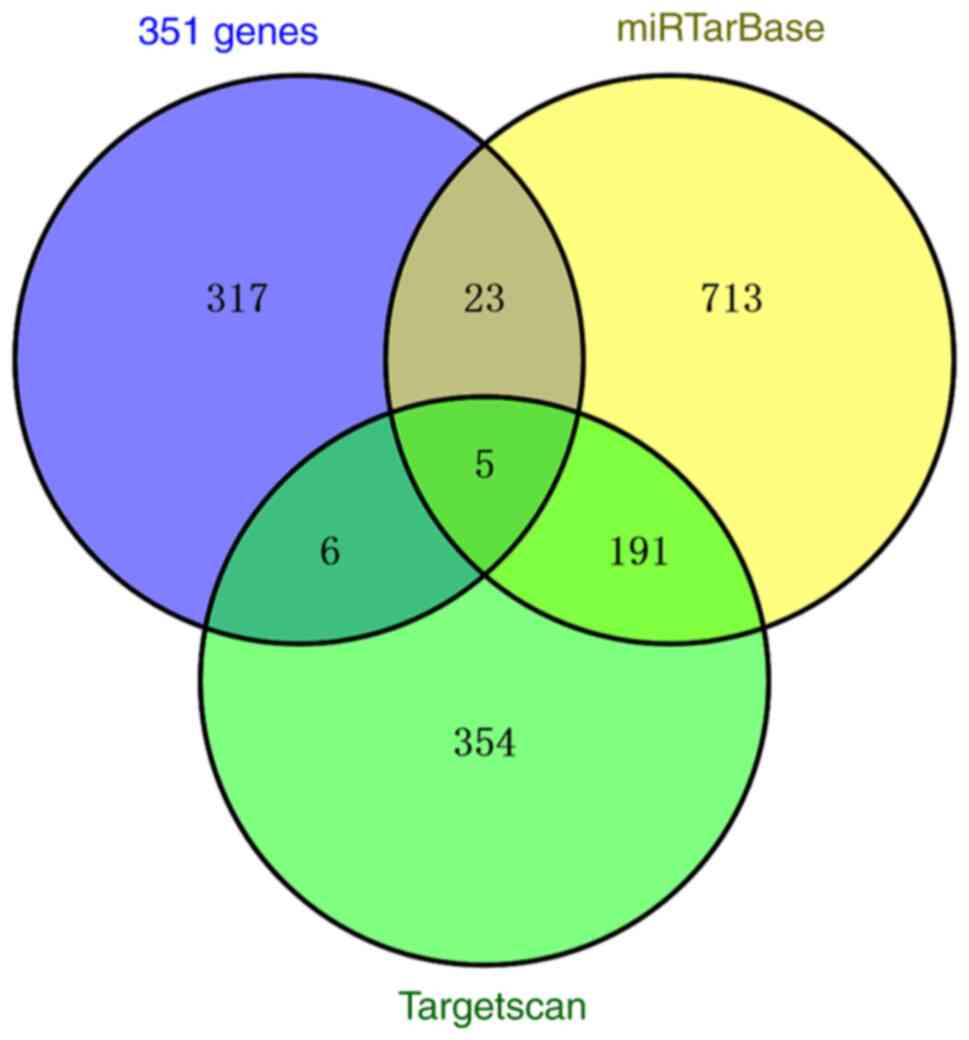
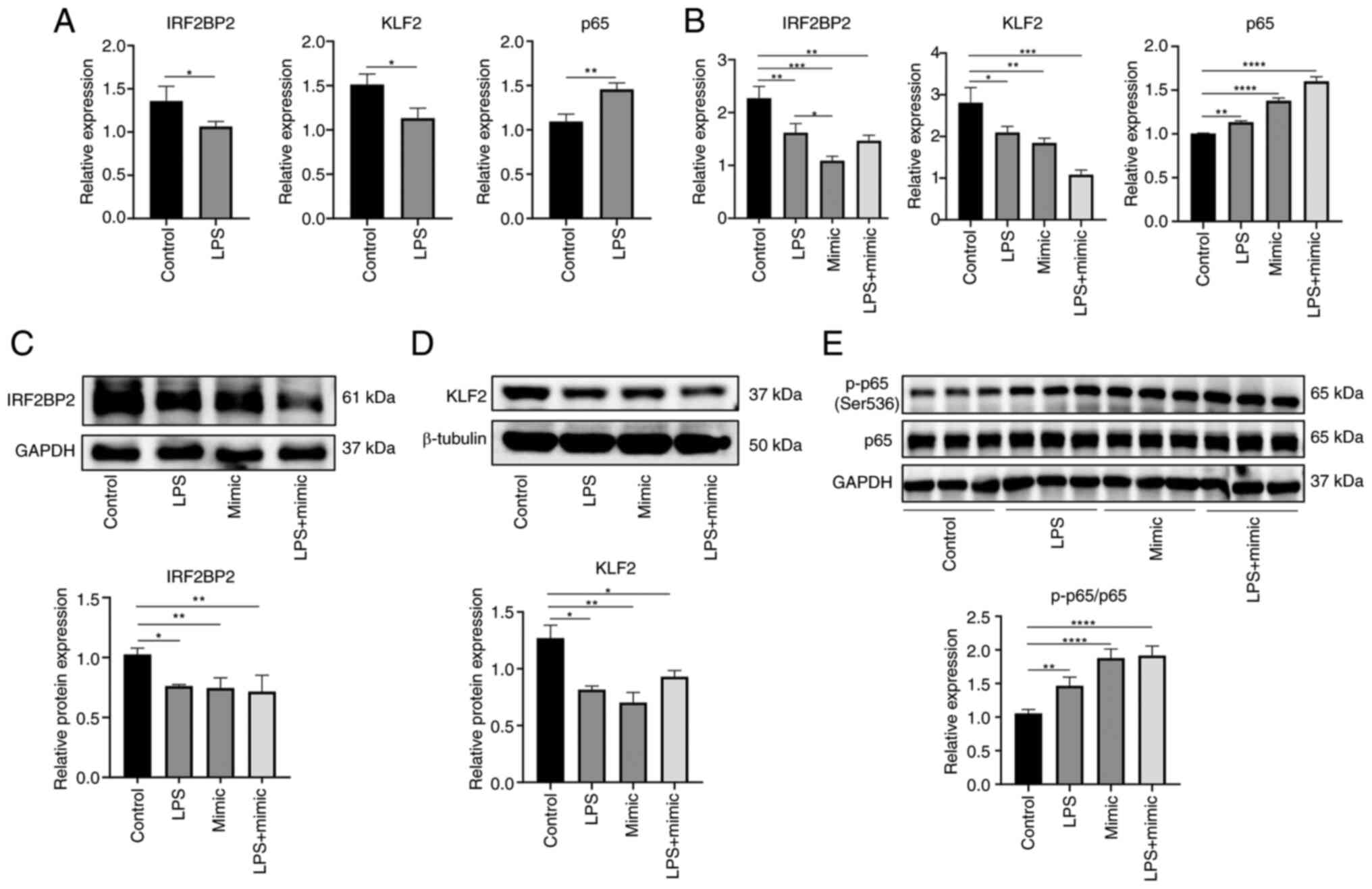
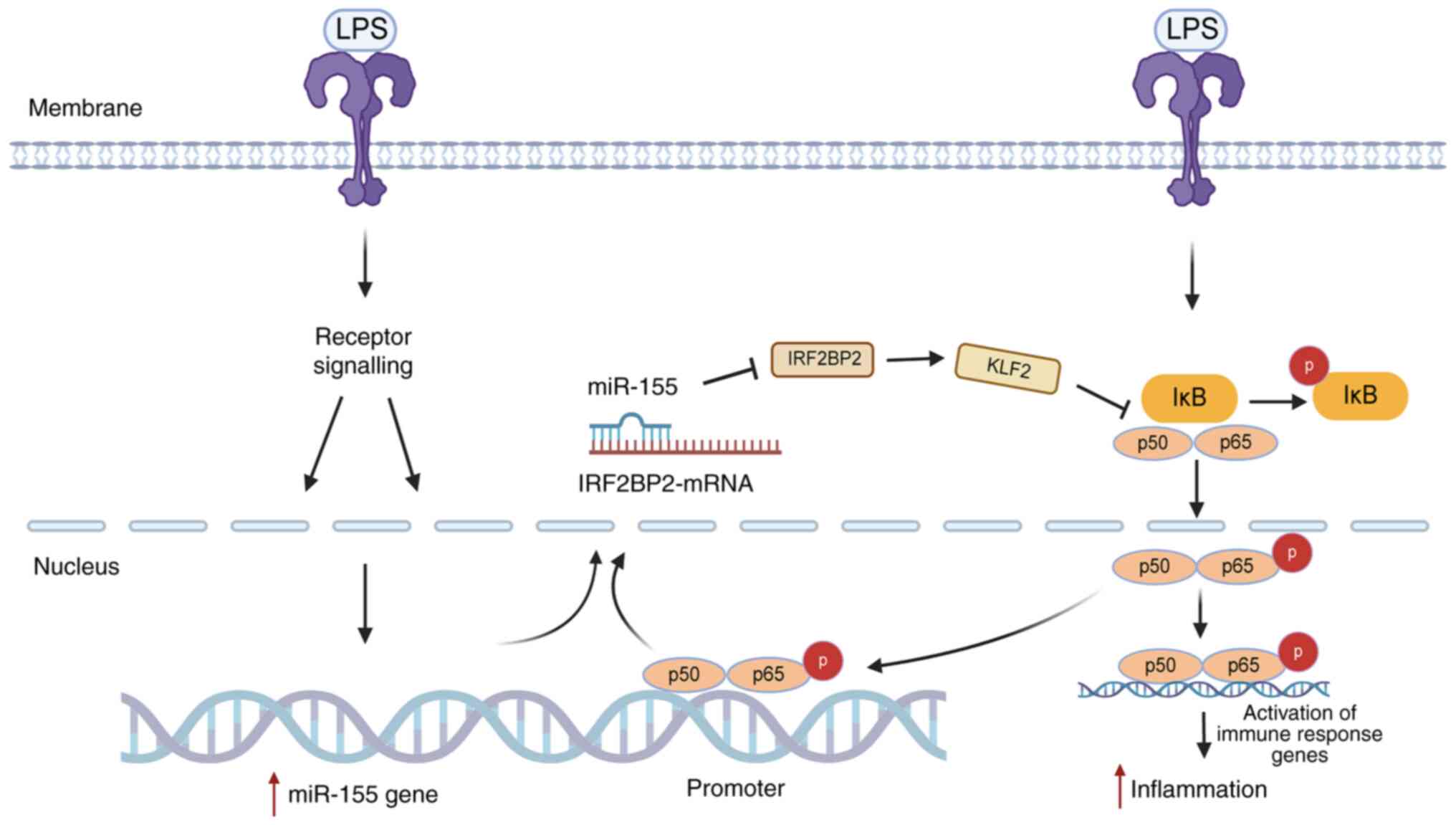
|
1
|
Boehncke WH and Schön MP: Psoriasis.
Lancet. 386:983–994. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hwang ST, Nijsten T and Elder JT: Recent
highlights in psoriasis research. J Invest Dermatol. 137:550–556.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chiricozzi A, Romanelli P, Volpe E,
Borsellino G and Romanelli M: Scanning the immunopathogenesis of
psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:1792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ciccia F, Triolo G and Rizzo A: Psoriatic
arthritis. N Engl J Med. 376:2094–2095. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE
and Barker JNWN: Psoriasis. Lancet. 397:1301–1315. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dopytalska K, Czaplicka A, Szymańska E and
Walecka I: The essential role of microRNAs in inflammatory and
autoimmune skin diseases-a review. Int J Mol Sci. 24:91302023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dopytalska K, Ciechanowicz P, Wiszniewski
K, Szymańska E and Walecka I: The role of epigenetic factors in
psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 22:92942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang SC, Alalaiwe A, Lin ZC, Lin YC,
Aljuffali IA and Fang JY: Anti-inflammatory microRNAs for treating
inflammatory skin diseases. Biomolecules. 12:10722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beer L, Kalinina P, Köcher M, Laggner M,
Jeitler M, Abbas Zadeh S, Copic D, Tschachler E and Mildner M:
miR-155 contributes to normal keratinocyte differentiation and is
upregulated in the epidermis of psoriatic skin lesions. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:92882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
García-Rodríguez S, Arias-Santiago S,
Blasco-Morente G, Orgaz-Molina J, Rosal-Vela A, Navarro P,
Magro-Checa C, Martínez-López A, Ruiz JC, Raya E, et al: Increased
expression of microRNA-155 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells
from psoriasis patients is related to disease activity. J Eur Acad
Dermatol Venereol. 31:312–322. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xu L and Leng H, Shi X, Ji J, Fu J and
Leng H: MiR-155 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis
by PTEN signaling pathway in the psoriasis. Biomed Pharmacother.
90:524–530. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pastor TP, Peixoto BC and Viola JPB: The
transcriptional co-factor IRF2BP2: A new player in tumor
development and microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6553072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Oksvold P,
Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J, Habuka M, Tahmasebpoor S,
Danielsson A, Edlund K, et al: Analysis of the human
tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of
transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics.
13:397–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Ma YL, Xia JL and Gao X: Suppressing
Irf2bp2 expressions accelerates metabolic syndrome-associated brain
injury and hepatic dyslipidemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
503:1651–1658. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ramalho-Oliveira R, Oliveira-Vieira B and
Viola JPB: IRF2BP2: A new player in the regulation of cell
homeostasis. J Leukoc Biol. 106:717–723. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen HH, Keyhanian K, Zhou X, Vilmundarson
RO, Almontashiri NA, Cruz SA, Pandey NR, Lerma Yap N, Ho T, Stewart
CA, et al: IRF2BP2 reduces macrophage inflammation and
susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 117:671–683. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cruz SA, Hari A, Qin Z, Couture P, Huang
H, Lagace DC, Stewart AFR and Chen HH: Loss of IRF2BP2 in microglia
increases inflammation and functional deficits after focal ischemic
brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 11:2012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feng X, Lu T, Li J, Yang R, Hu L, Ye Y,
Mao F, He L, Xu J, Wang Z, et al: The tumor suppressor interferon
regulatory factor 2 binding protein 2 regulates Hippo pathway in
liver cancer by a feedback loop in mice. Hepatology. 71:1988–2004.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hari A, Cruz SA, Qin Z, Couture P,
Vilmundarson RO, Huang H, Stewart AFR and Chen HH:
IRF2BP2-deficient microglia block the anxiolytic effect of enhanced
postnatal care. Sci Rep. 7:98362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li T, Luo Q, He L, Li D, Li Q, Wang C, Xie
J and Yi C: Interferon regulatory factor-2 binding protein 2
ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy via AMPK-mediated
anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis. Inflammation. 43:1464–1475.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Piruzian E, Bruskin S, Ishkin A, Abdeev R,
Moshkovskii S, Melnik S, Nikolsky Y and Nikolskaya T: Integrated
network analysis of transcriptomic and proteomic data in psoriasis.
BMC Syst Biol. 4:412010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gauthier J, Vincent AT, Charette SJ and
Derome N: A brief history of bioinformatics. Brief Bioinform.
20:1981–1996. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ni X and Lai Y: Keratinocyte: A trigger or
an executor of psoriasis? J Leukoc Biol. 108:485–491. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xiuli Y and Honglin W: miRNAs flowing up
and down: The concerto of psoriasis. Front Med (Lausanne).
8:6467962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jinnin M: Various applications of
microRNAs in skin diseases. J Dermatol Sci. 74:3–8. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu R, Zeng J, Yuan J, Deng X, Huang Y,
Chen L, Zhang P, Feng H, Liu Z, Wang Z, et al: MicroRNA-210
overexpression promotes psoriasis-like inflammation by inducing Th1
and Th17 cell differentiation. J Clin Invest. 128:2551–2568. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raaby L, Langkilde A, Kjellerup RB, Vinter
H, Khatib SH, Hjuler KF, Johansen C and Iversen L: Changes in mRNA
expression precede changes in microRNA expression in lesional
psoriatic skin during treatment with adalimumab. Br J Dermatol.
173:436–447. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sonkoly E, Wei T, Janson PC, Sääf A,
Lundeberg L, Tengvall-Linder M, Norstedt G, Alenius H, Homey B,
Scheynius A, et al: MicroRNAs: Novel regulators involved in the
pathogenesis of psoriasis? PLoS One. 2:e6102007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Q, Wu DH, Han L, Deng JW, Zhou L, He
R, Lu CJ and Mi QS: Roles of microRNAs in psoriasis: Immunological
functions and potential biomarkers. Exp Dermatol. 26:359–367. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Luo Q, Zeng J, Li W, Lin L, Zhou X, Tian
X, Liu W, Zhang L and Zhang X: Silencing of miR-155 suppresses
inflammatory responses in psoriasis through inflammasome NLRP3
regulation. Int J Mol Med. 42:1086–1095. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Zhao X, Li J, Zhou L, Chang W, Li
J, Hou R, Li J, Yin G, Li X and Zhang K: MiR-155 inhibits TP53INP1
expression leading to enhanced glycolysis of psoriatic mesenchymal
stem cells. J Dermatol Sci. 105:142–151. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang H, Zhang Y, Luomei J, Huang P, Zhou R
and Peng Y: The miR-155/GATA3/IL37 axis modulates the production of
proinflammatory cytokines upon TNF-α stimulation to affect
psoriasis development. Exp Dermatol. 29:647–658. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Koeppel M, van Heeringen SJ, Smeenk L,
Navis AC, Janssen-Megens EM and Lohrum M: The novel p53 target gene
IRF2BP2 participates in cell survival during the p53 stress
response. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:322–335. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liang Y, Zhou Y and Shen P: NF-kappaB and
its regulation on the immune system. Cell Mol Immunol. 1:343–350.
2004.
|
|
39
|
Wu J, Ding J, Yang J, Guo X and Zheng Y:
MicroRNA roles in the nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in
cancer. Front Immunol. 9:5462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Alexandrov P, Zhai Y, Li W and Lukiw W:
Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated, NF-kB-, miRNA-146a- and
miRNA-155-mediated molecular-genetic communication between the
human gastrointestinal tract microbiome and the brain. Folia
Neuropathol. 57:211–219. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McConnell BB and Yang VW: Mammalian
Krüppel-like factors in health and diseases. Physiol Rev.
90:1337–1381. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jha P and Das H: KLF2 in regulation of
NF-κB-mediated immune cell function and inflammation. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:23832017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Das M, Lu J, Joseph M, Aggarwal R, Kanji
S, McMichael BK, Lee BS, Agarwal S, Ray-Chaudhury A, Iwenofu OH, et
al: Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) regulates monocyte differentiation
and functions in mBSA and IL-1β-induced arthritis. Curr Mol Med.
12:113–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mahabeleshwar GH, Qureshi MA, Takami Y,
Sharma N, Lingrel JB and Jain MK: A myeloid hypoxia-inducible
factor 1α-Krüppel-like factor 2 pathway regulates gram-positive
endotoxin-mediated sepsis. J Biol Chem. 287:1448–1457. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Novodvorsky P and Chico TJA: The role of
the transcription factor KLF2 in vascular development and disease.
Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 124:155–188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Das H, Kumar A, Lin Z, Patino WD, Hwang
PM, Feinberg MW, Majumder PK and Jain MK: Kruppel-like factor 2
(KLF2) regulates proinflammatory activation of monocytes. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 103:6653–6658. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mahabeleshwar GH, Kawanami D, Sharma N,
Takami Y, Zhou G, Shi H, Nayak L, Jeyaraj D, Grealy R, White M, et
al: The myeloid transcription factor KLF2 regulates the host
response to polymicrobial infection and endotoxic shock. Immunity.
34:715–728. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nayak L, Goduni L, Takami Y, Sharma N,
Kapil P, Jain MK and Mahabeleshwar GH: Kruppel-like factor 2 is a
transcriptional regulator of chronic and acute inflammation. Am J
Pathol. 182:1696–1704. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
SenBanerjee S, Lin Z, Atkins GB, Greif DM,
Rao RM, Kumar A, Feinberg MW, Chen Z, Simon DI, Luscinskas FW, et
al: KLF2 Is a novel transcriptional regulator of endothelial
proinflammatory activation. J Exp Med. 199:1305–1315. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Masalha M, Sidi Y and Avni D: The
contribution of feedback loops between miRNAs, cytokines and growth
factors to the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Exp Dermatol. 27:603–610.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|