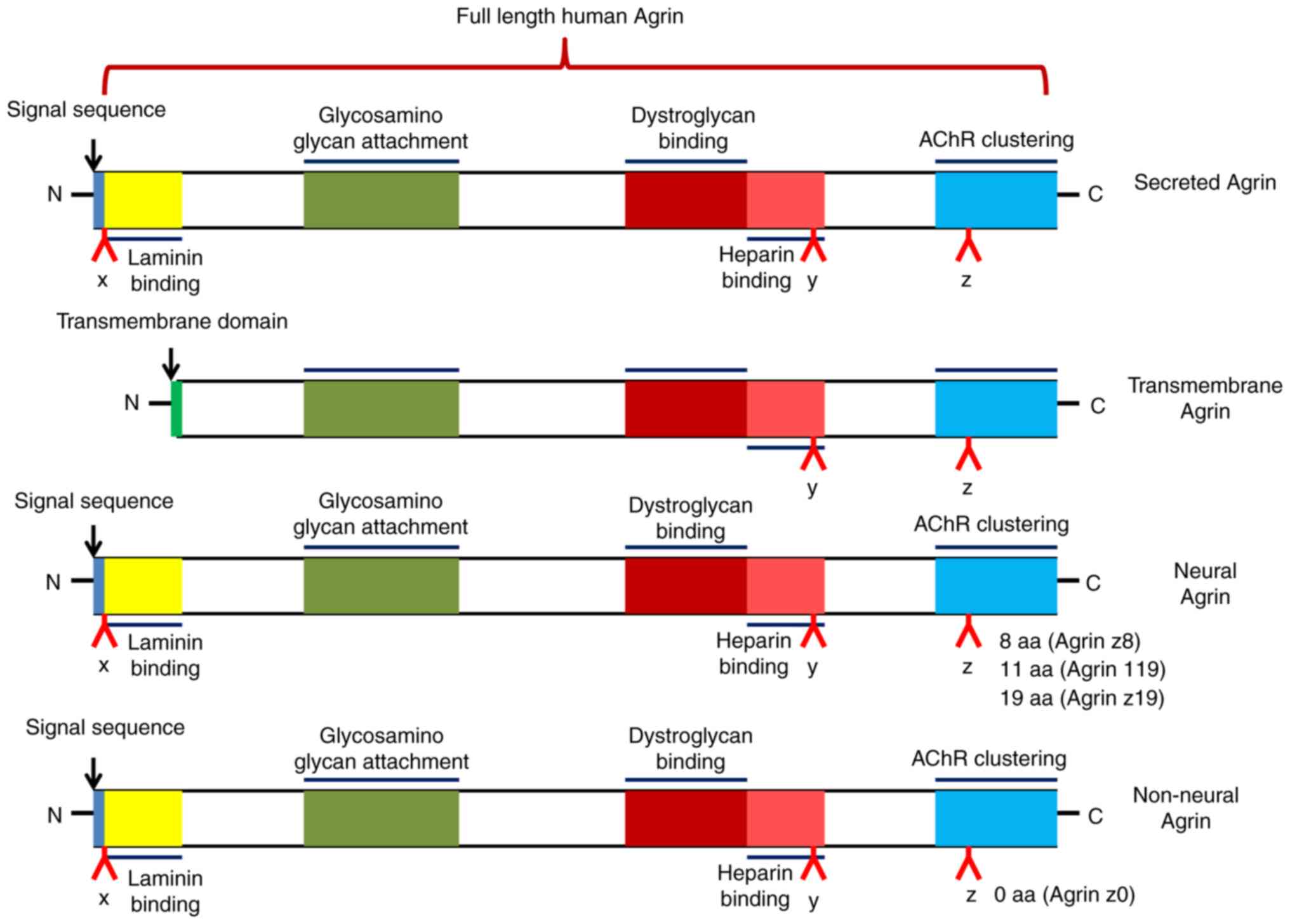
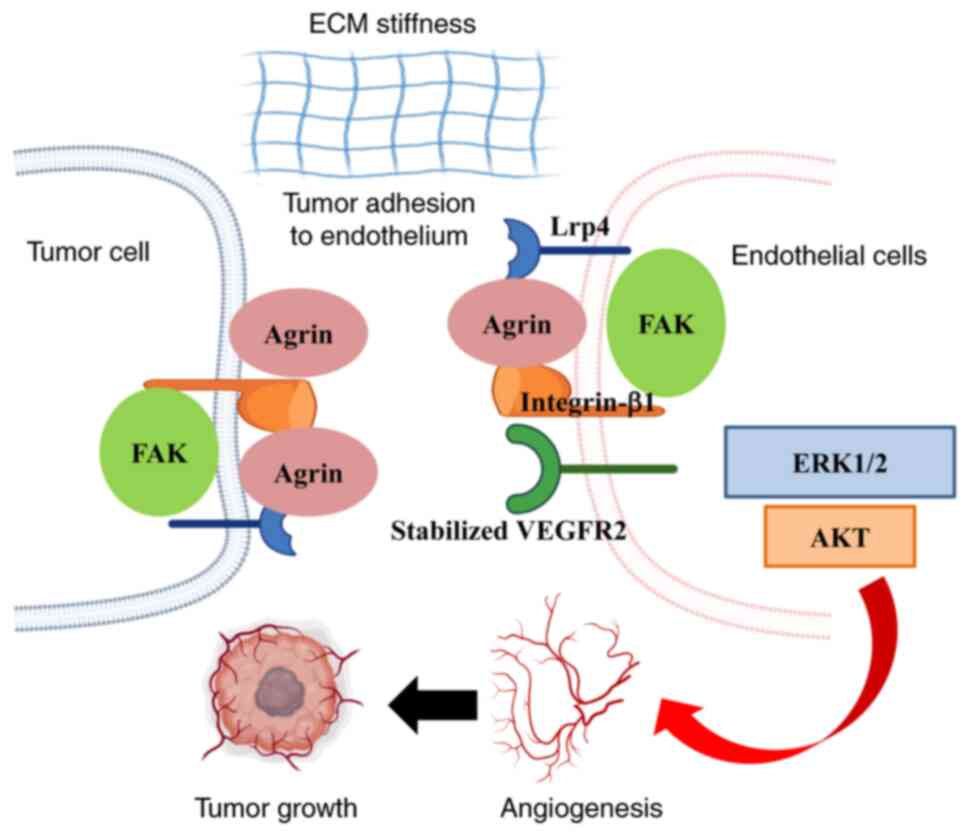
|
1
|
Mao AS and Mooney DJ: Regenerative
medicine: Current therapies and future directions. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 112:14452–14459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsim KW, Ruegg MA, Escher G, Kroger S and
McMahan UJ: cDNA that encodes active agrin. Neuron. 8:677–689.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chakraborty S and Hong W: Linking
extracellular matrix agrin to the hippo pathway in liver cancer and
beyond. Cancers (Basel). 10:452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xie T, Xu G, Liu Y, Quade B, Lin W and Bai
XC: Structural insights into the assembly of the agrin/LRP4/MuSK
signaling complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 120:e23004531202023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adamiok-Ostrowska A, Grzanka M and
Czarnocka B: Agrin is a novel oncogenic protein in thyroid cancer.
Oncol Lett. 26:4832023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Han L, Shi H, Ma S, Luo Y, Sun W, Li S,
Zhang N, Jiang X, Gao Y, Huang Z, et al: Agrin promotes non-small
cell lung cancer progression and stimulates regulatory T cells via
increasing IL-6 secretion through PI3K/AKT pathway. Front Oncol.
11:8044182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang ZQ, Sun XL, Wang YL and Miao YL:
Agrin promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of rectal
cancer cells via the WNT signaling pathway to contribute to rectal
cancer progression. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 41:363–370.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sarig R, Rimmer R, Bassat E, Zhang L,
Umansky KB, Lendengolts D, Perlmoter G, Yaniv K and Tzahor E:
Transient p53-mediated regenerative senescence in the injured
heart. Circulation. 139:2491–2494. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bassat E, Mutlak YE, Genzelinakh A,
Shadrin IY, Baruch Umansky K, Yifa O, Kain D, Rajchman D, Leach J,
Riabov Bassat D, et al: The extracellular matrix protein agrin
promotes heart regeneration in mice. Nature. 547:179–184. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li L, Xiong WC and Mei L: Neuromuscular
junction formation, aging, and disorders. Annu Rev Physiol.
80:159–188. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Oentaryo MJ, Tse AC and Lee CW: Neuronal
MT1-MMP mediates ECM clearance and Lrp4 cleavage for agrin
deposition and signaling in presynaptic development. J Cell Sci.
133:jcs2467102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gautam M, Noakes PG, Moscoso L, Rupp F,
Scheller RH, Merlie JP and Sanes JR: Defective neuromuscular
synaptogenesis in agrin-deficient mutant mice. Cell. 85:525–535.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Burgess RW, Nguyen QT, Son YJ, Lichtman JW
and Sanes JR: Alternatively spliced isoforms of nerve- and
muscle-derived agrin: Their roles at the neuromuscular junction.
Neuron. 23:33–44. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin W, Dominguez B, Yang J, Aryal P,
Brandon EP, Gage FH and Lee KF: Neurotransmitter acetylcholine
negatively regulates neuromuscular synapse formation by a
Cdk5-dependent mechanism. Neuron. 46:569–579. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Misgeld T, Kummer TT, Lichtman JW and
Sanes JR: Agrin promotes synaptic differentiation by counteracting
an inhibitory effect of neurotransmitter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:11088–11093. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim N and Burden SJ: MuSK controls where
motor axons grow and form synapses. Nat Neurosci. 11:19–27. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lin W, Burgess RW, Dominguez B, Pfaff SL,
Sanes JR and Lee KF: Distinct roles of nerve and muscle in
postsynaptic differentiation of the neuromuscular synapse. Nature.
410:1057–1064. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang X, Arber S, William C, Li L, Tanabe
Y, Jessell TM, Birchmeier C and Burden SJ: Patterning of muscle
acetylcholine receptor gene expression in the absence of motor
innervation. Neuron. 30:399–410. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Grabrucker S, Marizzoni M, Silajdzic E,
Lopizzo N, Mombelli E, Nicolas S, Dohm-Hansen S, Scassellati C,
Moretti DV, Rosa M, et al: Microbiota from Alzheimer's patients
induce deficits in cognition and hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain.
146:4916–4934. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goncalves JT, Schafer ST and Gage FH:
Adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus: From stem cells to behavior.
Cell. 167:897–914. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ming GL and Song H: Adult neurogenesis in
the mammalian brain: Significant answers and significant questions.
Neuron. 70:687–702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang H, Sathyamurthy A, Liu F, Li L,
Zhang L, Dong Z, Cui W, Sun X, Zhao K, Wang H, et al:
Agrin-Lrp4-Ror2 signaling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis
in mice. Elife. 8:e453032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang JF, Cao G, Koirala S, Reddy LV and Ko
CP: Schwann cells express active agrin and enhance aggregation of
acetylcholine receptors on muscle fibers. J Neurosci. 21:9572–9584.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu J, Oentaryo MJ and Lee CW: Local
protein synthesis of neuronal MT1-MMP for agrin-induced presynaptic
development. Development. 148:dev1990002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Uyen Dao TM, Barbeau S, Messeant J,
Della-Gaspera B, Bouceba T, Semprez F, Legay C and Dobbertin A: The
collagen ColQ binds to LRP4 and regulates the activation of the
Muscle-Specific Kinase-LRP4 receptor complex by agrin at the
neuromuscular junction. J Biol Chem. 299:1049622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao H, Zhao Z, Li J, Guo Z, Zhang F, Wang
K, Bai X, Wang Q, Guan Y, Wang Y, et al: Platelet-rich plasma
promotes skeletal muscle regeneration and neuromuscular functional
reconstitution in a concentration-dependent manner in a rat
laceration model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 672:185–192. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feng Z and Ko CP: Schwann cells promote
synaptogenesis at the neuromuscular junction via transforming
growth factor-beta1. J Neurosci. 28:9599–9609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang BG, Quigley AF, Bourke JL, Nowell
CJ, Myers DE, Choong PF and Kapsa RM: Combination of agrin and
laminin increase acetylcholine receptor clustering and enhance
functional neuromuscular junction formation In vitro. Dev
Neurobiol. 76:551–565. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ma L, Pan L, Liu W, Liu Y, Xiang X, Pan Y,
Zhang X and Jin L: Agrin influences botulinum neurotoxin a-induced
nerve sprouting via miR-144-agrin-MuSK signaling. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 8:152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gilhus NE, Tzartos S, Evoli A, Palace J,
Burns TM and Verschuuren JJGM: Myasthenia gravis. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 5:302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lazaridis K and Tzartos SJ: Autoantibody
specificities in myasthenia gravis; implications for improved
diagnostics and therapeutics. Front Immunol. 11:2122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yan M, Xing GL, Xiong WC and Mei L: Agrin
and LRP4 antibodies as new biomarkers of myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1413:126–135. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu Z, Zhang M, Jing H, Chen P, Cao R, Pan
J, Luo B, Yu Y, Quarles BM, Xiong W, et al: Characterization of
LRP4/agrin antibodies from a patient with myasthenia gravis.
Neurology. 97:e975–e987. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rivner MH, Quarles BM, Pan JX, Yu Z,
Howard JF Jr, Corse A, Dimachkie MM, Jackson C, Vu T, Small G, et
al: Clinical features of LRP4/agrin-antibody-positive myasthenia
gravis: A multicenter study. Muscle Nerve. 62:333–343. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ohno K, Ohkawara B and Ito M:
Agrin-LRP4-MuSK signaling as a therapeutic target for myasthenia
gravis and other neuromuscular disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
21:949–958. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hettwer S, Lin S, Kucsera S, Haubitz M,
Oliveri F, Fariello RG, Ruegg MA and Vrijbloed JW: Injection of a
soluble fragment of neural agrin (NT-1654) considerably improves
the muscle pathology caused by the disassembly of the neuromuscular
junction. PLoS One. 9:e887392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Z, Li M, Wood K, Hettwer S, Muley SA,
Shi FD, Liu Q and Ladha SS: Engineered agrin attenuates the
severity of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Muscle
Nerve. 57:814–820. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Kempermann G, Gage FH, Aigner L, Song H,
Curtis MA, Thuret S, Kuhn HG, Jessberger S, Frankland PW, Cameron
HA, et al: Human adult neurogenesis: Evidence and remaining
questions. Cell Stem Cell. 23:25–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sorrells SF, Paredes MF, Cebrian-Silla A,
Sandoval K, Qi D, Kelley KW, James D, Mayer S, Chang J, Auguste KI,
et al: Human hippocampal neurogenesis drops sharply in children to
undetectable levels in adults. Nature. 555:377–381. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li X, Sun B, Li J, Ye W, Li M, Guan F, Wu
S, Luo X, Feng J, Jia J, et al: Sepsis leads to impaired
mitochondrial calcium uptake and skeletal muscle weakness by
reducing the micu1: Mcu protein ratio. Shock. 60:698–706. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lv B, Min S, Xie F, Yang J and Chen J:
Alleviating sepsis-induced neuromuscular dysfunction linked with
acetylcholine receptors by agrin. J Surg Res. 241:308–316. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Abdalla A, Murali C and Amin A: Safranal
inhibits angiogenesis via targeting HIF-1α/VEGF machinery: In vitro
and Ex vivo insights. Front Oncol. 11:7891722022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Hanahan D and Folkman J: Patterns and
emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis.
Cell. 86:353–364. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Abdalla Y, Abdalla A, Hamza AA and Amin A:
Safranal prevents liver cancer through inhibiting oxidative stress
and alleviating inflammation. Front Pharmacol. 12:7775002022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bouabdallah S, Al-Maktoum A and Amin A:
Steroidal saponins: Naturally occurring compounds as inhibitors of
the hallmarks of cancer. Cancers (Basel). 15:39002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wiedmann L, De Angelis Rigotti F,
Vaquero-Siguero N, Donato E, Espinet E, Moll I, Alsina-Sanchis E,
Bohnenberger H, Fernandez-Florido E, Mulfarth R, et al: HAPLN1
potentiates peritoneal metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Nat Commun.
14:23532023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
He M, Cheng C, Tu J, Ji SS, Lou D and Bai
B: Agrin expression is correlated with tumor development and poor
prognosis in cholangiocarcinoma. J Int Med Res.
49:30006052110097222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chakraborty S, Lakshmanan M, Swa HL, Chen
J, Zhang X, Ong YS, Loo LS, Akincilar SC, Gunaratne J, Tergaonkar
V, et al: An oncogenic role of agrin in regulating focal adhesion
integrity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 6:61842015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chakraborty S, Njah K, Pobbati AV, Lim YB,
Raju A, Lakshmanan M, Tergaonkar V, Lim CT and Hong W: Agrin as a
mechanotransduction signal regulating YAP through the hippo
pathway. Cell Rep. 18:2464–2479. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Njah K, Chakraborty S, Qiu B, Arumugam S,
Raju A, Pobbati AV, Lakshmanan M, Tergaonkar V, Thibault G, Wang X
and Hong W: A role of agrin in maintaining the stability of
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 during tumor
angiogenesis. Cell Rep. 28:949–965.e7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bordeleau F, Mason BN, Lollis EM, Mazzola
M, Zanotelli MR, Somasegar S, Califano JP, Montague C, LaValley DJ,
Huynh J, et al: Matrix stiffening promotes a tumor vasculature
phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:492–497. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Frye M, Taddei A, Dierkes C,
Martinez-Corral I, Fielden M, Ortsater H, Kazenwadel J, Calado DP,
Ostergaard P, Salminen M, et al: Matrix stiffness controls
lymphatic vessel formation through regulation of a GATA2-dependent
transcriptional program. Nat Commun. 9:15112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chakraborty S, Njah K and Hong W: Agrin
mediates angiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer.
6:81–85. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kawahara R, Granato DC, Carnielli CM,
Cervigne NK, Oliveria CE, Rivera C, Yokoo S, Fonseca FP, Lopes M,
Santos-Silva AR, et al: Agrin and perlecan mediate tumorigenic
processes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e1150042014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Neill T, Schaefer L and Iozzo RV: Decoding
the matrix: Instructive roles of proteoglycan receptors.
Biochemistry. 54:4583–4598. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Scherbakov N, Knops M, Ebner N, Valentova
M, Sandek A, Grittner U, Dahinden P, Hettwer S, Schefold JC, von
Haehling S, et al: Evaluation of C-terminal agrin fragment as a
marker of muscle wasting in patients after acute stroke during
early rehabilitation. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 7:60–67. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yu D, Li HX, Liu Y, Ying ZW, Guo JJ, Cao
CY, Wang J, Li YF and Yang HR: The reference intervals for serum
C-terminal agrin fragment in healthy individuals and as a biomarker
for renal function in kidney transplant recipients. J Clin Lab
Anal. 31:e220592017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Sartori R, Hagg A, Zampieri S, Armani A,
Winbanks CE, Viana LR, Haidar M, Watt KI, Qian H, Pezzini C, et al:
Perturbed BMP signaling and denervation promote muscle wasting in
cancer cachexia. Sci Transl Med. 13:eaay95922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rivera C, Zandonadi FS, Sanchez-Romero C,
Soares CD, Granato DC, Gonzalez-Arriagada WA and Paes Leme AF:
Agrin has a pathological role in the progression of oral cancer. Br
J Cancer. 118:1628–1638. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bezakova G and Ruegg MA: New insights into
the roles of agrin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:295–308. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sulzmaier FJ, Jean C and Schlaepfer DD:
FAK in cancer: Mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat
Rev Cancer. 14:598–610. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Li D, Gu Q, Xie Z, Shen Q and Li H:
Clinical significance of nuclear localisation of agrin in lung
adenocarcinoma. Pol J Pathol. 70:198–204. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang QJ, Wan L and Xu HF: High expression
of agrin is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Math Biosci Eng. 16:7375–7383. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ye P, Fu Z, Chung JY, Cao X, Ko H, Tian
XY, Tang PM and Lui KO: Endothelial agrin is dispensable for normal
and tumor angiogenesis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 8:8104772022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhu Y, Do VD, Richards AM and Foo R: What
we know about cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
152:80–91. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Porrello ER, Mahmoud AI, Simpson E, Hill
JA, Richardson JA, Olson EN and Sadek HA: Transient regenerative
potential of the neonatal mouse heart. Science. 331:1078–1080.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zlatanova I, Sun F, Wu RS, Chen X, Lau BH,
Colombier P, Sinha T, Celona B, Xu SM, Materna SC, et al: An
injury-responsive mmp14b enhancer is required for heart
regeneration. Sci Adv. 9:eadh53132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Baehr A, Umansky KB, Bassat E, Jurisch V,
Klett K, Bozoglu T, Hornaschewitz N, Solyanik O, Kain D, Ferraro B,
et al: Agrin promotes coordinated therapeutic processes leading to
improved cardiac repair in pigs. Circulation. 142:868–881. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Mazzon C, Anselmo A, Cibella J, Soldani C,
Destro A, Kim N, Roncalli M, Burden SJ, Dustin ML, Sarukhan A and
Viola A: The critical role of agrin in the hematopoietic stem cell
niche. Blood. 118:2733–2742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Burgess RW, Dickman DK, Nunez L, Glass DJ
and Sanes JR: Mapping sites responsible for interactions of agrin
with neurons. J Neurochem. 83:271–284. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Guadix JA, Orlova VV, Giacomelli E, Bellin
M, Ribeiro MC, Mummery CL, Perez-Pomares JM and Passier R: Human
pluripotent stem cell differentiation into functional epicardial
progenitor cells. Stem Cell Reports. 9:1754–1764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Germani A, Foglio E, Capogrossi MC, Russo
MA and Limana F: Generation of cardiac progenitor cells through
epicardial to mesenchymal transition. J Mol Med (Berl). 93:735–748.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Smits AM, Dronkers E and Goumans MJ: The
epicardium as a source of multipotent adult cardiac progenitor
cells: Their origin, role and fate. Pharmacol Res. 127:129–140.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Jing X, Liu B, Deng S, Du J and She Q:
Agrin yes-associated protein promotes the proliferation of
epicardial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 77:94–99. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Sun K, Guo J, Guo Z, Hou L, Liu H, Hou Y,
He J, Guo F and Ye Y: The roles of the hippo-YAP signalling pathway
in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 90:1020152023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hou L, Fu W, Liu Y, Wang Q, Wang L and
Huang Y: Agrin promotes limbal stem cell proliferation and corneal
wound healing through hippo-yap signaling pathway. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 61:72020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Manner J, Schlueter J and Brand T:
Experimental analyses of the function of the proepicardium using a
new microsurgical procedure to induce
loss-of-proepicardial-function in chick embryos. Dev Dyn.
233:1454–1463. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Diman NY, Brooks G, Kruithof BP, Elemento
O, Seidman JG, Seidman CE, Basson CT and Hatcher CJ: Tbx5 is
required for avian and mammalian epicardial formation and coronary
vasculogenesis. Circ Res. 115:834–844. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
van Wijk B, Gunst QD, Moorman AF and van
den Hoff MJ: Cardiac regeneration from activated epicardium. PLoS
One. 7:e446922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lan Y, Pan H, Li C, Banks KM, Sam J, Ding
B, Elemento O, Goll MG and Evans T: TETs regulate proepicardial
cell migration through extracellular matrix organization during
zebrafish cardiogenesis. Cell Rep. 26:720–732.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Missinato MA, Tobita K, Romano N, Carroll
JA and Tsang M: Extracellular component hyaluronic acid and its
receptor Hmmr are required for epicardial EMT during heart
regeneration. Cardiovasc Res. 107:487–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Verzijl N, DeGroot J, Thorpe SR, Bank RA,
Shaw JN, Lyons TJ, Bijlsma JW, Lafeber FP, Baynes JW and TeKoppele
JM: Effect of collagen turnover on the accumulation of advanced
glycation end products. J Biol Chem. 275:39027–39031. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Erickson CB, Hill R, Pascablo D, Kazakia
G, Hansen K and Bahney C: A timeseries analysis of the fracture
callus extracellular matrix proteome during bone fracture healing.
J Life Sci (Westlake Village). 3:1–30. 2021.
|
|
84
|
Hausser HJ, Ruegg MA, Brenner RE and
Ksiazek I: Agrin is highly expressed by chondrocytes and is
required for normal growth. Histochem Cell Biol. 127:363–374. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Campanelli JT, Ferns M, Hoch W, Rupp F,
von Zastrow M, Hall Z and Scheller RH: Agrin: A synaptic basal
lamina protein that regulates development of the neuromuscular
junction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 57:461–472. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Eldridge S, Nalesso G, Ismail H,
Vicente-Greco K, Kabouridis P, Ramachandran M, Niemeier A, Herz J,
Pitzalis C, Perretti M and Dell'Accio F: Agrin mediates chondrocyte
homeostasis and requires both LRP4 and α-dystroglycan to enhance
cartilage formation in vitro and in vivo. Ann Rheum Dis.
75:1228–1235. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Eldridge SE, Barawi A, Wang H, Roelofs AJ,
Kaneva M, Guan Z, Lydon H, Thomas BL, Thorup AS, Fernandez BF, et
al: Agrin induces long-term osteochondral regeneration by
supporting repair morphogenesis. Sci Transl Med. 12:eaax90862020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gentili C and Cancedda R: Cartilage and
bone extracellular matrix. Curr Pharm Des. 15:1334–1348. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Grol MW and Lee BH: Gene therapy for
repair and regeneration of bone and cartilage. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
40:59–66. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Gomes KDN, Alves APNN, Dutra PGP and Viana
GSB: Doxycycline induces bone repair and changes in Wnt signalling.
Int J Oral Sci. 9:158–166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Bao Q, Chen S, Qin H, Feng J, Liu H, Liu
D, Li A, Shen Y, Zhao Y, Li J and Zong Z: An appropriate
Wnt/β-catenin expression level during the remodeling phase is
required for improved bone fracture healing in mice. Sci Rep.
7:26952017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Wang T, Zhang X and Bikle DD: Osteogenic
Differentiation of Periosteal Cells During Fracture Healing. J Cell
Physiol. 232:913–921. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
93
|
Ahn Y, Sims C, Murray MJ, Kuhlmann PK,
Fuentes-Antras J, Weatherbee SD and Krumlauf R: Multiple modes of
Lrp4 function in modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling during tooth
development. Development. 144:2824–2836. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Houschyar KS, Tapking C, Borrelli MR, Popp
D, Duscher D, Maan ZN, Chelliah MP, Li J, Harati K, Wallner C, et
al: Wnt pathway in bone repair and regeneration-what do we know so
far. Front Cell Dev Biol. 6:1702019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Shen C, Xiong WC and Mei L: LRP4 in
neuromuscular junction and bone development and diseases. Bone.
80:101–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Souza ATP, Lopes HB, Oliveira FS, Weffort
D, Freitas GP, Adolpho LF, Fernandes RR, Rosa AL and Beloti MM: The
extracellular matrix protein Agrin is expressed by osteoblasts and
contributes to their differentiation. Cell Tissue Res. 386:335–347.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Willadt S, Nash M and Slater C:
Age-related changes in the structure and function of mammalian
neuromuscular junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1412:41–53. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Taetzsch T, Tenga MJ and Valdez G: Muscle
fibers secrete FGFBP1 to slow degeneration of neuromuscular
synapses during aging and progression of ALS. J Neurosci. 37:70–82.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhao K, Shen C, Li L, Wu H, Xing G, Dong
Z, Jing H, Chen W, Zhang H, Tan Z, et al: Sarcoglycan alpha
mitigates neuromuscular junction decline in aged mice by
stabilizing LRP4. J Neurosci. 38:8860–8873. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Samuel MA, Valdez G, Tapia JC, Lichtman JW
and Sanes JR: Agrin and synaptic laminin are required to maintain
adult neuromuscular junctions. PLoS One. 7:e466632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Benjumea AM, Curcio CL, Duque G and Gomez
F: Dynapenia and sarcopenia as a risk factor for disability in a
falls and fractures clinic in older persons. Open Access Maced J
Med Sci. 6:344–349. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhang X, Zhang W, Wang C, Tao W, Dou Q and
Yang Y: Sarcopenia as a predictor of hospitalization among older
people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr.
18:1882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Stephan A, Mateos JM, Kozlov SV, Cinelli
P, Kistler AD, Hettwer S, Rulicke T, Streit P, Kunz B and
Sonderegger P: Neurotrypsin cleaves agrin locally at the synapse.
FASEB J. 22:1861–1873. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Kamiya K, Tachiki T, Sato Y, Kouda K,
Kajita E, Tamaki J, Kagamimori S and Iki M: Association between the
110-kDa C-terminal agrin fragment and skeletal muscle decline among
community-dwelling older women. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.
14:2253–2263. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Drey M, Sieber CC, Bauer JM, Uter W,
Dahinden P, Fariello RG and Vrijbloed JW; FiAT intervention group:
C-terminal Agrin Fragment as a potential marker for sarcopenia
caused by degeneration of the neuromuscular junction. Exp Gerontol.
48:76–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Racha P, Selvam S, Bose B, Bantwal G and
Sambashivaiah S: Circulating C-terminal agrin fragment: A potential
marker for sarcopenia among type 2 diabetes. Indian J Endocrinol
Metab. 26:334–340. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Pratt J, De Vito G, Narici M, Segurado R,
Pessanha L, Dolan J, Conroy J and Boreham C: Plasma C-terminal
agrin fragment as an early biomarker for sarcopenia: Results from
the GenoFit study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 76:2090–2096.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Denzer AJ, Brandenberger R, Gesemann M,
Chiquet M and Ruegg MA: Agrin binds to the nerve-muscle basal
lamina via laminin. J Cell Biol. 137:671–683. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Denzer AJ, Schulthess T, Fauser C,
Schumacher B, Kammerer RA, Engel J and Ruegg MA: Electron
microscopic structure of agrin and mapping of its binding site in
laminin-1. EMBO J. 17:335–343. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Raats CJ, van den Born J, Bakker MA,
Oppers-Walgreen B, Pisa BJ, Dijkman HB, Assmann KJ and Berden JH:
Expression of agrin, dystroglycan, and utrophin in normal renal
tissue and in experimental glomerulopathies. Am J Pathol.
156:1749–1765. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Goldberg S, Harvey SJ, Cunningham J,
Tryggvason K and Miner JH: Glomerular filtration is normal in the
absence of both agrin and perlecan-heparan sulfate from the
glomerular basement membrane. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
24:2044–2051. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Harvey SJ, Jarad G, Cunningham J, Rops AL,
van der Vlag J, Berden JH, Moeller MJ, Holzman LB, Burgess RW and
Miner JH: Disruption of glomerular basement membrane charge through
podocyte-specific mutation of agrin does not alter glomerular
permselectivity. Am J Pathol. 171:139–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Vestentoft PS, Jelnes P, Andersen JB, Tran
TA, Jorgensen T, Rasmussen M, Bornholdt J, Grovdal LM, Jensen CH,
Vogel LK, et al: Molecular constituents of the extracellular matrix
in rat liver mounting a hepatic progenitor cell response for tissue
repair. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 6:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Deng SX, Borderie V, Chan CC, Dana R,
Figueiredo FC, Gomes JAP, Pellegrini G, Shimmura S and Kruse FE;
The International Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Working Group: Global
consensus on definition, classification, diagnosis, and staging of
limbal stem cell deficiency. Cornea. 38:364–375. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Kolli S, Ahmad S, Lako M and Figueiredo F:
Successful clinical implementation of corneal epithelial stem cell
therapy for treatment of unilateral limbal stem cell deficiency.
Stem Cells. 28:597–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Whitcher JP, Srinivasan M and Upadhyay MP:
Corneal blindness: A global perspective. Bull World Health Organ.
79:214–221. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Sacchetti M, Rama P, Bruscolini A and
Lambiase A: Limbal stem cell transplantation: Clinical results,
limits, and perspectives. Stem Cells Int. 2018:80862692018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Ribatti D and d'Amati A: Hematopoiesis and
Mast Cell Development. Int J Mol Sci. 24:106792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Bruno E, Luikart SD, Long MW and Hoffman
R: Marrow-derived heparan sulfate proteoglycan mediates the
adhesion of hematopoietic progenitor cells to cytokines. Exp
Hematol. 23:1212–1217. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Sorg H and Sorg CGG: Skin wound healing:
Of players, patterns, and processes. Eur Surg Res. 64:141–157.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Xue M and Jackson CJ: Extracellular matrix
reorganization during wound healing and its impact on abnormal
scarring. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 4:119–136. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Chakraborty S, Sampath D, Yu Lin MO,
Bilton M, Huang CK, Nai MH, Njah K, Goy PA, Wang CC, Guccione E, et
al: Agrin-matrix metalloproteinase-12 axis confers a mechanically
competent microenvironment in skin wound healing. Nat Commun.
12:63492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Yu Lin MO, Sampath D, Bosykh DA, Wang C,
Wang X, Subramaniam T, Han W, Hong W and Chakraborty S: YAP/TAZ
drive agrin-matrix metalloproteinase-12 mediated diabetic skin
wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. May 27–2024.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Calvo F, Ege N, Grande-Garcia A, Hooper S,
Jenkins RP, Chaudhry SI, Harrington K, Williamson P, Moeendarbary
E, Charras G and Sahai E: Mechanotransduction and YAP-dependent
matrix remodelling is required for the generation and maintenance
of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Cell Biol. 637–646. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Sun X, Malandraki-Miller S, Kennedy T,
Bassat E, Klaourakis K, Zhao J, Gamen E, Vieira JM, Tzahor E and
Riley PR: The extracellular matrix protein agrin is essential for
epicardial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition during heart
development. Development. 148:dev1975252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|